Kinetic Molecular Model
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
1
New cards
Kinetic Molecular Model
Explains the properties of solids and liquids in terms of the following:
* __Intermolecular forces of attraction__
* __Kinetic energy of the individual particles__
* __Intermolecular forces of attraction__
* __Kinetic energy of the individual particles__
2
New cards
Kinetic Energy
the ability to cause changes in matter
3
New cards
Kinetic Energy
it is __dependent on the temperature__ of substance (rise in temperature increases the KE, making particles move more vigorously)
4
New cards
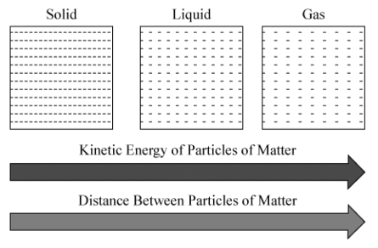
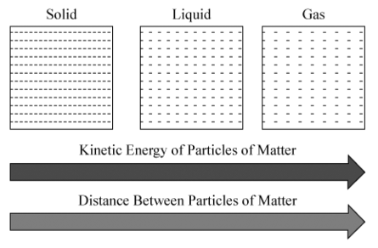
Relationship between kinetic energy and distance between particles
Directly Proportional
5
New cards
London dispersion forces
When __two non-polar molecules__ approach each other, an instantaneous dipole moment forms
6
New cards
London dispersion forces
Weakest type of intermolecular force
7
New cards
Dipole-dipole Forces
only __Polar molecules__ can experience this force
8
New cards
Dipole-dipole Forces
Ex: a slightly negative side of the water molecule is attracted to a slightly positive side of the water molecule
9
New cards
Hydrogen bonds
special type of dipole-dipole
10
New cards
Ion-Dipole Forces
Exists between an __ion (charged particle) and a polar molecule__
11
New cards
Ion-Dipole Forces
Positive side of the molecule is attracted to the negative ion and the negative side of the molecule is attracted to the positive ion