3. Ryanef123 Endo 3 - Radiology (Dr. Monteiro) - edited
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
Which type of radiograph captures the entire tooth? (Crown --> Apex)
periapical radiograph
Which type of radiograph views the periapical tissues?
periapical radiograph
Which type of radiograph evaluates caries, existing restorations, and previously initiated therapy?
Bitewing radiograph
Which type of radiograph has an excellent projection to assess periodontal tissue?
Bitewing radiograph
Which type of radiograph presents an accurate representation of corona pulp anatomy?
Bitewing radiograph
Which type of radiograph is recommended in trauma cases to rule out fractures of teeth and the alveolus?
Panoramic radiographs
Which type of radiograph is a dimensionally accurate view of tooth and surrounding structures?
CBCT
_______ are the most commonly used radiograph in endodontics
Periapical radiograph
What views can a periapical radiograph be taken from?
- Mesial
- Distal
- Parallel
Which type of radiograph is NECESSARY for periapical diagnosis, intraoperatively and post-operatively?
Periapical radiograph
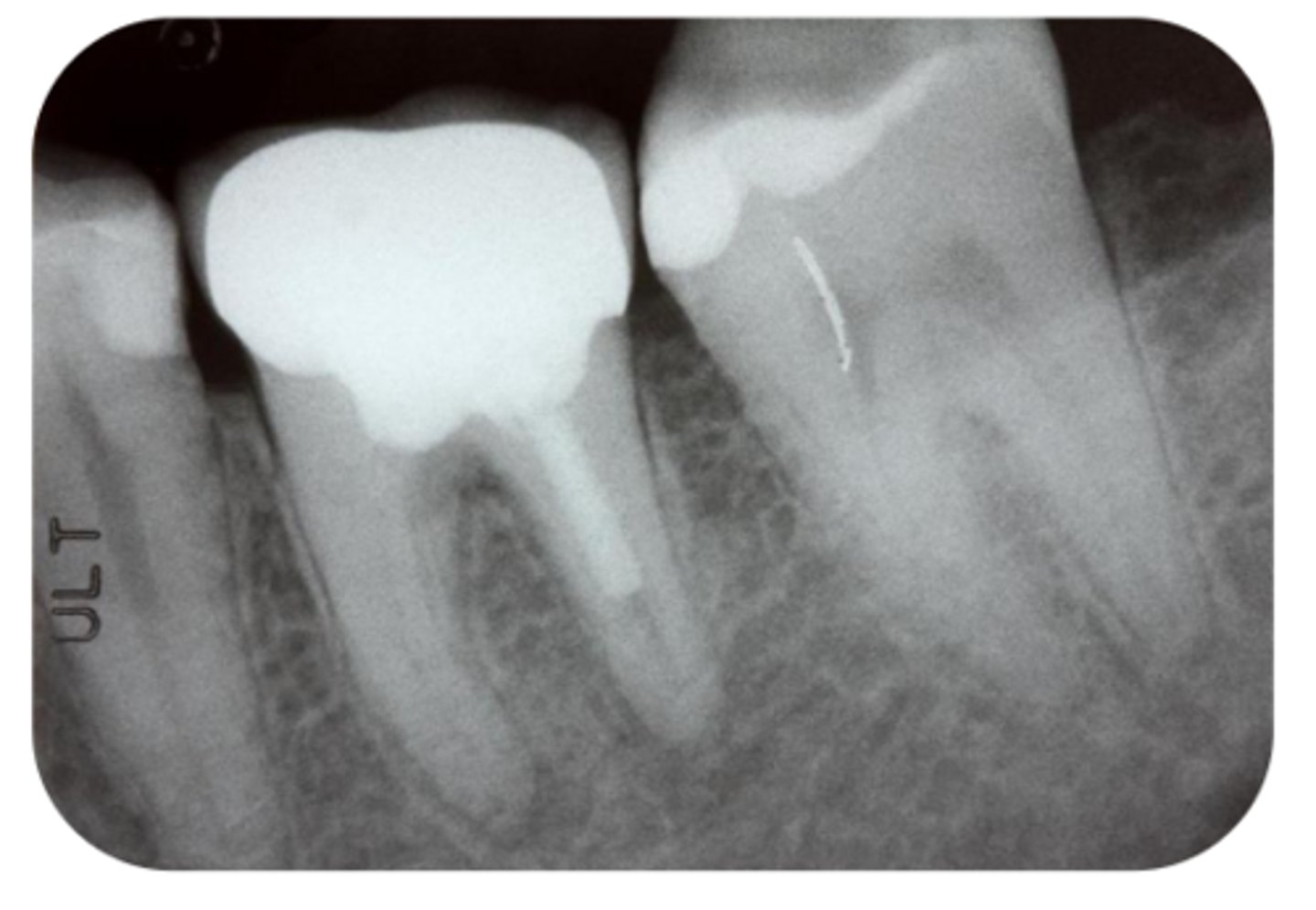
What are the radiographic findings on #19?
- Crown
- Post D Canal
- PARL Mesial and Distal Root
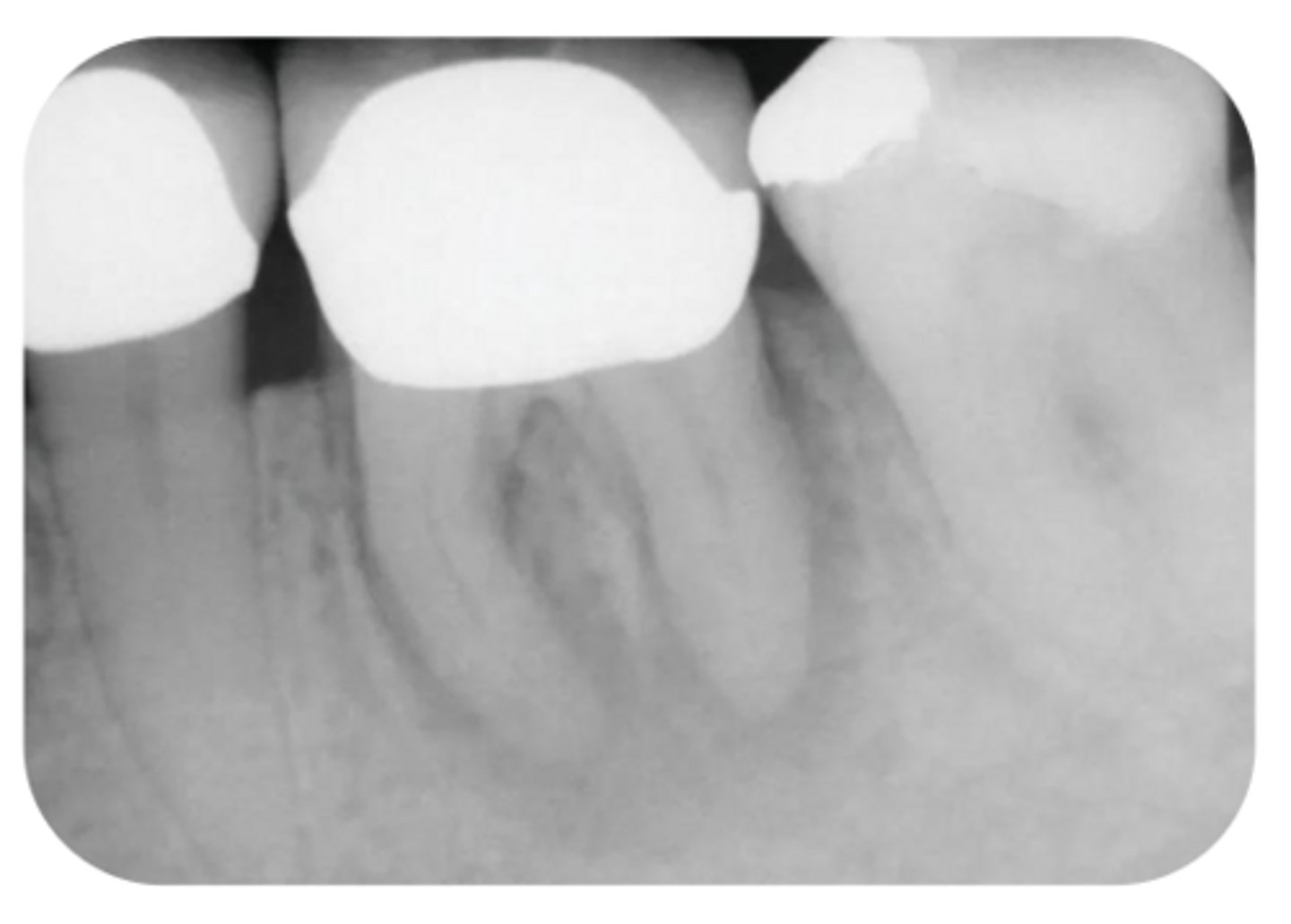
What are the radiographic findings on #19?
- Crown
- PARL in Mesial and Distal Root
- Discontinuation of LD
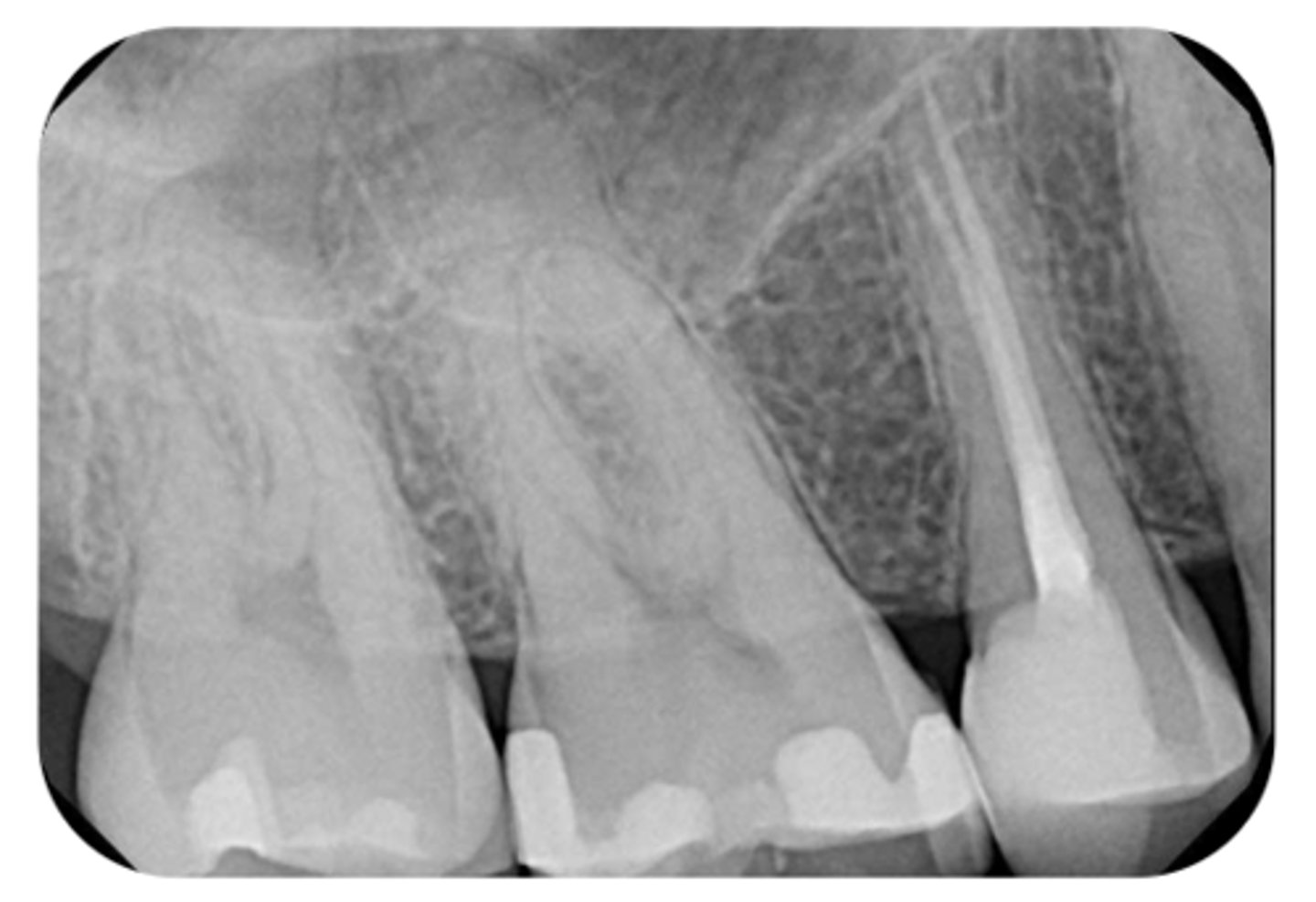
What are the radiographic findings on #4?
- DO Composite
- RCT
- No PARL
- LD intact
- PDL normal
T/F: A bitewing should be straight-on, with as little overlap as possible
true
which type of radiograph provides the only way to judge extent of decay, restorability and status of restorations
bitewing radiograph
which type of radiograph shows the position of the bone in relation to the CEJ of the teeth?
bitewing radiograph
Which type of radiograph is necessary for understanding pulp chamber anatomy?
bitewing radiograph
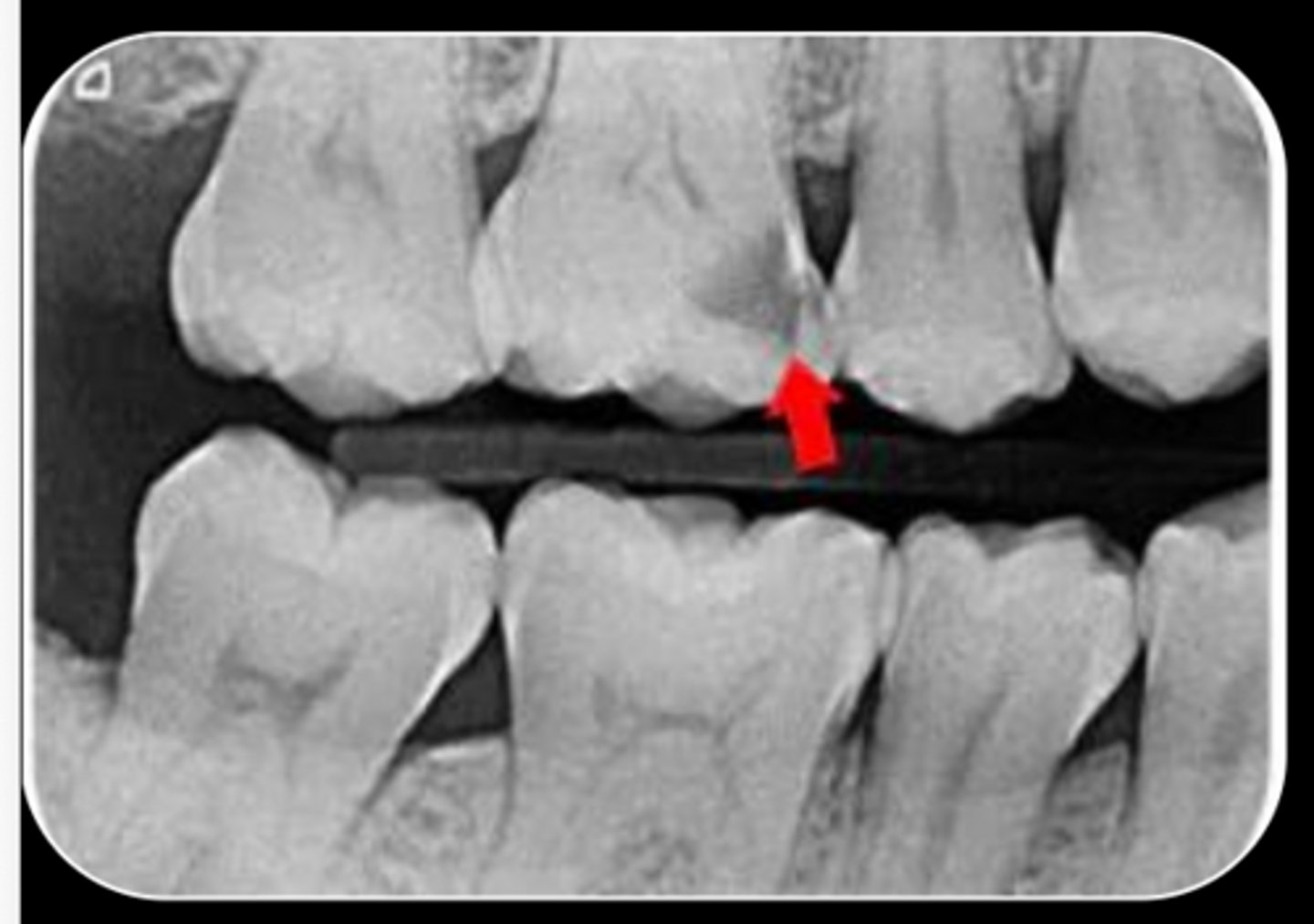
What are the radiographic findings on #3?
- M Caries
- Pulp stones
- Pulp chamber receeded
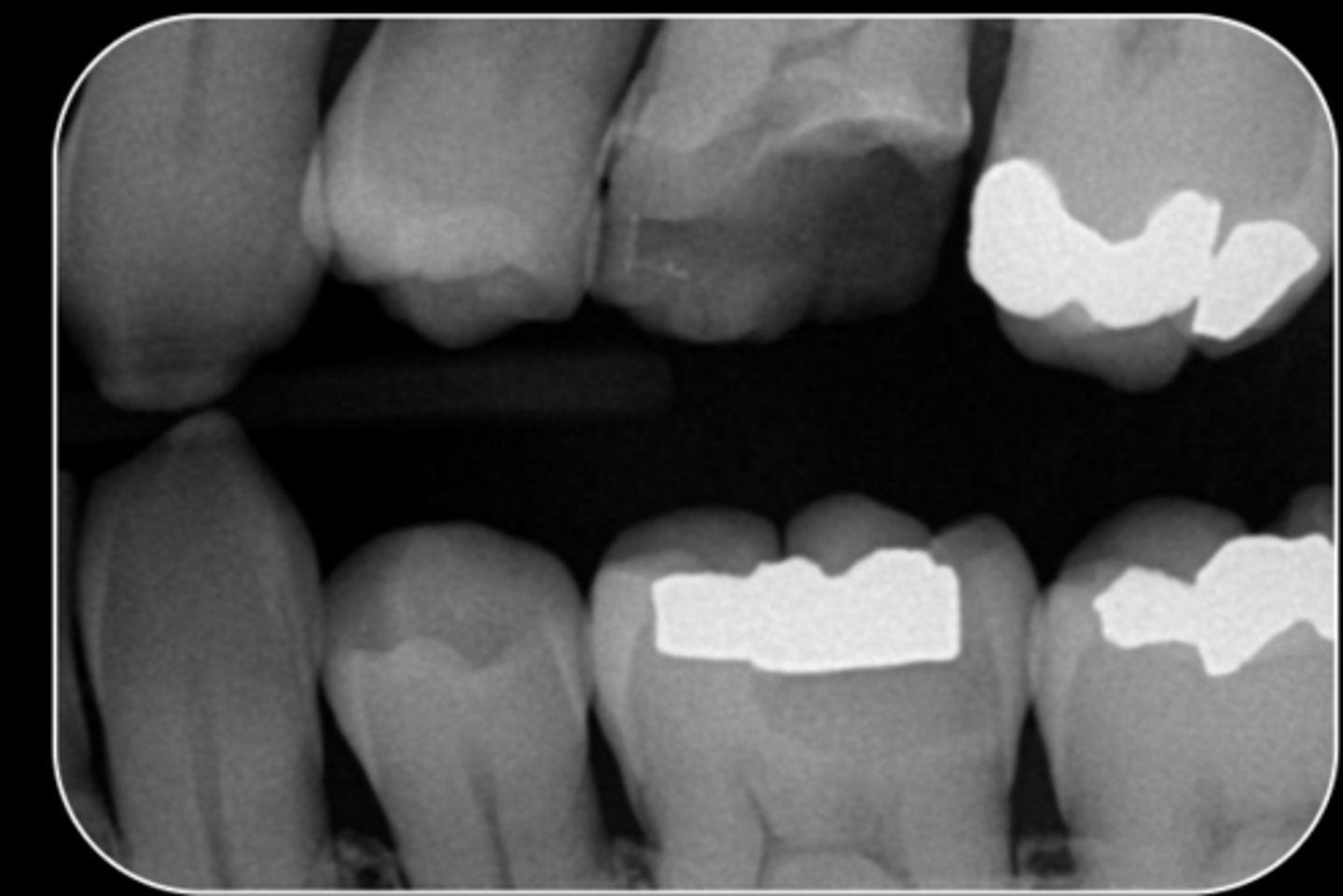
What are the radiographic findings on #14?
- Fracture Mesial-Distal
- Caries approximating pulp chamber
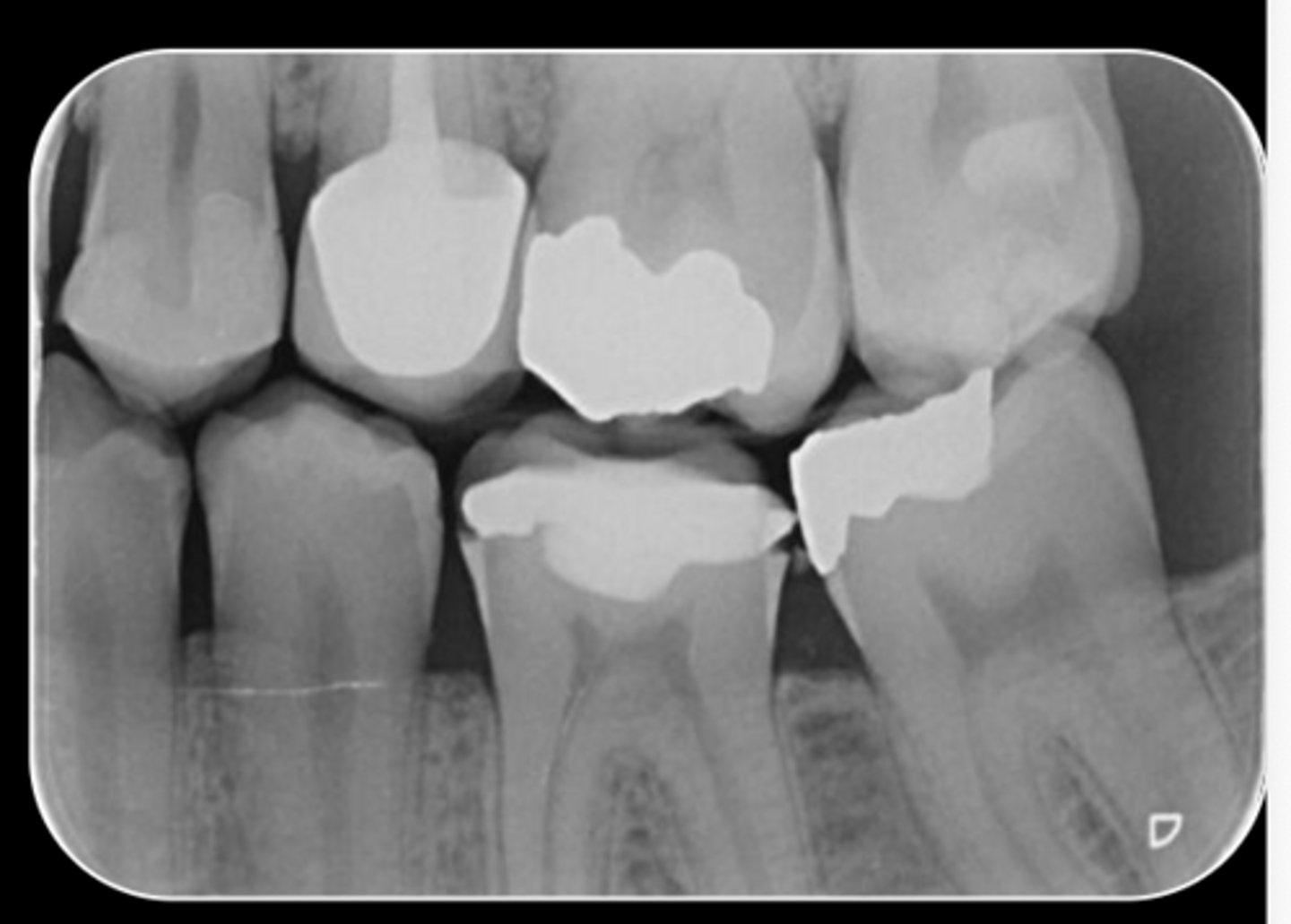
What are the radiographic findings on #13?
- Crown
- Post

What type of dental radiograph?
Conventional Film
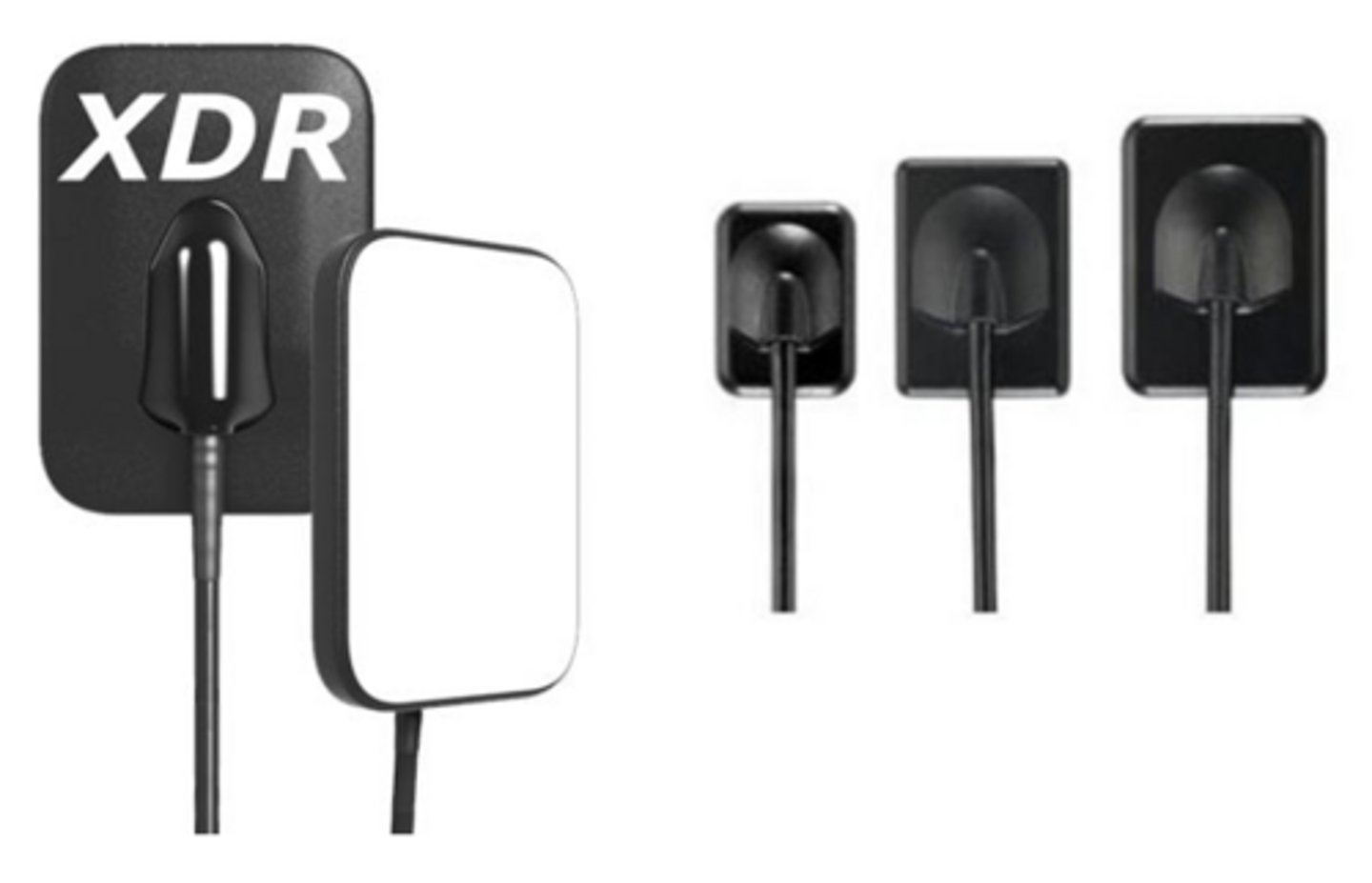

What type of dental radiograph?
Digital Sensor
What size sensor is used in...
- Pedodontics
- Small mouth
- Gag reflex
size 1
What size sensor is primarily used?
size 2
What MUST be placed on the patient to take EVERY Radiograph?
Lead apron
What type of imaging system?
- 3D rendering of a small area
- Can be useful as an adjunct but is not yet the standard of care
- Used for re-treatments, resorptions cases and unusual anatomy
- Coronal, axial, and sagittal views
CBCT
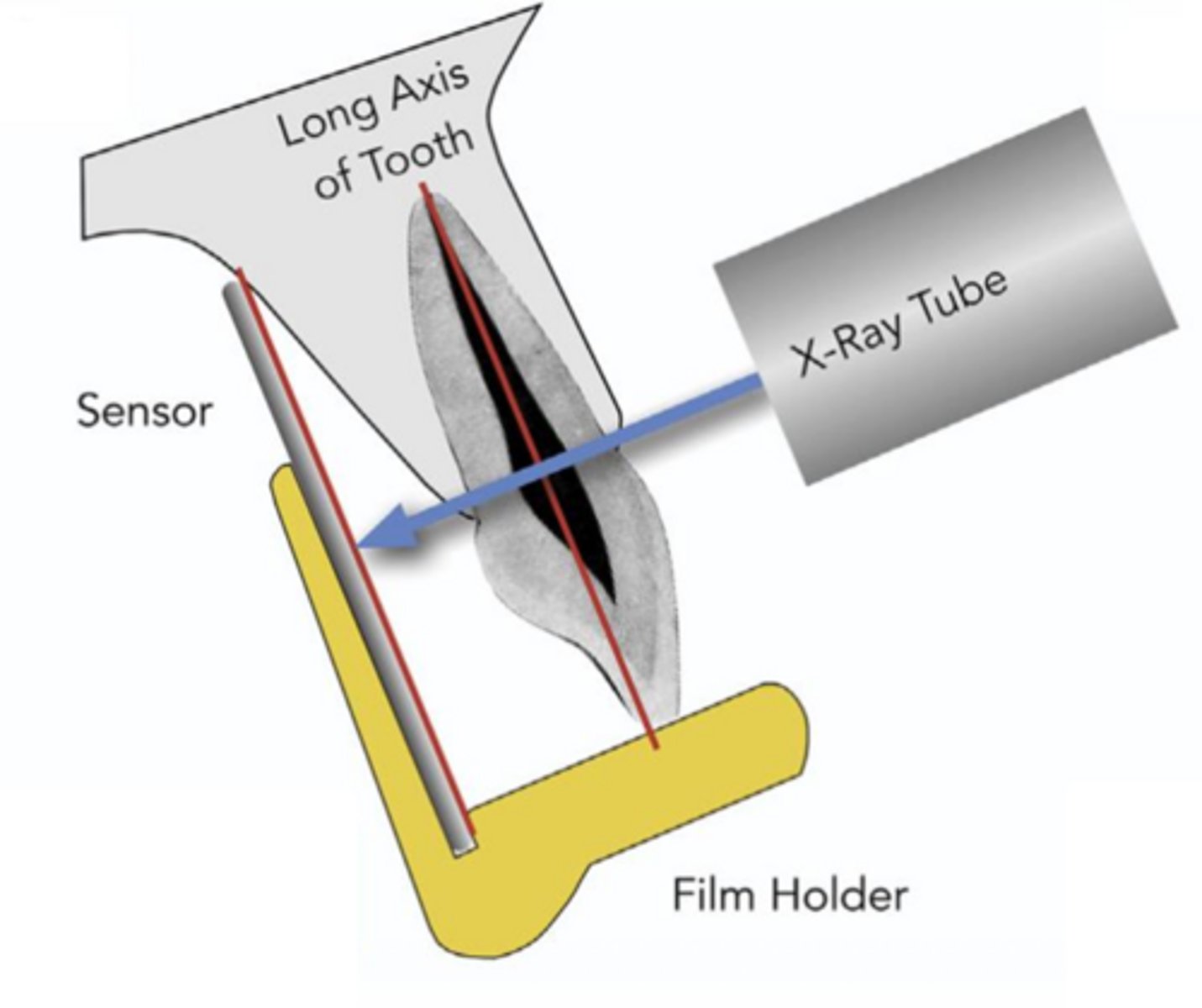
ID the sensor technique:
- Accurate, reliable and easy to do
- Film/sensor is laid parallel to the long axis of the tooth
- Source of x-ray beam is perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth
paralleling technique
ID the sensor technique:
paralleling technique
In the paralleling technique, the film/sensor is laid ________ to the long axis of the tooth.
parallel
In the paralleling technique, the source of x-ray beam is ________ to the long axis of the tooth:
perpendicular
To obtain an accurate maxillary radiograph, the sensor should be placed near the _______
midline of the palate
(NOT placed against the palatal aspect of the teeth)
Improper sensor placement of maxillary radiographs will result in what?
foreshortening/missing structures
To obtain an accurate mandibular radiograph, the sensor should be placed between the _______ and _______
tongue and the mylohyoid ridge
When taking a mandibular radiograph, what does the patient have to do?
Relax the floor of the mouth and tongue
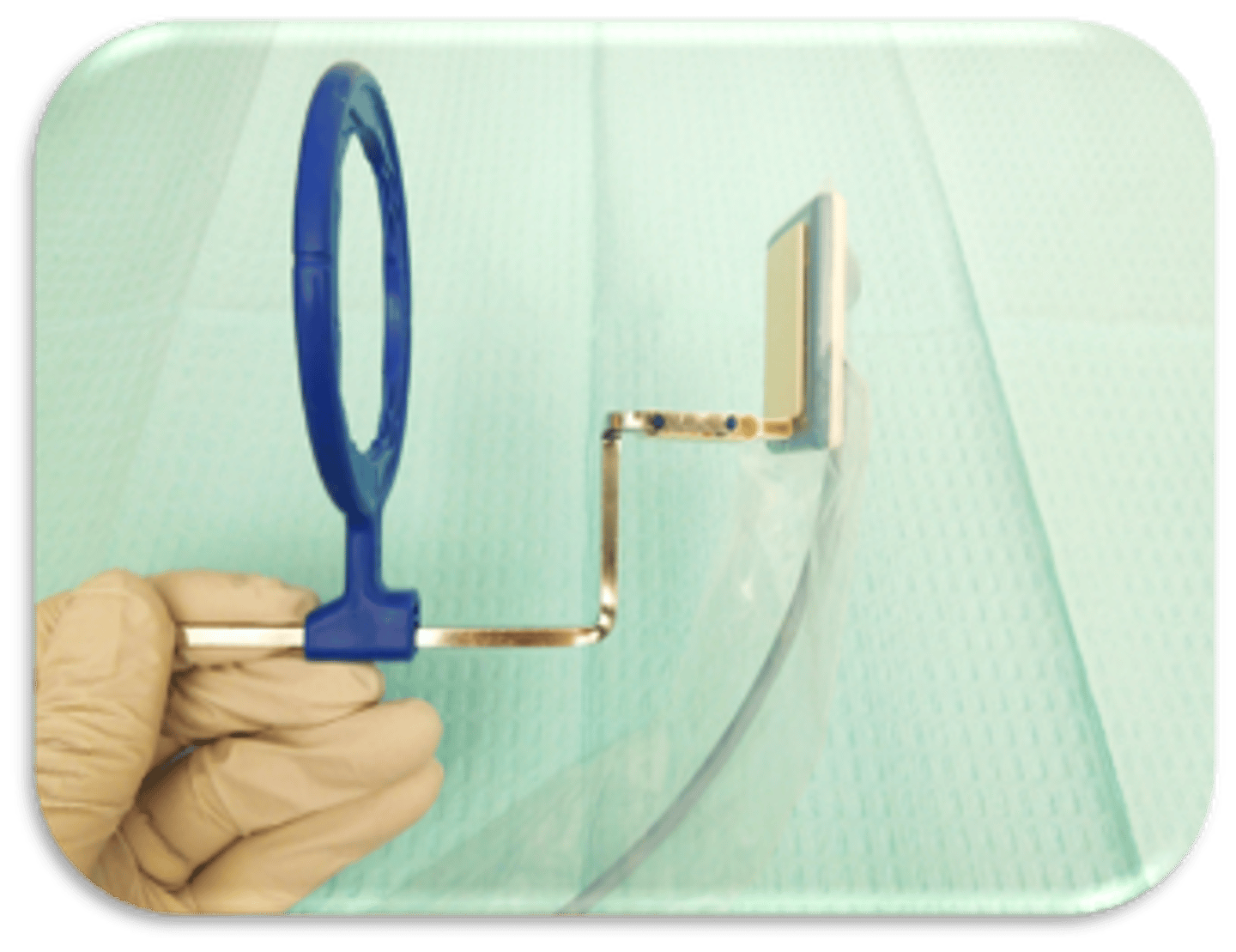
This device is used to capture what type of radiograph?
anterior PA
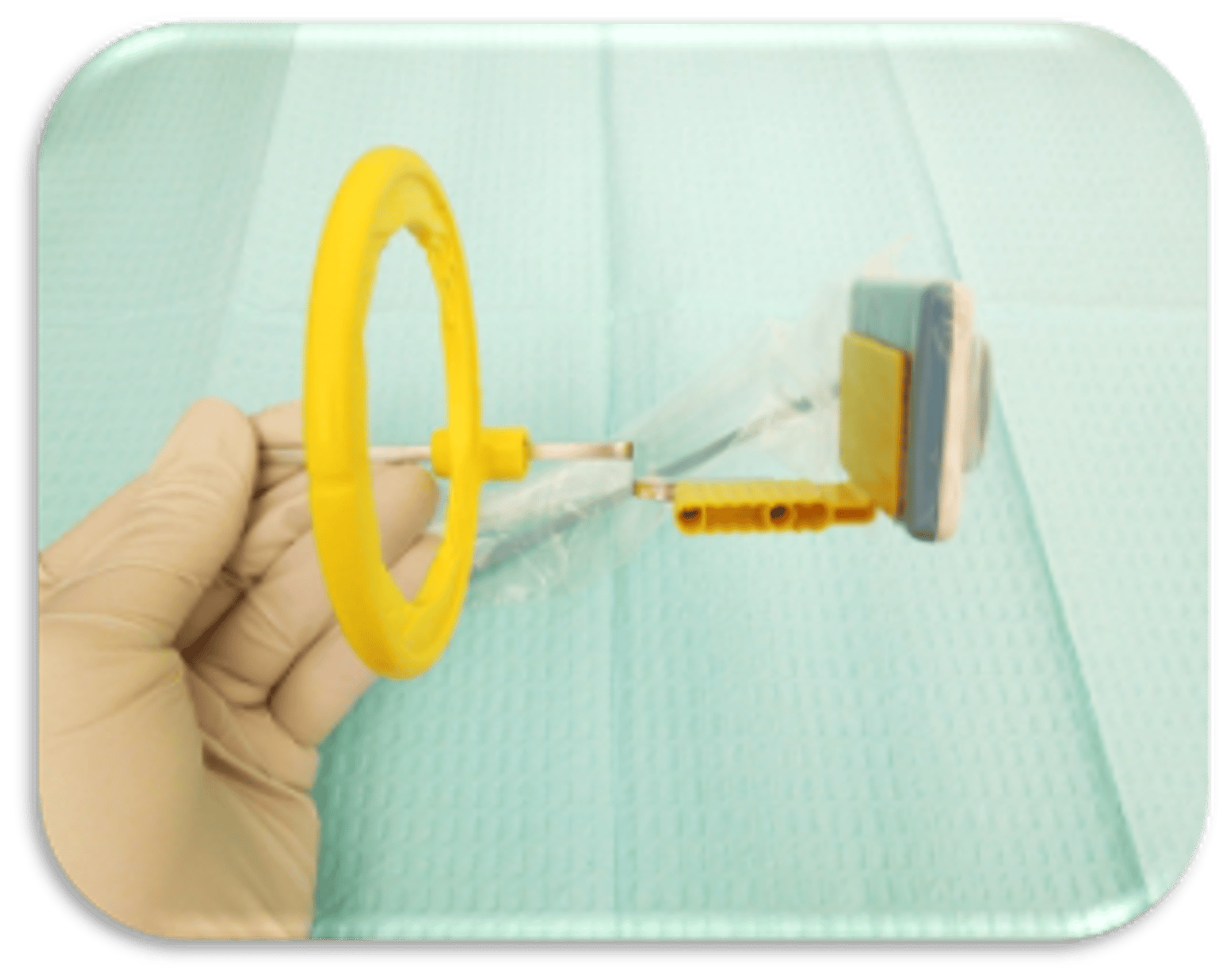
This device is used to capture what type of radiograph?
posterior PA
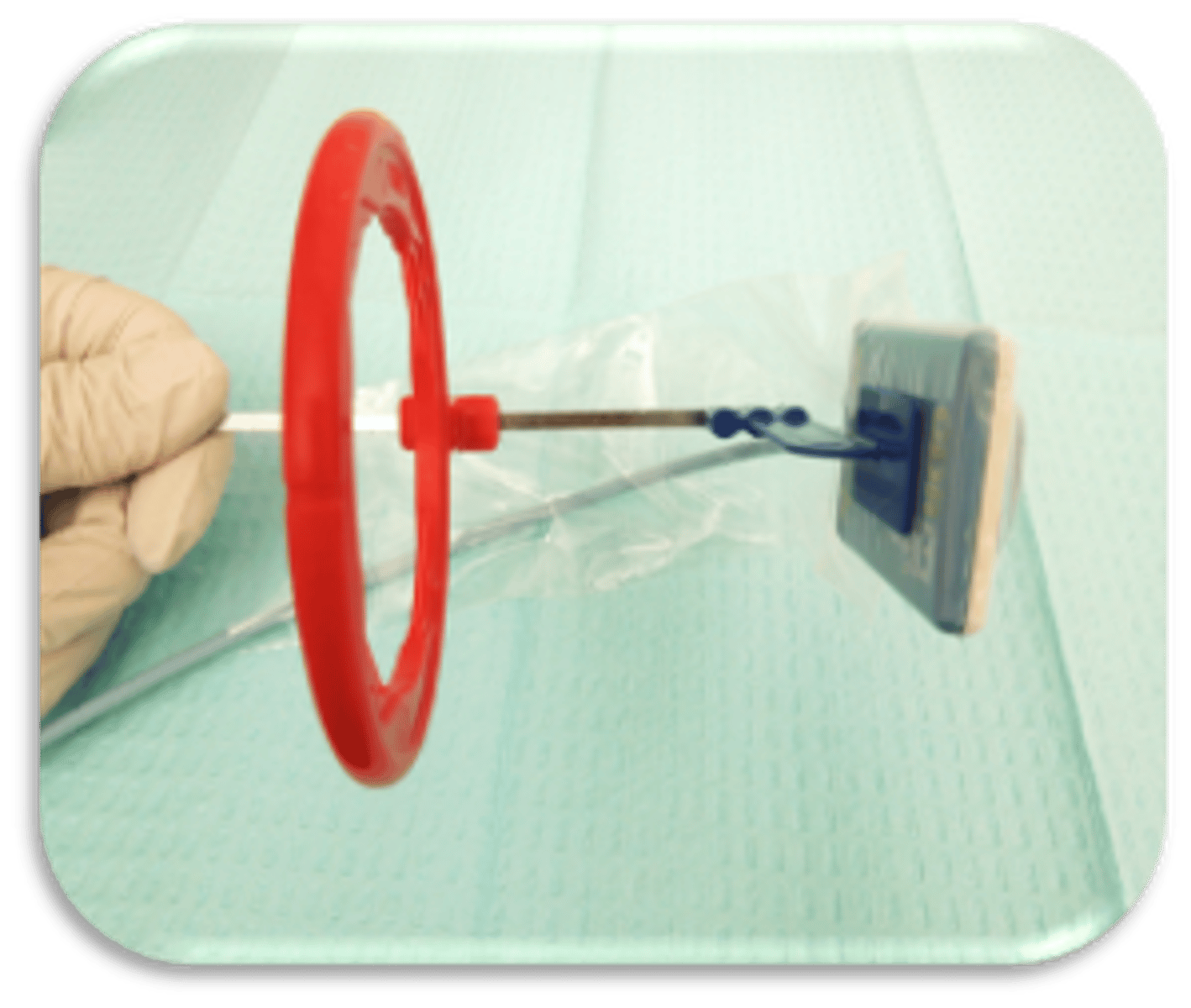
This device is used to capture what type of radiograph?
posterior BW
ID the sensor technique:
- Film/sensor is placed next to the tooth
- X-ray beam is directed perpendicular to the imaginary line which bisects the angle formed by the long axis of the tooth and the long axis of the film/sensor
bisecting angle technique
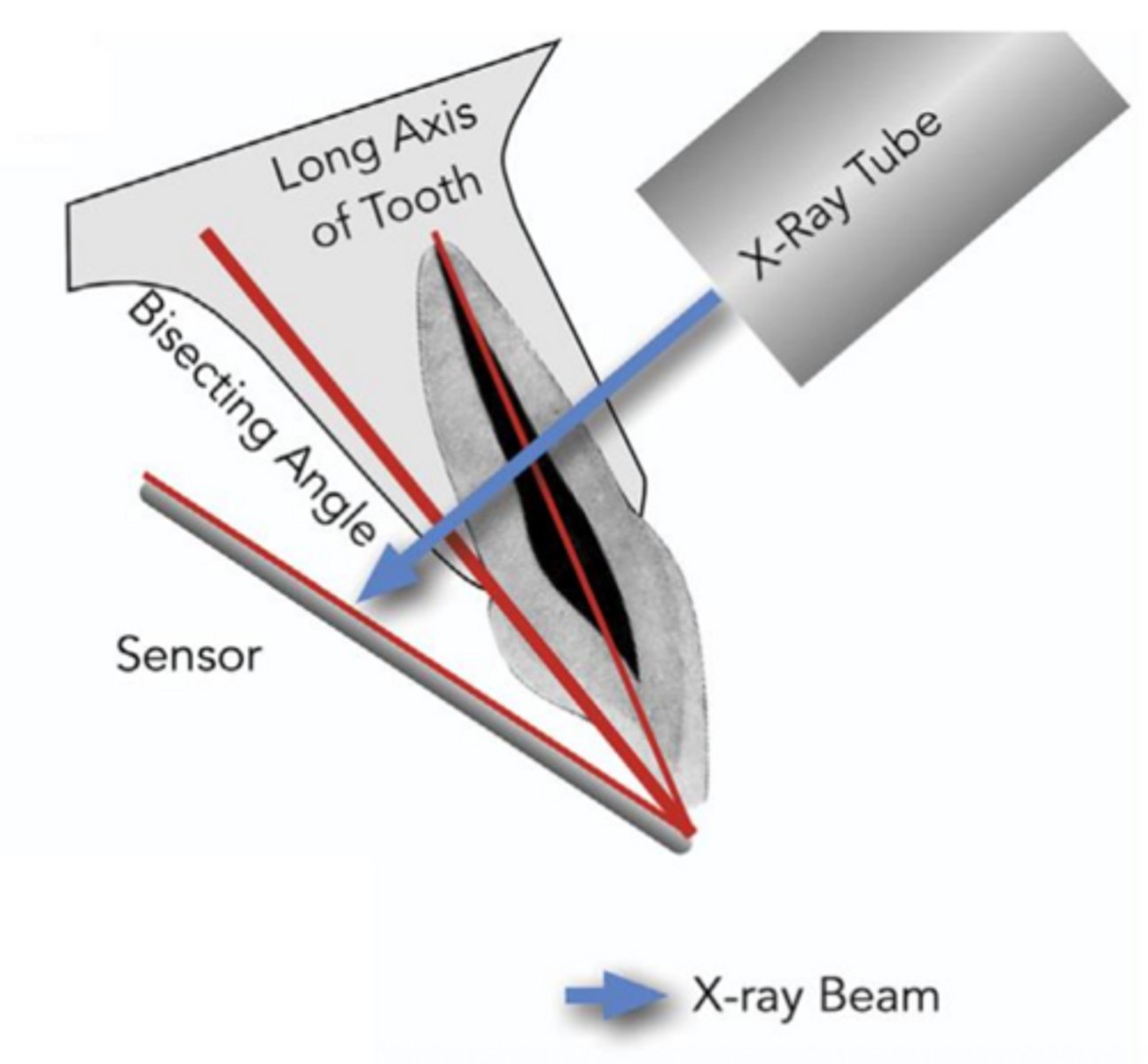
ID the sensor technique:
bisecting angle technique
In the bisecting angle technique, the X-ray beam is directed ________ to the imaginary line which bisects the angle formed by the long axis of the tooth and the long axis of the film/sensor.
perpendicular
In the bisecting angle technique, the film/sensor is placed _______ the tooth.
next to
In the bisecting angle technique, if the vertical angulation is excessive, it will result in image _______
foreshortening
In the bisecting angle technique, if the vertical angulation is insufficient, it will result in image _______
elongation
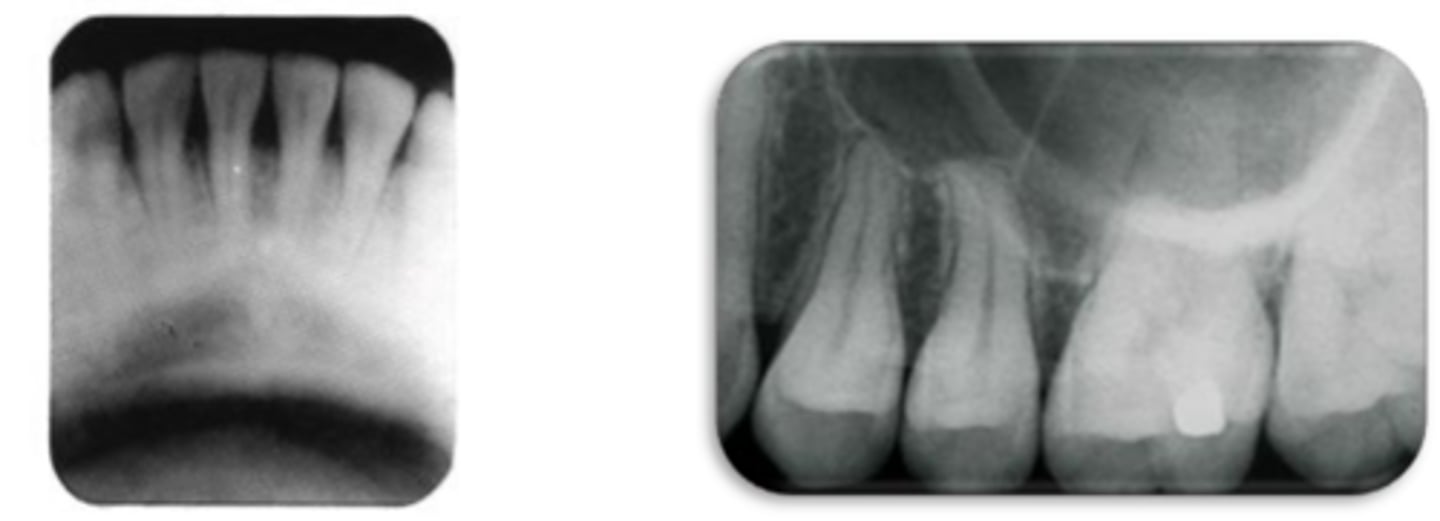
This photo was taken with the bisecting angle technique. What went wrong?
Vertical angulation is excessive --> Foreshortened image
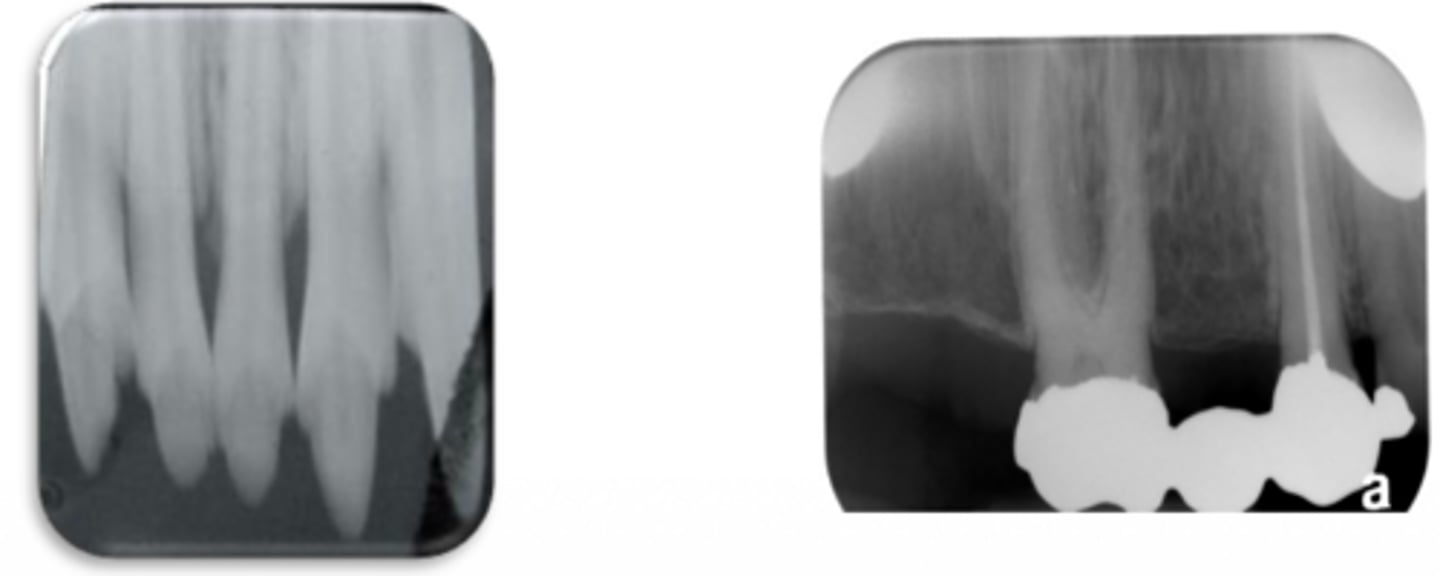
This photo was taken with the bisecting angle technique. What went wrong?
Insufficient vertical angulation --> Elongated image
What are 2 advantages of the bisecting angle technique?
- More comfortable for the patient
- No anatomical limitations
What are 2 disadvantages of the bisecting angle technique?
- No Rinn-type holder: more opportunity for cone cuts and distortions
- Film/sensor is more prone to move
which radiographic technique is best used for an endo pre-op eval?
paralleling technique
which radiographic technique is best used for an endo intra-op eval?
bisecting angle technique
which radiographic technique is best used for an endo post-op eval?
paralleling technique
which radiographic technique is best used anatomical limitations like small mouth, shallow palate, torus?
bisecting angle technique
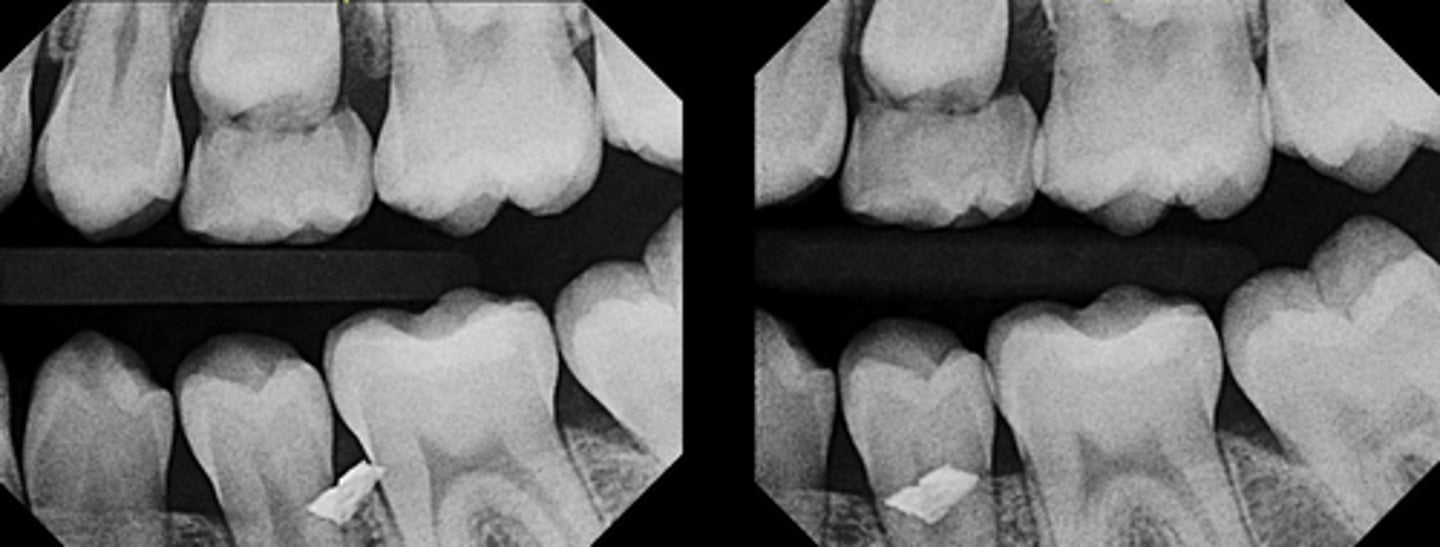
What does this photo emphasize the importance of?
Rubber dam must ALWAYS be on for clinical endodontic treatment!!!
How can you place the size 2 film to take a radiograph of the maxillary central incisor?
- Placement of hemostat on green tab
- Wind sensor cord around hemostat
- Placement under dental dam for maxillary anterior tooth
SLOB rule stands for what?
- Same Lingual
- Opposite Buccal
At least how many PAs do you need for the SLOB rule?
At least 2 PAs
- 1 PA straight on
- 1 PA with x-ray tube shifted from either mesial or distal direction.
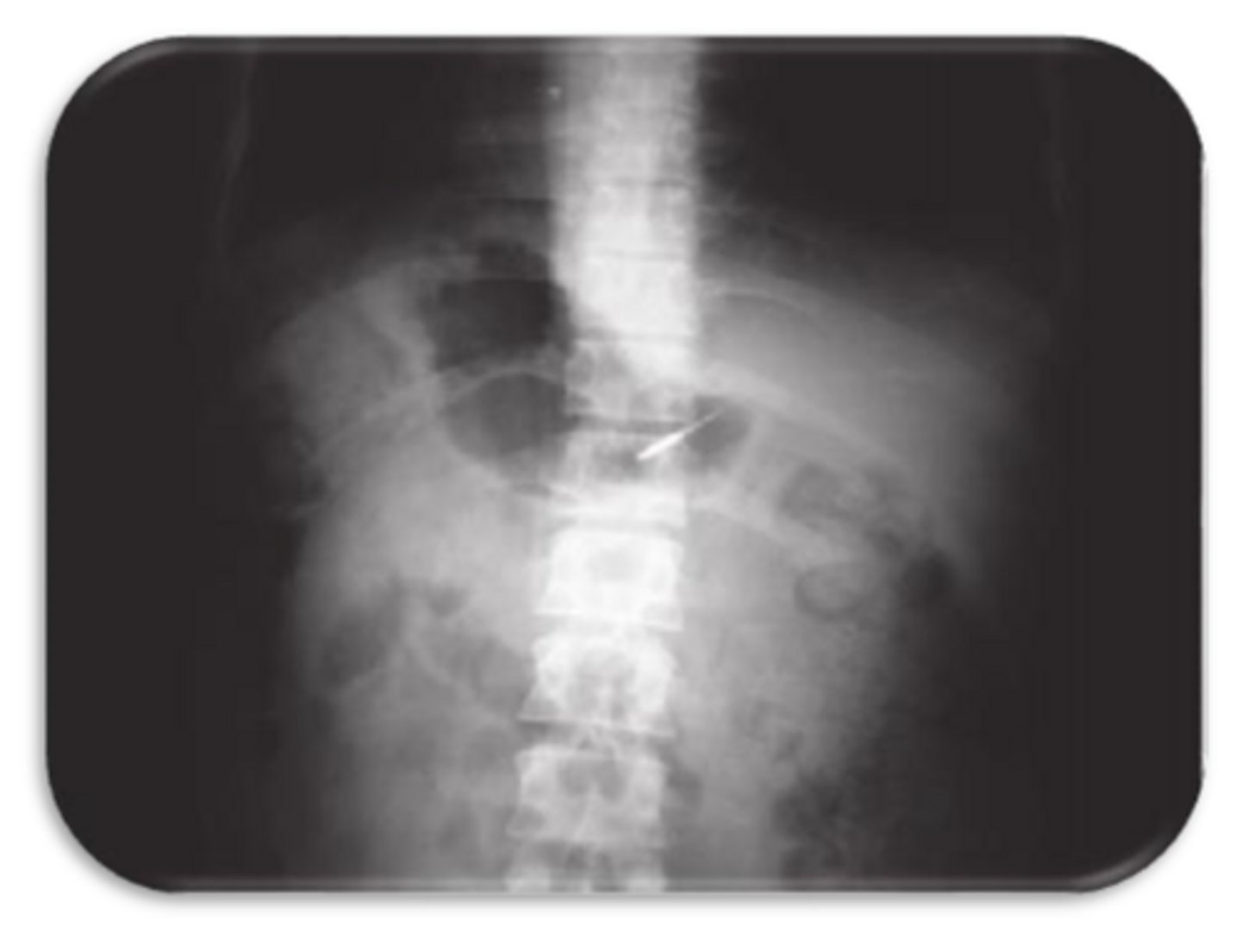
If an object moves in the SAME direction as tube shifts, the object is __________
LINGUAL
If an object moves in the OPPOSITE direction as tube shifts, the object is __________
BUCCAL
Is this foreign object lingual or buccal to the teeth?
buccal
A 35-year-old patient presents with spontaneous pain in the maxillary first molar. The pulpal diagnosis is symptomatic irreversible pulpitis and periapical diagnosis of symptomatic apical periodontitis, and nonsurgical root canal therapy is initiated.
During access preparation, the clinician identifies the mesiobuccal canal but suspects an additional
canal in the same root.
Two periapical radiographs are obtained:
- The first radiograph is taken with normal horizontal angulation.
- The second radiograph is taken with a distal horizontal tube shift.
On the second image, the suspected canal appears to move distally, in the same direction as the tube shift.
Based on these findings, where is the suspected canal most likely located?
A. Buccal to the main mesiobuccal canal
B. Lingual (palatal) to the main mesiobuccal canal
C. Apical to the main canal
D. Distal to the main canal
B. Lingual (palatal) to the main mesiobuccal canal
All of the following require a thorough knowledge of what?
- Distinguish between normal anatomical landmarks and the radiolucent shadows associated with pathosis of the roots of teeth
- Determine the buccal or lingual position of root fractures, perforations and resorptive processes
- Distinguish between internal and external root resorption
- Locate foreign bodies in trauma cases
- Locate anatomical landmarks (i.E. Mandibular canal, maxillary sinus) in relation to the root apex during periapical surgery
- Locate hidden apices prior to periapical surgery by placing a small opaque object (lead foil) on bone near the estimated apex
- Determine the number, location, shape, size, and direction of various roots and root canals during instrumentation and obturation
The ability to apply the SLOB rule
ID the structure:
A sheet of compact alveolar bone that lies adjacent to the periodontal membrane i.e. lining of the alveolus
lamina dura
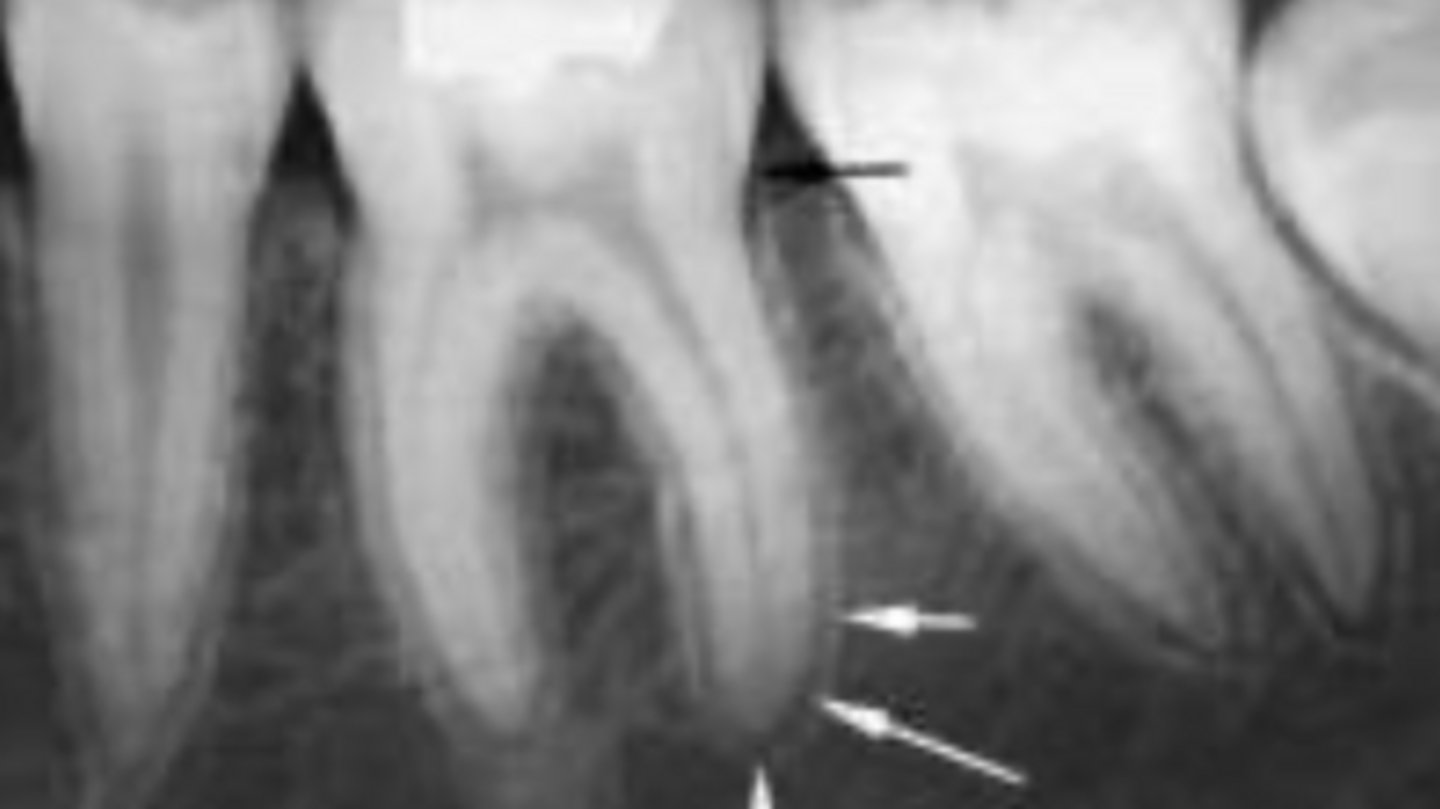
ID the structure:
lamina dura
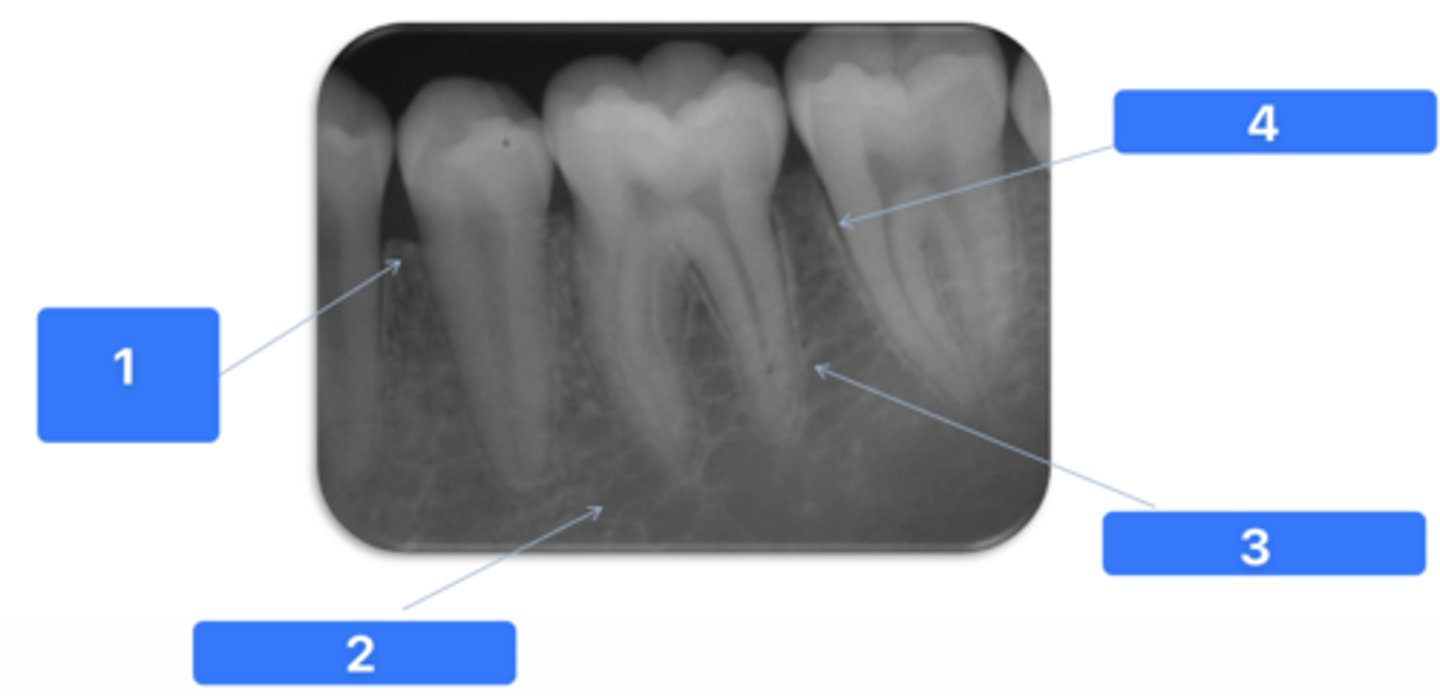
ID the structure at #1:
Alveolar crest
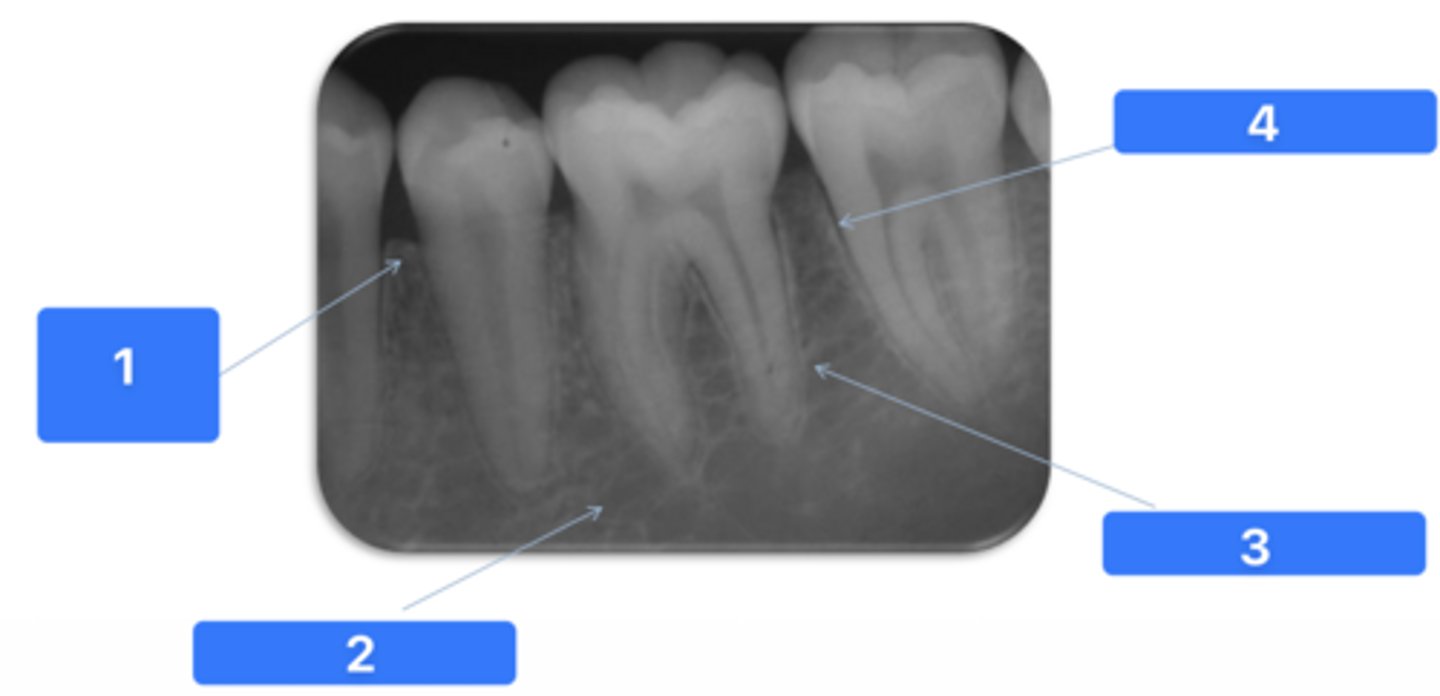
ID the structure at #2:
Medullary bone
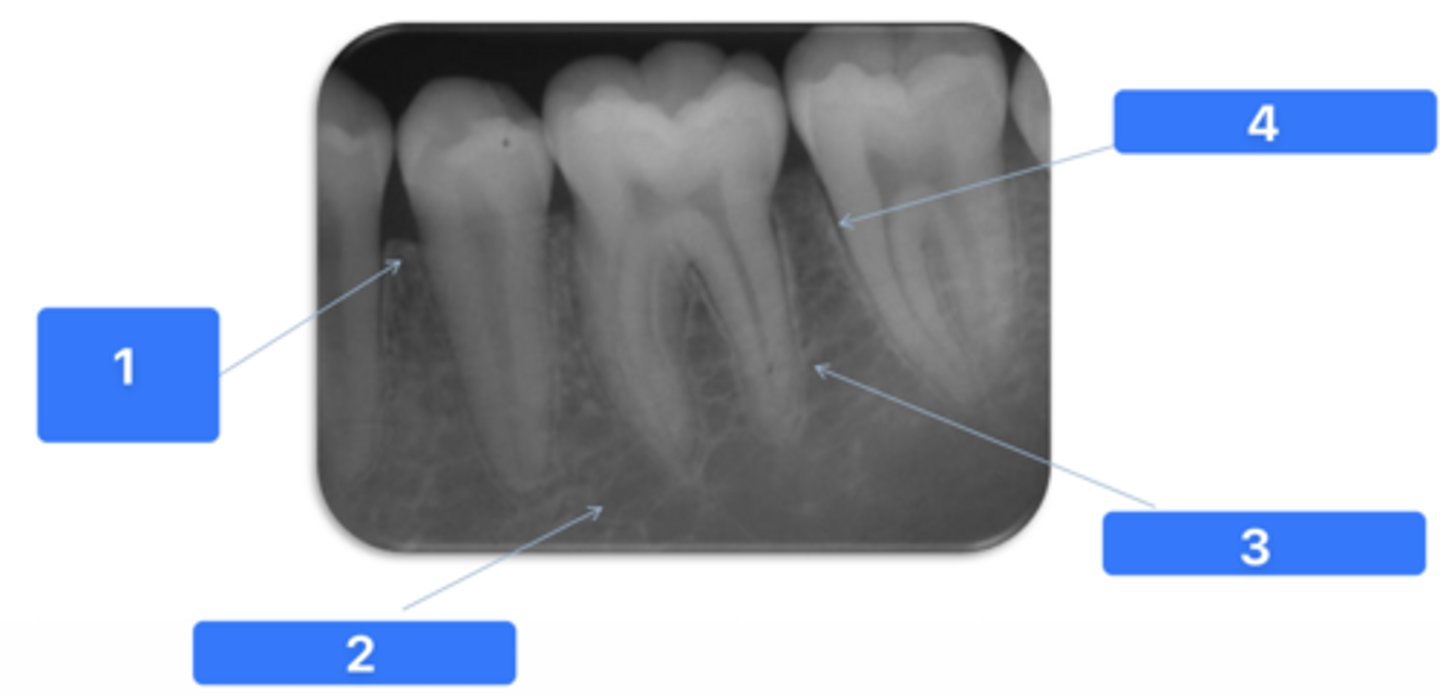
ID the structure at #3:
Lamina dura
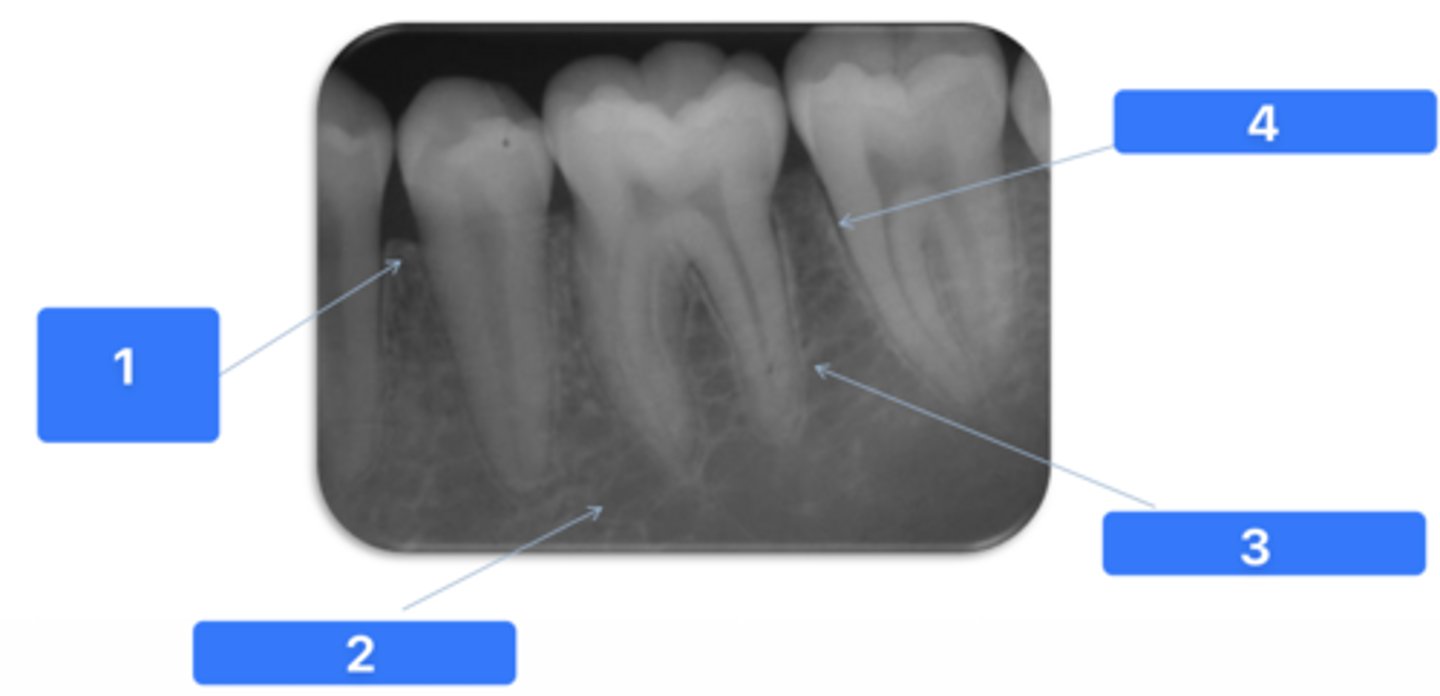
ID the structure at #4:
PDL space
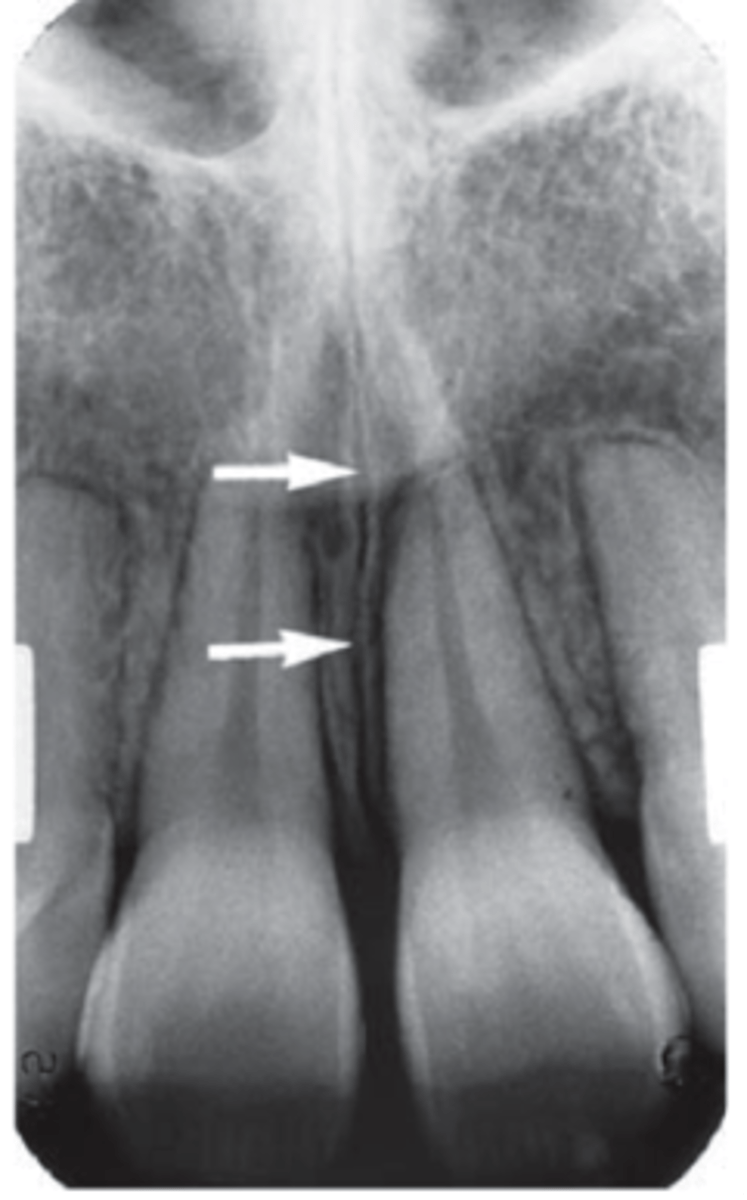
ID the structure:
intermaxillary suture
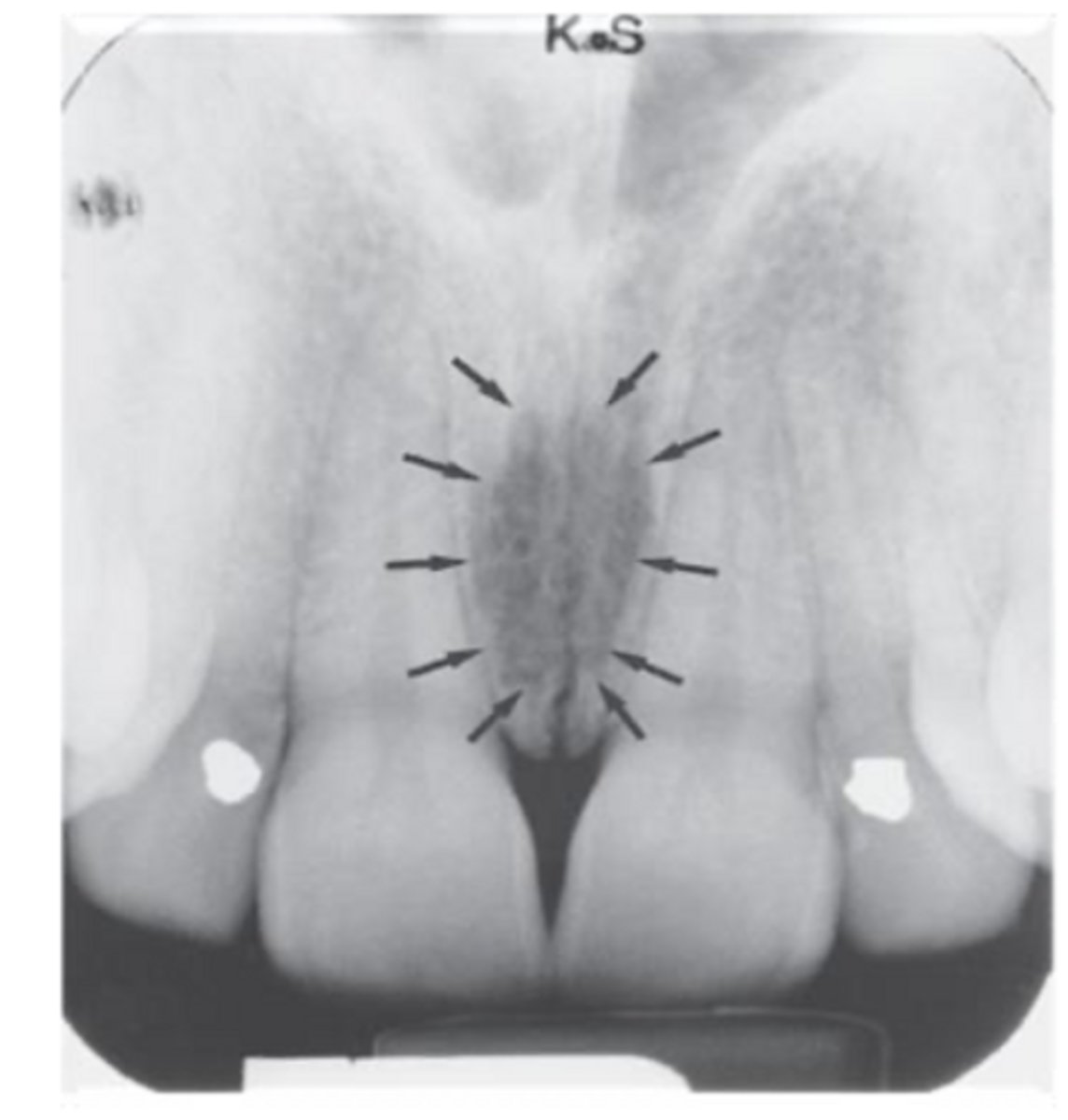
ID the structure:
nasopalatine foramen
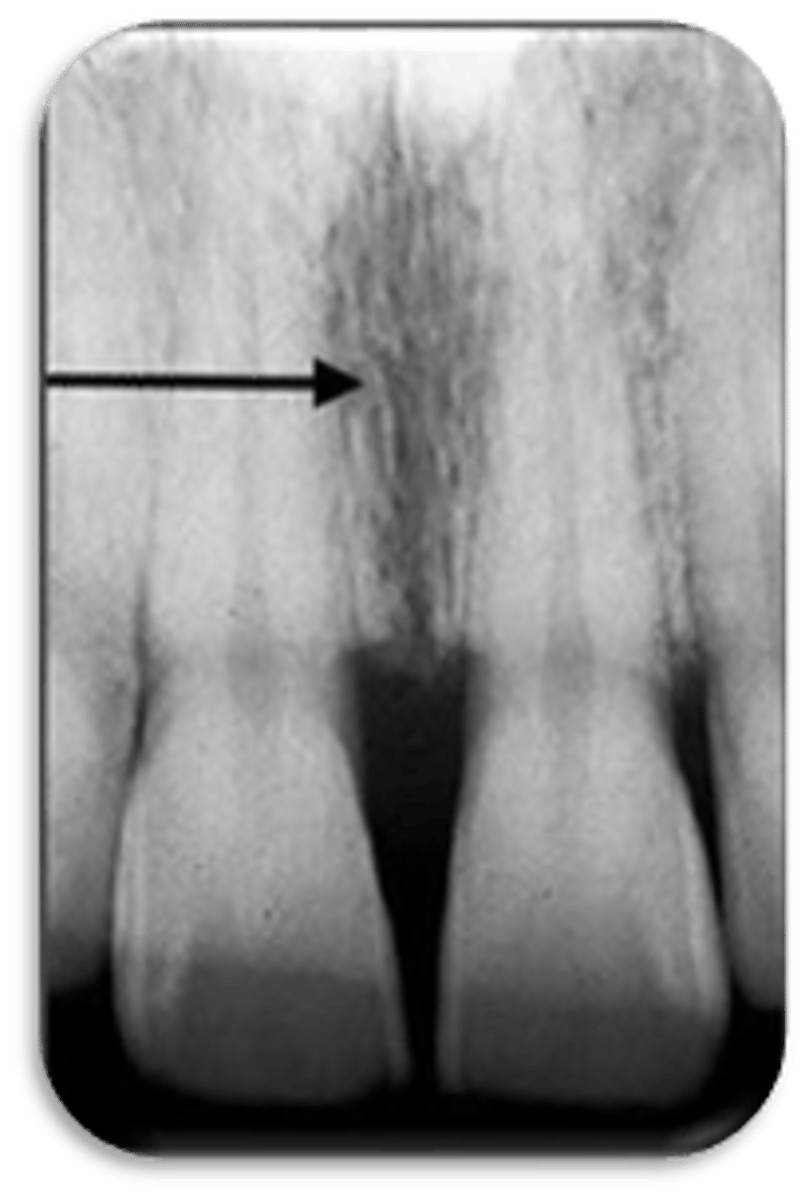
ID the structure:
nasopalatine foramen
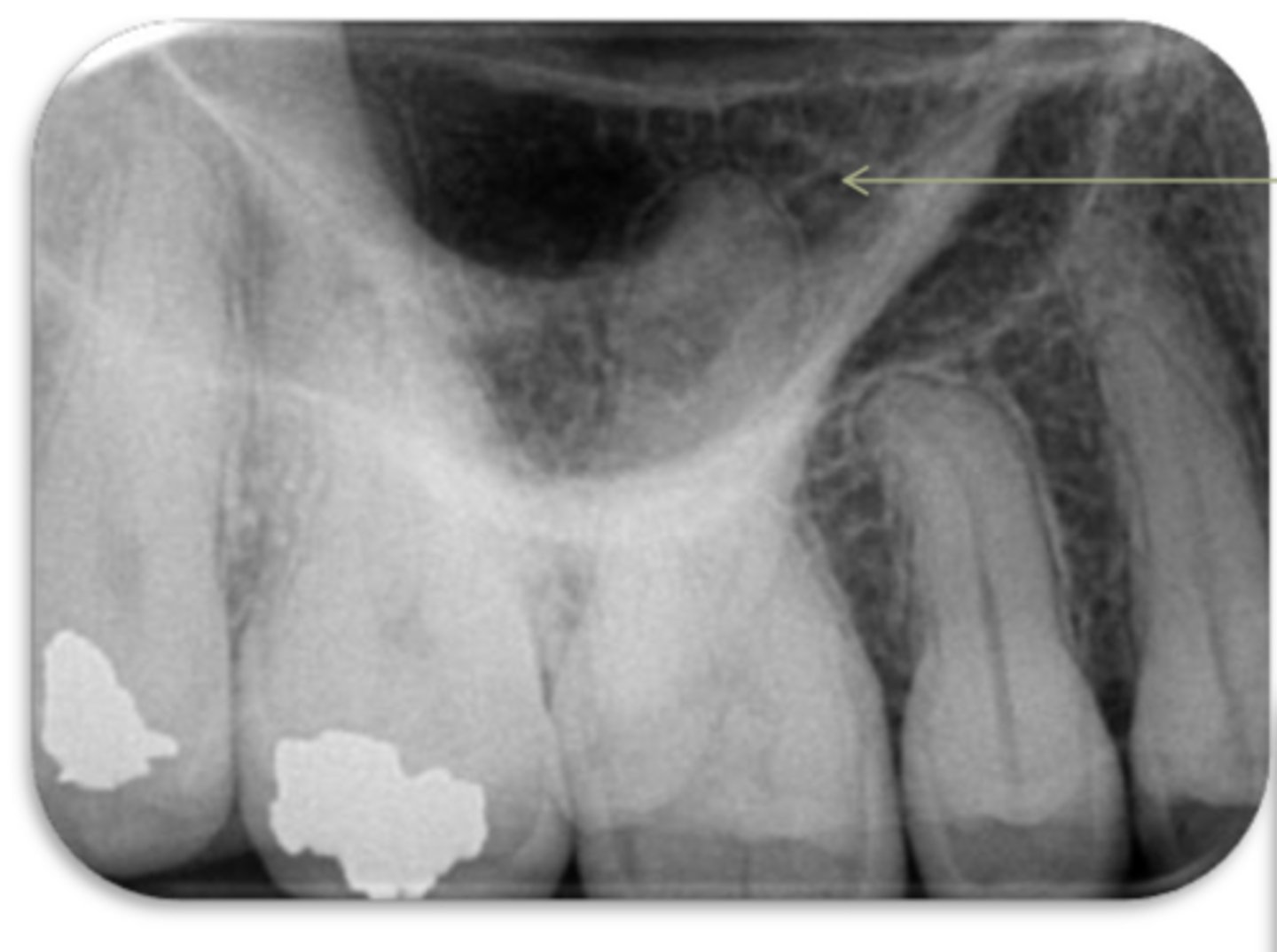
ID the structure:
maxillary sinus
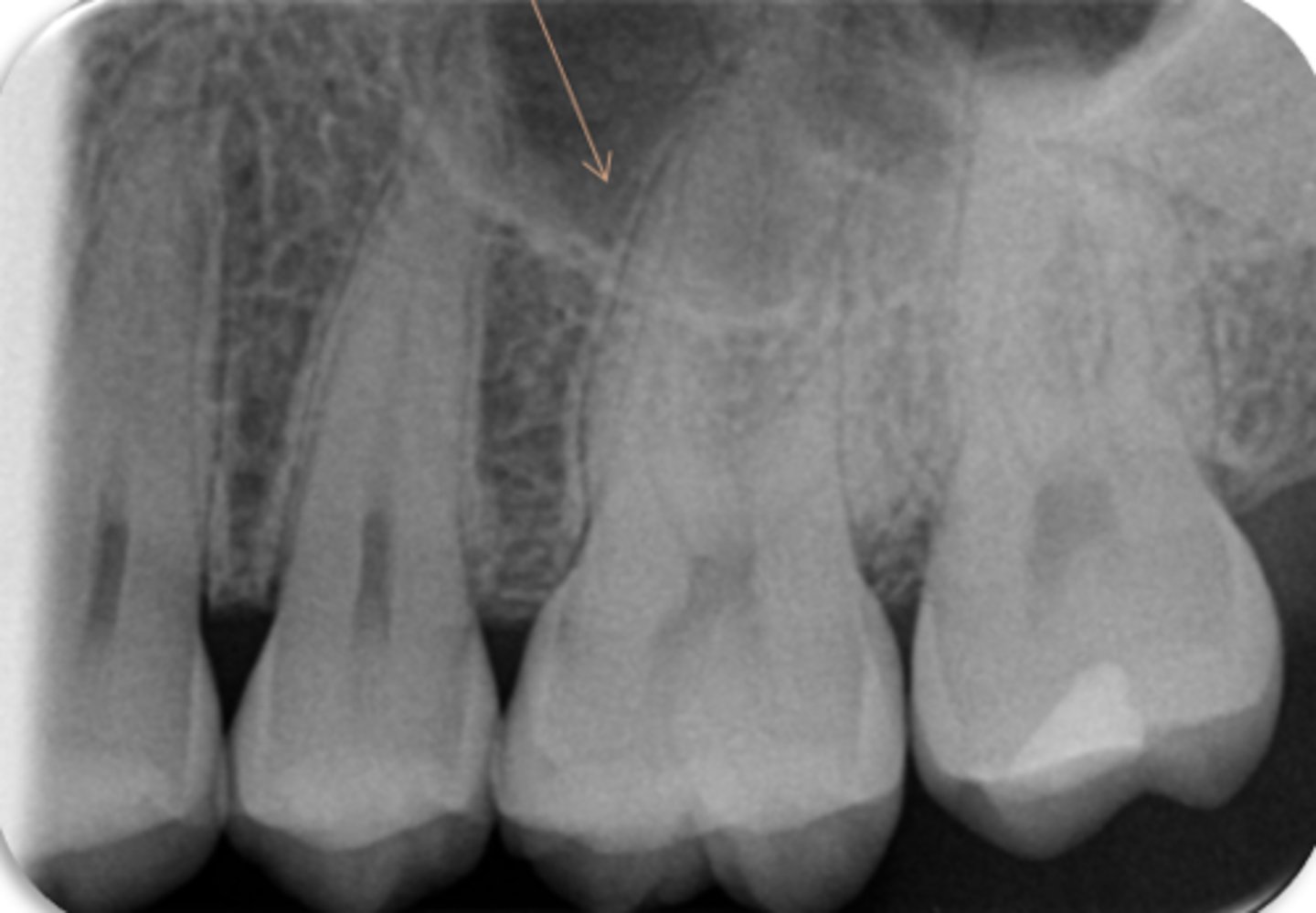
ID the structure:
maxillary sinus
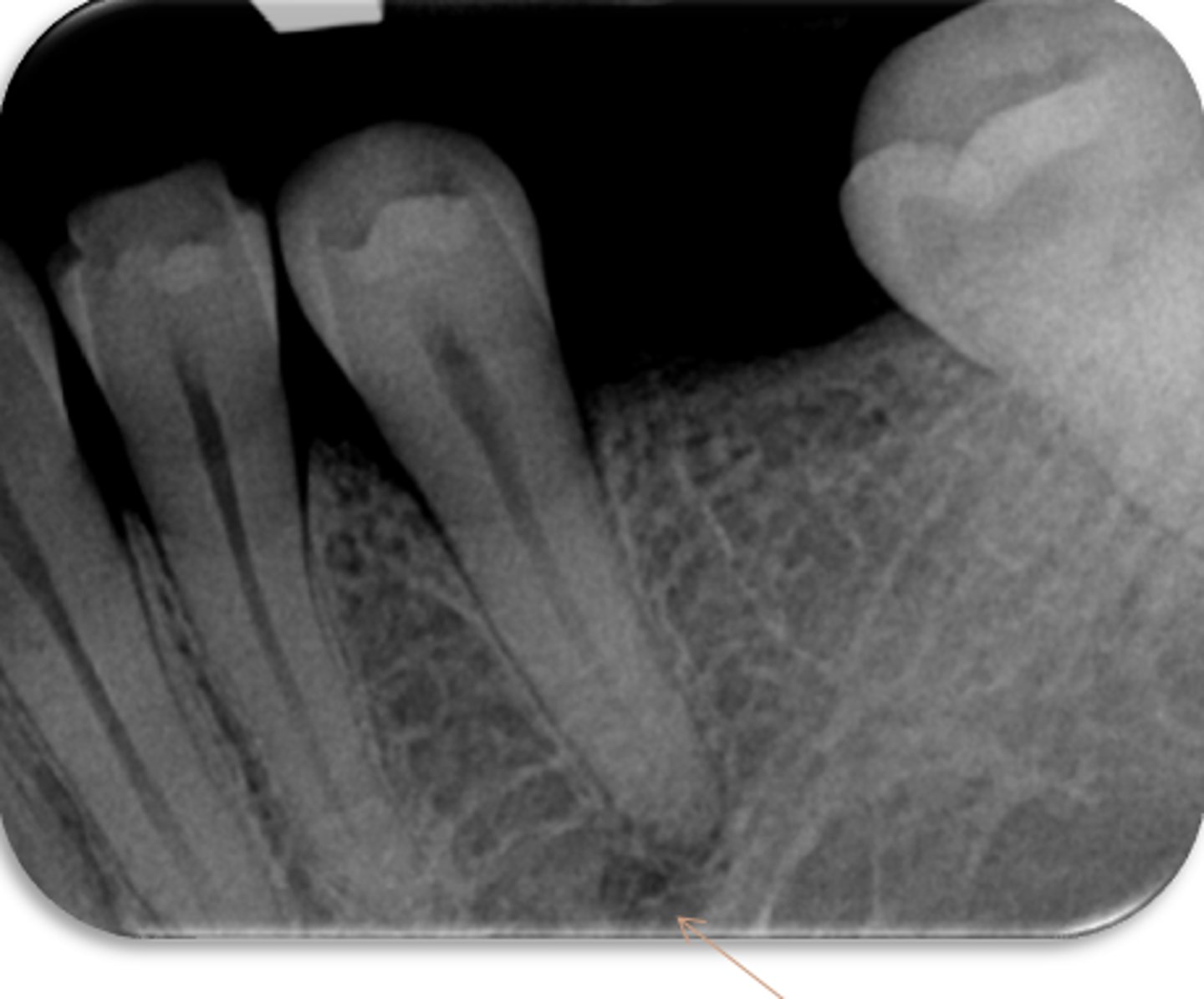
ID the structure:
mental foramen
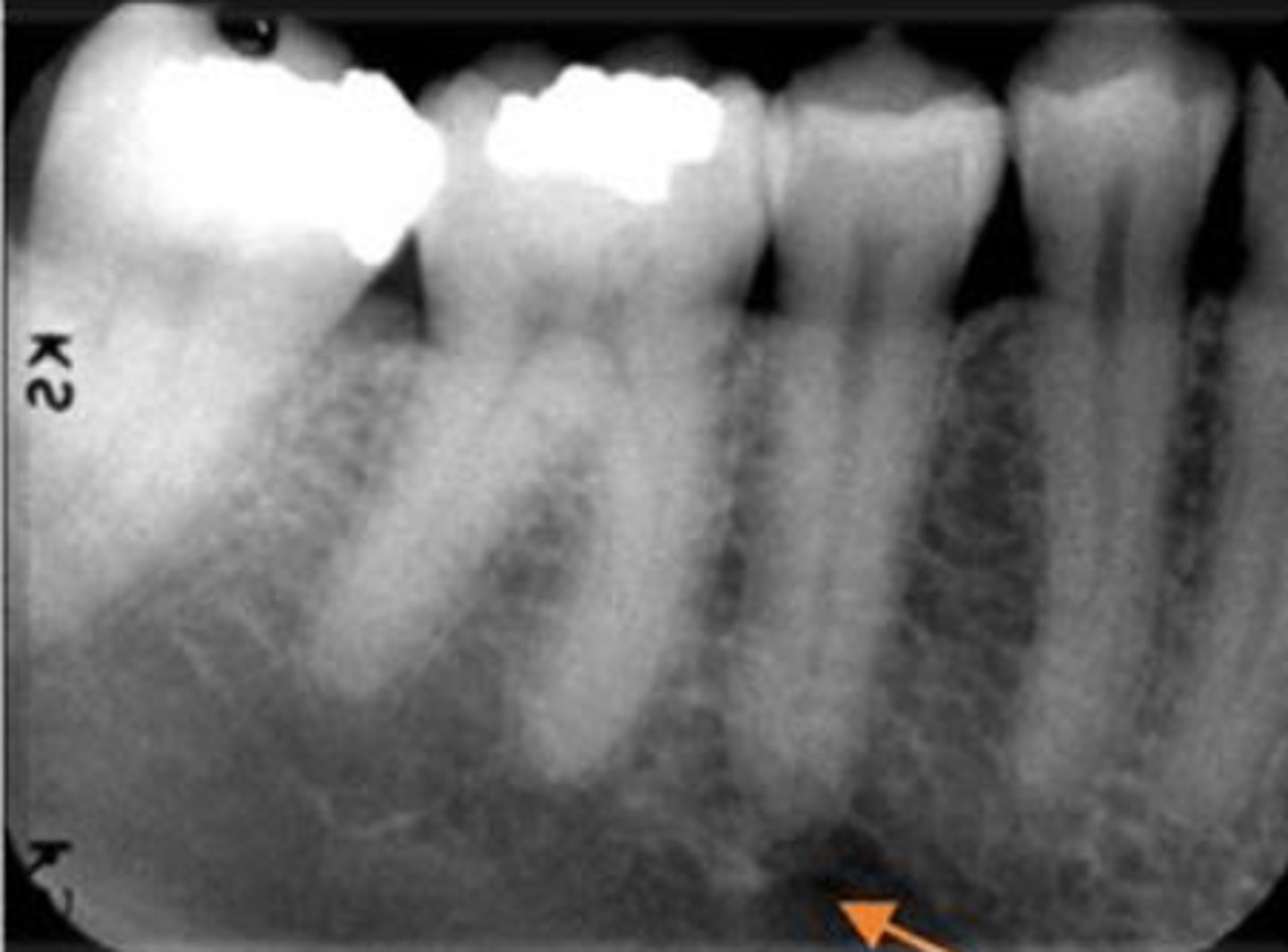
ID the structure:
mental foramen
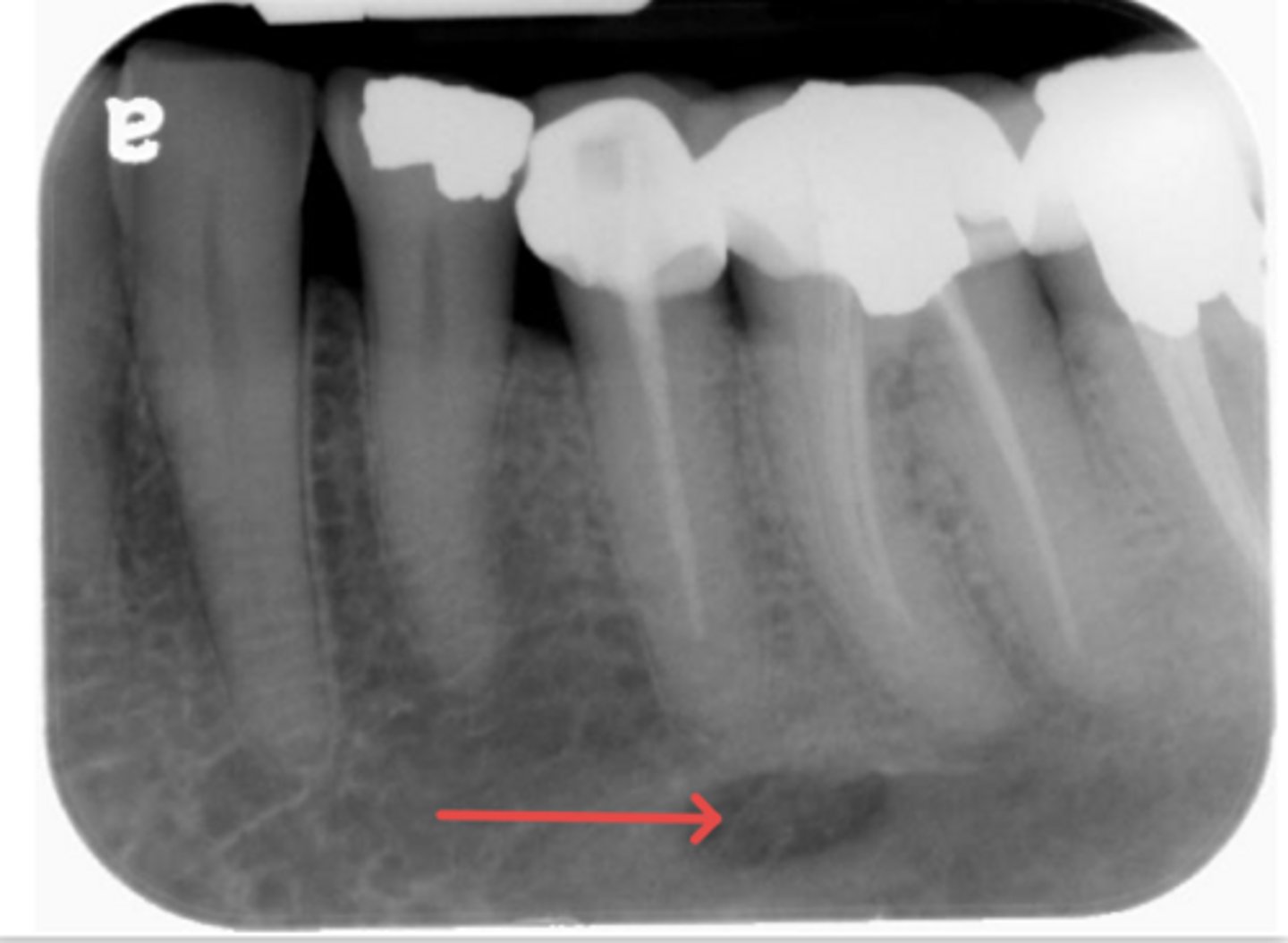
ID the structure:
mental foramen
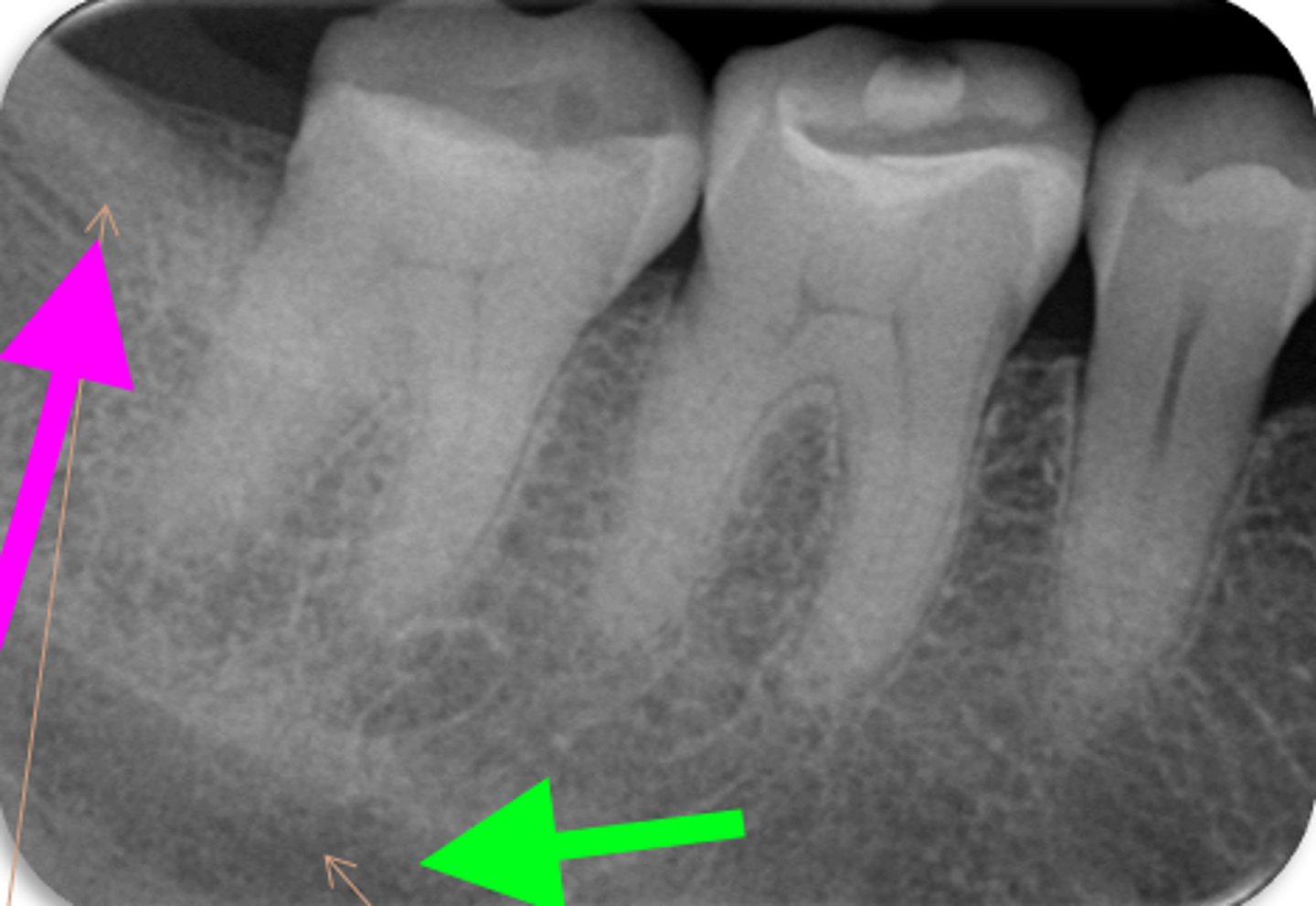
ID the structure with the purple arrow:
external oblique line
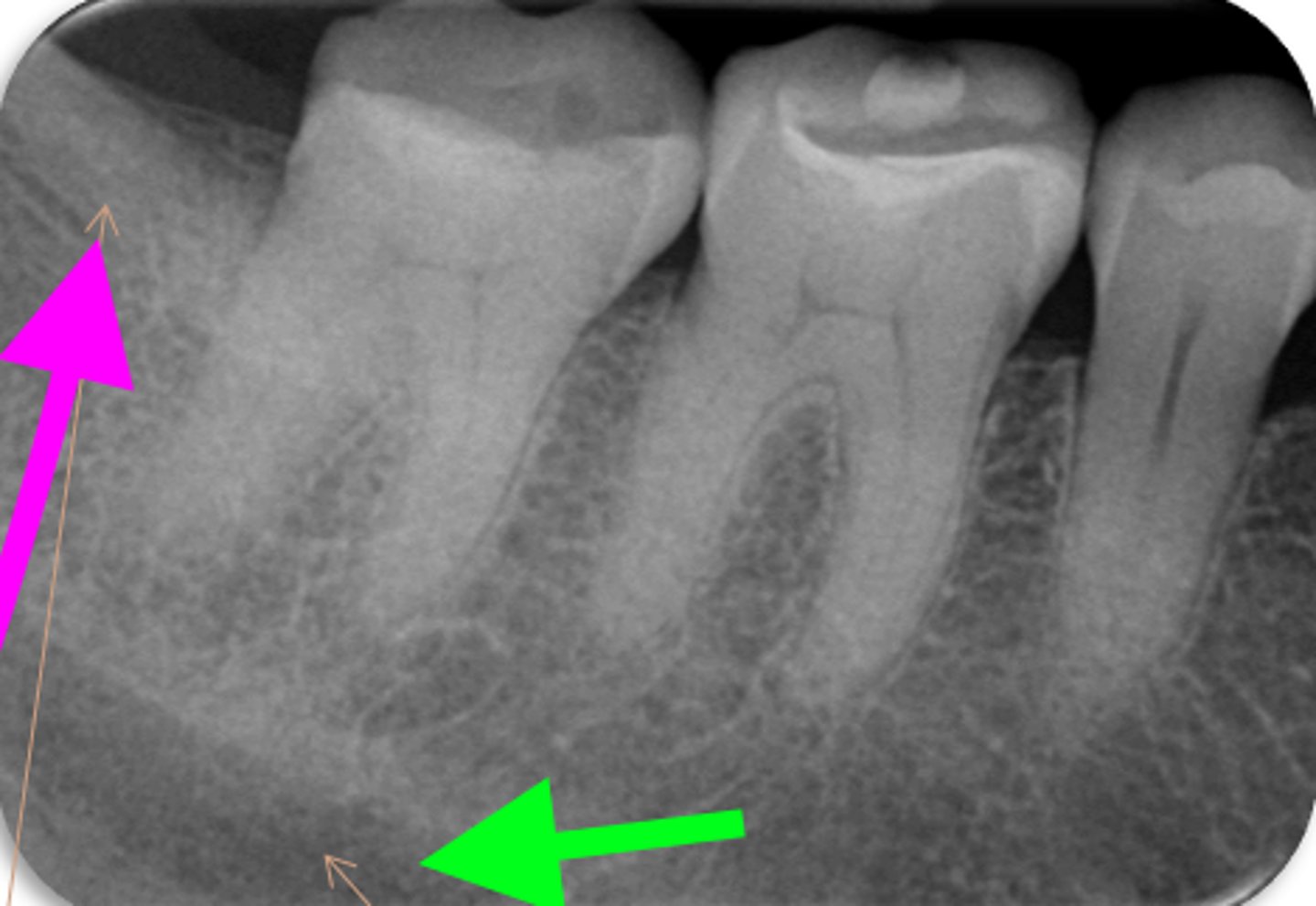
ID the structure with the green arrow:
inferior alveolar nerve canal
ID the structure:
submandibular gland fossa
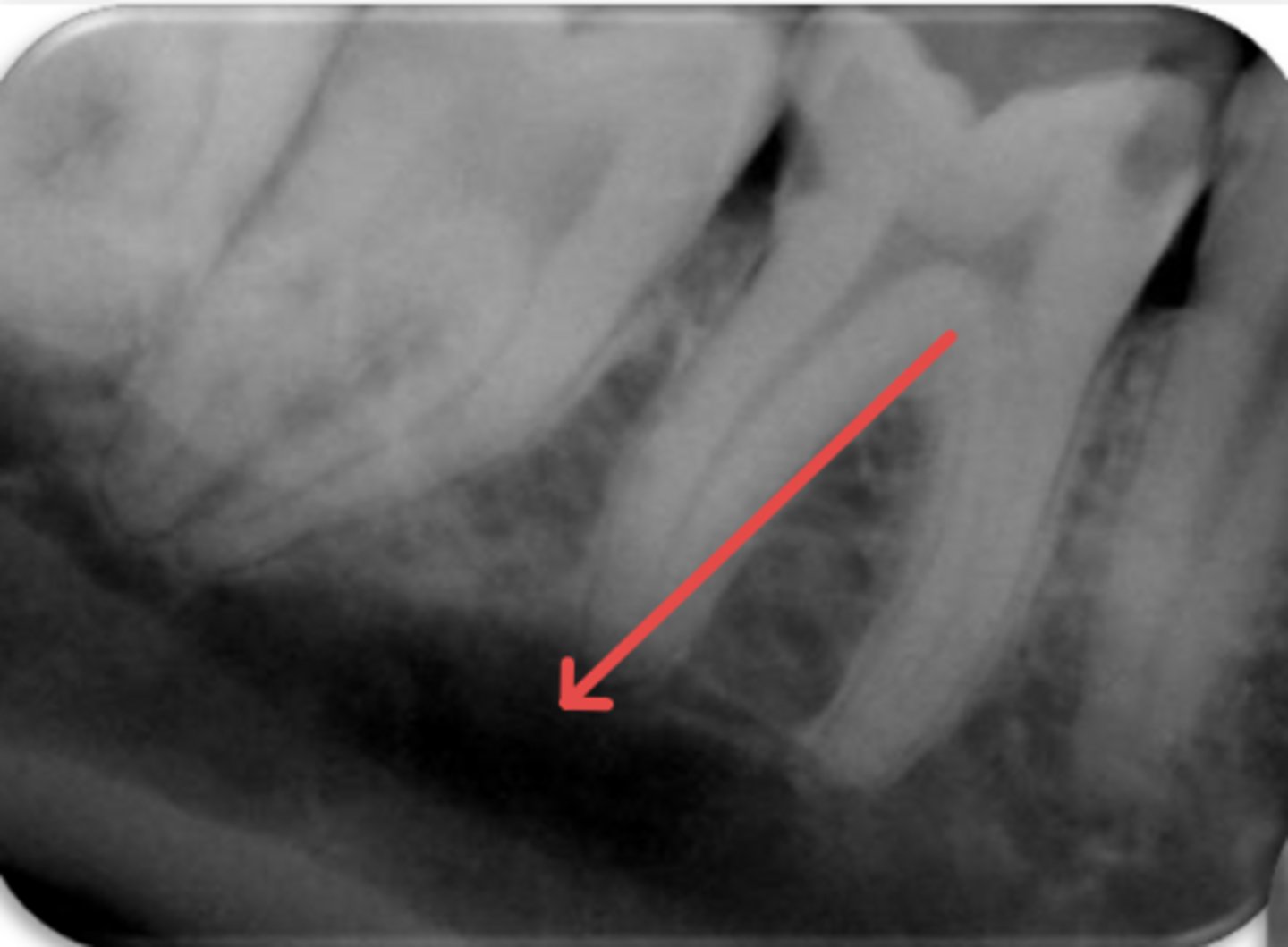
ID the structure:
submandibular gland fossa
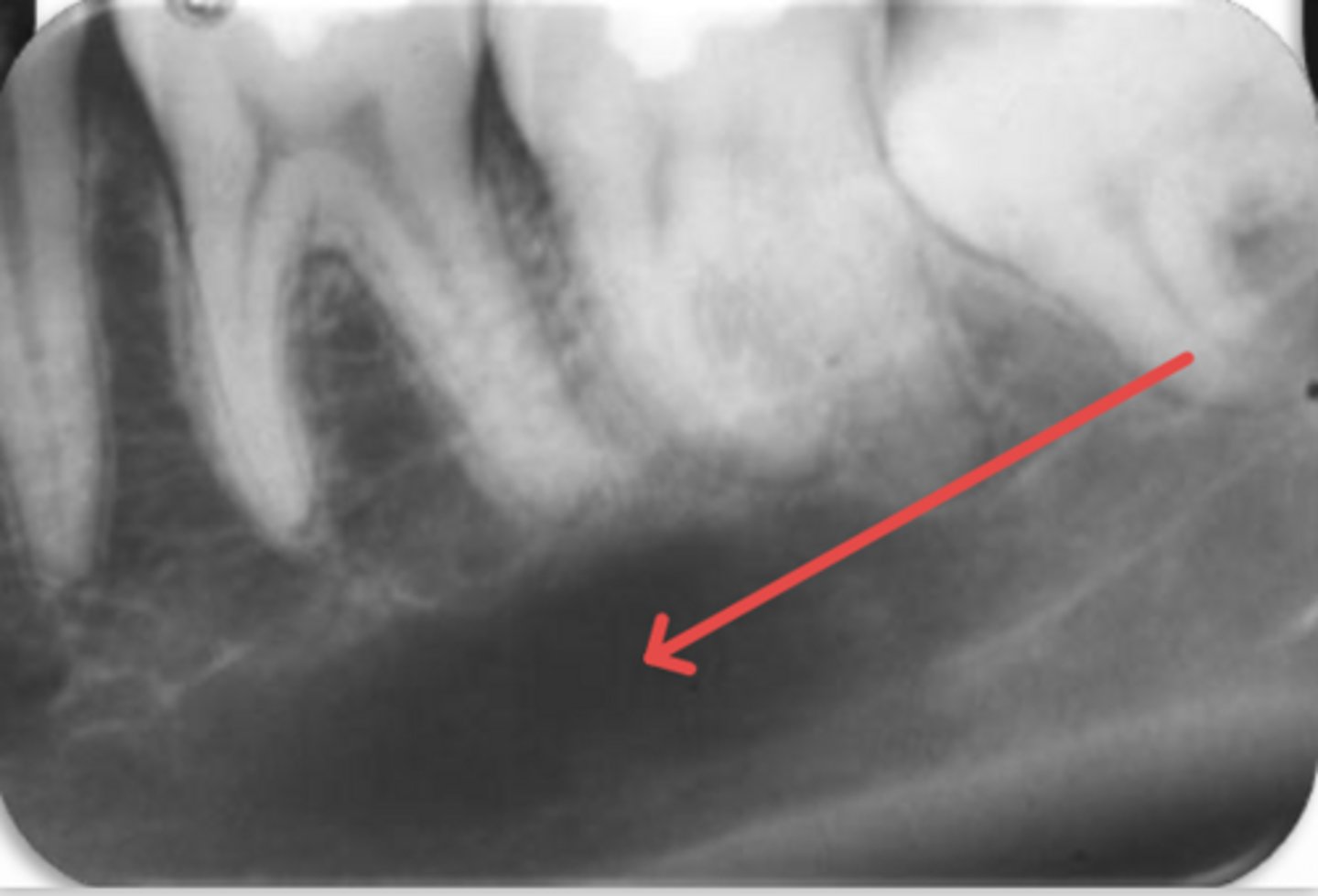
ID the structure:
submandibular gland fossa
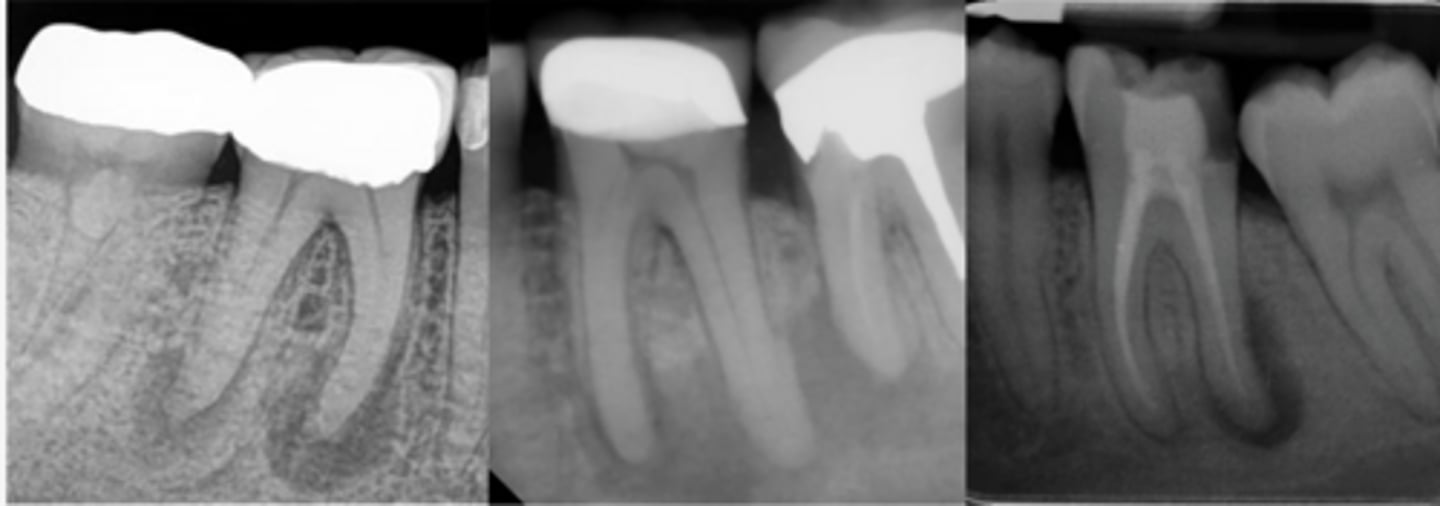
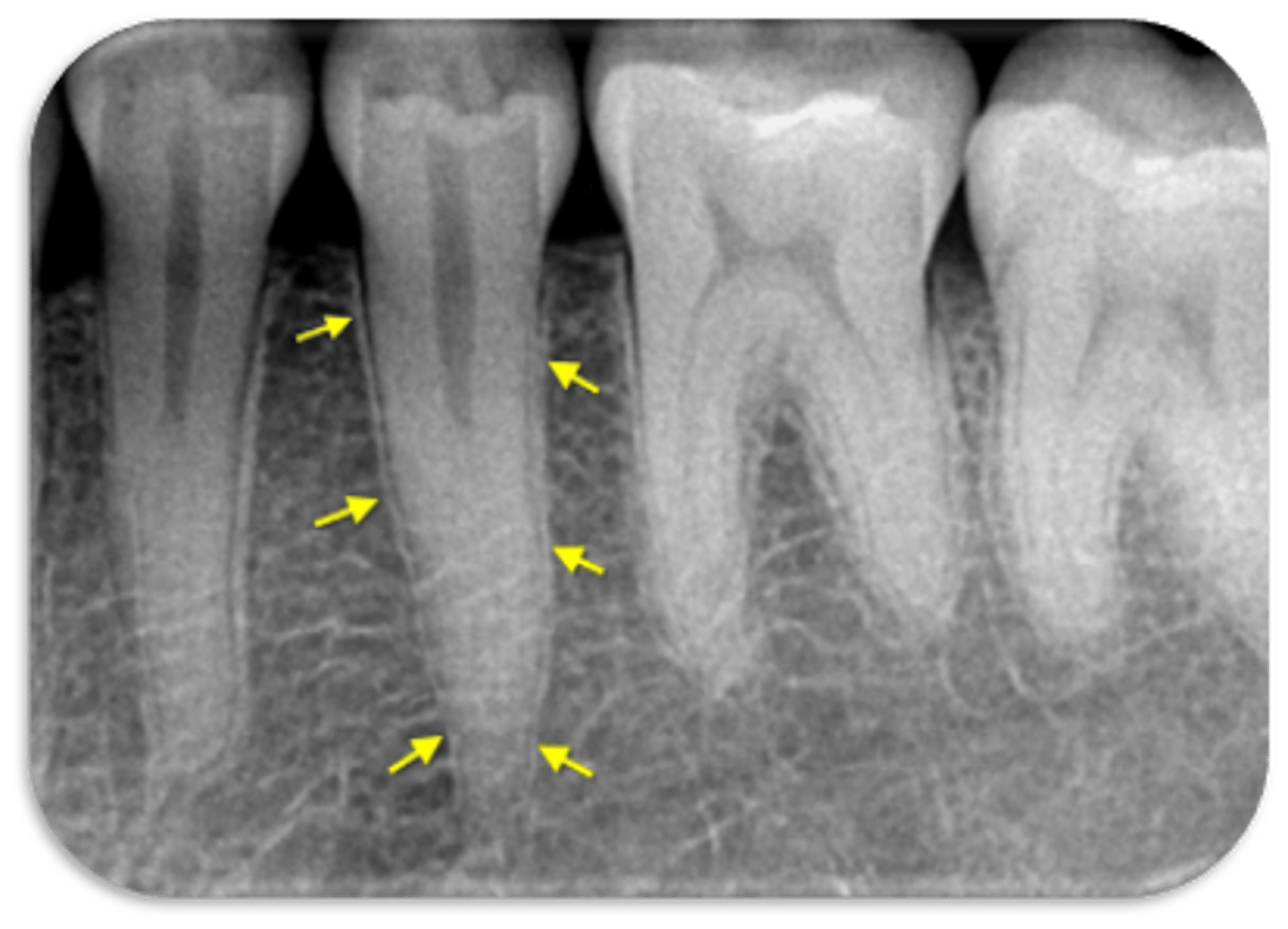
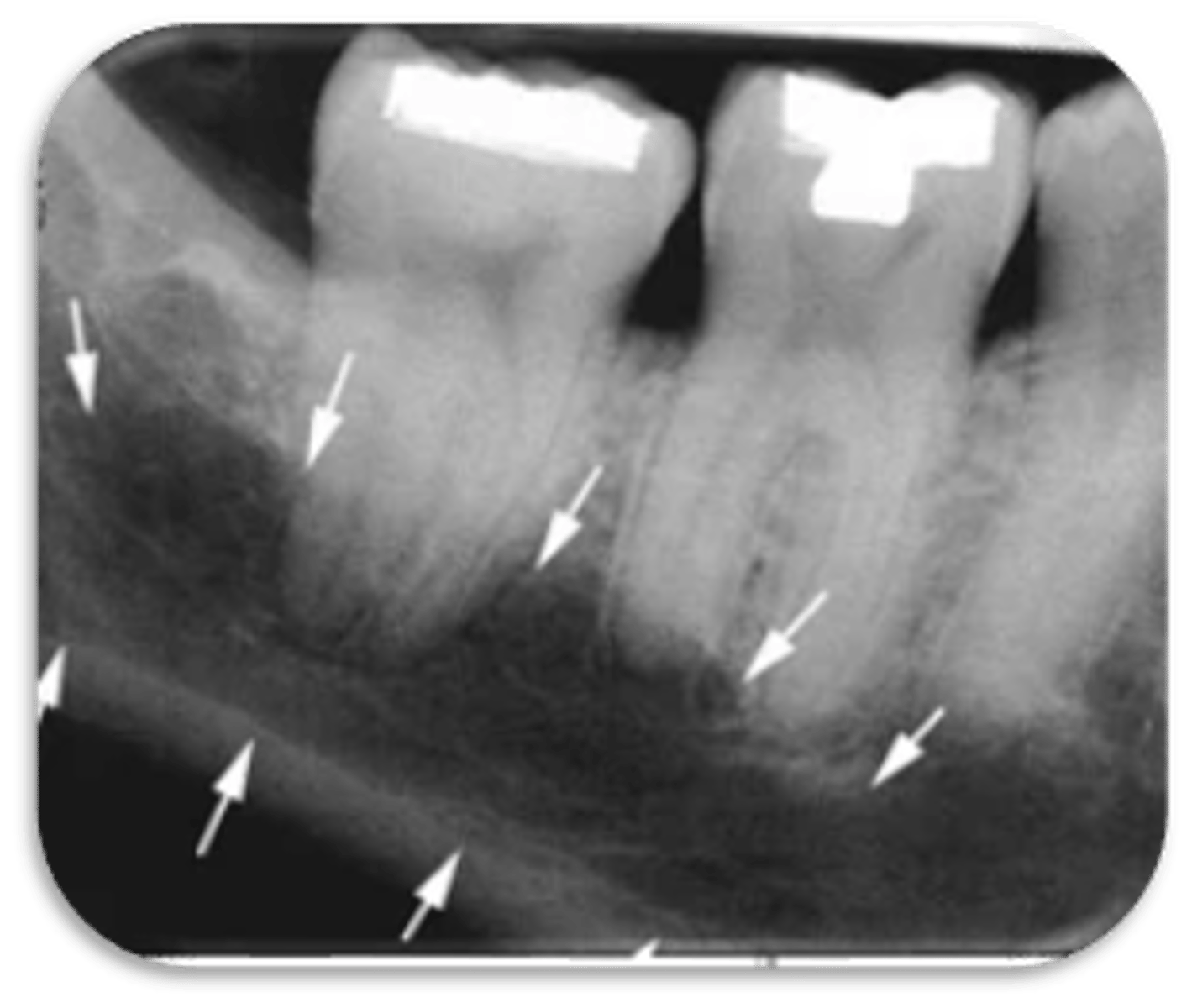
ID the problems:
Areas of rarefaction
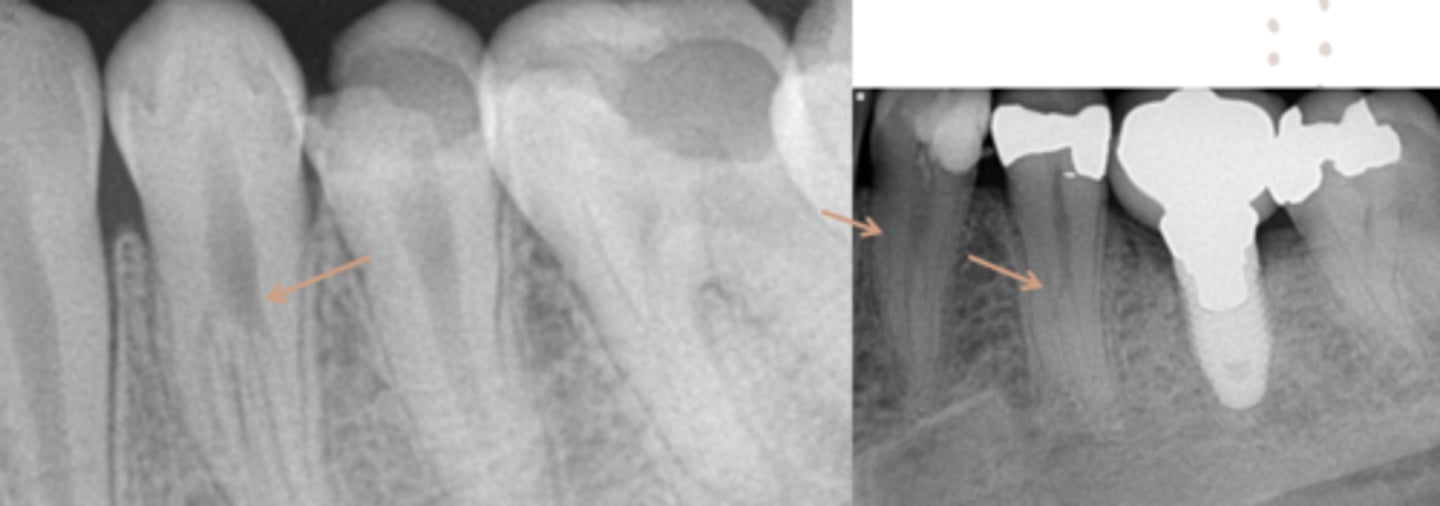
ID the problem:
splitting canals
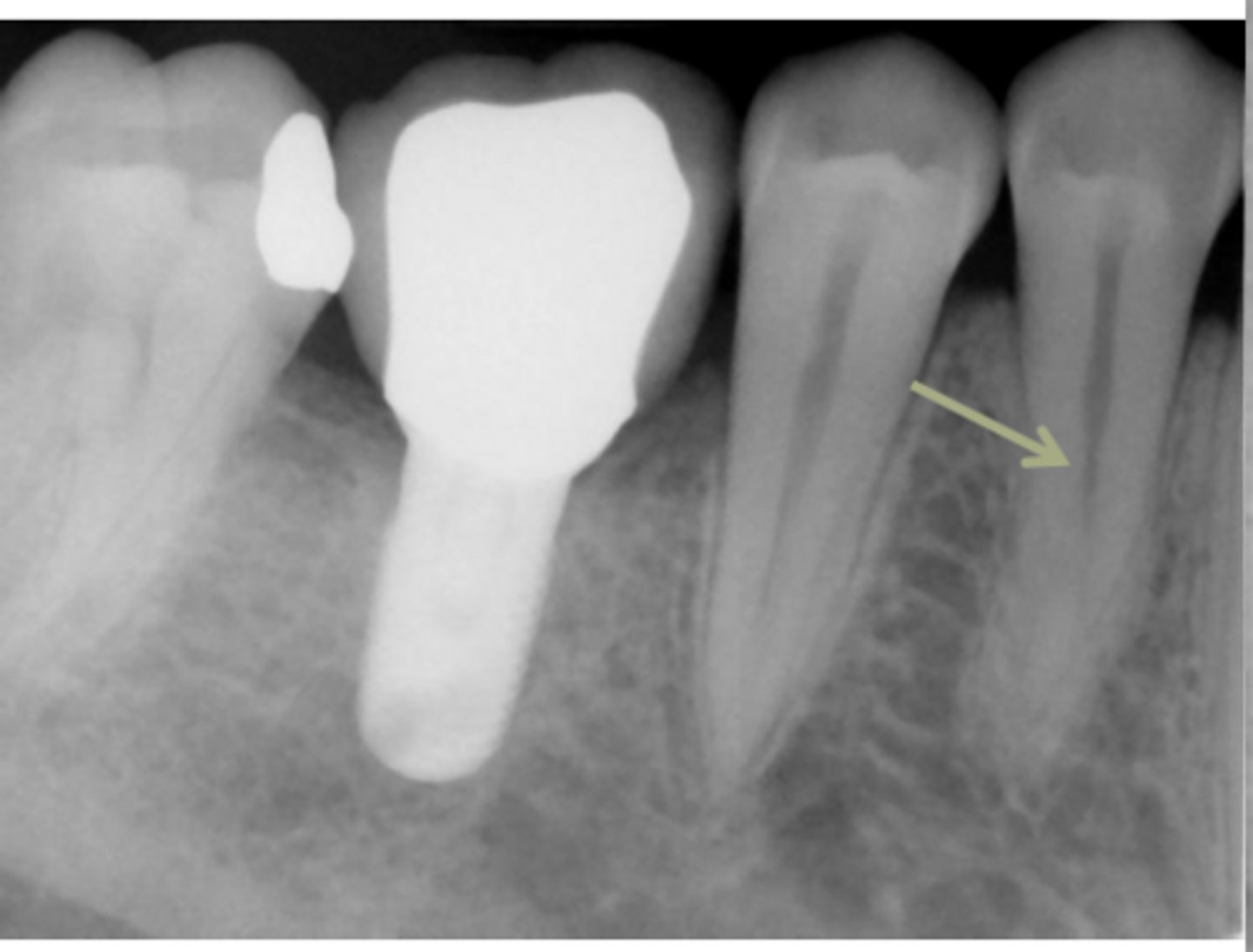
ID the problem:
splitting canals
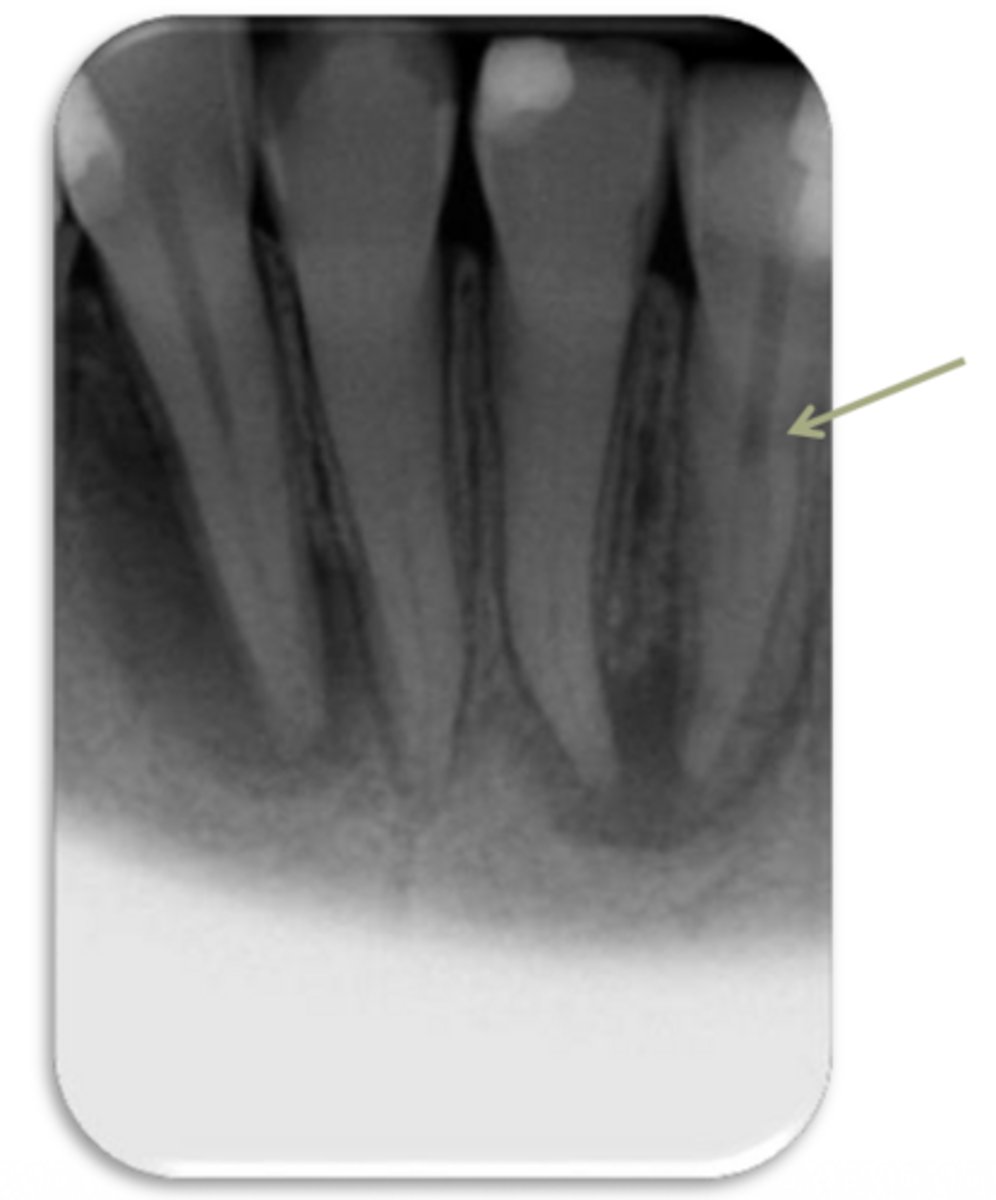
ID the problem:
splitting canals
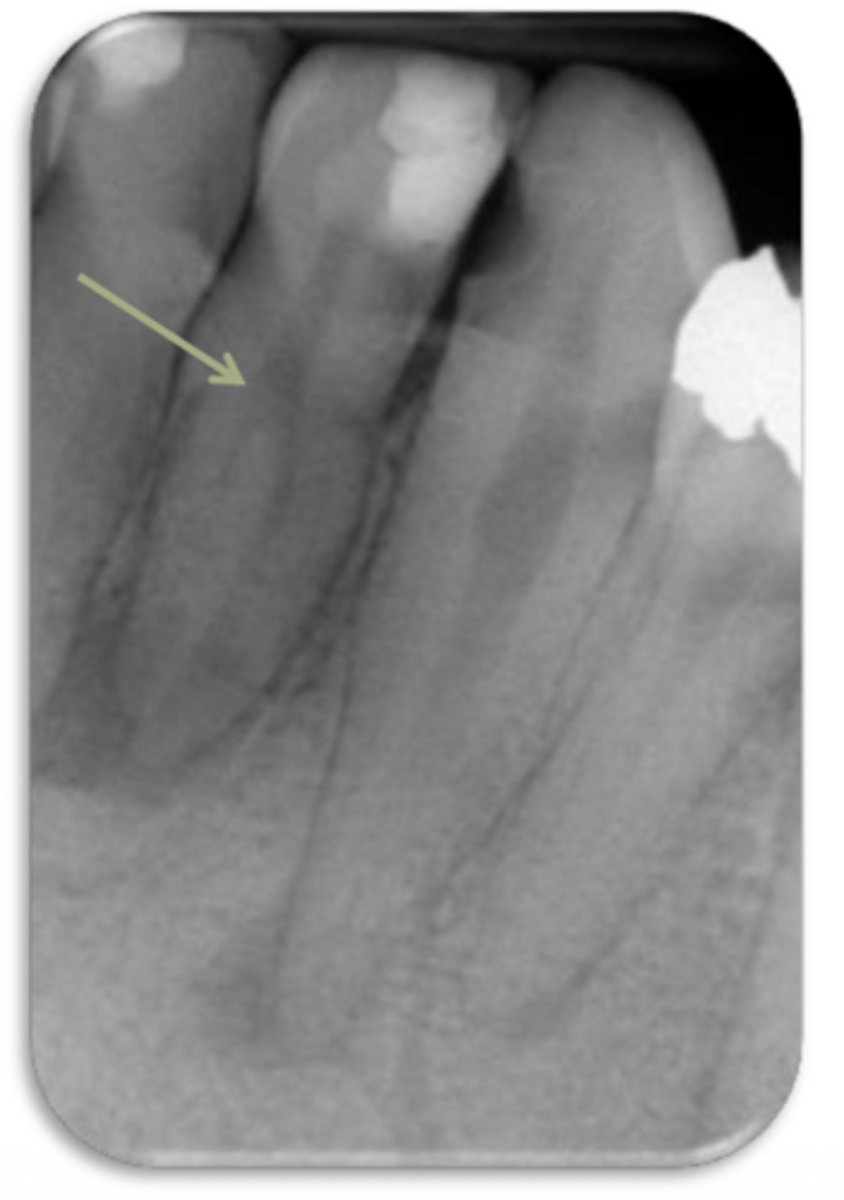
ID the problem:
splitting canals
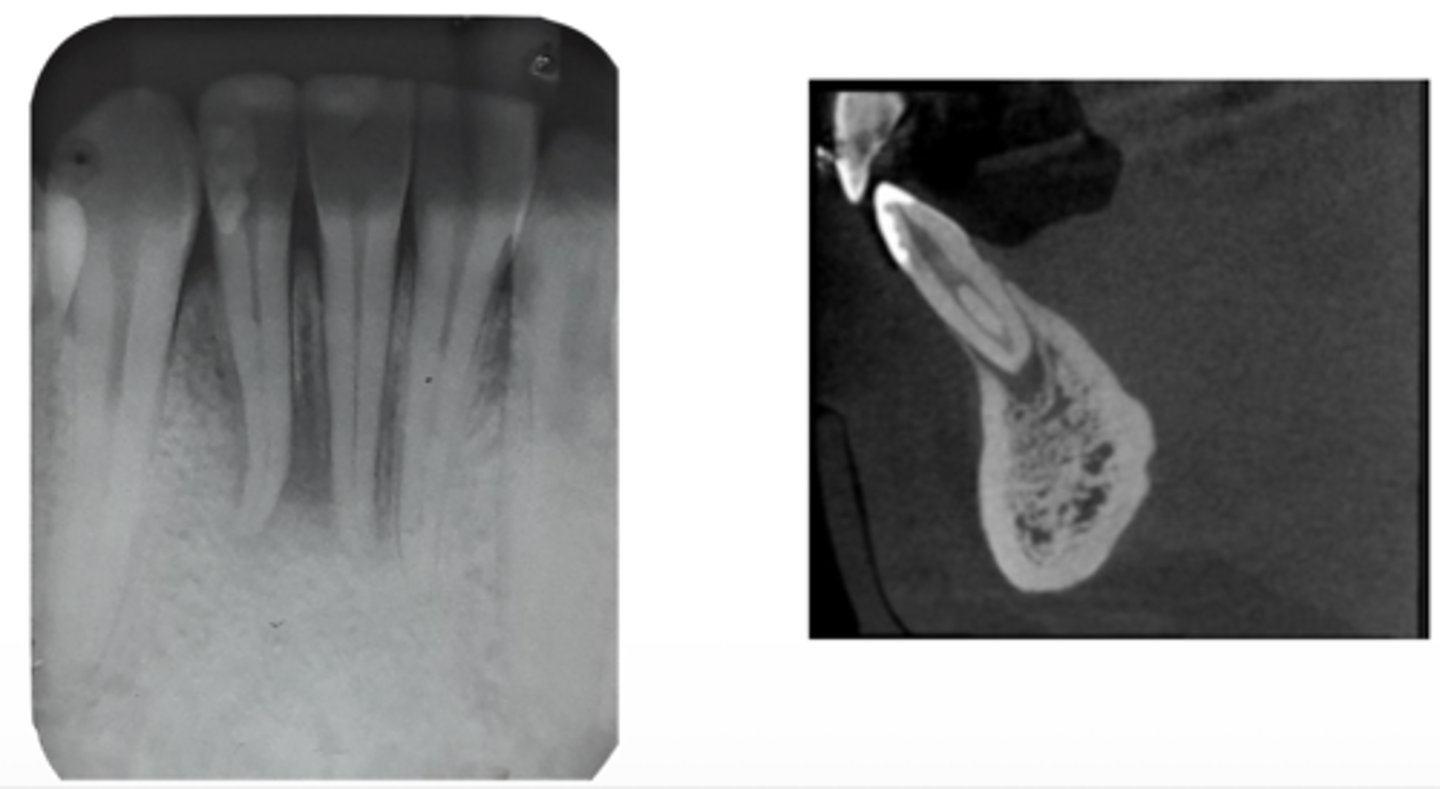
ID the problem:
splitting canals
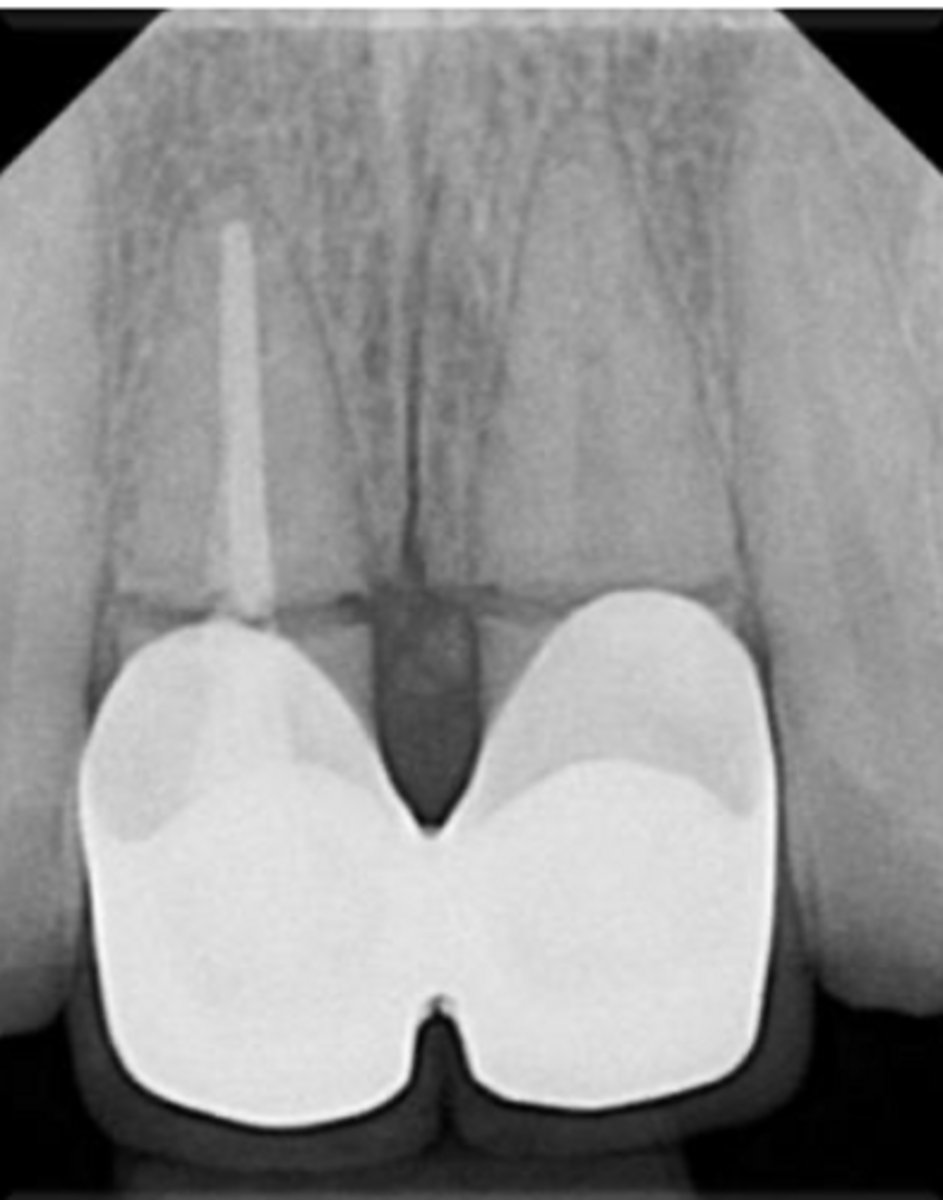
ID the problem:
fracture
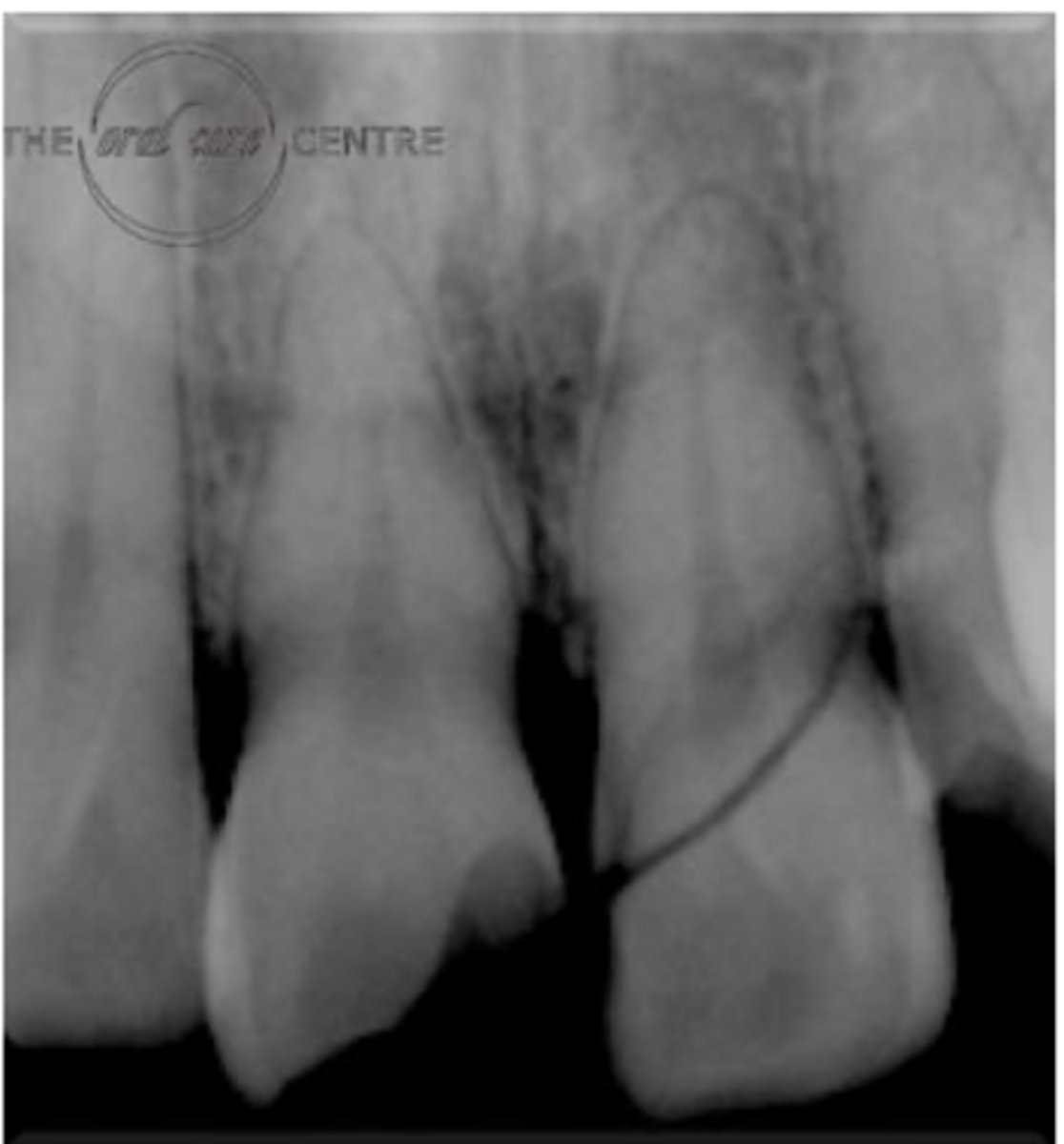
ID the problem:
fracture
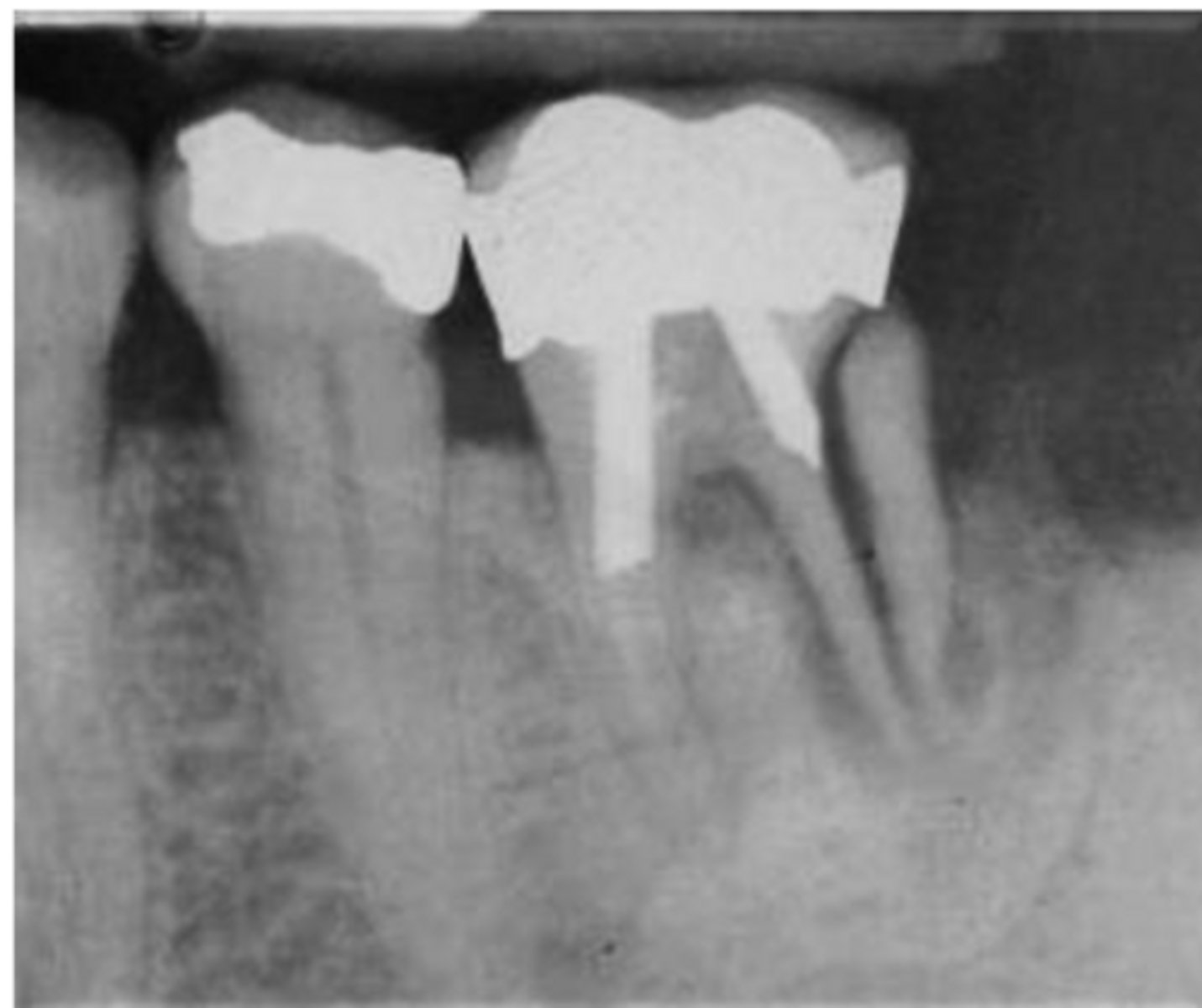
ID the problem:
fracture
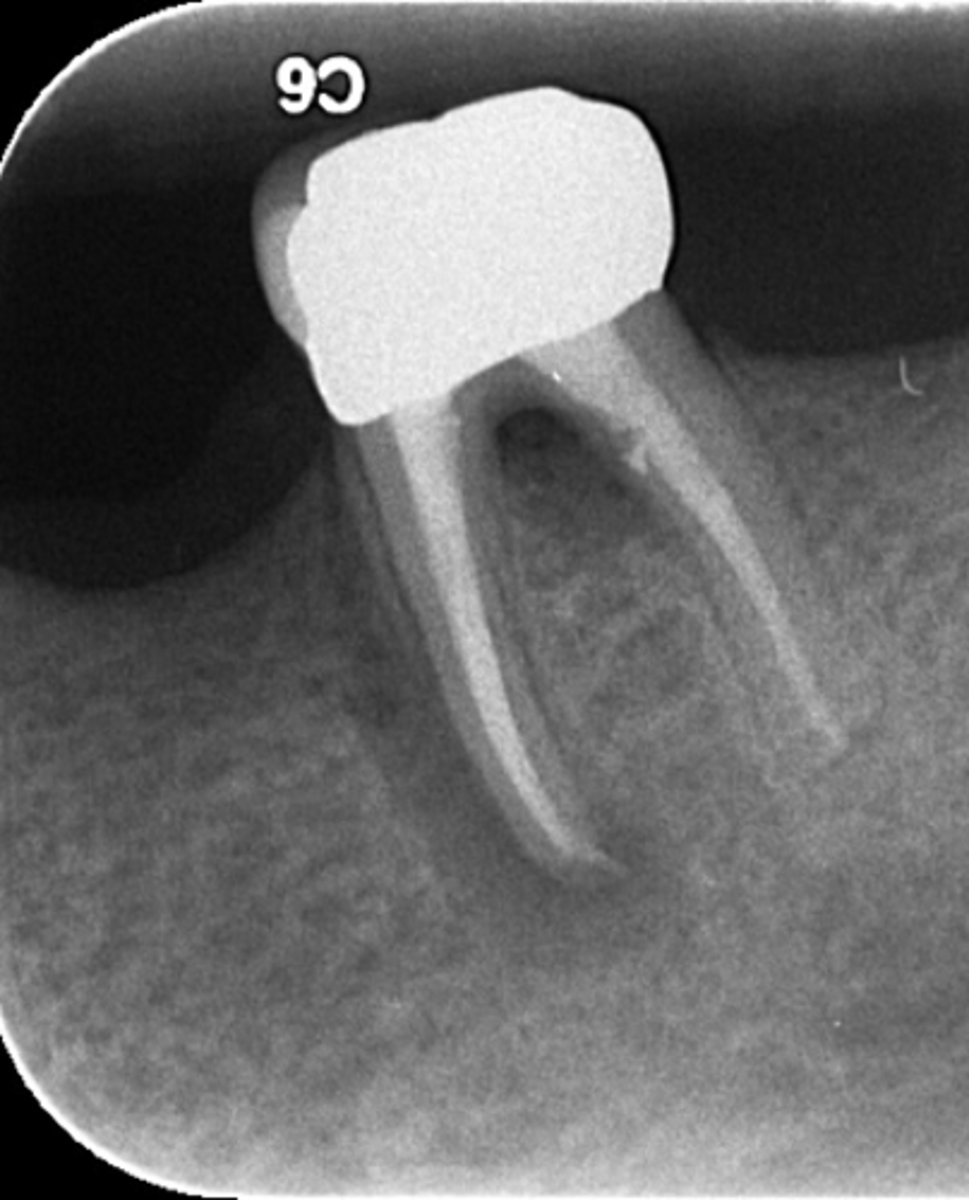
ID the problem:
fracture
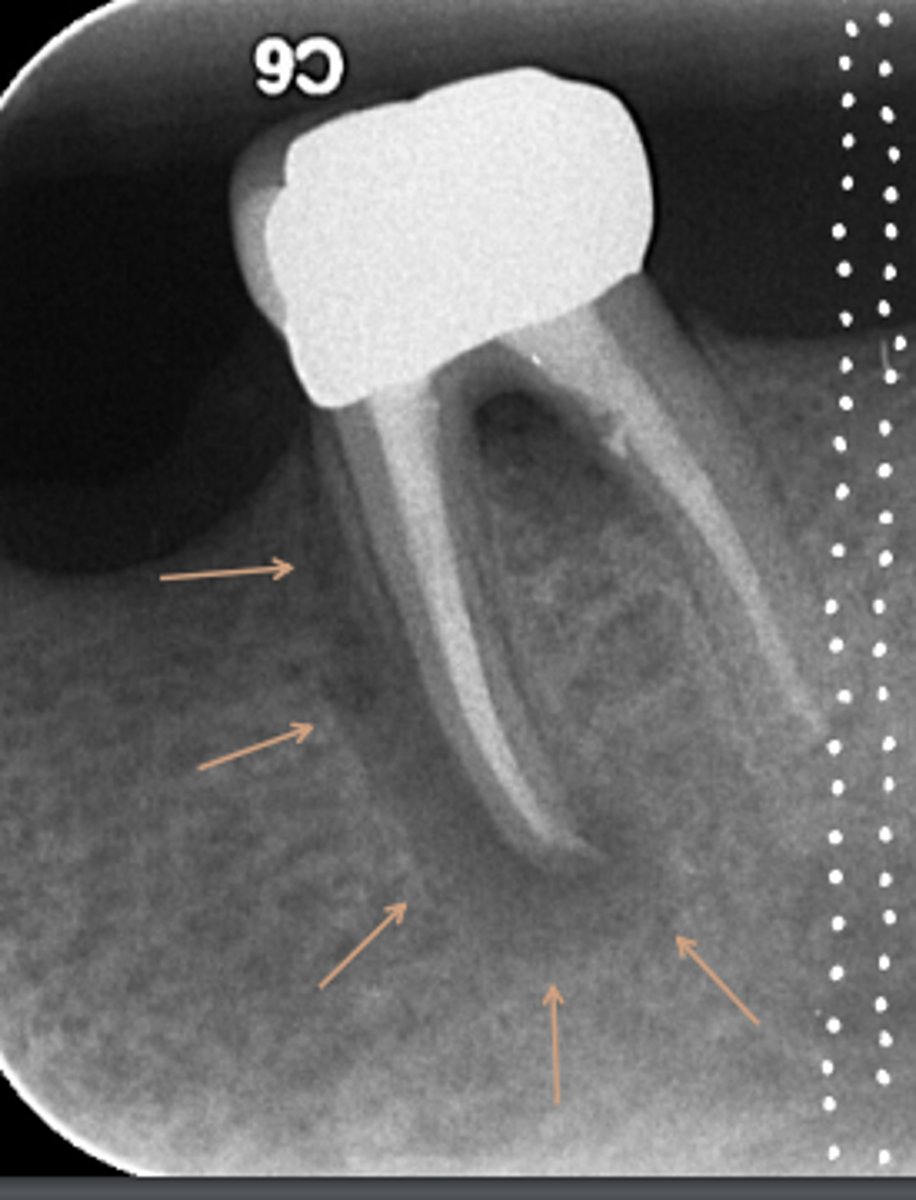
ID the problem:
vertical root fracture
ID the problem:
- May not show on PA radiographs
Presents with signs of:
- J-shaped lesion/lateral radiolucency
- Isolated deep pocket
- Coronally located swelling or sinus tract
vertical root fracture
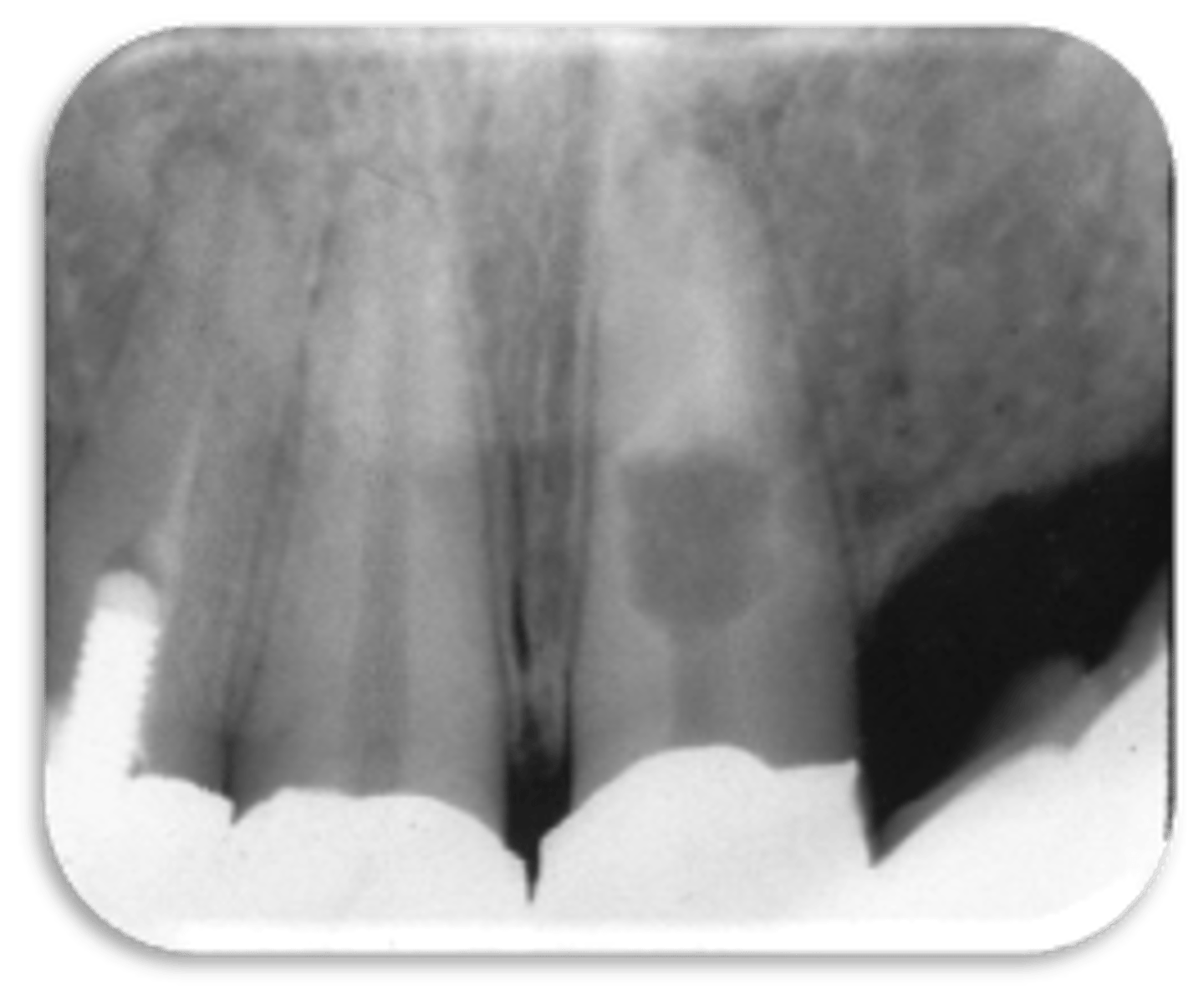
ID the problem:
- Ballooning out of root canal
internal resorption
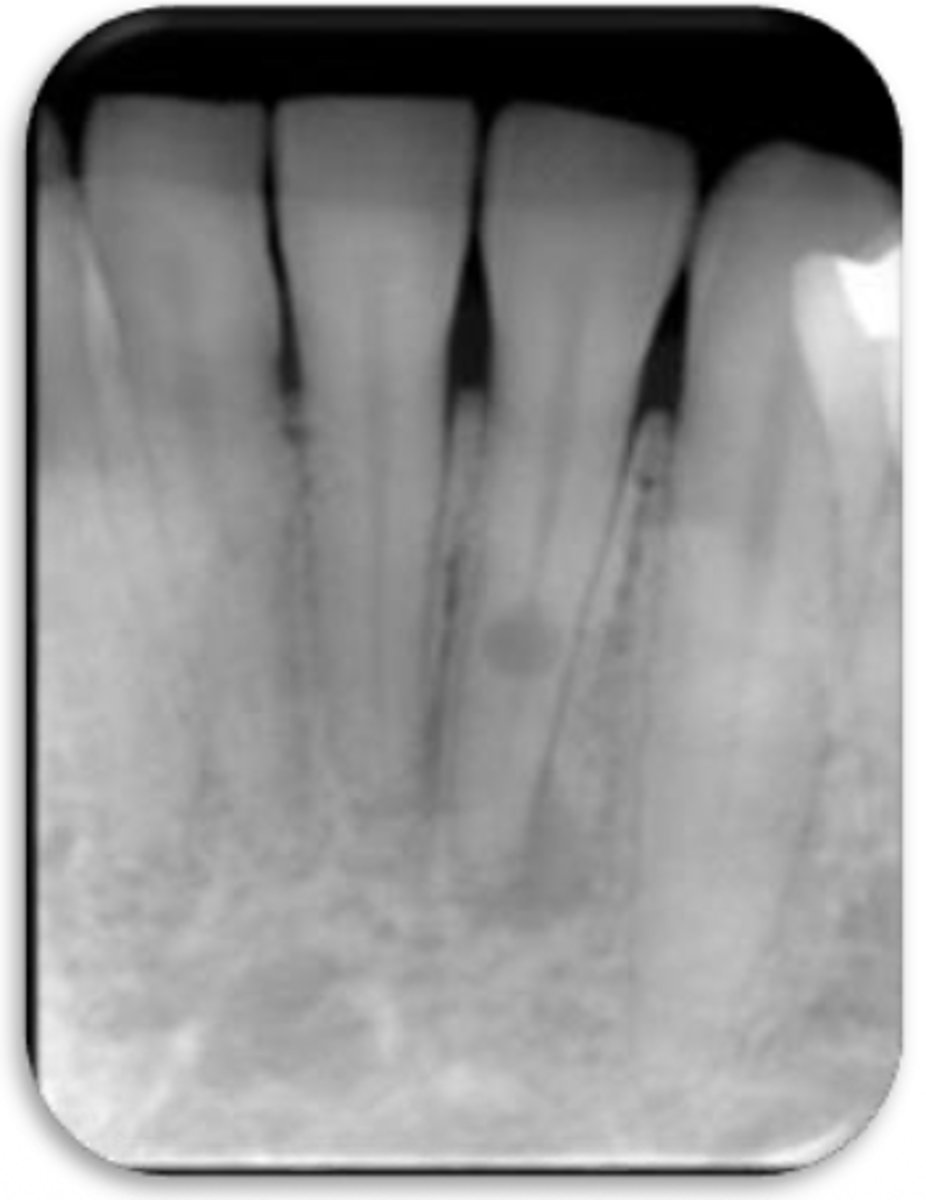
ID the problem:
internal resorption
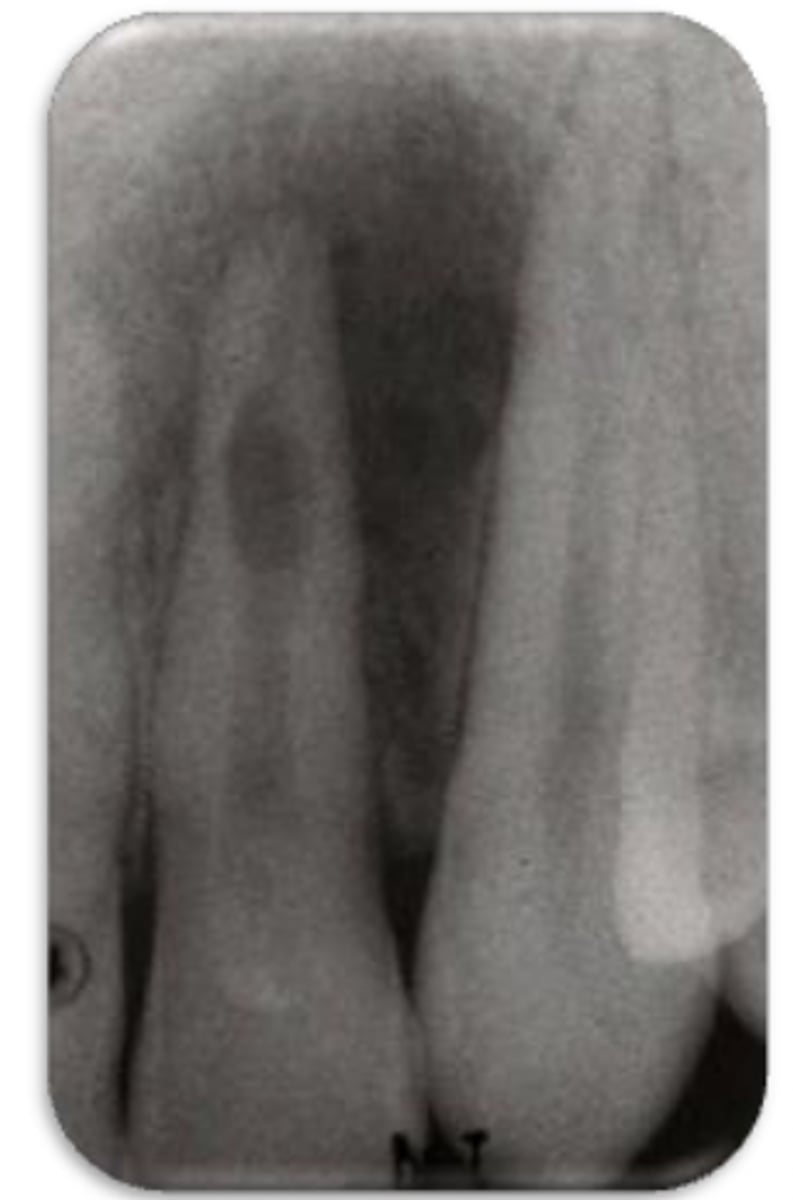
ID the problem:
internal resorption
How can you confirm if a root has internal resorption?
Take a few different angles
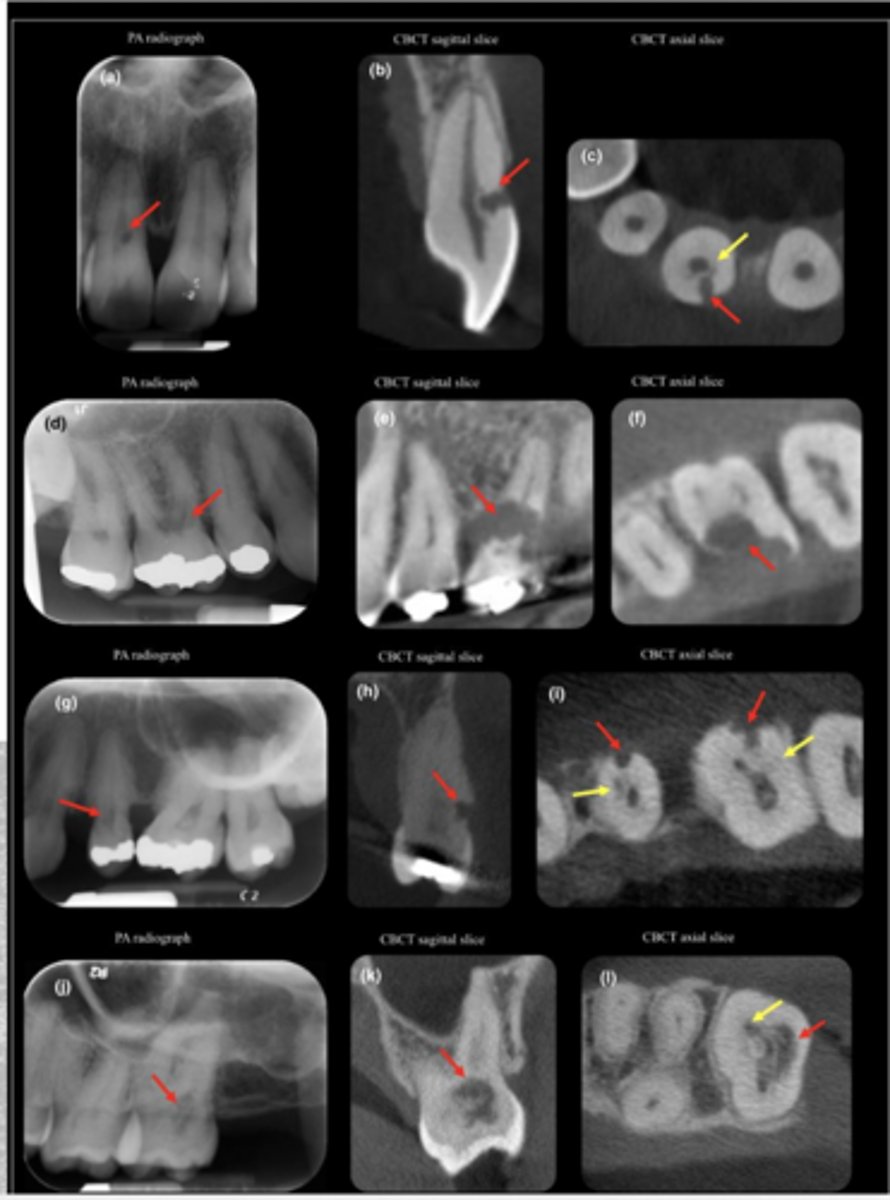
ID the problem:
external resorption
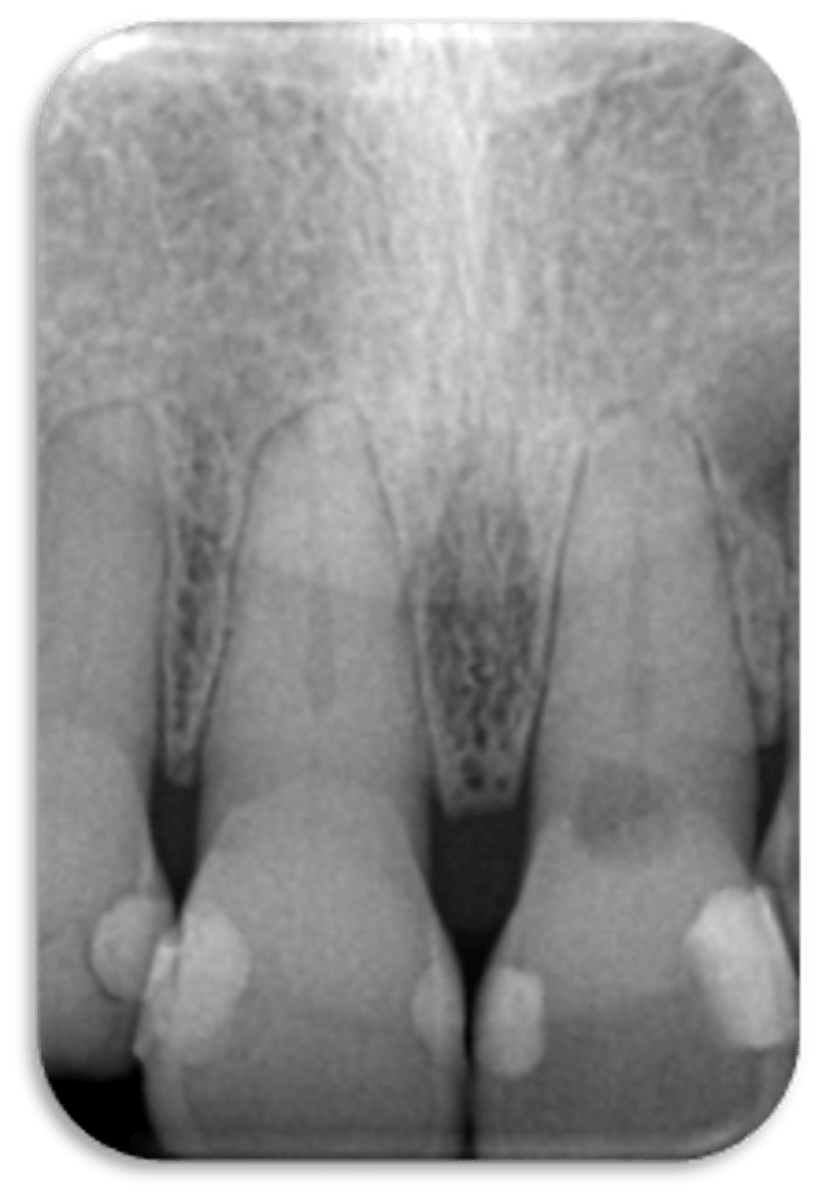
ID the problem:
external resorption
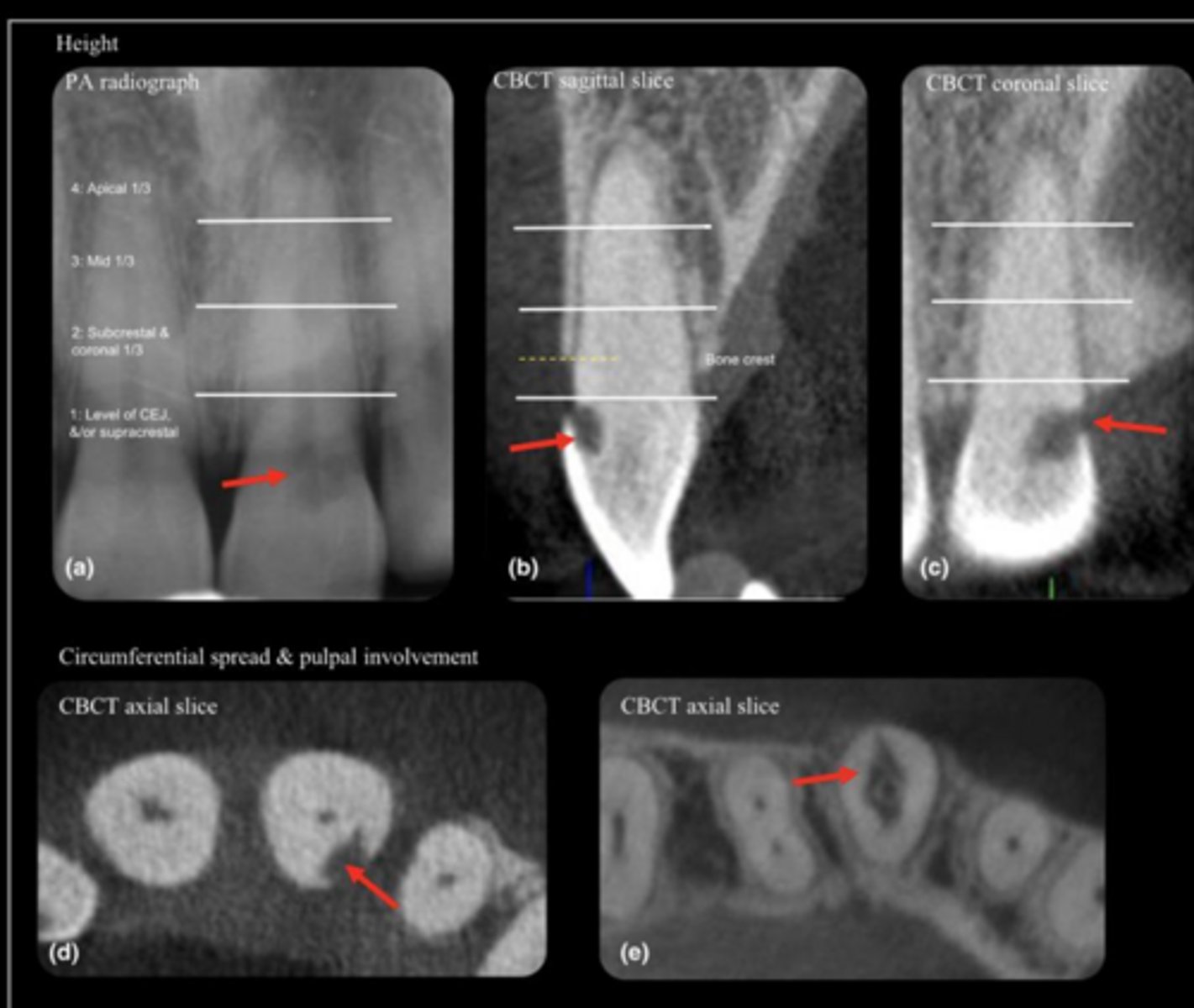
ID the problem:
external resorption
What radiographs should you take pre-op?
- 1 PA
- 1 BW
When should you take radiographs for intra-op?
- Locating canals
- Guide file
- Final file
- Master cone
- Sear down/ partial pack
- Backfill