Periodicity AQA (specification from 2015)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:28 PM on 11/1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
1
New cards
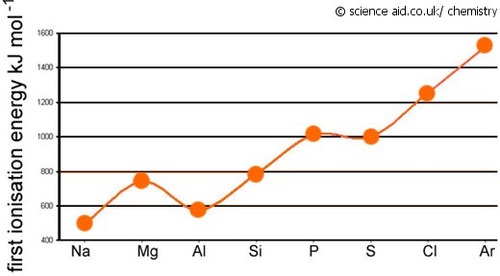
Describe and explain the general trend in ionisation energy across Period 3 (Na to Ar)
The general trend is that ionisation energy increases across Period 3 (Na to F)
2
New cards
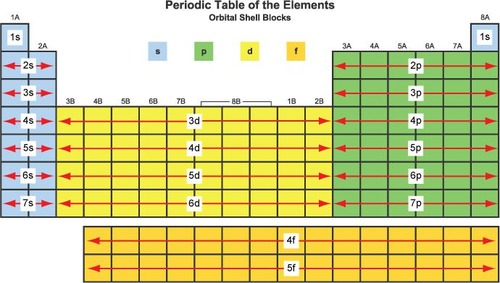
Using the periodic table state which groups make up the 's' block
group 1 & 2
3
New cards
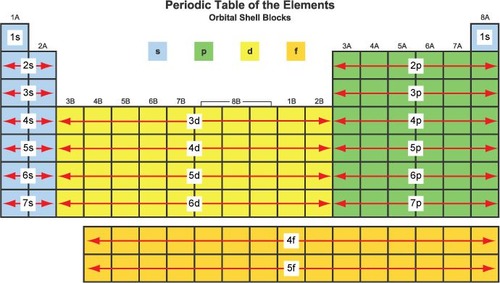
Using the periodic table state which groups make up the 'p' block
Group 3,4,5,6,7 & 8 (0)
4
New cards
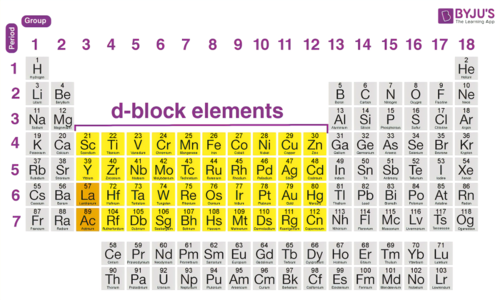
What block do the Transition metals belong to?
'd' block
5
New cards
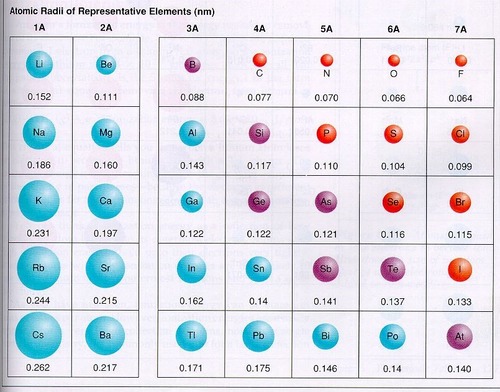
State and explain the trend in ATOMIC RADIUS going across period 3 (Na to Ar)
The atomic radius DECREASES (Na to Ar)
The atomic number increases (there are more protons in the nucleus)
The shielding is constant (electrons added to the same outer shell)
The force of attraction between the nucleus and OUTER ELECTRONS INCREASES
The atomic number increases (there are more protons in the nucleus)
The shielding is constant (electrons added to the same outer shell)
The force of attraction between the nucleus and OUTER ELECTRONS INCREASES
6
New cards
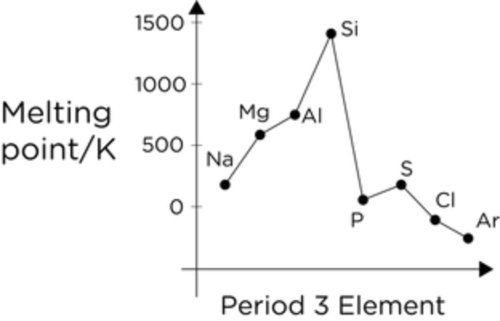
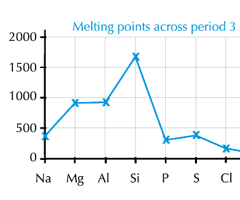
Describe the trend in melting point/boiling across period 3 (Na to Ar)
Na to Al: The melting point increases.
Al to C: A significant increase in melting point at Carbon
C to P: The melting point drops significantly at phosphorous
P to S to Cl: There is a small increase at sulphur, a drop to Chlorine and a further drop to Argon
Al to C: A significant increase in melting point at Carbon
C to P: The melting point drops significantly at phosphorous
P to S to Cl: There is a small increase at sulphur, a drop to Chlorine and a further drop to Argon
7
New cards
With reference to the bonding type, explain the trend in melting point/boiling point across period 3 part 1 (Na to Al)
Na to Al : metallic bonding (giant)
metallic bond strength increases
-the size of the metal ion decreases
-the charge on the ion increases
Increasing amount of energy needed to overcome the bonds
metallic bond strength increases
-the size of the metal ion decreases
-the charge on the ion increases
Increasing amount of energy needed to overcome the bonds
8
New cards
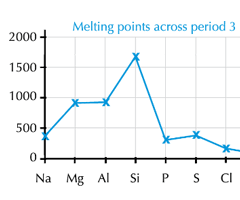
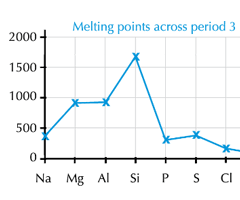
With reference to the bonding and structure, explain the trend in melting point/boiling point across period 3 part 2 (Silicon)
Silicon is macromolecular (giant)
-many, strong covalent bonds to break
-this requires a lot of energy to overcome
-many, strong covalent bonds to break
-this requires a lot of energy to overcome
9
New cards
With reference to the bonding and structure, explain the trend in melting point/boiling point across period 3 part 3 (P to Cl)
P to Cl: These are simple molecules with weak intermolecular forces of attraction between molecules (strong covalent bonds between atoms)
The elements exist as:- P₄, S₈ and Cl₂
Weak Van Der Waals forces exist between the molecules. These increase with increasing numbers of electrons (increasing Mr). So, S₈ has a higher melting point than P₄ and Cl₂ has the lowest melting point
The elements exist as:- P₄, S₈ and Cl₂
Weak Van Der Waals forces exist between the molecules. These increase with increasing numbers of electrons (increasing Mr). So, S₈ has a higher melting point than P₄ and Cl₂ has the lowest melting point
10
New cards
State which elements deviate from the general trend in ionisation energy across Period 3 (Na to F). Explain why this happens.
Aluminium:
-the electrons lost in Al is from the 3p subshell
- this is further away from the nucleus than the 3s electron lost by Magnesium
- the attraction between the nucleus and the outer electrons in Al is less than for Mg
Sulphur:
- the electron lost by S is in a paired orbital
-There is mutual repulsion between the electrons, so it is easier to remove
-the electrons lost in Al is from the 3p subshell
- this is further away from the nucleus than the 3s electron lost by Magnesium
- the attraction between the nucleus and the outer electrons in Al is less than for Mg
Sulphur:
- the electron lost by S is in a paired orbital
-There is mutual repulsion between the electrons, so it is easier to remove
11
New cards
Describe and explain the general trend in ionisation energy down groups in the Periodic table
Ionisation energy decreases down the groups
- as you go down the group the atomic radius increases
- the outer electrons are further from the nucleus
-shielding increases & so does atomic number
The attraction between the outer electrons and the nucleus decreases
- as you go down the group the atomic radius increases
- the outer electrons are further from the nucleus
-shielding increases & so does atomic number
The attraction between the outer electrons and the nucleus decreases
12
New cards
An element in Period 3 has the following successive ionisation energies in kJmol⁻¹ (1st IE onwards).
State the element and explain your answer
577, 1816, 2744, 11577, 14842, 18379, 23326 ,27465, 31853, 38473
State the element and explain your answer
577, 1816, 2744, 11577, 14842, 18379, 23326 ,27465, 31853, 38473
Aluminium
-There is a LARGE jump in Ionisation Energy between the 3rd and 4th value
-the 4th ionisation energy is removing an electron from a shell closer to the nucleus
-this electron has significantly less shielding hence the large jump in Energy need to remove it
-There is a LARGE jump in Ionisation Energy between the 3rd and 4th value
-the 4th ionisation energy is removing an electron from a shell closer to the nucleus
-this electron has significantly less shielding hence the large jump in Energy need to remove it
13
New cards
What is Periodicity? (2)
The regular (1) repeating pattern of physical or chemical properties (1)
14
New cards
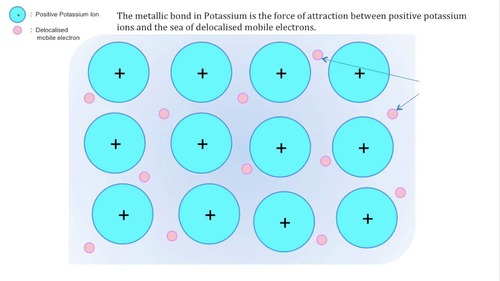
Draw a diagram of the bonding in potassium
Explain the bonding
Explain the bonding
At least 9 ions in three rows
each ions has +1 charge and there is a delocalised electron present for each ion.
STRONG electrostatic forces of attraction between the positive metal ions and the sea of delocalised electrons in a lattice
each ions has +1 charge and there is a delocalised electron present for each ion.
STRONG electrostatic forces of attraction between the positive metal ions and the sea of delocalised electrons in a lattice
15
New cards
Use the explanation of bonding in potassium to explain the physical properties of metals : melting point
melting points are high because many, strong electrostatic forces of attraction between the positive metal ion and the sea of delocalised electrons which require a lot of energy to overcome
16
New cards
Use the explanation of bonding in potassium to explain the physical properties of metals: electrical conductivity
Conduct Electricity because -the delocalised electrons are free to move and carry charge
17
New cards
Use the explanation of bonding in potassium to explain the physical properties of metals: malleable
Malleable: the layers of metal ions can slide over each other without breaking the metallic bond
18
New cards
Explain why diamond has a high melting point
Diamond is macromolecular
-it has many, strong covalent bonds which require a large amount of energy to overcome
-it has many, strong covalent bonds which require a large amount of energy to overcome
19
New cards
Explain why diamond does not conduct electricity but graphite does
Each carbon in diamond makes four covalent bonds - so there are no free electrons
Each carbon in graphite makes three bonds so there is one free electron per carbon which is mobile and able to carry charge
Each carbon in graphite makes three bonds so there is one free electron per carbon which is mobile and able to carry charge
20
New cards
Explain why S, P and Cl do not dissolve well in water.
S, P and Cl has Van Der Waals intermolecular forces. Water makes hydrogen bonds between molecules of water.
It would mean breaking the stronger hydrogen bonds in water to form weaker Van der Waals between water and S (P or Cl). This is energetically unfavourable.
It would mean breaking the stronger hydrogen bonds in water to form weaker Van der Waals between water and S (P or Cl). This is energetically unfavourable.