Medterm Unit 2 Test
1/876
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
877 Terms
angi/o ; vas/o
vessel (ch.5 - combining forms)
aort/o
aorta (ch.5 - combining forms)
arteri/o
artery (ch.5 - combining forms)
arteriol/o
arteriole (ch.5 - combining forms)
ather/o
fatty substance (ch.5 - combining forms)
atri/o
atrium (ch.5 - combining forms)
cardi/o ; coron/o
heart (ch.5 - combining forms)
embol/o
plug (ch.5 - combining forms)
fibrin/o
fibers (ch.5 - combining forms)
isch/o
to hold back (ch.5 - combining forms)
myocardi/o
heart muscle (ch.5 - combining forms)
phleb/o ; ven/o
vein (ch.5 - combining forms)
sept/o
wall (ch.5 - combining forms)
son/o
sound (ch.5 - combining forms)
sphygm/o
pulse (ch.5 - combining forms)
steth/o ; pector/o
chest (ch.5 - combining forms)
thromb/o
clot (ch.5 - combining forms)
valv/o ; valvul/o
valve (ch.5 - combining forms)
varic/o
dilated vein (ch.5 - combining forms)
vascul/o
blood vessel (ch.5 - combining forms)
ventricul/o
ventricle (ch.5 - combining forms)
venul/o
venule (ch.5 - combining forms)
peripher/o
away from center (ch.5 - combining forms)
-cardia
heart condition (ch.5 - suffixes)
-manometer
instrument to measure pressure (ch.5 - suffixes)
-ole ; -ule
small (ch.5 - suffixes)
-pressor
to press down (ch.5 - suffixes)
-spasm
involuntary muscle contraction (ch.5 - suffixes)
-tension
pressure (ch.5 - suffixes)
-tonic
pertaining to tone (ch.5 - suffixes)
lungs, liver, kidneys
places where blood takes waste products from cells (ch.5 - A&P of cardiovascular system)
The heart
averages 60-100bpm, or about 100,000 beats per day
located in mediastinum, about the size of a fist
Heart layers
Endocardium
-inner lining of heart chambers
-smooth, thin layer; reduces friction
Myocardium
-thick muscle that contracts to develop pressure required to pump blood thru blood vessels
Epicardium
-forms visceral layer of pericardial sac
-fluid between layers of pericardial sac reduces friction as heart beats
diastole
chambers’ relaxation phase (ch.5 - blood flow thru heart)
systole
chambers’ contraction phase (ch.5 - blood flow thru heart)
Conduction system of heart (overall)
under control of autonomic nervous system
special tissue w/in heart conducts electrical impulses
-this tissue stimulates chambers to contract in the correct order
(ch.5 - conduction system of heart)
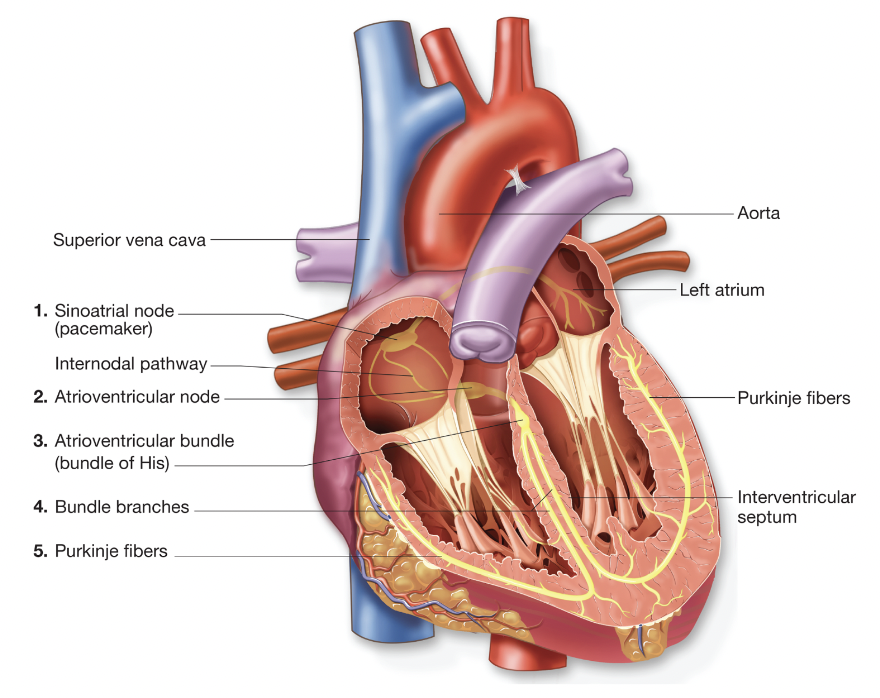
Conduction system of heart (step 1)
sinoatrial (SA) node begins electrical impulse → wave of electricity moves from SA node thru atria → atria contracts
(ch.5 - conduction system of heart)
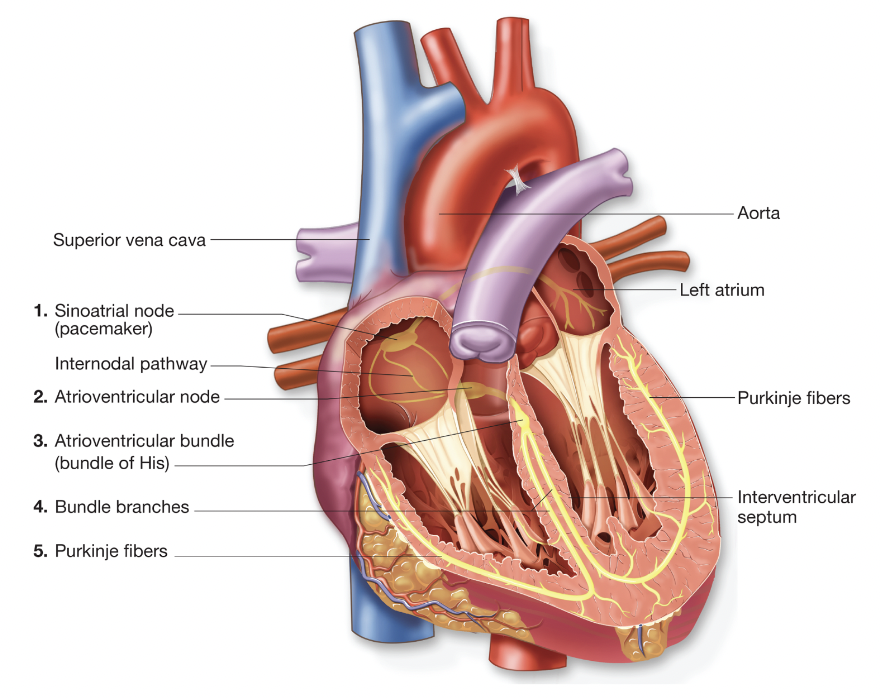
Conduction system of heart (step 2)
atrioventricular (AV) node is stimulated (ch.5 - conduction system of heart)
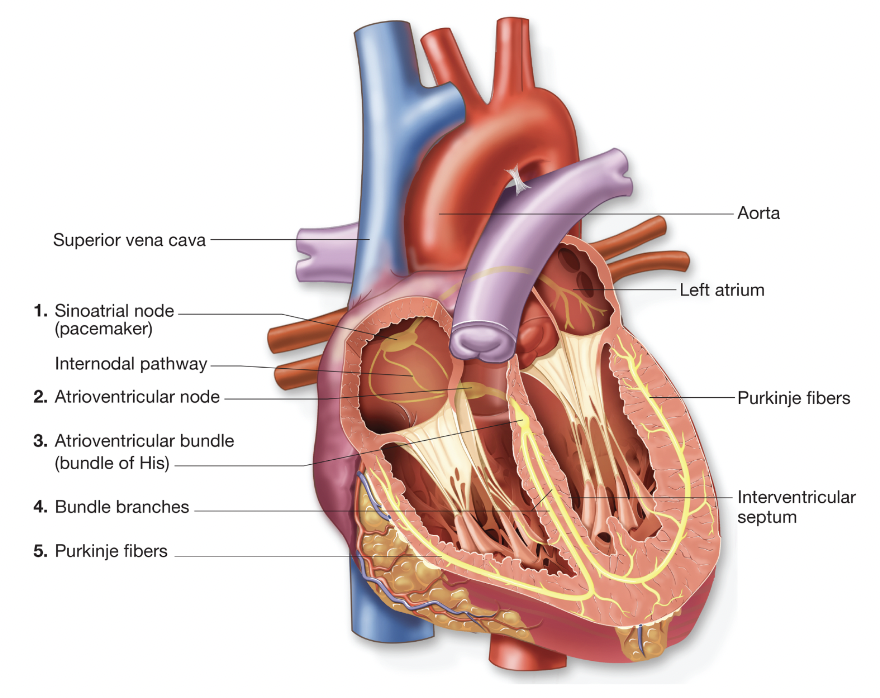
Conduction system of heart (step 3)
AV node transfers stimulation to the atrioventricular (AV) bundle (ch.5 - conduction system of heart)
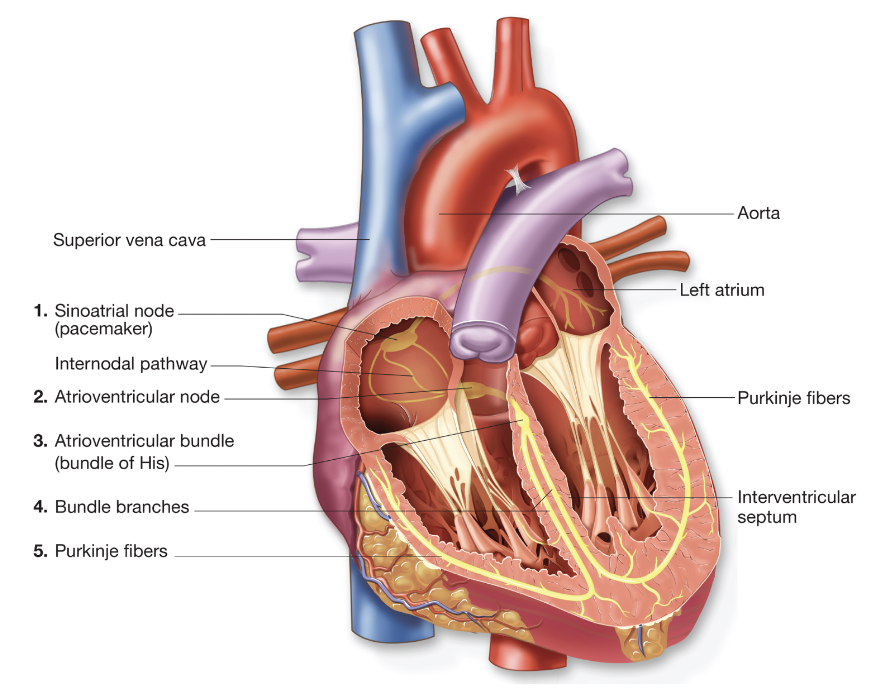
Conduction system of heart (step 4)
the electrical wave travels from the AV bundle down the bundle branches (ch.5 - conduction system of heart)
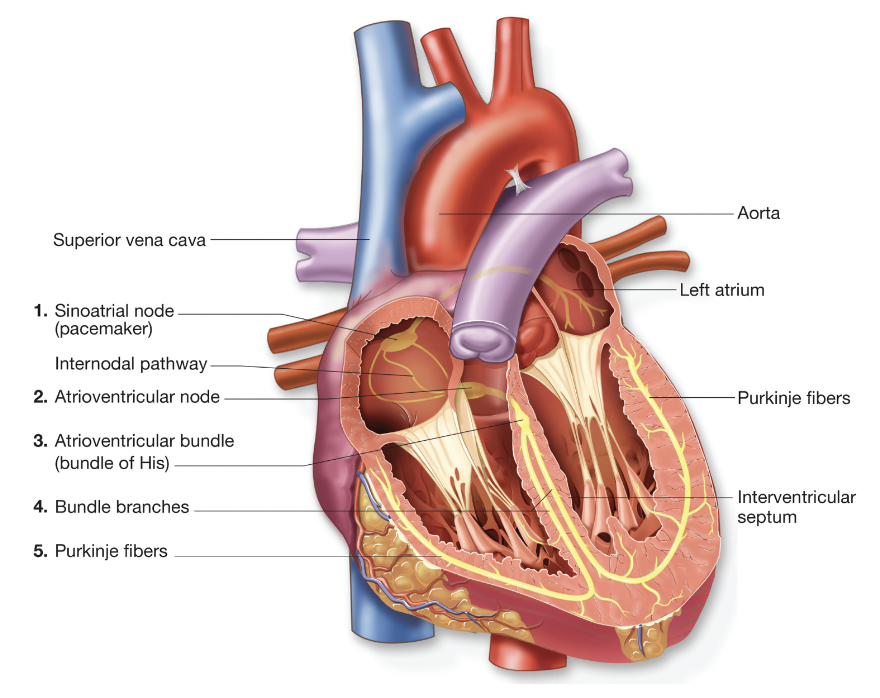
Conduction system of heart (step 5)
Purkinje fibers in ventricular myocardium are stimulated → ventricles contract (ch.5 - conduction system of heart)
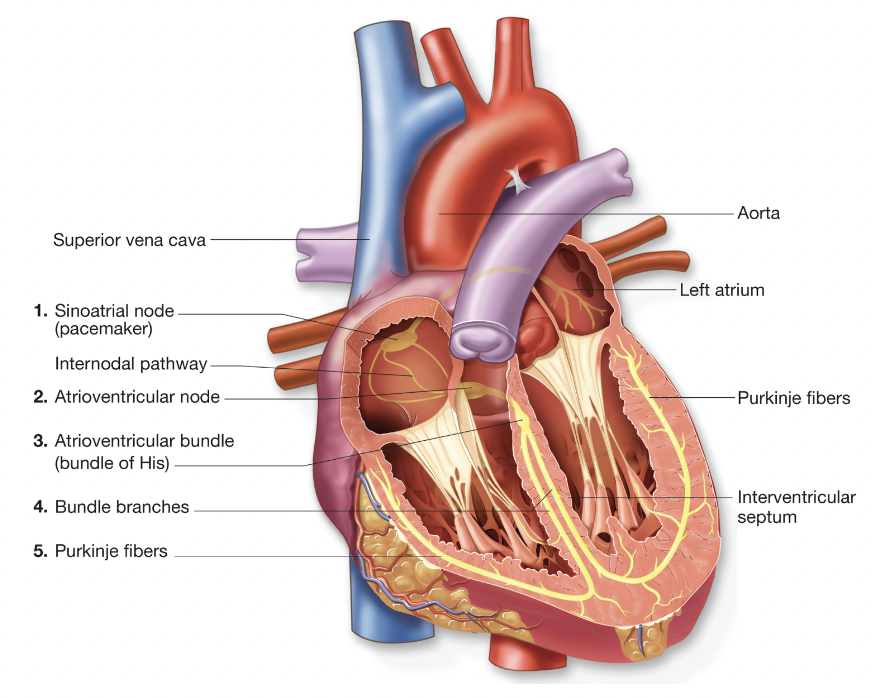
EKG
electrocardiogram wave record
-P wave: corresponds to contraction of the atria
-QRS complex: correlates to ventricles contracting
-T wave: represents preparation for next series of complexes
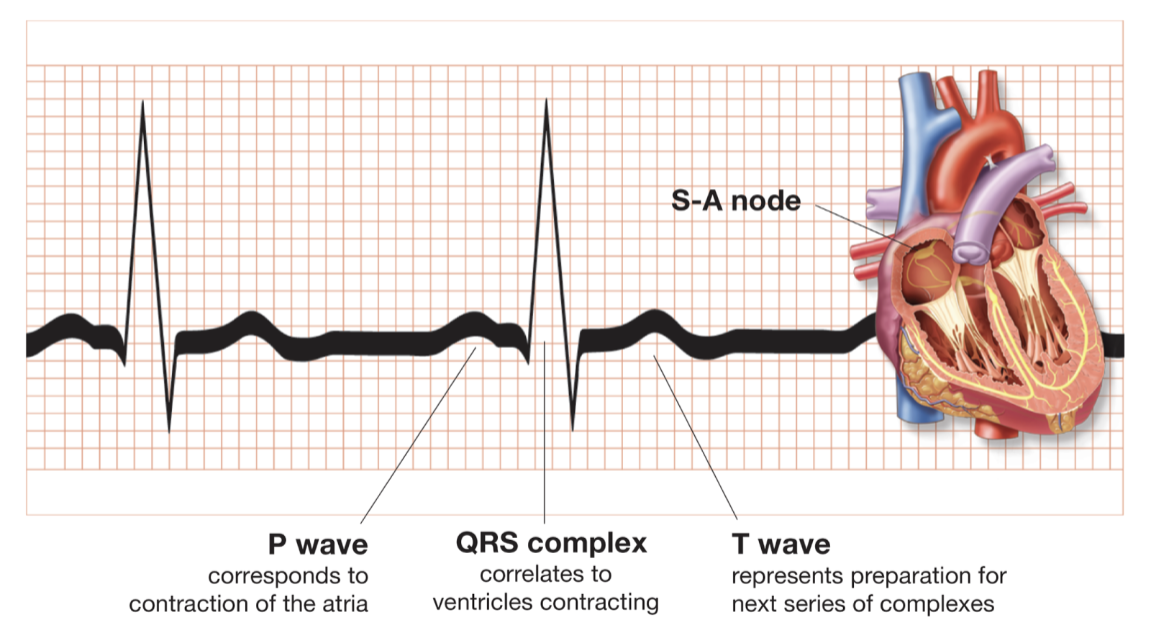
arteries, capillaries, veins
3 types of blood vessels (ch.5 - blood vessels)
lumen
channel w/in blood vessels (ch.5 - blood vessels)
comparative structure of arteries, capillaries, veins
all 3 have lumen and endothelium
capillaries don’t have external elastic membrane, smooth muscle, internal elastic membrane
veins are the only vessels w/ valves
(ch.5 - blood vessels)
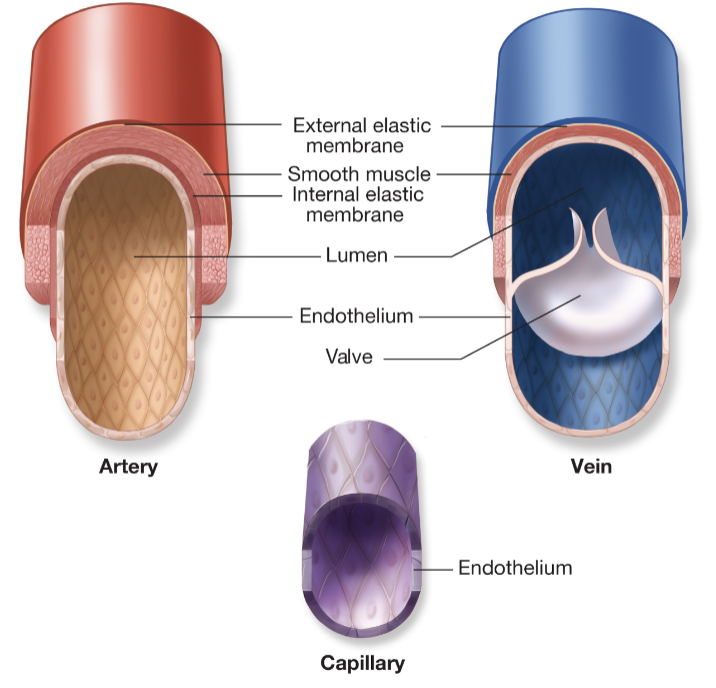
arteries
thick-walled and can contract or relax
coronary arteries go to myocardium (right, left, and left anterior descending branch)
become smaller arterioles as they branch
(ch.5 - blood vessels)
capillaries
network of tiny, thin-walled blood vessels
place of diffusion
-oxygen and nutrients diffuse out, CO2 and waste diffuse in
(ch.5 - blood vessels)
veins
thin walled, valvular vessels w/ low pressure
begin as venules that gradually merge and become larger
(ch.5 - blood vessels)
blood pressure
measures force exerted by blood against vessel walls
-during systole: highest reading (under a lot of pressure)
-during diastole: lowest reading (under little pressure)
120(systolic) / 80(diastolic)
may be affected by characteristics of blood and blood vessels
-elasticity of arteries
-diameter of blood vessels
-viscosity of blood
-amount of resistance to blood flow
(ch.5 - pulse and blood pressure)
pulse (p)
the surge of blood caused by the heart contraction
-commonly measured at throat or wrist
-in general, pulse rate is equal to heart rate
(ch.5 - blood vessels)
aneurysm
weakness and ballooning of arterial wall; commonly seen in abdominal and cerebral arteries (ch.5 - blood vessels)
arteriorrhexis
a ruptured artery (ch.5 - blood vessels)
arteriosclerosis
hardening and loss of elasticity of arterial walls; often due to atherosclerosis (ch.5 - blood vessels)
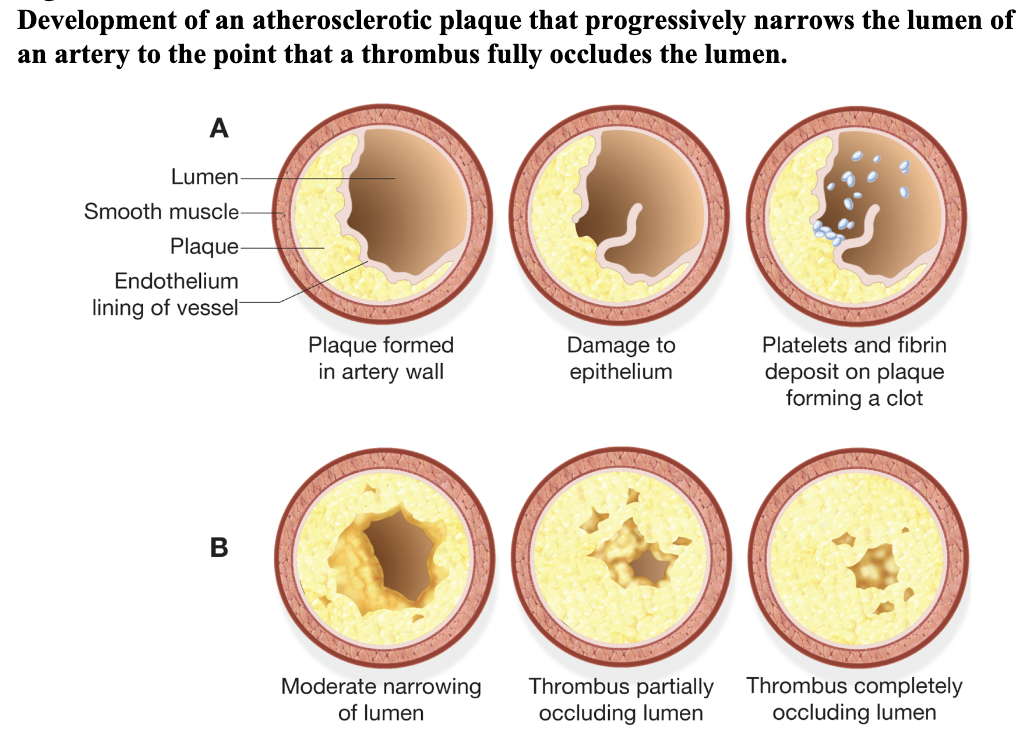
atheroma
deposit of fatty substance in wall of artery, bulges into and narrows artery; also called a plaque (ch.5 - blood vessels)
atherosclerosis
most common form of arteriosclerosis; lipid plaques form in arterial wall (ch.5 - blood vessels)
coarctation of the aorta (CoA)
severe congenital narrowing of aorta (ch.5 - blood vessels)
hemorrhoids
varicose veins in rectal and anal region (ch.5 - blood vessels)
hypertension (HTN)
high blood pressure; essential or primary hypertension due to CV disease; secondary hypertension results from another disease (ch.5 - blood vessels)
hypotension
decrease in blood pressure; may be due to shock or anemia (ch.5 - blood vessels)
patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
congenital heart anomaly where fetal connection between pulmonary artery and aorta fails to close at birth (ch.5 - blood vessels)
peripheral vascular disease (PVD)
abnormal condition affecting any blood vessel outside heart; symptoms may include pain, pallor, and blocked circulation (ch.5 - blood vessels)
Raynaud’s phenomenon
periodic ischemic attacks affecting extremities; especially fingers, toes, ears, and nose; extremities become cyanotic; triggered by cold exposure (ch.5 - blood vessels)
thrombophlebitis
inflammation of vein resulting in blood clots w/in a vein (ch.5 - blood vessels)
varicose veins
swollen and distended veins; often in the legs (ch.5 - blood vessels)
cardiovascular technologist/technician
healthcare professional trained to perform a variety of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures including electrocardiography, echocardiography, and exercise stress tests (ch.5 - medical specialties)
infarct
area of necrotic tissue due to loss of blood supply (ch.5 - signs and symptoms)
ischemia
local and temporary deficiency of blood supply due to a circulatory obstruction (ch.5 - signs and symptoms)
murmur
a sound in addition to normal heart sounds; may or may not indicate an abnormality
orthostatic hypotension
sudden drop in blood pressure when standing up suddenly (ch.5 - signs and symptoms)
palpitations
pounding, racing heartbeats (ch.5 - signs and symptoms)
plaque
yellow, fatty deposit of lipids in an artery; hallmark of atherosclerosis (ch.5 - signs and symptoms)
regurgitation
to flow backwards; in CV system refers to backflow of blood through a valve (ch.5 - signs and symptoms)
thrombus
blood clot w/in a blood vessel, may partially or completely occlude blood vessel; or a hard collection of fibrin, blood cells, and tissue debris that is the result of the blood-clotting process (ch.5,6 - signs and symptoms)
angina pectoris
severe pain and sensation of constriction around heart; caused by myocardial ischemia (ch.5 - heart conditions)
cardiac arrest
complete stopping of heart activity (ch.5 - heart conditions)
cardiomegaly
an abnormally enlarged heart (ch.5 - heart conditions)
cardiomyopathy
myocardial disease; may be caused by viral infection, congestive heart failure, or alcohol abuse, common reason for heart transplant (ch.5 - heart conditions)
congenital septal defect (CSD)
hole, present at birth, in heart septum; allows mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood (ch.5 - heart conditions)
congestive heart failure (CHF)
left ventricle muscle is too weak to efficiently pump blood; results in weakness, breathlessness, and edema (ch.5 - heart conditions)
coronary artery disease (CAD)
poor blood supply to heart muscle due to obstruction of coronary arteries; may cause angina pectoris and heart attack (ch.5 - heart conditions)
endocarditis
inflammation of membranes lining the heart; if cause is bacterial, a bacterial colony called vegetation may form (ch.5 - heart conditions)
heart valve prolapse
cusps too loose and fail to shut tightly; allows regurgitation (ch.5 - heart conditions)
heart valve stenosis
cusps too stiff; unable to shut tightly; allows regurgitation (ch.5 - heart conditions)
myocardial infarction (MI)
occlusion of coronary artery; results in a myocardial infarct; a heart attack (ch.5 - heart conditions)
tetralogy of Fallot
combination of four congenital anomalies; pulmonary stenosis, interventricular septal defect, improper placement of aorta, hypertrophy of right ventricle; requires immediate surgery (ch.5 - heart conditions)
arrhythmia
irregularity in heart beat or action (ch.5 - arrhythmias)
bundle branch block (BBB)
electrical impulse is blocked from traveling down the bundle of HIS or bundle branches (ch.5 - arrhythmias)
fibrillation
serious arrhythmia characterized by abnormal quivering or contraction of heart fibers; may result in cardiac arrest (ch.5 - arrhythmias)
flutter
atria beat too rapidly but maintain a regular pattern (ch.5 - arrhythmias)
auscultation
listening to sounds w/in body using a stethoscope (ch.5 - medical procedures)
sphygmomanometer
blood pressure cuff; measures blood pressure (ch.5 - medical procedures)
stethoscope
instrument for listening to body sounds (ch.5 - medical procedures)
cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)
procedure to restore cardiac output and oxygenated air for a person in cardiac arrest; uses chest compressions and artificial respiration (ch.5 - medical procedures)
defibrillation
procedure that converts irregular heartbeats, such as fibrillation, using an electric shock (ch.5 - medical procedures)
extracorporeal circulation (ECC)
routing blood to a heart-lung machine during a surgical procedure (ch.5 - medical procedures)
implantable cardioverterdefibrillator (ICD)
device implanted into the heart to deliver an electric shock to restore normal heart rhythm; especially helpful for ventricular fibrillation (ch.5 - medical procedures)
pacemaker implantation
device implanted into the heart to substitute for the natural pacemaker (ch.5 - medical procedures)
sclerotherapy
injection of salt solution to treat varicose veins (ch.5 - medical procedures)
thrombolytic therapy
use of drugs, such as streptokinase or tissue-type plasminogen activator, to dissolve clots and restore blood flow (ch.5 - medical procedures)