Chemistry Exam Review SNC1W1
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards on Chemistry Exam Review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Pure substance
A substance that is made up of only one type of particle.
Mixture
A substance that is made up of more than one type of particle.
Solution
A uniform mixture of two or more substances where you can only see one phase.
Mechanical mixture
A mixture in which you can distinguish between different types of matter.
Alloy
A solid solution of two or more metals.
Physical property
A characteristic of a substance that can be determined without changing its composition.
Qualitative property
A property of a substance that is not measured and does not have a numerical value.
Quantitative property
A property of a substance that is measured and has a numerical value.
Physical change
A change in which the composition of the substance remains unaltered.
Chemical property
A characteristic of a substance that is determined when the composition of the substance changes.
Chemical change
A change in the starting substance(s) and the production of one or more new substances.
Density
The mass per unit volume of a substance.
Element
A pure substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler chemical substance by any physical or chemical means.
Compound
A pure substance composed of two or more different elements that are chemically joined.
Atomic number
The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus.
Mass number
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
Ancient Greeks
The first concept of the atom can be traced back to them
the word atom comes from the Greek Atomos, meaning indivisible.
Democritus reasoned that if you broke matter down into smaller pieces, you would eventually reach the point where it could not be broken down any further
Alchemists
Their major contribution to atomic theory was technological advances which allowed for the development of modern science.
lab glassware and equipment, alloys, handling procedures for dangerous chemicals
Dalton's Atomic Model
Suggested that atoms were solid, indivisible spheres; main problem was that his theory did not address how things acquire electrical charge.
Thomson's Atomic Model
Atoms were composed of a uniform positive charge, with negatively charged electrons embedded in them. Positive charge was not uniformly distributed, nor were electrons simply embedded within the atom.
Rutherford's Atomic Model
Proposed the nuclear model of the atom. The atom has a very small, heavy nucleus (protons) surrounded by electrons; most of the atom is empty space; model did not adequately address electron behaviour.
Bohr's Atomic Model
Similar model to Rutherford, except that electrons are found in fixed energy levels around the nucleus.
Chadwick
Discovered the neutron.
Test for hydrogen gas
a burning splint that produces a "popping" sound
Test for oxygen gas
a glowing splint that bursts into flames
Test for carbon dioxide
Limewater mixed with the gas turns milky
metal that s liquid at room temp
Mercury
Metals that are not silver in colour
Gold and copper
Metals that are magnetic
Iron(Fe), cobalt(Co), nickel(Ni), neodymium(Nd)
Characteristic of silicon
Solid, silver, brittle, lustre, semi conducter, not magnetic
Non-Metal that is a conductor
Graphite
clues of a chemical change
change of colour
bubbles of gas produced
heat and/or light is released or absorbed
change of odour
a precipitate is produced
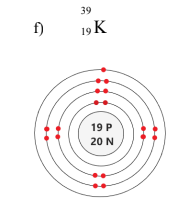
How to draw Bohr-Rutherford diagrams
Wrting the number of protons and neutrons as #p #n in a circle in the middle
Drawing the electrons on rings in the order 2,8,8,2
Sublimation
Solid-Gas
Depostion
Gas-solid