2.9-Structure of amino acids and proteins
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
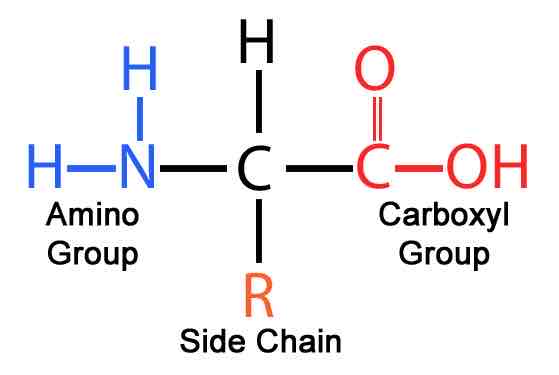
What is the general structure of an amino acid?
R-CH(NH2)-COOH
What is a dipeptide?
A peptide with 2 amino acids
What is a polypeptide?
A polypeptide with many amino acids
What role does water play in the production and breakdown of dipeptides?
Water is produced during the condensation reaction. Water is broken down during the hydrolysis reaction
Define protein
A molecule made up of amino acids
What is the R group?
The side group that changes depending on the amino acid
What is a peptide bond?
A covalent bond that links amino acids together to form a protein
What is the primary structure
The amino acid sequence
What is the secondary structure
The form a protein assumes after having folded up
What is the tertiary structure
The three dimensional structure of the entire polypeptide chain
What is the quaternary structure
The arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains that produce a complete protein
What is a conjugated protein
A protein with another chemical group attached
What is a globular protein
A protein that is water soluble and shaped like a sphere after folding
What is a fibrous protein
Long strands of polypeptide chains that have cross linkages due to hydrogen bonds
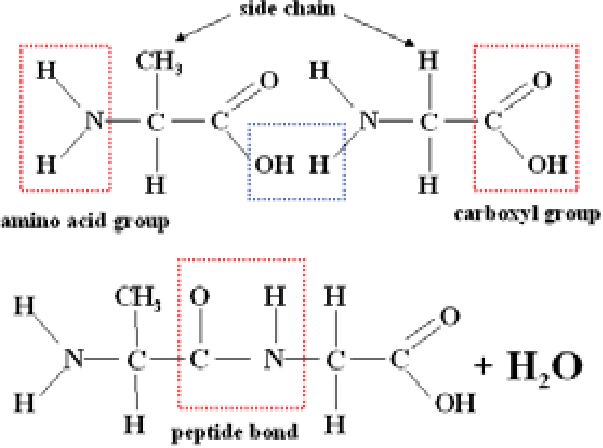
How is a peptide bond formed?
Condensation reaction.
OH removed from Hydroxyl group. H removed from amine group.
Explain how the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain determines the three dimensional shape of a functional protein
The sequence of amino acids determines the order of the R groups. This affects where the hydrogen bonds form in the secondary structure. Then affects where the ionic/covalent bonds form in tertiary structure