2.1.3 The Neuron HBS Human Body Systems PLTW WCHS Mr. Alasti
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What does a neuron generally do?
Enables your body to send signals to and from the brain
Clinical Researchers
Works with humans to determine the safety and effectiveness of medications, devices, diagnostic products, and treatment regimens intended for human use. Clinical research can be used for prevention, treatment, diagnosis, or relief from symptoms of a disease
Experimental Researchers
Focus on cells and model organisms to study the properties of drugs and materials
How do clinical researchers and experimental researchers work together?
They work together to expand the knowledge base about the brain and nervous system to reduce the burden of neurological diseases
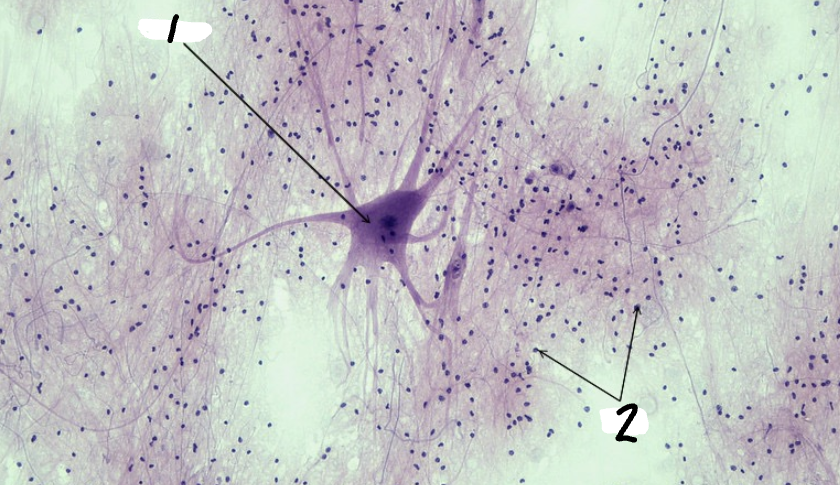
Label the image
Neuron
Glia
Neurons
Primary signaling cells of the nervous system; they send and receive electrical and chemical signals to communicate with each other in the nervous system and with other types of cells in the body
Glial Cells
Cells in the nervous system that provide protection and maintain homeostasis for neurons
What are neurons and glial cells responsible for when working together?
All sensations, movements, thoughts, memories, and feelings
What are the three essential parts of all neurons?
A cell body
An axon
Dendrites
Cell Body
Central part of a neuron that contains the nucleus and is the main structural component of gray matter
Axon
A long nerve cell process that usually conducts impulses away from the cell body
Dendrites
Any of the usually branching protoplasmic processes that conduct impulses toward the cell body of a neuron
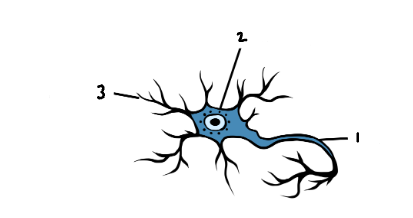
Label the image
Axon
Cell Body
Dendrite
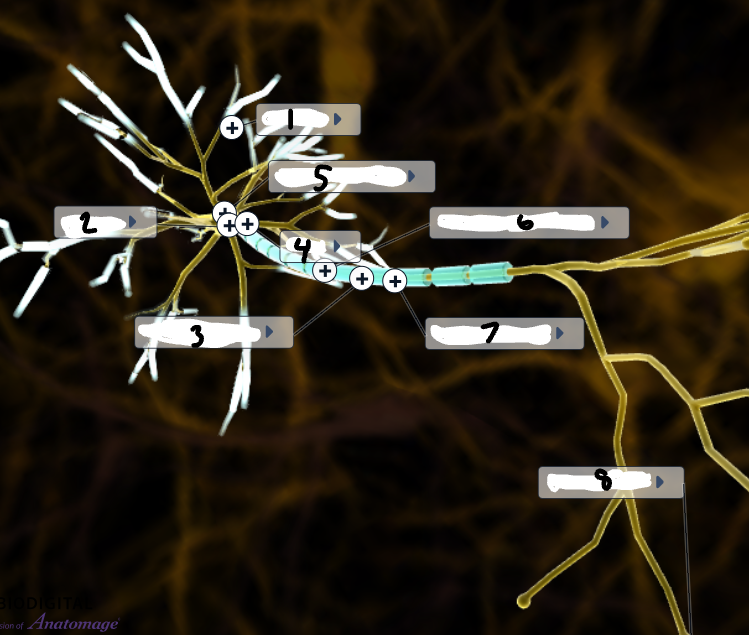
Label the image
Dendrite
Nucleus
Node of Ranvier
Axon
Soma (Cell Body)
Normal Myelin Sheath
Node of Ranvier
Axon Terminal
Schwann Cell
The cell that produces the myelin sheath
Axon Terminals
The ending of axons; the location where axons make contact with other nerve or effector cells
Myelin Sheath
In a neuron, an insulating coat of cell membrane from Schwann cells that is interrupted by nodes of Ranvier
Nodes of Ranvier
The gaps in the myelin sheath of nerve cells found between neighboring Schwann cells
What do glial cells (or neuroglia) care for?
Neurons; they also maintain the environment neurons are in
Do glial cells have axons or dendrites?
No
Can glial cells generate action potentials or nerve impulses?
No
What are the 6 major types of glial cells?
Ependymal Cells
Oligodendrocytes
Satellite Cells
Astrocytes
Microglial Cells
Schwann Cells
What can happen when glial cells do not function properly?
Various problems can occur, including diseases and tumors
What causes most brain tumors?
Mutations in glial cells
What do many neurodegenerative diseases (multiple sclerosis) involve?
Damage to myelin sheaths
Which cells produce the myelin sheaths that are damaged in diseases like multiple sclerosis?
Schwann cells
What neurons are pictured?
Rat hypothalamus neurons

What neurons are pictured?
Rat neonatal retinal cells, bipolar

What neurons are pictured?
Mouse CD1 cortex neurons, multipolar
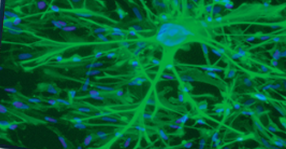
What neurons are pictured?
Normal human astrocytes
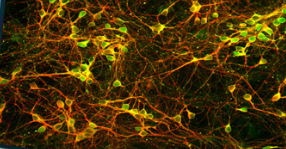
What neurons are pictured?
Rat brain cortex neurons

What neurons are pictured?
Rat brain microglia
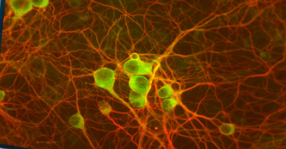
What neurons are pictured?
Rat cerebellar cells, unipolar
How are neurons classified?
By their function
What are the three basic groups of neurons?
Sensory
Motor
Interneurons
Synapse
The place at which a nervous impulse passes from one neuron to another
Neurotransmitter
A substance (as norepinephrine or acetylcholine) that transmits nerve impulses across a synapse
Multipolar Neuron
Makes multiple connections with other cells using dendrites, and is the most common kind of motor and interneuron
What type of neuron are 99% of neurons?
Multipolar
Bipolar Neuron
A rare neuron used for your main senses in the eyes, ears, and nose (sight, hearing, and smell)
Pseudounipolar Neuron
The most common type of sensory neuron found within our hands, feet, and skin
Unipolar Neuron
A neuron not found in humans
What are the three broad types or three main categories of neurons?
Sensory, motor, and interneurons
Job of sensory neurons
Sense what’s in the environment and send signals to the spinal column (CNS)
Job of interneurons
Receive signals sent from sensory neurons, and process and send a signal to motor neurons
Job of motor neurons
Act upon the signal sent from interneurons
Afferent neurons
Carry information to the CNS
Efferent neurons
Carry information away from the CNS
How are hormones similar to radio signals?
It takes a long time for them to get going and land on their target cells, which act like antennas to receive the signal, and then it lasts a long time
How are nerves similar to old-school telephone lines?
They are fast acting and fast finishing, and the only way to stimulate it again is to send another nerve signal
What are the myelin sheaths made out of?
Fat
What are the gaps between the myelin sheaths?
Nodes of Ranvier
What subsystem of the nervous system are interneurons (association neurons) part of?
CNS