BIOL 2403 - A&P - Minich - chapter 7 - skeletal system
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
SUPPORT, PROTECTION, aid in movement, storage of minerals, site for blood cell formation
What four parts do the skeletal system include?
Bones, cartilage ligaments, tendons
how do you classify (describe) bone structure?
Rigidity
How do you classify (describe) cartilage?
Flexible and cushioning
How do you classify (describe) ligaments?
Connects bone to bone
How do you classify (describe) tendons?
Connects muscle to bone
Bone (osseous) is a type of _________ Tissue?
Connective
Bone (osseous) is composed of what?
Four types of cells, extracellular matrix
What are the four types of bone cells?
Osteoprogenitor, osteoblast, osteosite, osteoclast
Genitor=
Generates
Blasts=
build
cytes=
mature
clasts
crashers
Where are osteoprogenitors located?
bone surfaces
where are osteoblasts located
bone surfaces
where are osteocytes located?
trapped inside bone
Where are osteoclasts located
bone surfaces
What are the functions of osteoprogenitors?
STEM CELLS - become osteoblasts
what are the functions of osteoblasts?
produces osteoid (semisolid, organic component of bone matrix) - mineralizes and hardens -> gets trapped in the matrix and becomes osteocytes
What are the functions of osteocytes
maintain bone matrix, regulate activity of osteoblast and osteoclasts
What are the functions of osteoclasts
large multi-nuclear cells involved in BONE RESPORPTION, REMOVAL of bone tissue
osteoblasts start off _______ then mineralize
soft and squishy
What causes the mineralization of osteoblasts?
calcium and phosphorus
What is the composition of the bone matrix
collagen and salt crystals
How much collagen is in extracellular bone matrix?
90%
What does collagen do for bones?
makes it strong and flexible
What do the salt crystals do for bones in the extracellular matrix?
provide hardness
Bone matrix constantly undergoes process of _________ and ________
formation; resorption
Formation involves secretion of ______ by _______ followed by mineralization
osteoid; osteoblasts
resporption involves breakdown of ______________ components by ________
bone matrix; osteoclasts
What two things do resorption release?
hydrochloric acid and enzymes
What are the two types of bone?
compact (cortical/dense) and spongy (trabecular)
How does compact bone look?
smooth and solid
Compact bone is ___% bone mass
80
Definition of osteon
small and cylindrical. basic functional and structural unit of mature compact bone
osteon=
one
osteon will become _________
solid
What is osteon composed of?
central canal (blood vessels and nerves)
lamallae (ring-like layer of bone tissue - surrounds the central canal)
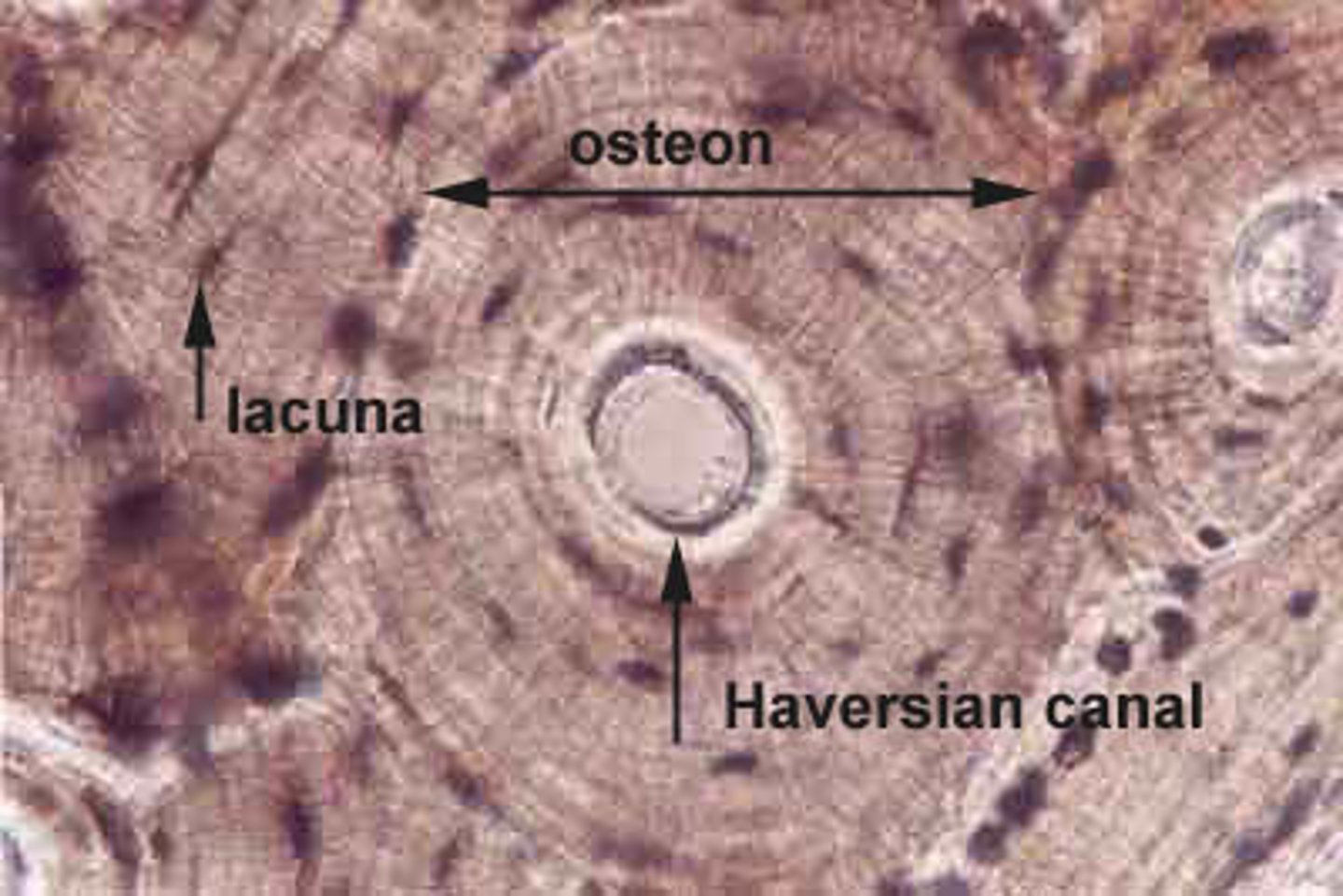
osteocytes are found in spaces (______) between ______________
lacunae; lamellae
what are canaliculi
tiny channels that connect neighboring lacunae in central canal - permitting intercellular contact
Canaliculi allow transport of....
nutrients, gases, wastes between blood vessels and osteocytes
how does spongy bone look?
porous, lattice-like
spongy bone is ___% bone mass
20
what is the definition of trabeculae
lattice and norrow rods. provide great resistance to stresses, but reduces weight. bone marrow fills spaces between
describe the appearance of long bones
greater in length than width
describe the appearance of short bones
length nearly equal to their width
describe the appearance of flat bones and explain why they are shaped that way
they have flat, thin surfaces that may be slightly curved. They provide extensive surfaces for muscle attachment and protect underlying soft tissues
describe the appearance of irregular bones
elaborate, sometimes complex shapes and do not fit into any of the preceding categories
What are the three main sections of long bone?
diaphysis, epiphysis, metaphysis
What is the diaphysis?
elonngated shaft
what is the function of diaphysis?
leverage and major weight support
what is the epiphysis?
knobby region at the ends of long bone
What kind of cartilage covers the epiphysis?
hyaline
what is the metaphysis
regio between diaphysis and epiphysis
epiphysial growth plate
thin layer of hyaline cartilage that provides for lengthwise bone growth (until the age of 25)
What epiphysial plate turns into the _______________
epiphysial line
What are the linings of bone (two types)
periosteum and endosteum
periosteum covers ______surface of bone
outer
what are the two layers of periosteum
outerfibrous and innercellular
What does the outerfibrous layer of periosteum do?
protects; anchors blood vessels and nerves to bone surfaces; attachment site for ligaments and tendons
what does the innercellular layer of the periosteum include?
osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts, osteoclasts
What does endosteum do?
covers internal surfaces of bone
What does endosteum include?
osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts, osteoclasts
what is the gross anatomy of other bone classes?
outer compact bone, inner spongy bone, no medullary cavity
bones are highly ________
vascular
blood vessels enter and exits the bone through a ________
foramen
nerves that supply bone accompany _______
blood vessels
bone marrow is the ______ CT of bone
soft
red bone marrow is _________ (blood cell forming)
hemopoietic
bone marrow contains ___________ CT, ________ blood cells, and ____
reticular; immature; fat
where is red bone marrow located in children?
in the spongy bone and medullary cavity of long bones
yellow bone marrow is the product of _________________ that turns into a _______ substance
red bone marrow; fatty
yellow bone marrow can __________________ red bone marrow
convert back to
Cartilage is ________ connective tissue
semi-solid
What is cartilage composed of?
cells and extracellular matrix
extracellular matrix in cartilage
gel-like ground substance RICH IN WATER
extracellular matrix in cartilage allows cartilage to be ....
highly compressible (NO CALCIUM)
extracellular matrix in cartilage is reinforced by what?
fibrous proteins (elastin and collagen)
cartilage is composed of which cells?
chondroblasts and chondrocytes
Chondro=
cartilage
cartilage has ____ blood vessels
no
cartilage is often covered with fibrous membrane-
perichondrium
peri=
around
What are the type major types of bone cartilage?
hyaline, elastic, fibrous
Hyaline cartilage is the ________ abundant cartilage. it is reinforced with _______ collagen
abundant; thin
What are some examples of hyaline cartilage in the body
articular (joint), costal, nasal cartilages
elastic cartilage is the most ______ due to the large amount of ______
flexible; elastin
Where can elastic cartilage be found?
external ear and the EPIGLOTTIS of the larynx only
fibrous cartilage is the most P and _______ resistant. it is reinforced with ____ collagen
stretch; thick
Where can fibrous cartilage be found?
knee, intervertebral discs
What are the two types of cartilage growth?
interstitial and appositional
interstitial=
growing from the inside
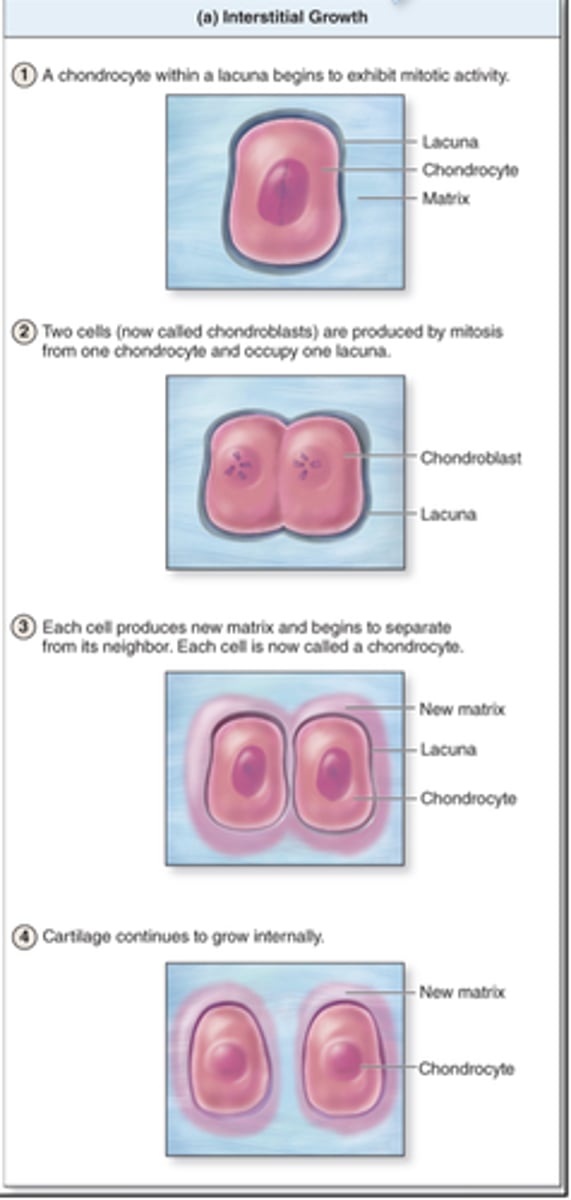
What is the process of interstitial growth?
1. chondrocytes divide into two chondroblasts
2. chondroblasts secrete matrix
3. each cell becomes a chondrocyte within its own lacuna
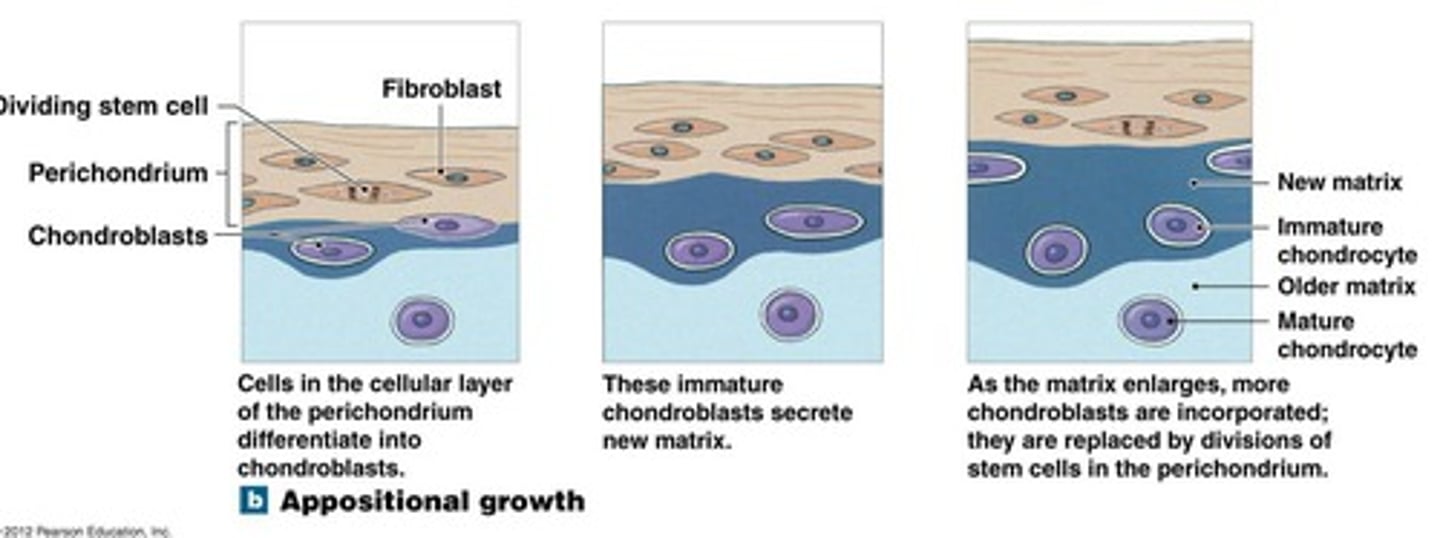
Appositional=
adding layers (grows in layers)
What is the process of appositional growth?
1. the stem cells within the perichondrium divide producing chondroblasts
2. new chondrblasts start producing matrix ADDING A LAYER to the old cartilage
What is the cartilage growth pattern?
1. during early embryonic development: interstitial and appositional
2. as cartilage matures - it becomes semi-rigid, cannot expand -> only appositional growth
3. fully matured cartilage does not grow but will inhibit limited growth after injury
Ossification (osteogenesis)
the formation and development of bone tissue?
When does the development of bone tissue begin?
it begins in the 8th week of embryonic development and continues into childhood and adolescence
ossification=
forms bone
endochondrial=
inside of cartilage