forensic toxicology and pharmacology
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
forensic toxicology
study of poisons that may have legal implications
toxicologist
drugs after ingested into body
two phase approach —> presumptive and confirmatory test
seized drug analysts
drug as physical evidence
tracking drugs in the body
ADME
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion
metabolized mostly in liver
amphetamine
stimulants —> excitatory condition —> increased heart rate, blood pressure and respiratory rate
euphoria
cocaine
stimulant —> extracted from coca leaves with HCl
—> when treated with base —> “crack” cocaine
metabolized to methylecgonine
cannabionoids
psychoactive compounds found in marijuana
tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
a cannabinoid
—> euphoria, perceptive alterations, memory impairment, mood swings, hallucinations and delusions and paranoia
polypharmacy
using multiple prescription drugs
gas chromatography (GC)
for testing chemical components of a mixture
more than 350 mg/dL — death
cyanide poisoning
fasting acting form is gas hydrogen cyanide
death occurs within minutes
fatal level: 2500 ng/pmL
carbon monoxide poisoning
blood carboxyhemoglobin over 60% is at risk of death
testing in forensic toxicology
two step approach —> presumptive/screening and confirmatory test
confirm by finding toxins in two location (eg. blood and urine)
immunoassays
screening test —> antibodies used —> only reacts when substance is present
!! not 100% specific
thin-layer chromatography (TLC)
screening test
silica gel covered plate + extracted specimen in organic solvent —> spotted onto the plate
plate placed in tank —> mobile phase
slow moving compound —> don’t react with silica
cheap and is the primary method
gas chromatography
confirmatory test
GC + detection system
mobile phase=carrier gas = an inert gas (H, N, He)
paired with mass spectrometer (MS) —> GC-MS
retention time = how long it takes for sample to move thru column
Electron impact
ionization scheme used in MS
mass spectrometry
most common is quadruple mass filter
compound in GC ionized —> electron impact —> find molecule
liquid mass chromatography
compatible with all organic compounds (don’t have to be converted to gas form)
good for thermolabile and hydrophilic stuff
colourimetric testing
for measuring metals
cheap
high detection levels
needs lots of sample
inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS)
measures metals
more modern
low detection level
small sample size
$$$
pharmacokinetics
how a drug/ toxin moves thru the body
toxicogenomics
how genetics play a role in how toxic a drug/poison is for a person
drugs affects when taken → absorbed —> tissues —> metabolized — > relies on enzymatic activity —> can be metabolized at different rates
drug testing in dead ppl
used to find manner of death
not studied well (ethical reasons)
postmortem redistribution —> concentration changes that occur after death —> drugs move to different regions of the body
controlled substances act (CSA)
US code —> define use of controlled substances —> divided drugs into schedules (groups) based on potential for abuse and medical use
1984 —> allowed drug enforcement administration (DEA) to temp. add substance to schedule
schedules
Schedule I —> high potential for abuse, not accepted as medicine (heroin)
Schedule II —> high potential for abuse and have accepted medical uses (cocaine, morphine, methamphetamine)
Schedule III —> less potential for abuse and addiction (anabolic steroids, barbiturates)
Schedule IV and IV —> decreasing risk, increasing legit uses (over the counter cough medicines)
SWGDRUG
Scientific working group for the analysis of seized drugs
provides recommendations for types/min number of tests requires to identified seized drugs
3 categories for analytical techniques for identification of controlled substances
Category A —> specific examinations
Category B —> moderately specific techniques
Category C —> Nonspecific Techniques
botanical examinations
identification of controlled substances
—> identify physical characteristics specific to plants that are considered controlled substances
chemical examinations
identification of controlled substances
—> using wet chemical or instrumental techniques to identify specific substances
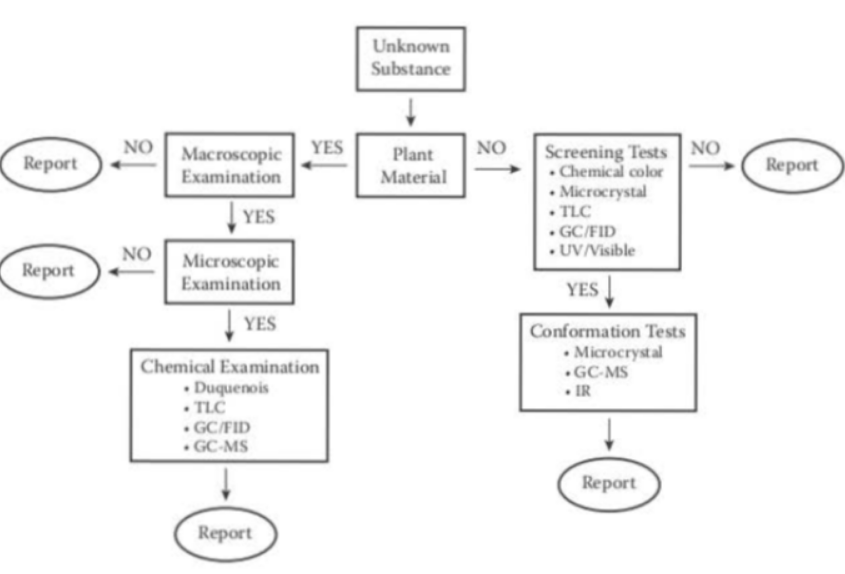
plant matter analysis
plant —> macro examination —> mico exam. —> chem. exam
not plant —> screening test —> confirmation test
top four botanical examination caseload
marijuana
peyote
mushrooms
opium
marijuana
cannabis sativa
identify: (2 steps)
physical traits (—> macro and micro)
establish presence of plant resin that has psychoactive stuff
micro. exam. —> cystolithic hairs (bear-claw shaped) on t level of lead
duquenois-levine test —> chem. colour test to confirm presence of weed in sample
hashish
resin from marijuana isolated from plant
found as oil or in cake form to be smoked
federal law (US) doesn’t care between marijuana and hashish
—> duquenois-levine test is all needed to identify
peyote
Lophophora williamsii (small mexican cactus)
has mescaline —> hallucinogenic effects

mushrooms 🍄
components within the mushroom (psilocin, psilocybin) are controlled substances
additional step to confirm the Ps is needed
over a dozen mushrooms types contain the Ps
caps can be white to tan, stems off-white+bluy gray staining
chemical examinations
needs identification of specific compound within mixtures
steps (SEC)(“chem will just take a SEC lol) —> screening, extraction, confirmation
two types —>
wet chem. —> screening methods, sample prep. (non specific)
instrumental procedures → screening methods, confirmatory tools
chemical colour tests (chem. examinations)
chem reactions → gives info abt structure of the substance
can indicate presence of generic molecular structure
small amount of substance transferred to well and test reagent is added
+ and - controles
microcrystal tests (chem. examinations)
test samp. dissolved in solution containing reagent → reaction where nique solid crystals form
this test relies on comparison of crytals formed and those formed by reference standard → subjective
extractions (chem. examinations)
used to separate compound of interest from rest of the sample
type of extractions
physical extraction (physically removing particles)
dry washing
dry extractions (solvent removes compound from sample)
liquid extractions (utilizing solubility characteristics)
infrared (IR) spectroscopy (instrumental examination)
uses compound ability to absorb IR light → solid samples good
organic compounds absorb different portions of IR spectrum → absorbance charts→ unique → library ok known IR spectra of compounds used for comparison
clandestine drug laboratories
illegal places that make controlled substances
clandestine lab chemist → forensic chemist w/ training in clandestine manufacturing techniques