Chapter 4 tissues
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Epithelial tissues
lines hollow organs
connective tissues
protects ans supports and blinds organs ex(bone, blood, cartilage)
What tissue would fat be
connective
muscular tisssue
generates physical force to make the body move
nervous tissue
detects changes in the body and responds by generating naive impulses
epithelia tissue
cells arranged in continuous sheets
true or false epithelial tissue can be single or multiple layered
true
single layer
single
multiple layer
stratified
in epithelial tissues cells are ____ packed together
closely
epithelial tissues are found at
a boundary betweenween two different environments
epithelial will always
have a free surface somewhere that has space on top of it
two types of epithelial
cover and Line, glandular co
covering And lining
covers outer surfaces, lines inner surfaces
glandular epithelium
forms most glands of the body to produce some sort of product , sweat gland, oil glands
general functions of epithelium
protection of underlying tissues, secretion, absorption, diffusion, filtration, sensory
special features of epithelial
abundance of cells, specialized contact pointsanchored to a basement membrane, polarity(basal, apical), support by connective tissue (basement membrane), avascular, high regeneration, nervous innervation
apical surface
faces body surface
basal surface
opposite of apical surface, adheres to basement membrane
because epithelial tissue is a vascular it is dependent on
diffusion
Regeneration results from
high motif activity
True or false classify epithelial first shape of cells, second arrangement of cell layers
false vice versa
cubodial
square
squamous
flat
columnar
like a column, longer than flat
you name the cell shape on the most
apical surface
simple squamous
one layer flat cells (thinnest layer possible), allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration,
What is a component of all tissue cells
cells and extracellular matrix
epithelial tissues cover body surfaces and lines hollow organs aswell as `
body cavities and ducts. They also form glands and protect underlying structures.
connective tissue binds organs aswell as
store energy as fat
muscular tissue generates physical force needed to make body structures and generate
body heat
simple
1 cell layer
cuboidial
square
a simple cubodial epithelium function is
secretion and absorption (part of the gland produces substance
) ex: sweat
simple cubodial epithelium can be found in
Kidney tubules, ducts and secretory portions of small glands, ovary surface
epithelial cell always faces
free surface
hollow space
lumen
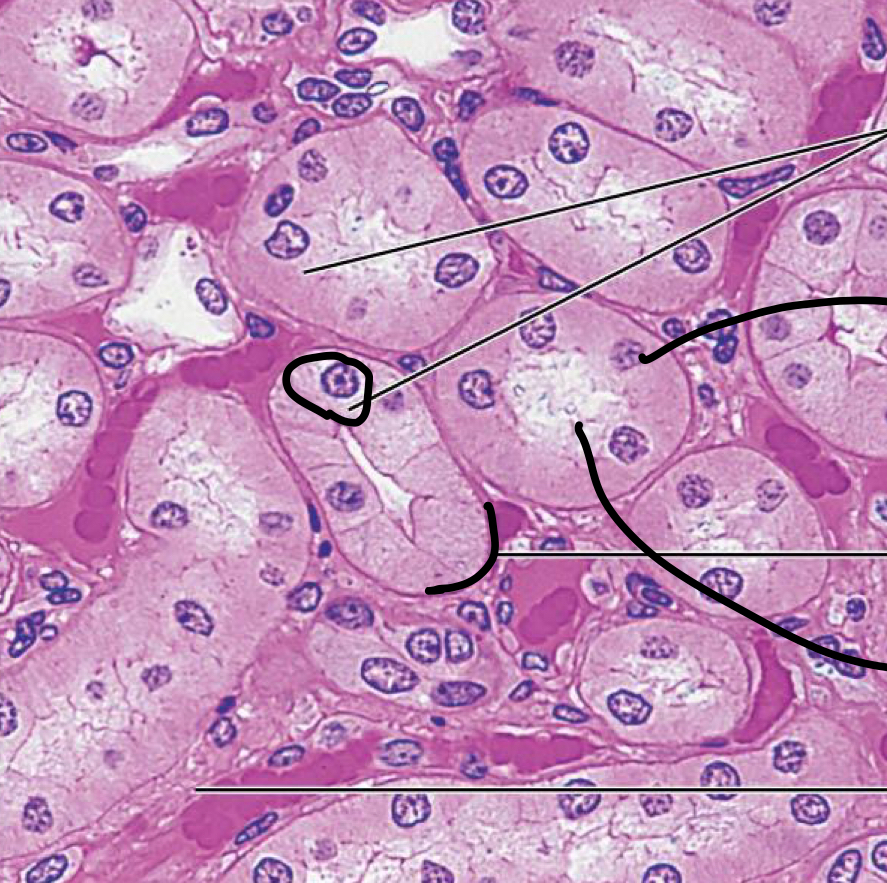
What cell is this
simple cubodial epithelium
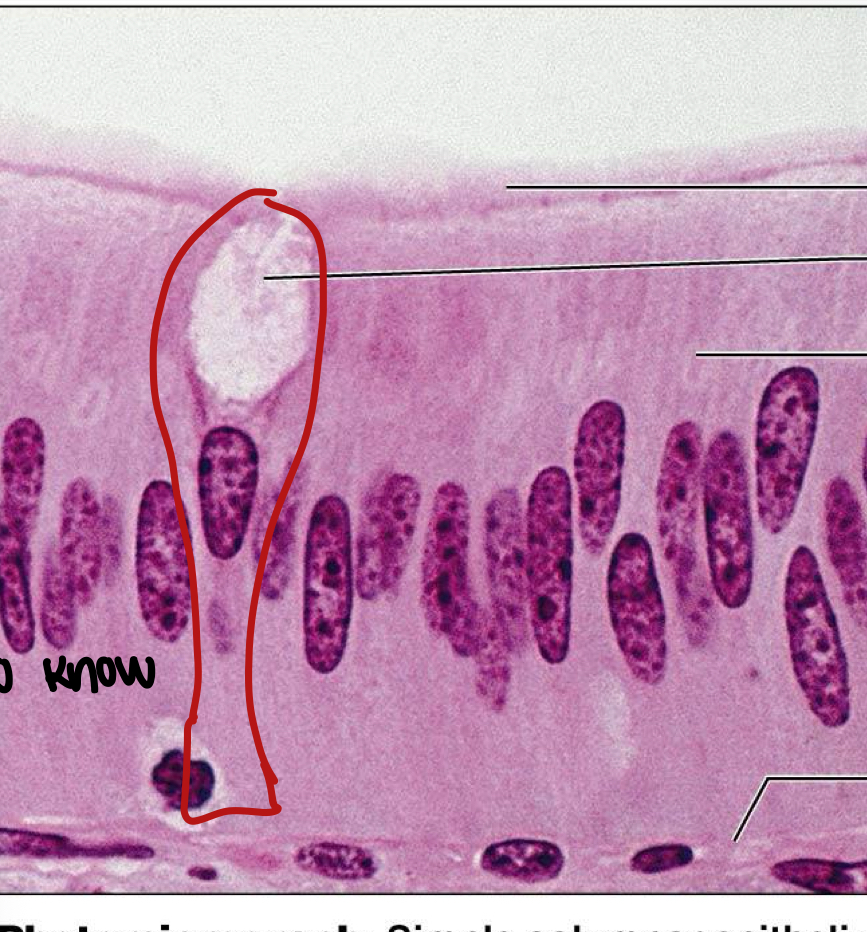
What cell is this
simple columnar epithelium
simple columnar epithelium is described as
a single layer of tall cells with round oval nuclei, some cells bear cilia, layer may contain mucus secreting unicellular glands
simple columnar epithelial cilia microtubules are at the
apical surface of the epithelial
simp0le columnar epithelium function
absorption, secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances, cilliated thype propels mucus by cilliary action
where do noncililated simple columnar epithelium reside
lines most of the digestive tract, gallblaffer and excretory ducts of some glands
where do cilliated simple columnar epithelium reside
small bronchi, uterine tubes, and some regions of the uterus
what are goblet cells
specialized epithelial cells that produce mucous
cilia is often associated with
mucous
pseudostratified columnar epithelium description
single layer of cells differing heights, some not reaching the free surface, nuclei seen at different levels, may contain goblet cells and bear cilia
pseudostratified columnar epithelium function
secretion of mucus, propulsion of mucus by ciliary action