Intro to Graphics
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is Graphics?
The field of computing that deals with generating, manipulating, and displaying visual content using computers
Includes image creation, rendering, animation, modelling, etc
Covers both 2D (flat) and 3D (volumetric) content.
Visual: Include examples of rendered 3D objects, GUI design, and video game scenes
Graphics Output
In the beginning, this was text-only output
It then developed into 2D graphics output (+ text)
And finally, into 3D graphics output (+ 2D + text)
Ultimately, the purpose of a graphics hardware is to accelerate output of graphics to a device
Types
2D graphics are flat images
3D graphics represent objects with depth
Vector graphics use mathematical equations to define shapes, allowing for scaling without quality loss
It is perfect for scalable designs and clear lines but may not handle complex images well. It used by graphic artists and designers (scalability)
Raster graphics use a grid of pixels, which can become pixelated when resized
It is best for rich, detailed images but can lose quality when resized. It is best for digital photos and print materials
Display Resolution
Refers to the number of pixels displayed on the screen horizontally and vertically
Measured in pixels, determines the sharpness and clarity of a display.
Higher resolution = more pixels = sharper and more detailed images
What does a Resolution of 1920×1080 mean?
1920 pixels horizontally (width)
1080 pixels vertically (height)
Why is Resolution Important?
Image Quality: Higher resolutions give sharper images
Workspace: More pixels = more screen space (can fit more windows)
Performance Impact: Higher resolutions require more powerful graphics hardware
Aspect Ratio: Affects how wide/tall the display appears (e.g., 16:9 is standard widescreen)
Output Devices
monitors
connections
Monitors
Display equipment without a built-in RF receiver for TV signals
Often higher-end abilities than TVs
CRT
variable resolution and refresh rate, ‘built in smoothing’, heavy
refresh with a beam of electrons scanning across the inside of the cathode ray tube
LCD/’Flat-Screen’
fixed resolution and scaling, efficient, light
images update all in one go
Connections
VGA: 15 pin analogue connector; the “external monitor” cable with screws.
DVI: 25+5 digital + analogue; first digital connector
HDMI: dominant digital connector, includes extra channels such as audio and data
DisplayPort: digital, taking over from HDMI?
USB-C: alternate mode to display video too
Graphics Card/Video Card/Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
Hardware component responsible for rendering and displaying images, videos, and animations on your computer monitor
It works with CPU to process and output visual data
If use gaming, video editing, three-dimensional (3D) modelling, or other graphic-intensive activities, a dedicated one is essential
It offloads the graphical processing from CPU, resulting in improved performance and smoother visuals
Are Integrated Graphics in CPUs as powerful as Graphics Cards?
no, if you want the best visuals and performance, a graphics card is necessary
Direct Memory Access (DMA)
A method for other components in the computer to perform data transfers without the CPU having to shuffle the bits around
Modern peripherals like graphics cards and disks make a lot of use of this to move lots of data around efficiently
It is a technology that enables HW devices (disk drives, graphics & network cards) to transfer data directly to and from RAM without involving CPU for each data transfer
It enhances system performance by offloading data transfer tasks from the CPU, leading to faster data transfer speeds and reduced CPU overhead
It is useful for devices that need to move large amounts of data quickly and efficiently, such as disk drives, graphics cards, and network cards
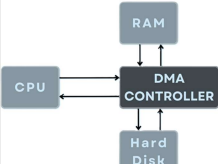
DMA Controller
Instead of the CPU handling each data transfer byte by byte, it manages the transfer, allowing the CPU to focus on other tasks
2D Images Colour Modes
Define how colours are represented and stored in an image
Each mode determines:
How many colour channels are used
What kind of information each pixel stores
How much memory the image takes
Storing 2D Images
Each pixel contains colour information
It as a grid or table with rows and columns
Basic Idea:
The X-axis (horizontal) = width of the image
The Y-axis (vertical) = height of the image
Each cell in this 2D grid = one pixel with colour info
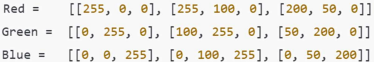
Colour Images (RGB Model)
Colour images use 3 channels:
Red – Green - Blue
Stored as 3 matrices of the same size
E.g: A 3×3 colour image (RGB) is:
Palette Based/Indexed Colour Mode
Stores image pixels not as full colour values, but as indexes (references) to a limited table of colours called a palette
Each pixel = index to a colour in the palette, not the colour itself
So instead of storing full RGB values per pixel, we store smaller numbers (indexes) to save memory
3D Graphics
Digital representations of objects that appear to have depth, in addition to height and width. It just like objects in the real world
They simulate a three-dimensional space using mathematical models, allowing you to rotate, scale, and view objects from any angle
The process of drawing them is generally referred to as rendering. Initially, it was done in software
3D vs 2D Graphics
Feature | 2D Graphics | 3D Graphics |
Dimensions | Width + Height | Width + Height + Depth |
Realism | Limited | High (with lighting, shading) |
Storage | Simple (pixels) | Complex (geometry, textures) |
Examples | Logos, icons, photos | Games, simulations, animation |
How 3D becomes 2D
When we create 3D models in computer graphics (e.g., for games, movies, simulations), we eventually need to display them on a 2D screen (like a monitor or phone). This transformation is called Projection
Using a camera perspective, just like taking a photo of a real 3D object. This 2D result is what we see on screens
NVIDIA GeForce
A brand of graphics cards designed by NVIDIA
Dedicated GPUs used in gaming laptops, desktops, and high-performance PCs
Released the first GeForce 256 (1999), the world’s first GPU
Built for high-quality gaming and real-time rendering
Supports ray tracing and AI-enhanced graphics
Frequently used in eSports, VR, and game development