Chapter 11: Foreign Exchange rates
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What is an open economy?
It is one which interacts with other countries through various economic transactions.
What are the 3 ways by which the linkages between an economy with the rest of the world are established?
Output Market: An economy can trade in goods and services with the rest of the world.
Financial Market: An economy can buy or sell financial assets from/to other countries.
Labour market: Firms can choose whether to locate production and workers can choose where to work
How does foreign trade influence aggregate demand?
When Indians buy foreign goods, this spending escapes as a leakage from the circular flow of income decreasing aggregate demand.
Our exports to foreigners enter as an injection into the circular flow, increasing the aggregate demand for goods produced within the country
What are the aspects of the commitment of the government to ensure that the national currency will be freely convertible into another asset?
The ability to convert freely in unlimited amounts
The price at which conversion takes place
Which system ensures stability in international transactions?
International Monetary System
What is the foreign exchange rate?
It refers to the rate at which currency of one country is converted into currency of the other country.
What is Foreign Exchange?
It refers to the sum total of the stocks of:
Foreign currencies
Securities and bonds issued by foreign corporates and governments.
What is the foreign exchange rate?
It refers to the price of one currency in terms of another. It can be defined in 2 alternate ways:
Number of units of domestic currency required to buy a unit of foreign currency.
Number of units of foreign currency that can be purchased in exchange for a unit of domestic currency. It represents the external purchasing of a currency. It is the rate at which exports and imports of a nation are valued at a given point of time.
Mention the types of Foreign Exchange Rate Systems.
Fixed exchange rate system
Flexible Exchange rate System
Managed Floating Rate System
What is the Fixed Exchange Rate System?
It refers to a system in which the rate of exchange of a currency is fixed by the government. Under this system, government is responsible to stabilise the exchange rate. To do so, the government buys foreign currency when the exchange rate is low and sells foreign currency when the exchange rate is high. To achieve stability in exchange rate, the government has to maintain large reserves of foreign currencies.
What were the 2 systems of fixed exchange rate?
Gold Standard system of exchange: (1870-1914): Gold was taken as the common unit of parity. Each country defined the value of their currency in terms of gold.
The Bretton Woods System: (1944 - 1971) All currencies were pegged or related to the US Dollar.
Which organisation worked as the central institution in international monetary system to control the foreign exchange market?
International Monetary Fund
What are the Merits of the Fixed Exchange Rate?
It ensures stability in the exchange rate
Coordination of macro policies becomes convenient.
It prevents speculation in foreign exchange market.
It encourages international investment
What are some demerits of fixed exchange system?
It does not encourage venture capital
It is difficult to determine foreign exchange rate
There is a possibility of under or over valuation of the currency
Government has to maintain 100% gold reserves.
What is the Flexible Exchange rate System?
It refers to a system in which exchange rate between currencies of different countries is determined by the market forces of demand and supply.
There is no government intervention in the foreign exchange market.
Exchange rate is determined by the market forces of demand and supply.
It is called flexible because it tends to change with changes in market forces.
What is the exchange rate called when the demand for foreign currency is equal to its supply?
Par Rate of Exchange
Normal Rate
Equilibrium Rate of Foreign Exchange
What are the merits of flexible exchange rate system?
It solves the problem of overvaluation or undervaluation of currencies.
There is no requirement of government to hold 100% gold reserves.
It encourages venture capitalism.
What are the demerits of the Flexible Exchange Rate System?
There is no stability.
Speculation in foreign exchange market may discourage foreign investment.
This discourages international trade.
What is the Managed Floating Rate System?
It refers to a system in which foreign exchange rate is determined by market forces and the central bank influences the exchange rate through intervention in the foreign exchange market.
The central bank intervenes as a bulk buyer or seller of foreign exchange to control fluctuations in the exchange rate.
When the exchange rate is high, the central bank starts selling foreign exchange from its reserves to bring it down and vice-versa.
What is also called the ‘hybrid’ system, between Fixed Rate and Flexible Exchange rate System?
Managed Floating Rate System
What is the meaning of dirty floating?
If a country’s Central Bank manipulates the exchange rate to influence the value of a country’s currency, it is called dirty floating.
What are the differences between Fixed Exchange Rate and Foreign Exchange Rate?
Baisis | Fixed Exchange Rate | Flexible Exchange Rate |
Meaning | It is fixed in terms of gold or any other currency by the government | It is determined by the market forces of demand and supply of foreign currency. |
Effect of market forces | It does not change with changes in demand and supply of foreign exchange rate. | It changes with the changes in demand and supply of foreign exchange. |
Control of Government | There is full government control in determining the exchange rate | There is no government control in determining the exchange rate. |
Stability | It generally remains stable. Any variation is initiated by the government | It changes whenever there is a change in market forces of demand and supply. |
Change in the value of domestic currency |
|
|
What are the sources or determinants of demand for foreign exchange?
Import of goods and services: It has to make payment in foreign exchange.
Tourism: They require foreign exchange to meet their expenditure abroad.
Remittances by Foreigners Working in India: These foreign workers earn their income in India. They send it back to their homeland.
Repayment of Interest and Loans: Paying interest to repay the loans to foreign lenders.
Extension of loans to foreigners: If India needs to extend assistance to other countries, India will demand foreign exchange.
Investments: There will be demand of foreign exchange when investments are made by India in other countries.
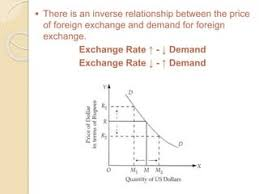
What is the relation between price of foreign exchange and demand for foreign exchange?
Other things being equal, there is an inverse relationship between the price of foreign exchange and the demand for foreign exchange. At a higher price, the cost of purchasing foreign goods rise, therefore, less of foreign exchange is demanded and vice versa.
Draw the curve to depict the inverse relationship between price and demand of foreign exchange.
What are the sources or determinants of supply for foreign exchange?
Export of goods and services: Whenever foreigners purchase our goods and services, we are paid in foreign exchange. The supply of foreign exchange in India’s foreign exchange increases.
Foreign tourists in India: They spend foreign exchange in our country.
Remittance by Indians working abroad: They send their savings back to their homeland, India.
Foreign Direct Investment by MNCs: This results in flow of foreign exchange in India.
Purchase of shares by Foreign investors: Results in flow of foreign exchange to the Indian share markets.
Deposits by Non-resident Indians: Foreign exchange flows in the Indian foreign exchange market.
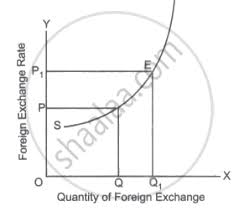
What is the relation between price of foreign exchange and supply for foreign exchange?
The supply of foreign exchange has a direct relationship with the price of foreign exchange, other things being equal.
If the price of foreign exchange goes up, the cost of purchasing goods from India reduces therefore the quantity supplied of foreign exchange will also rise.
If the price of foreign exchange falls, the quantity supplied of foreign exchange will also fall.
Draw the curve to depict the direct relationship between price and supply of foreign exchange.
Determine the Equilibrium rate of foreign exchange. Mention the observations.
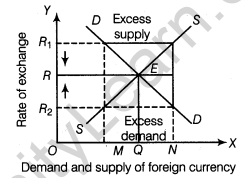
Equilibrium rate of exchange is established at a point where the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of foreign exchange are equal.
Negatively sloped demand curve and positively sloped supply curve of foreign exchange intersect each other at point E
Point E shows equilibrium between demand and supply of foreign exchange.
Point E corresponds to equilibrium rate of exchange which is OR
At this price, OM quantity of foreign exchange is demanded and supplied.
Depict the equilibrium point of foreign exchange and explain the levels of excess demand and excess supply.
At a price higher than equilibrium rate, there will be excess supply of foreign exchange in India’s foreign markets. This will push down the price of foreign exchange. It will cause extension in demand and contraction in supply till it reaches the equilibrium position.
On the other hand, if the rate is lower than the equilibrium price, it will give rise to excess demand of foreign exchange. This will pull up the rate of foreign exchange.
What are the causes of the change in the rate of foreign exchange?
Currency depreciation
Currency appreciation
What is the meaning of depreciation of Domestic Currency / Appreciation of Foreign Currency?
It refers to the decrease in the value (external purchasing power) of domestic currency in terms of foreign currency. It occurs when there is an increase in the domestic currency price.
A rise in the exchange rate implies depreciation of Indian rupee.
What are the causes for rise in exchange rate? Explain their observations.
Increase in demand for foreign exchange: Observations;
Due to increase in demand, the DD curve shifts to the left.
New equilibrium point is achieved
Due to excess demand there is competition among buyers, which pushes the price upwards
Due to increase in price, supply extends.
Market demand and supply now coincide at point E1.
Decrease in supply of foreign exchange: Observations:
Due to fall in supply of foreign exchange, the supply curve shifts to the left.
This causes excess demand.
This causes competition among buyers which pushes the prices upwards.
Due to rise in price, the demand contracts..
Market demand and market supply of foreign exchange now becomes equal at E1.
What are the effects of depreciation of domestic currency on foreign trade?
Effect of depreciation on exports: It encourages exports. It means that one dollar can be exchanged for more rupees. It means that with one dollar, more goods can be purchased from India. This will encourage exports.
Effect of depreciation on imports; It discourages imports. It means a fall in the value of domestic currency in terms of foreign currency. It means that 1 dollar will be exchanged for more rupees. It means that more domestic currency will be required to buy goods worth 1 dollar. It means that imports will be discouraged.
What is the difference between devaluation and depreciation of currency?
Devaluation: It is the fall of the value of domestic currency in relation to foreign currency as planned by the government. It is not determined by the market forces of demand and supply.
Depreciation: It is the fall in the value of domestic currency in relation to foreign currency in a situation wherein exchange rate is determined by the forces of demand and supply in the international money market.
What is the meaning of Appreciation of Domestic Currency / Depreciation of Foreign Currency?
It refers to the increase in the value (external purchasing power) of domestic currency in terms of foreign currency. It occurs when there is a decrease in the domestic currency price to buy a unit of foreign currency. A fall in the exchange rate implies appreciation of Indian rupee.
What are the causes for decrease in the exchange rate? Explain their observations.
Fall in demand of foreign currency. Observations:
Due to decrease in demand of foreign exchange, the demand curve shifts to left.
This causes excess supply
This leads to competition among sellers which pulls the price downwards.
Due to decrease in price, supply contracts.
Market demand and Market supply become equal again at E1.
Rise in supply of foreign currency:
Due to rise in supply of foreign currency, the supply curve shifts to the right
This causes excess supply.
Due to increase in supply, there is more competition among sellers which pushes the price downwards.
Due to fall in price, the demand extends.
Market demand and market supply becomes equal again at point E2..
What are the effects of appreciation of domestic currency on foreign trade?
Effect of appreciation of domestic currency on exports: It means the increase in the value of the domestic currency in terms of foreign currency. It means that 1 dollar can be exchanged for fewer rupees. It implies that with the same dollar, less goods can be purchased from India. This will discourage imports by the USA from India. Therefore, exports will decrease.
Effect of appreciation of domestic currency on imports: It means the increase in the value of domestic currency in terms of foreign currency. It means that 1 dollar can be exchanged for fewer rupees. It implies that for one dollar, less units of domestic currency are required. Therefore, imports from the USA will increase.
What are the causes of the rise in demand for foreign currency?
The demand for foreign currency increases due to the appreciation of domestic currency.
When the price of foreign currency falls, its demand rises for speculative purposes as now it is available at a lower price.
It makes imports cheaper as the domestic country has to pay lesser price now.
Tourism to the foreign country increases as travelling abroad has now become relatively cheaper.
Fall in exchange rate would increase the level of investment abroad.
What are the causes of the rise in supply for foreign currency?
The demand for foreign currency increases due to the depreciation of domestic currency.
When price of foreign currency rises, it encourages exports as with the same unit of foreign currency, more goods can be purchased from domestic country.
Supply of foreign exchange rises due to increasing tendency towards making speculative gains in the domestic country. '
When the price of foreign currency rises, investment from the foreign country into the domestic country rises as purchasing power of foreign currency in the domestic country rises.
Tourism into the domestic country rises as travelling to the domestic country has now become cheaper.
Appreciation of foreign currency increases direct purchases by the non-residents in the domestic country.
What is the meaning of the foreign exchange market?
It is defined as the market in which foreign currencies are bought and sold. It is a system where buyers and sellers of foreign currency provide facilities in trading of foreign currencies. These constitute foreign exchange brokers, commercial banks, other authorised dealers and monetary authorities.
It is the market where national currencies are traded for one another.
What are the functions of the Foreign Exchange Market?
Transfer Function: It arises when some transaction between residents of 2 countries takes place. It implies transfer of purchasing power in terms of foreign exchange across different countries of the world.
Credit Function: Like domestic trade, foreign trade also depends on credit. Foreign exchange market provides for credit in Foreign trade transactions. Bills of exchange are used as credit instruments for international payments.
Hedging Function: It implies protection against the risk concerning variations in foreign exchange rate. Demand and supply of foreign exchange is committed at some commonly agreed rate even when the commitments are to be honoured on some later date.
What is a spot market?
It refers to a market wherein current transactions in foreign exchange take place. The sale and purchase of foreign currency is affected at the prevailing rate of exchange on the spot. The delivery of foreign exchange is also affected instantaneously.
What is the spot rate?
It is the rate at which current transactions take place. A two day margin is required to settle the transactions as payment through cheques requires clearance time.
What is a Forward Market?
In a forward transaction in a foreign exchange market:
contracts to purchase and sell foreign exchange are entered on ‘SPOT’.
the price at which the foreign exchange will be sold/purchased is decided in advance on ‘SPOT’
payment will be made on the specified date in the future.
the forward seller may charge a premium or offer a discount on the spot rate.
What is the forward rate?
It is the rate at which forward transactions take place.