Week 1 - Tissues & Nervous System
1/39
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
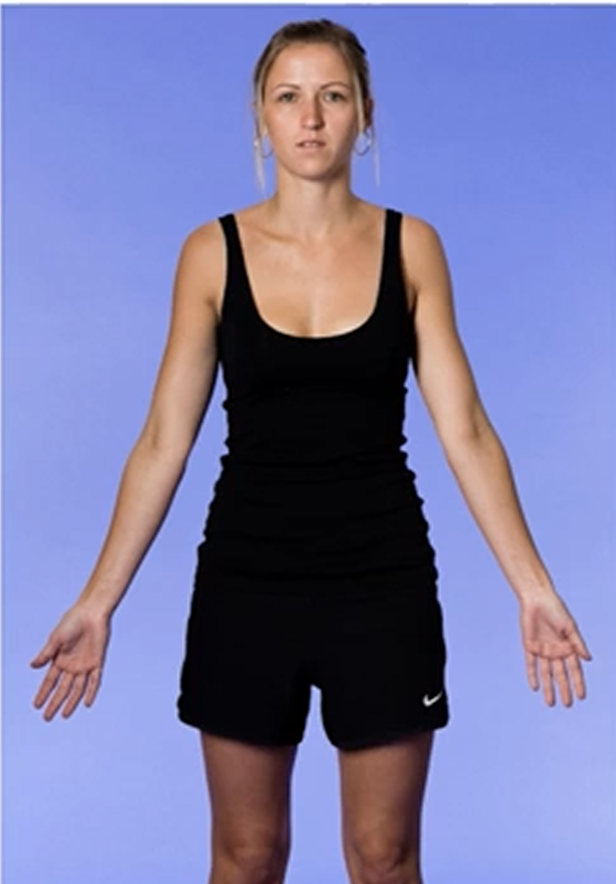
Anatomical Position
Refers to the standard orientation or position of an individual, typically upright, arms near the side of the body, and palms facing forward.

Bone
A rigid body tissue that is a part of the skeleton and plays an important role in the structure and support of movement.
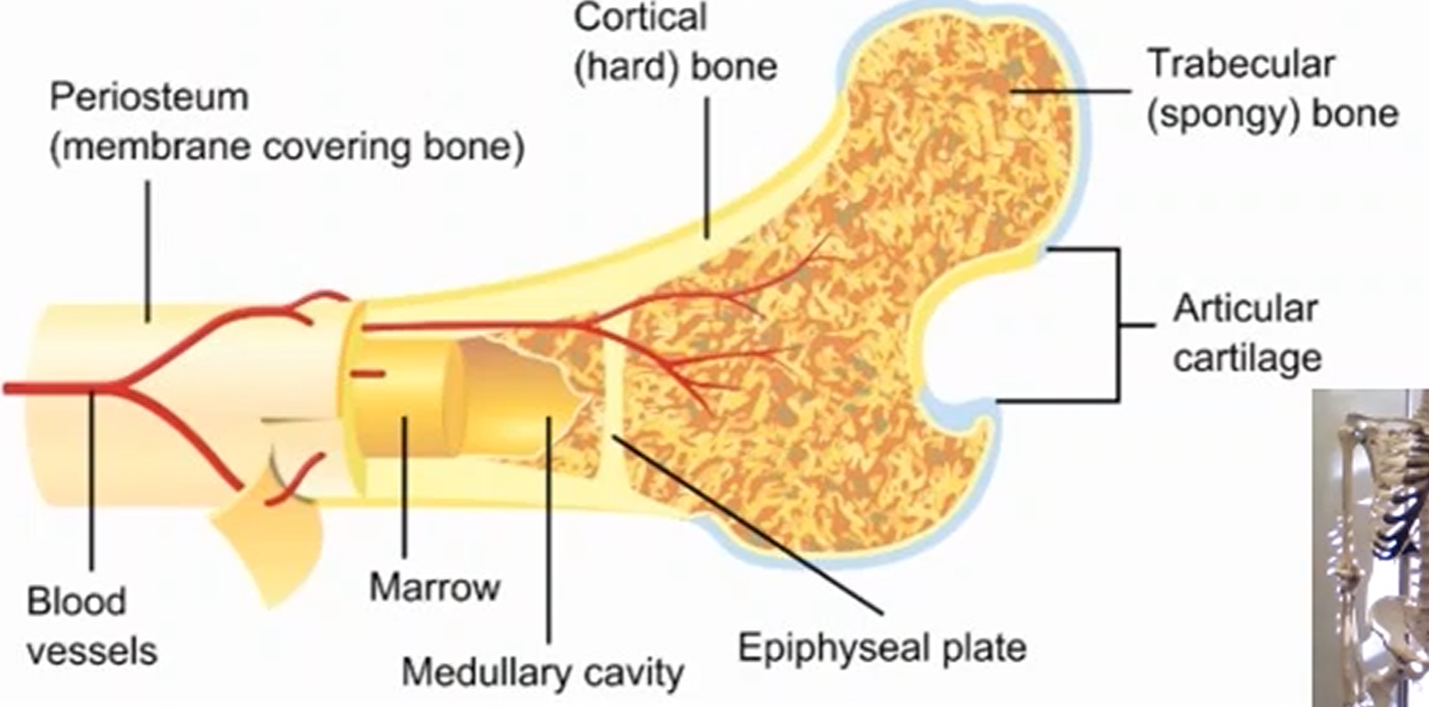
What are four key features of a bone?
Periosteum
Cortical (Compact Bone)
Trabecular (Spongy/Cancellous Bone)
Medullary Cavity
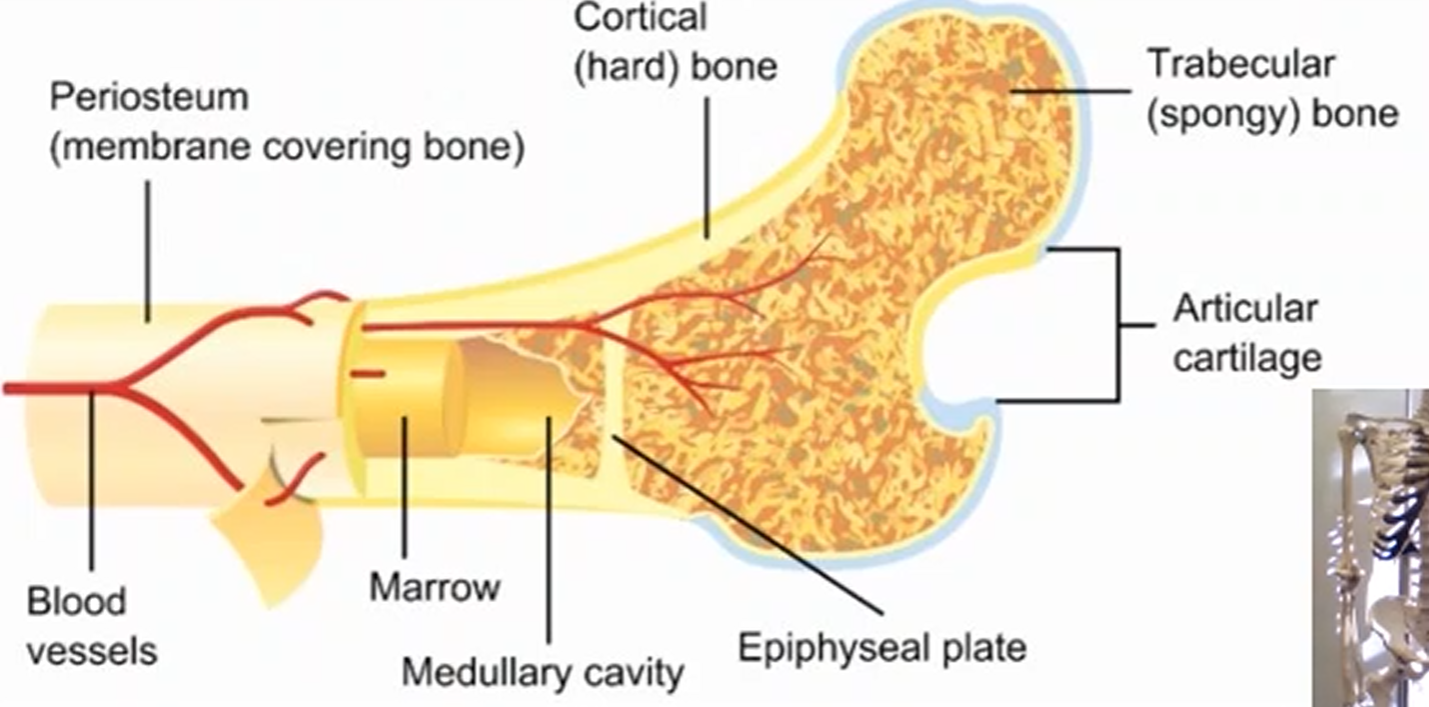
What is a periosteum and its function?
A dense outer membrane that covers the bone to provide nerve supply throughout the body.
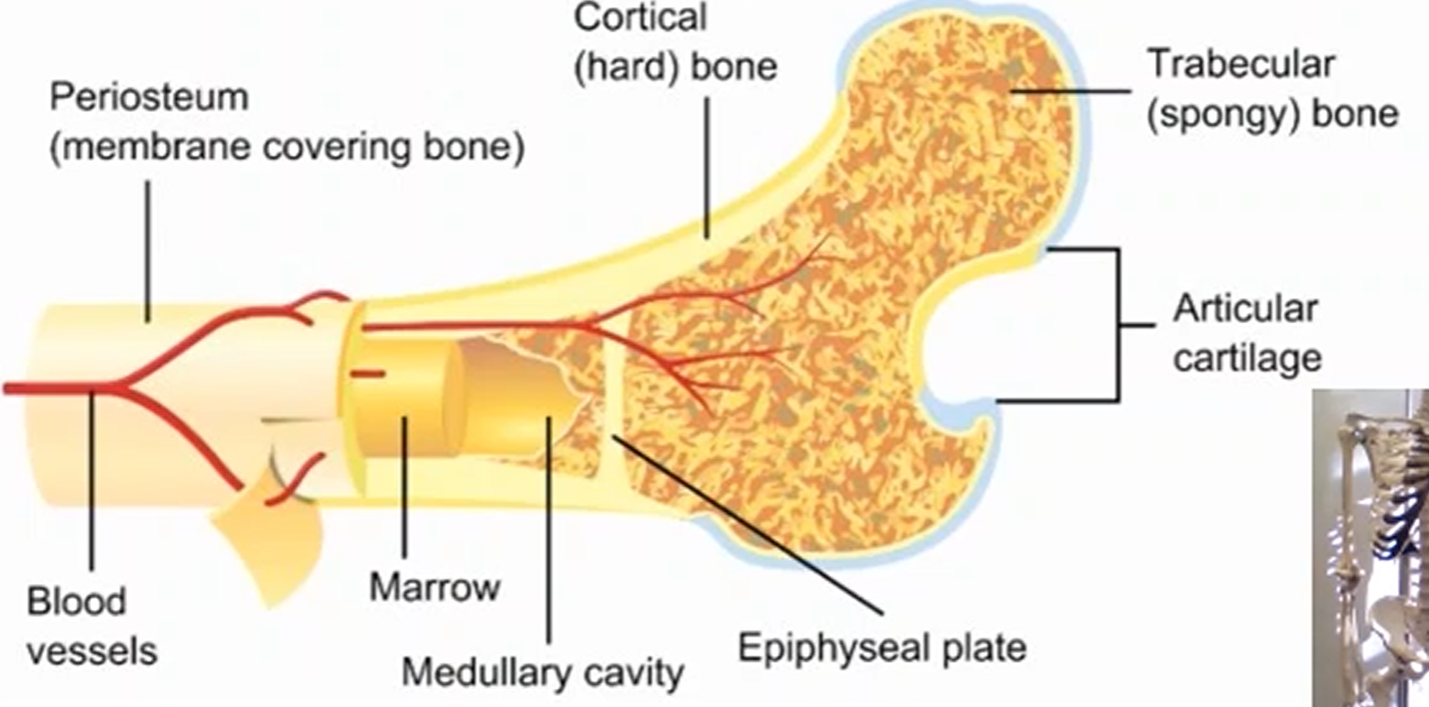
What is a cortical bone and its function?
A dense outer layer of the bone that provides strength and support to the bone.
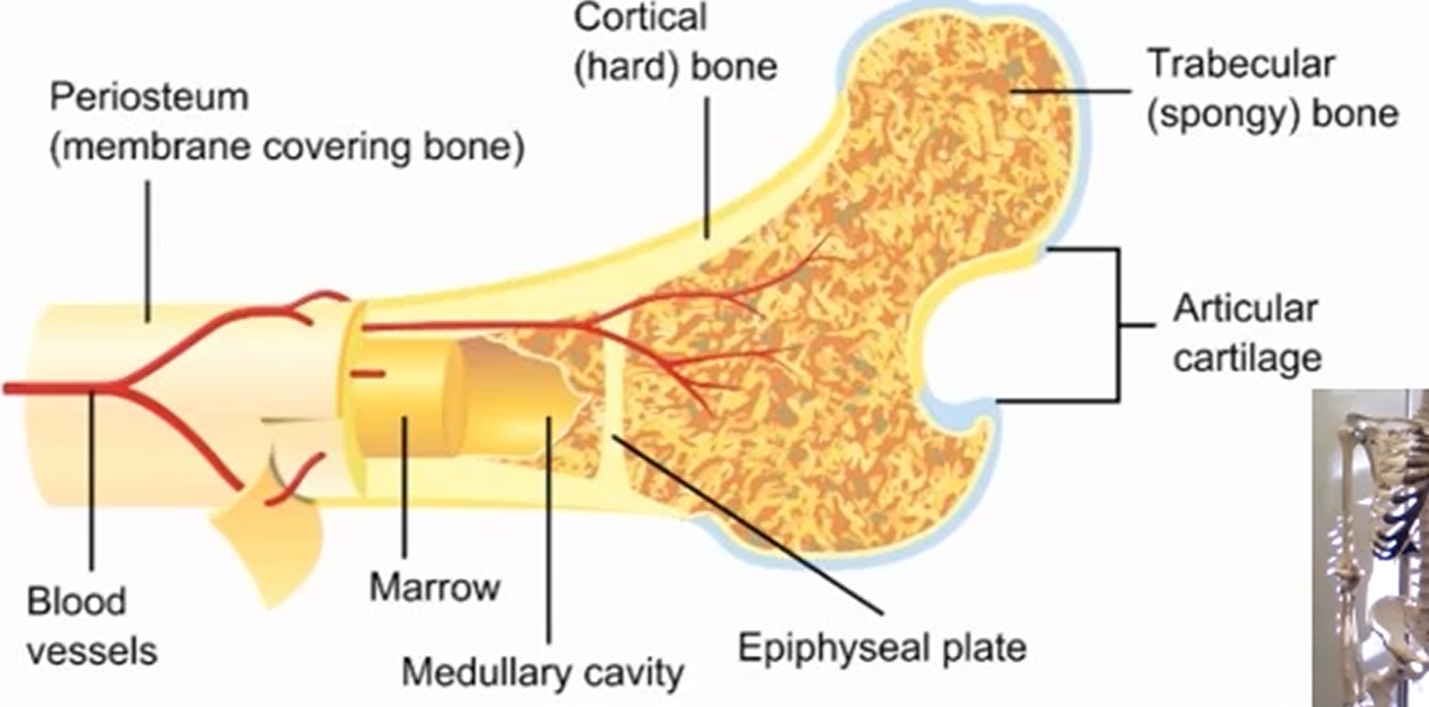
What is a trabecular bone and its function?
A thinner outer layer of the bone, made up of structs and plates at different angles that can rearrange itself in movement especially in physical activity.
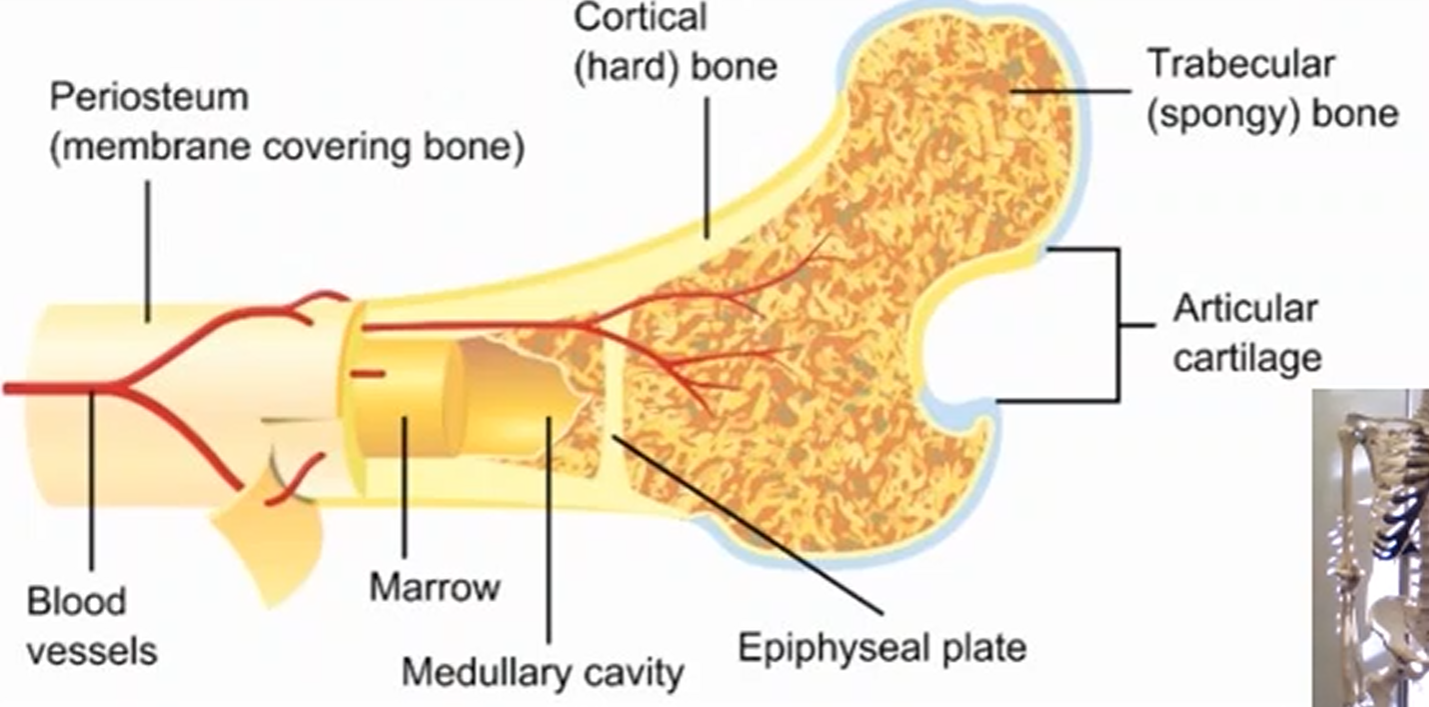
What is the medullary cavity and its function?
A cavity that acts as storage for various resources like bone marrow, fats, and specific cells that make red and white blood cells.
Articular Surface (aka joint or articulation)
Where the cartilage is found, that covers the surface of bones, providing protection to joints and facilitates movement.
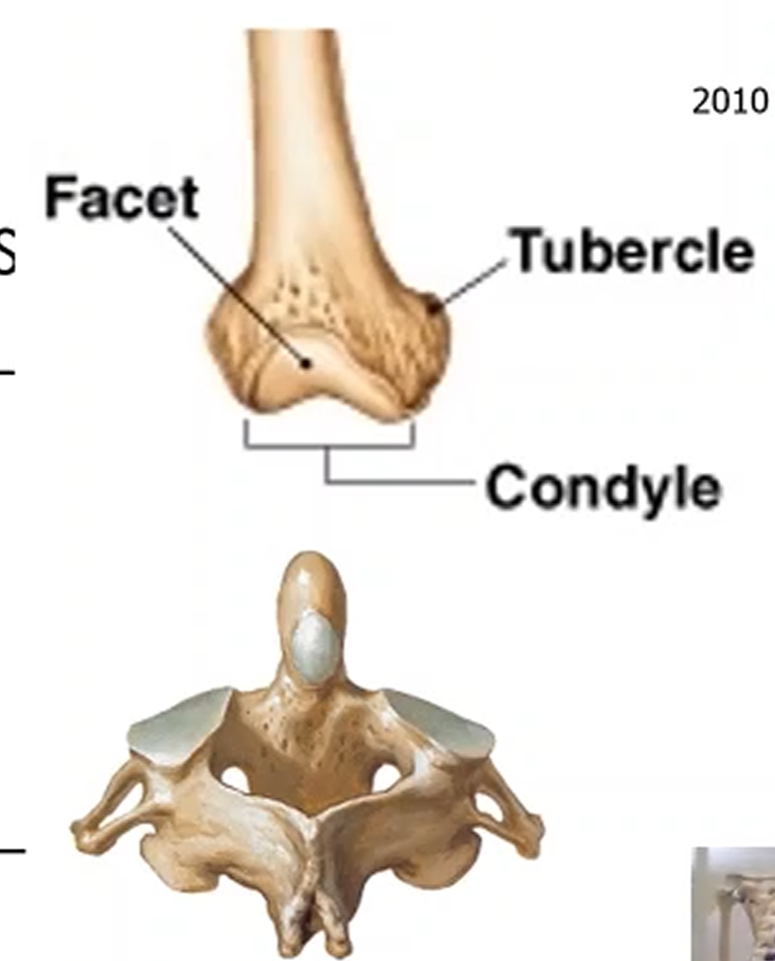
Fossa (Depression)
Grooves or indentations in the bone.
What is the difference between foramen and canal?
Foramen are openings in the bone that allows blood vessels, nerves, or other structures to enter or exit the bone whereas canal acts as a pathway for structures to travel through.
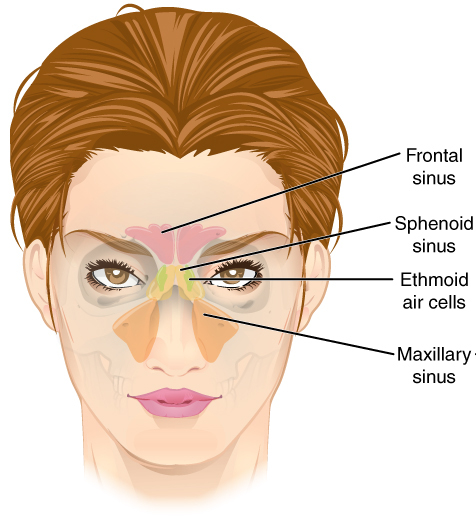
Paranasal sinuses
A type of air-filled spaces located in the face that is responsible for respiration and filtering what enters the body.
Synovial Joints
A type of joint that are freely movable, allowing for movement.
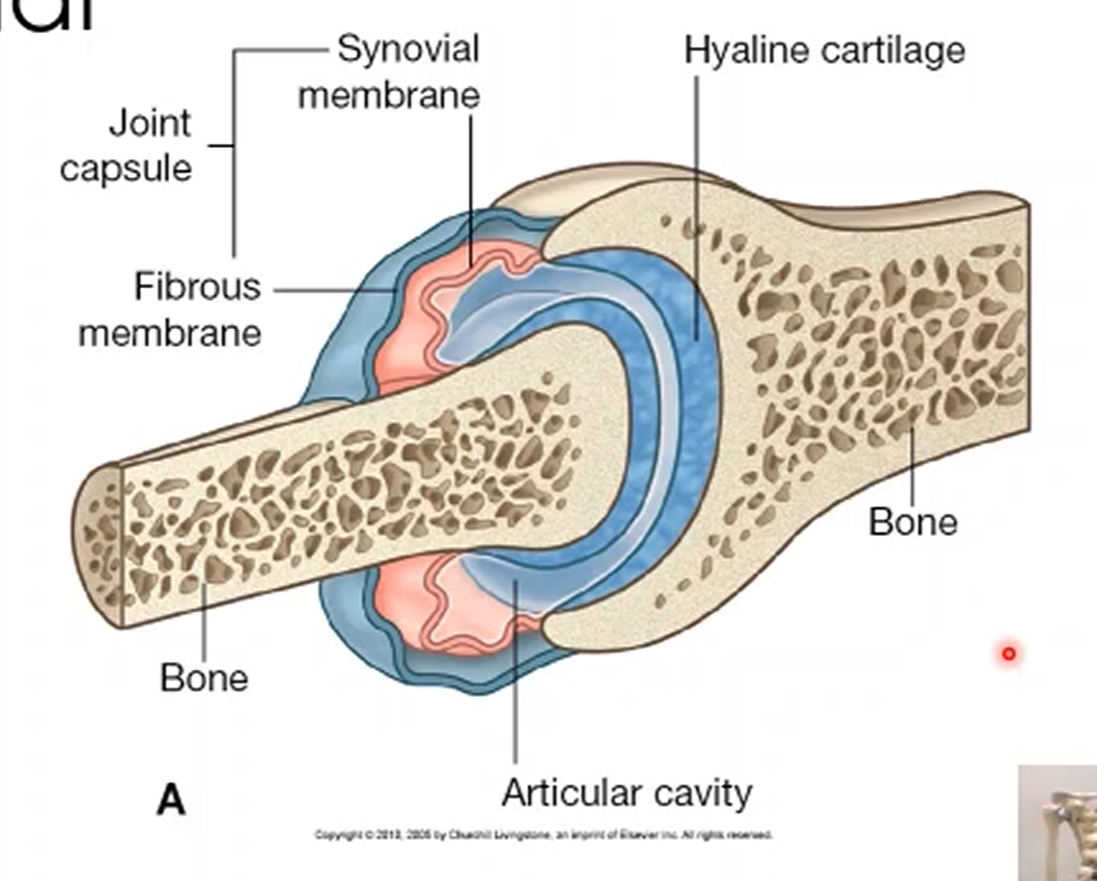
What are six features of synovial joints?
Bone
Cartilage
Outer joint capsule
Inner synovial membrane lining of joint
Ligament
Synovial fluid
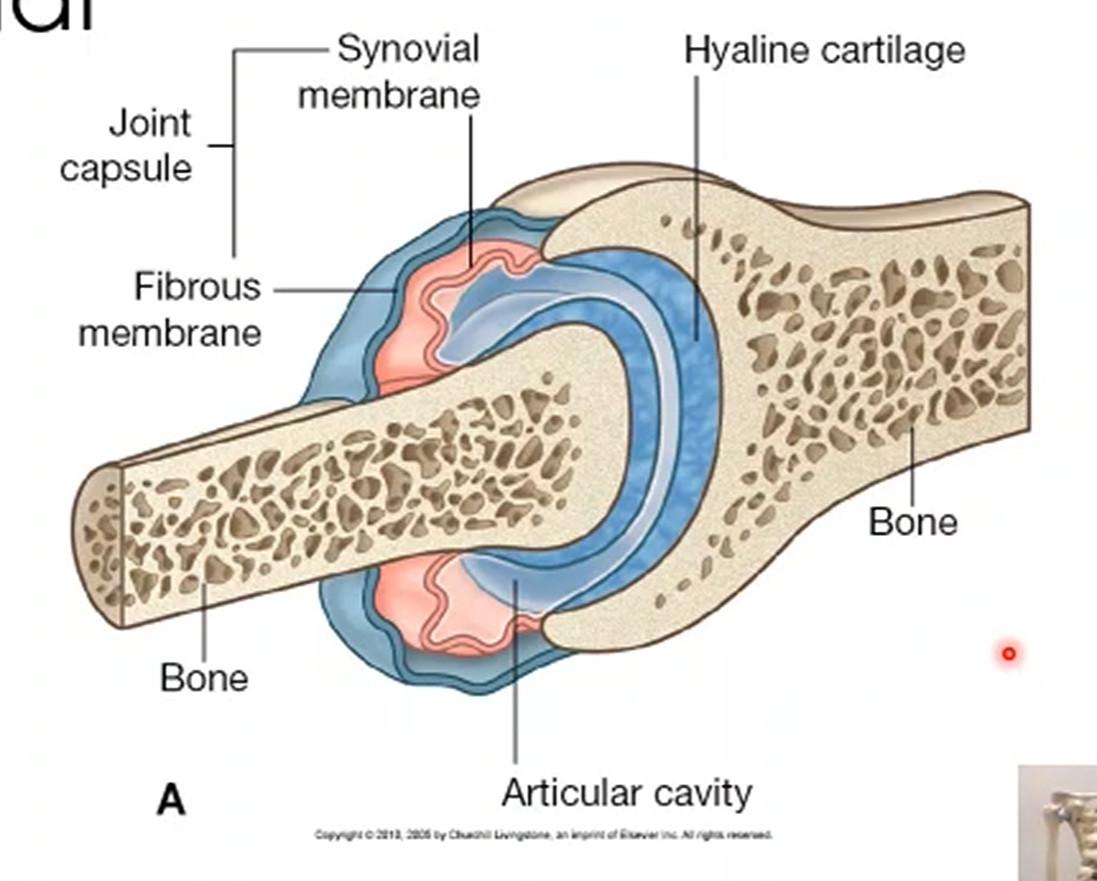
What is the outer joint capsule and its function?
The outer joint capsule is a fibrous joint that encloses two ends of the bone that articulates.
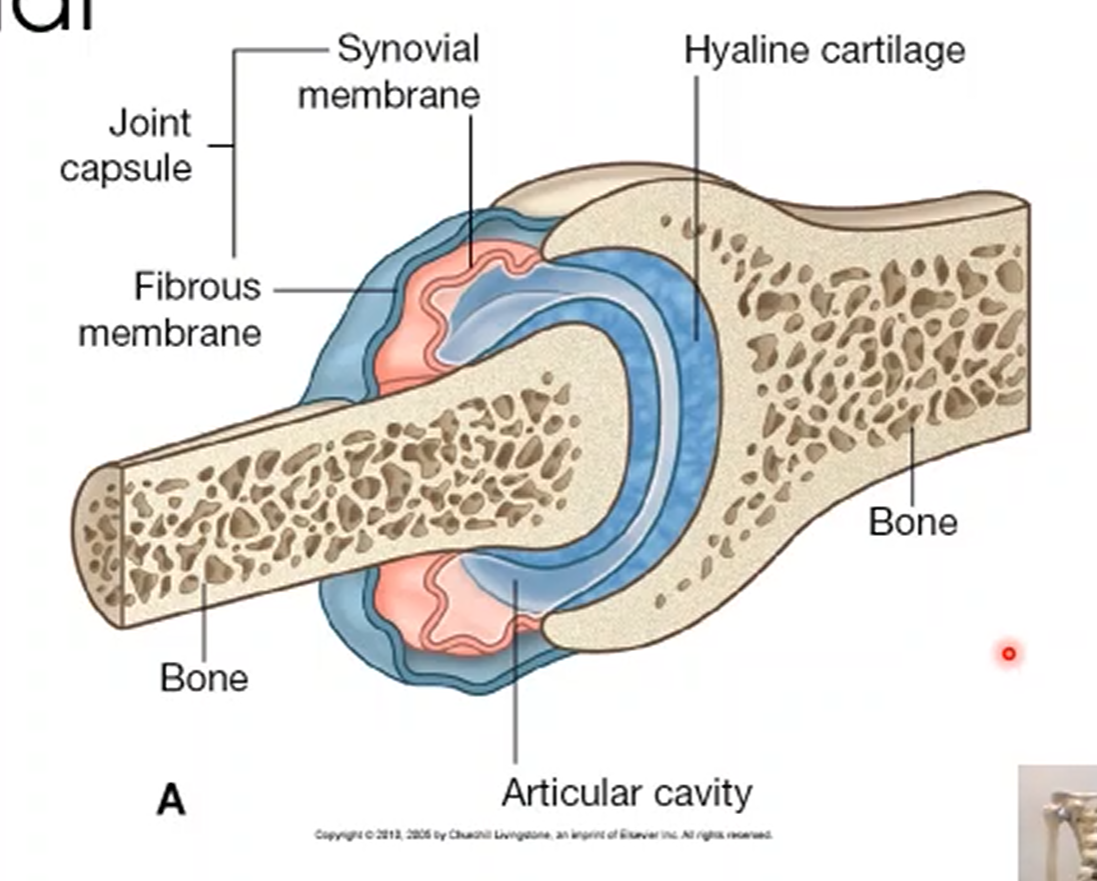
What is the synovial membrane and its function?
Synovial membrane provides blood supply and produces synovial fluid, a lubricant that covers the end of the bone which can reabsorb fluid and recreate it to keep the joints alive.
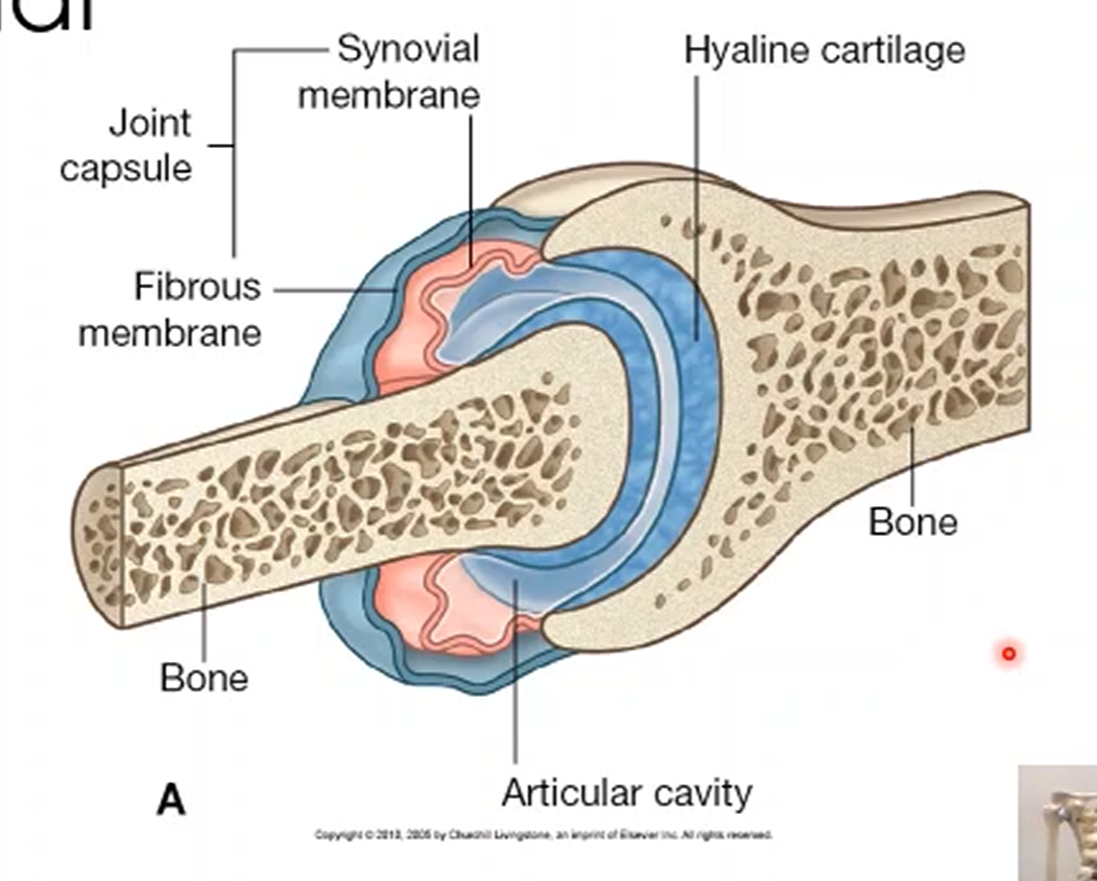
What is a ligament and its function?
A type of connective tissue that connects the bone to other bones and provide stability to the joint.
What are four main shapes a bone can take?
Long, short, flat, and irregular.
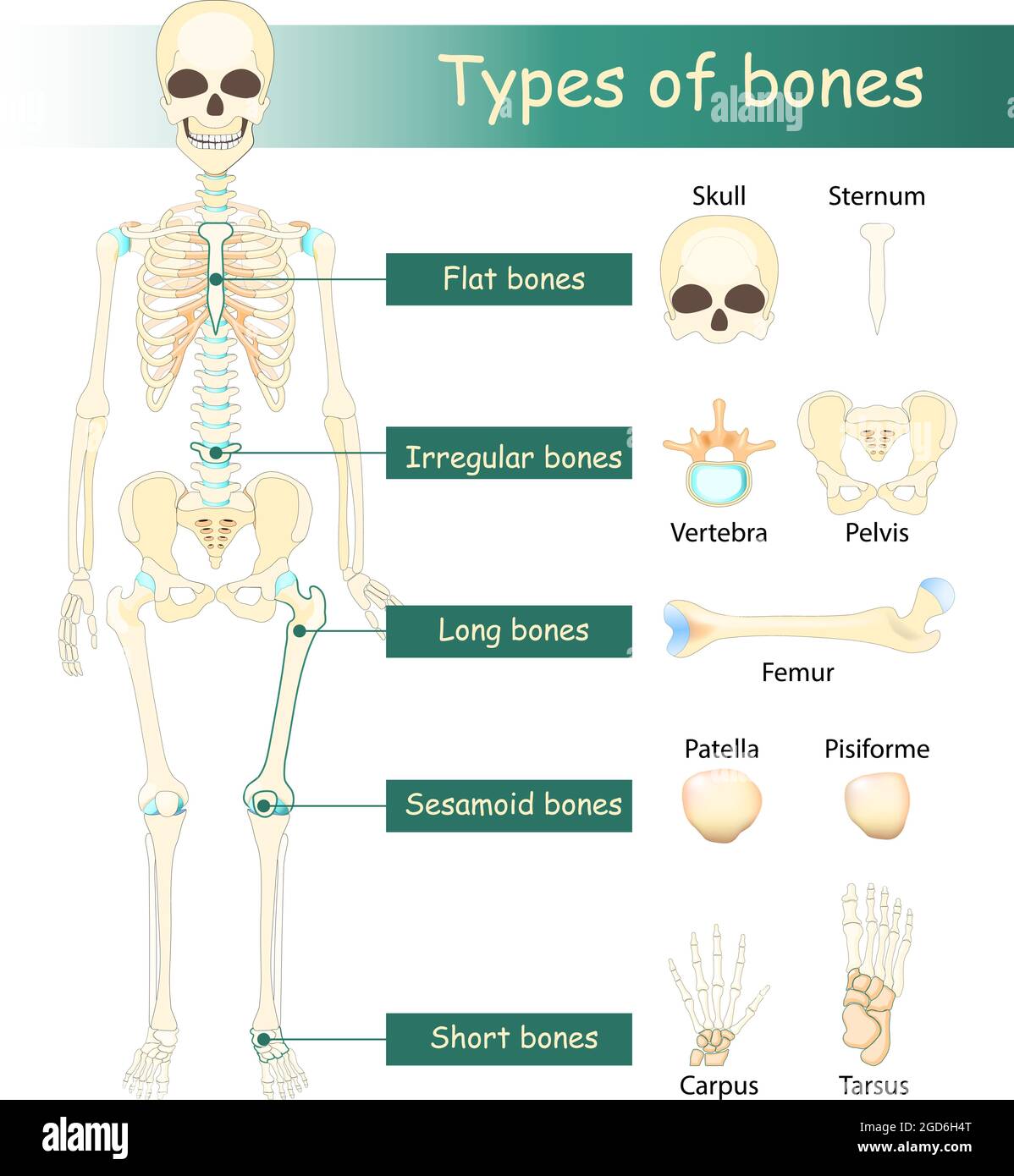
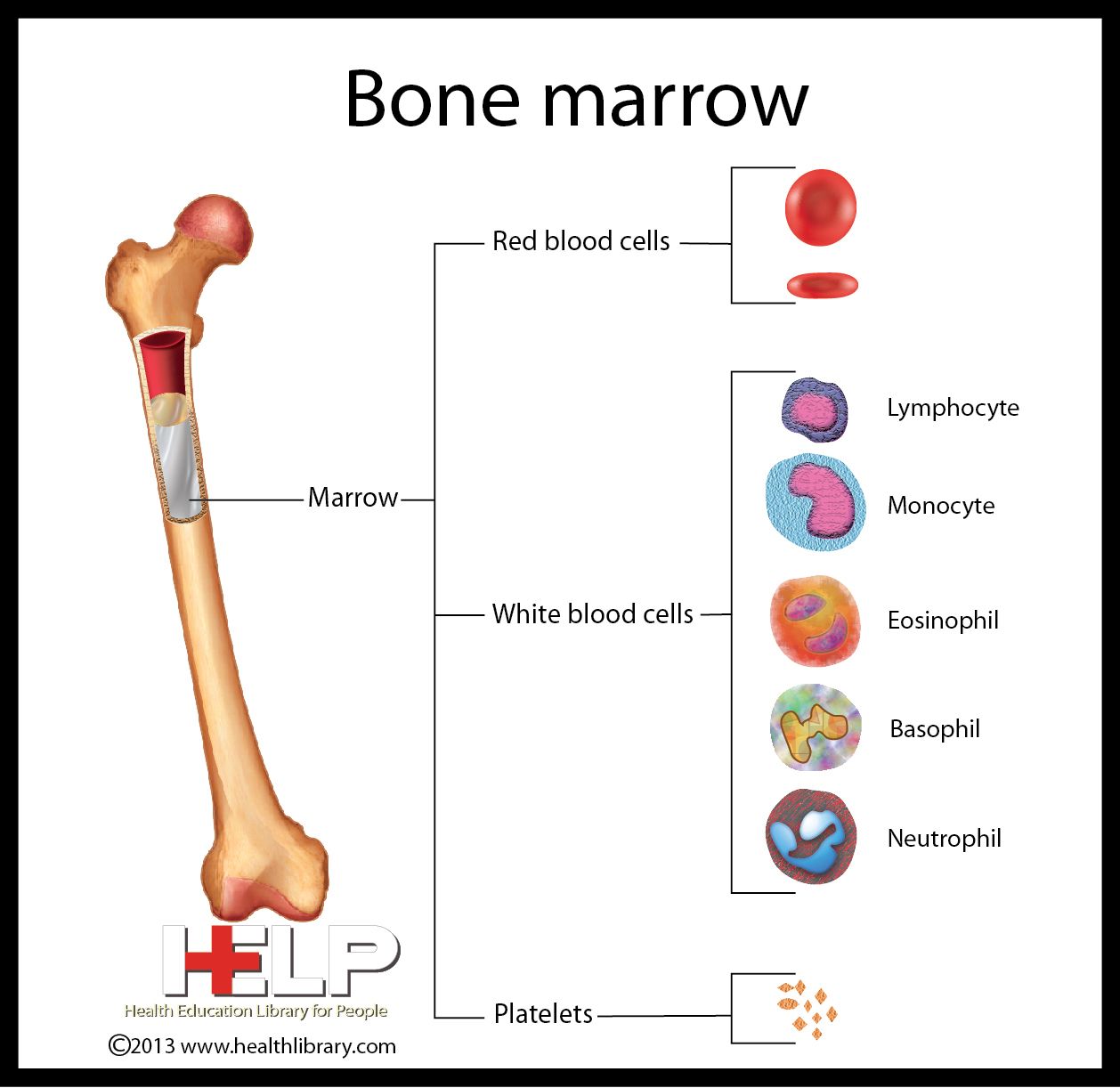
What is bone marrow and its function?
A soft tissue found within all bones that is responsible for multiple roles in the body including making white and red blood cells and platelets and can store fat to be used as energy.
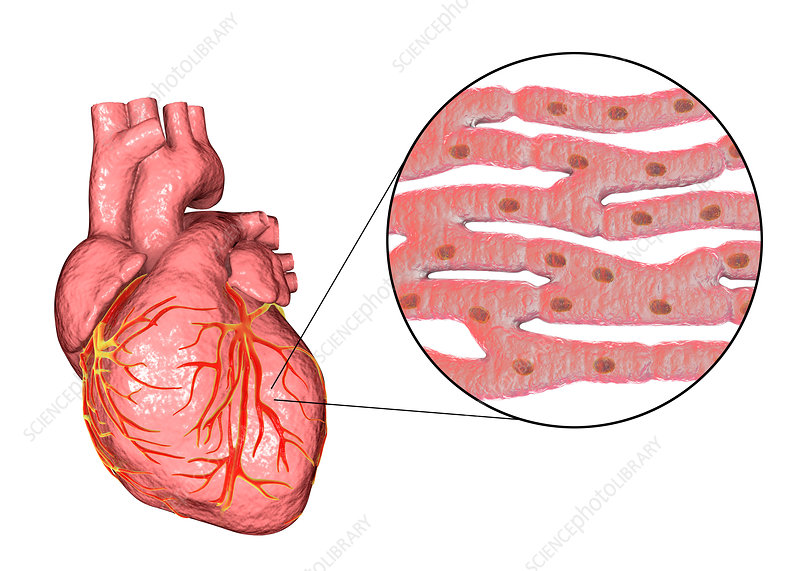
What are three types of muscle?
Cardiac Muscle
Smooth Muscle
Skeletal Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
A type of muscle that is regulated by the heart’s pacemaker and is involuntary aka we cannot control.
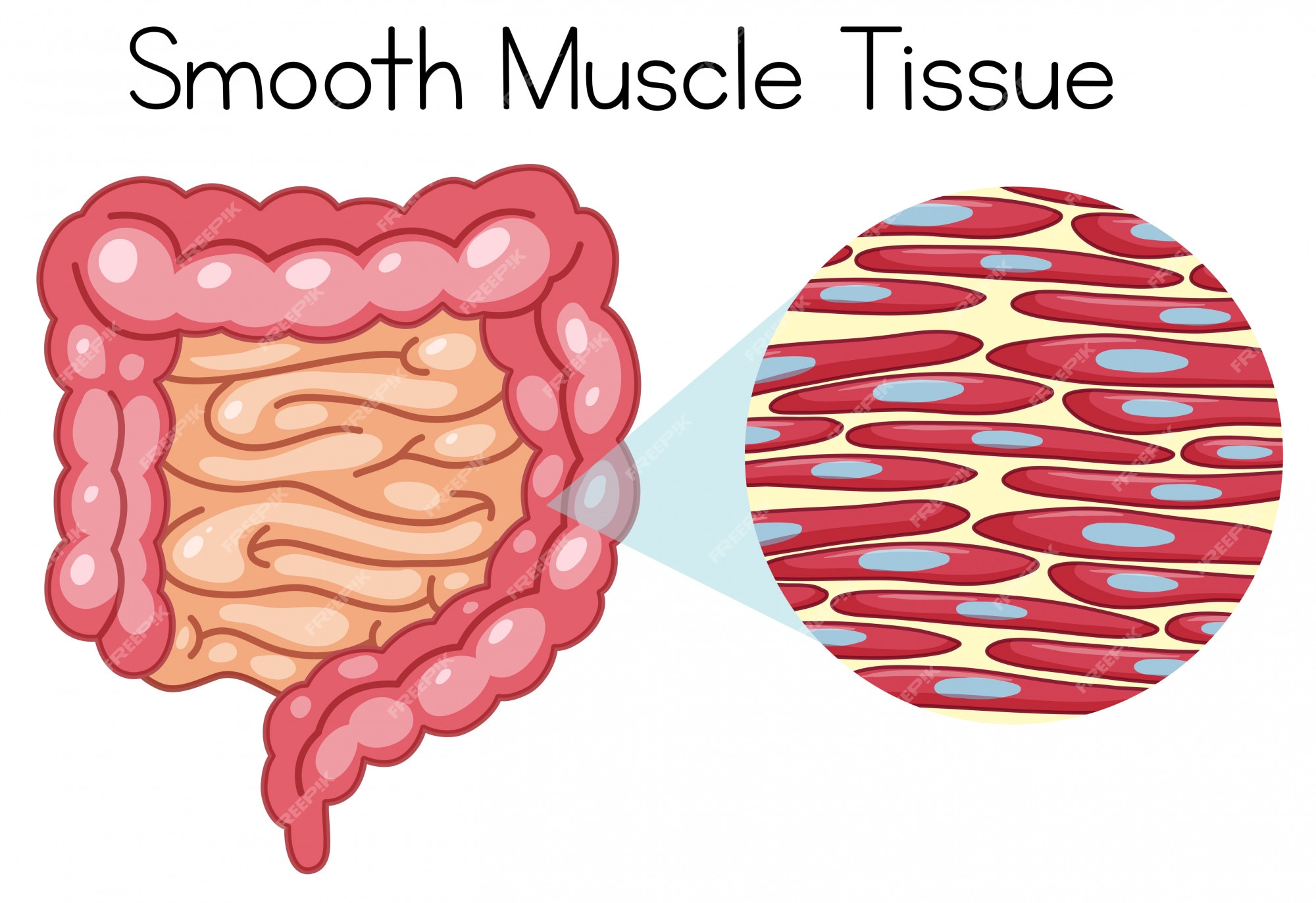
Smooth Muscle
A type of muscle located in the arteries, digestive, and urinary tracts and is involuntary aka we cannot control.
Skeletal Muscle
A type of muscle that produces skeletal movement and is voluntary aka we can control.
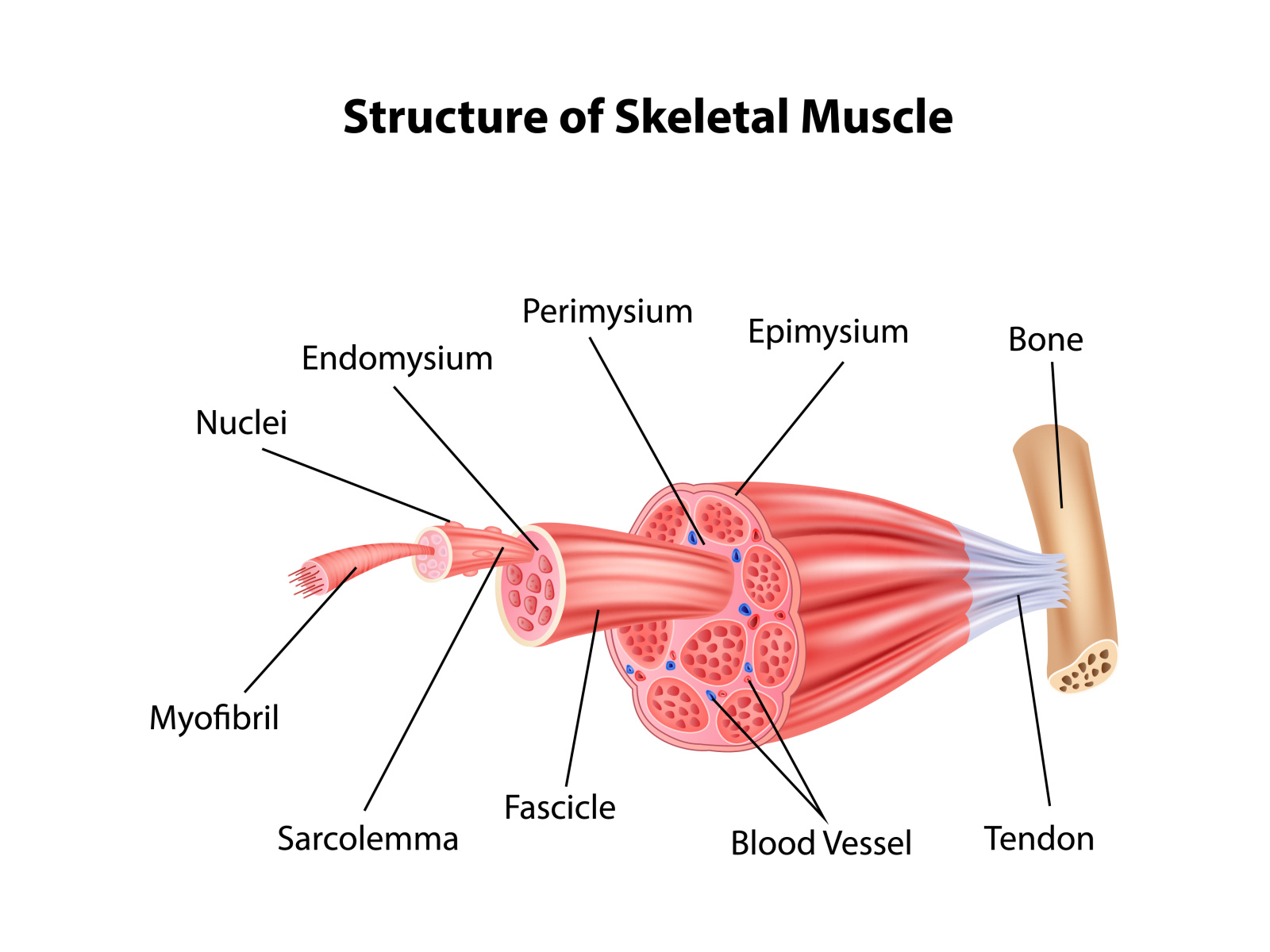
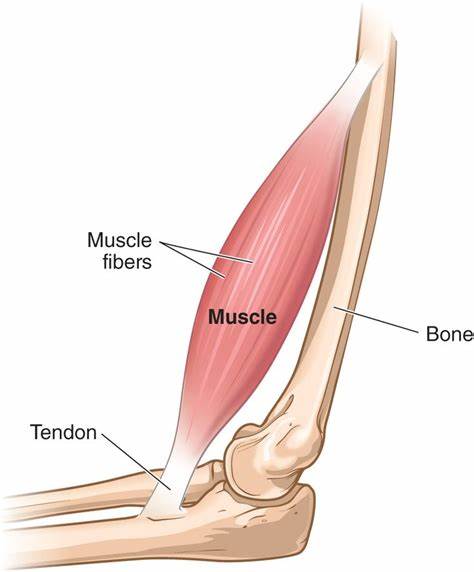
What is a tendon and its function?
A type of connective tissue that connects muscle to bone which can absorb the impact of muscles when moving, preventing injury.
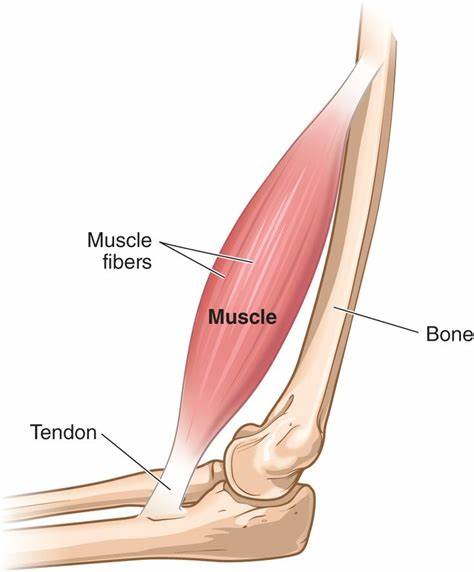
When describing how muscles work, what four factors do we discuss?
Origin of muscle
Insertion
Action
Innervation
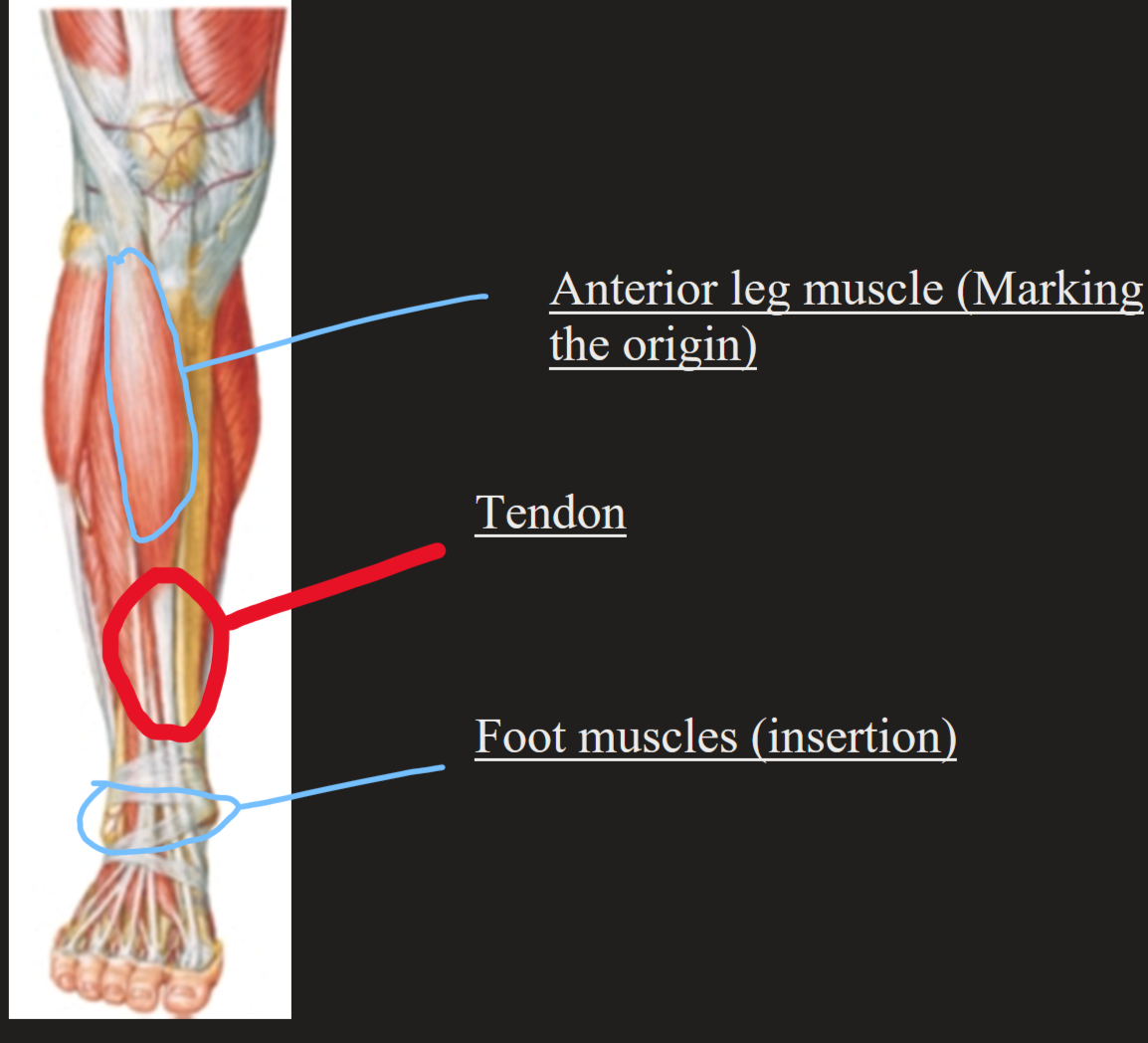
Origin of muscle
Muscle fibres that are attached to the periosteum which can cross a joint to form tendons.
Insertion
Where the tendon attaches skeletal muscles to bones.
Action
Contraction of muscle that pulls insertion towards the origin.
Innervation
What nerve gives the muscle its message to move.
What is the difference between prime movers/agonist and antagonist?
Prime movers are muscles that perform the intended motions whereas antagonist perform the opposite motions of the prime movers.
What are the three movements of muscle?
Concentric
Eccentric
Isometric
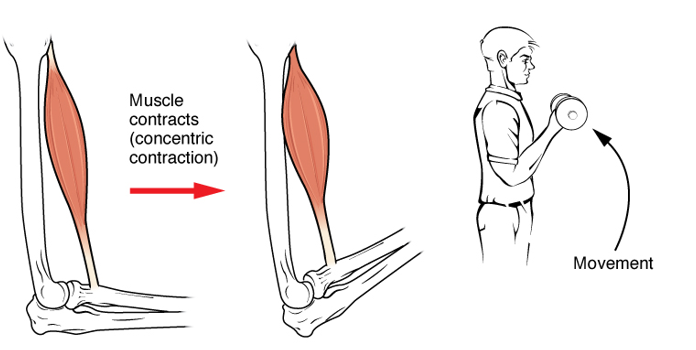
Concentric
Refers to the movement of muscles getting shorter as it moves towards a specific body part.
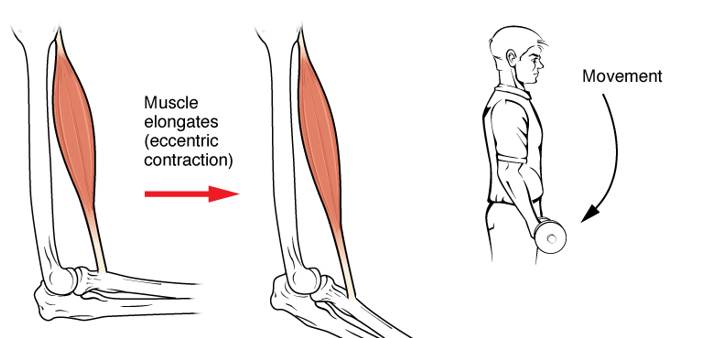
Eccentric
Refers to the movement of muscles getting longer as it moves away from a specific body part.
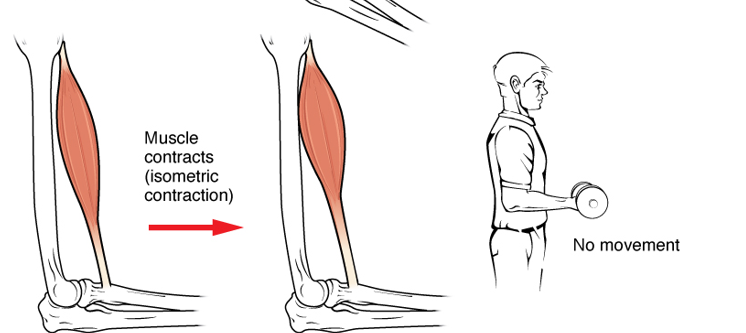
Isometric
Refers to the static position of the muscle where it stays the same length.
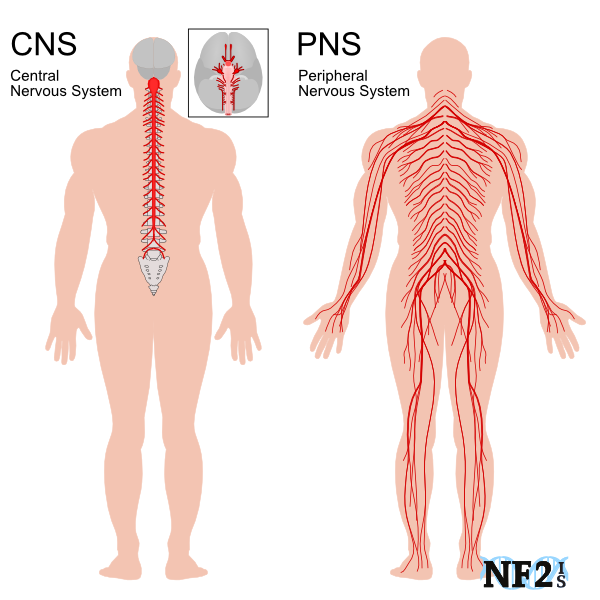
What is the difference between central and peripheral nervous system?
Central nervous system (CNS) comprises of the brain and spinal cord whereas peripheral (PNS) is everything else.
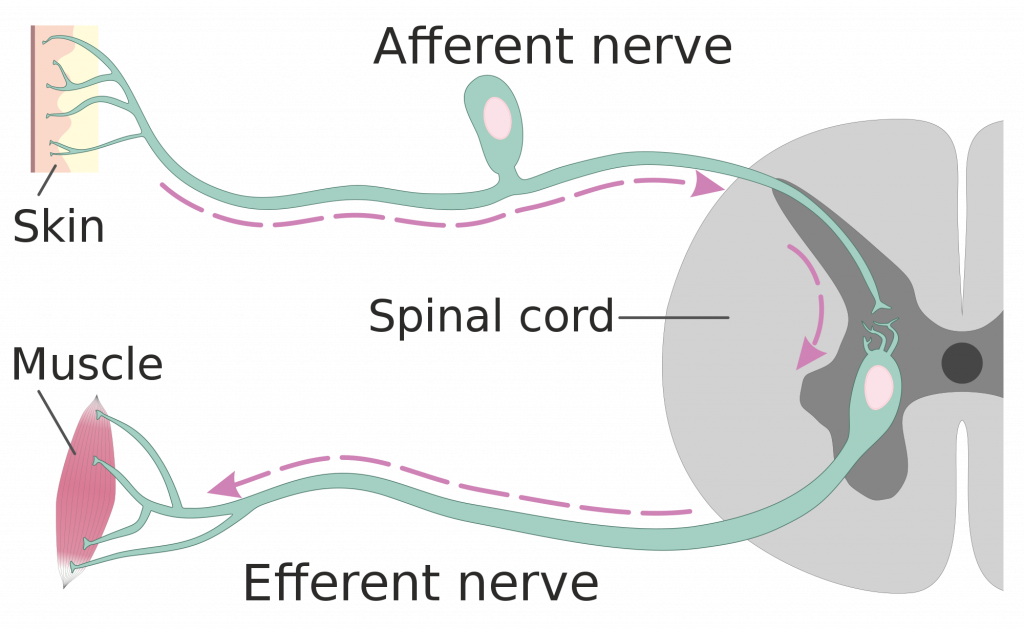
What is the difference between afferent and efferent neurons?
Although both are neurons, afferent neurons are sensory neurons that send impulses to the CNS whereas efferent neurons are motor neurons that receive signals from CNS to PNS.
What is the difference between somatic and autonomic nervous system?
Both are efferent divisions of the nervous system, where somatic is responsible for voluntary control of muscles whereas autonomic is responsible for involuntary control of effects within the body.
Spinal Nerve
A combination of motor and sensory nerves involved in carrying signals between the spinal cord and body and is responsible for receiving and responding to stimuli.
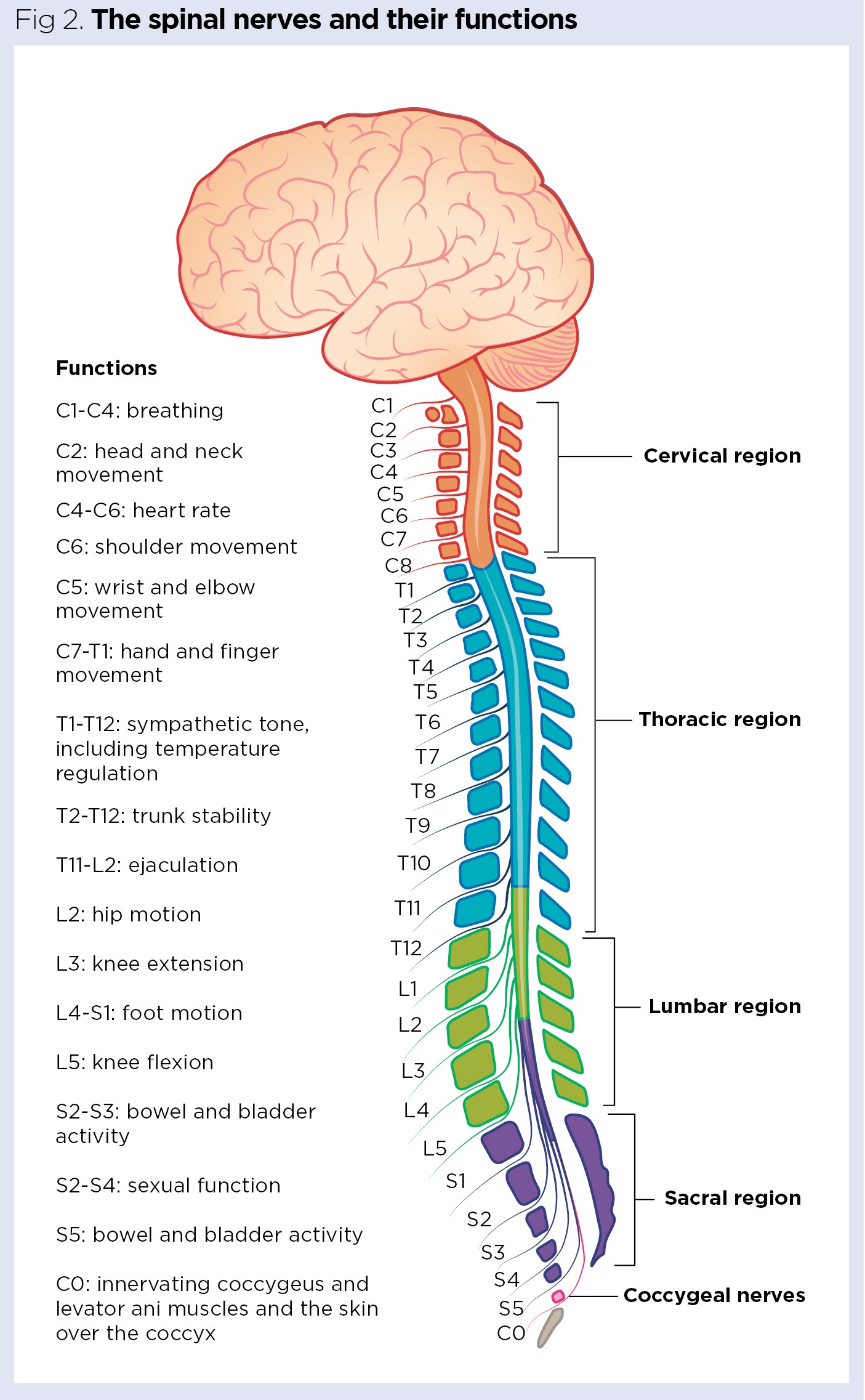
What muscle assists the tendon?
Synergist that stabilises the joint and enhances movement by providing additional force.
What do you call an immoveable joint?
Synarthrosis
What is bursae and its function?
Bursae are small pockets of synovial fluid that reduce friction and act as shock absorber where ligaments and tendons rub against other tissues.