Central Dogma of Biology
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
DNA
double stranded; in nucleus; contains ALL genetic info.; A--T, C--G
RNA
single stranded; can leave nucleus and go to cytoplasm or ribosome; contains info to make a protein;
A--U; C--G
mRNA
messenger RNA; can leave the nucleus, carries the code for the protein
rRNA
ribosomal RNA; make up a ribosome
tRNA
transfer RNA; carries the amino acids to the ribosome
Goal of protein synthesis:
To make a chain of proteins outside the nucleus
In protein synthesis, what molecule has the instructions?
DNA
DNA is located in:
nucleus
What organelle is used to make proteins?
ribosome
Ribosome is located in:
cytoplasm
Two stages of protein synthesis:
Transcription and translation
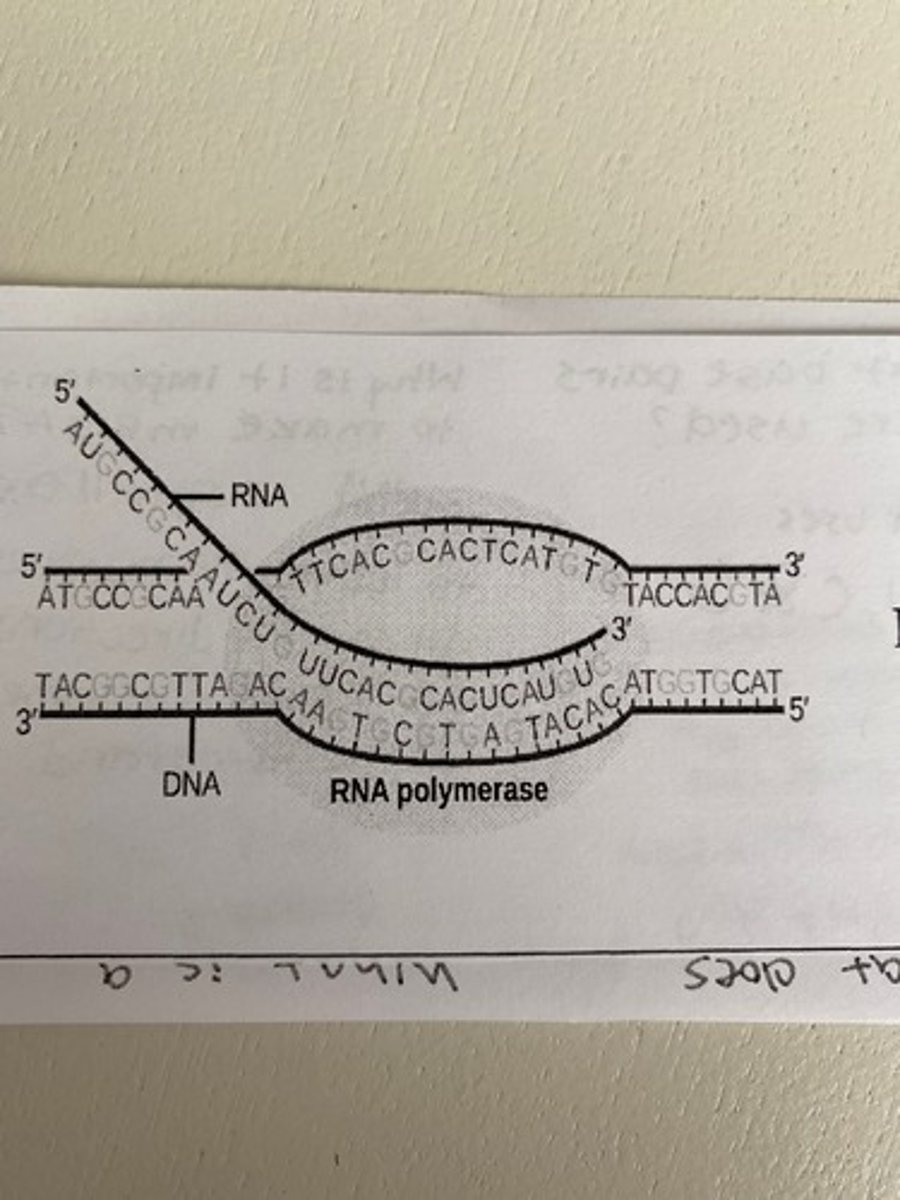
Transcription
DNA---mRNA, in nucleus
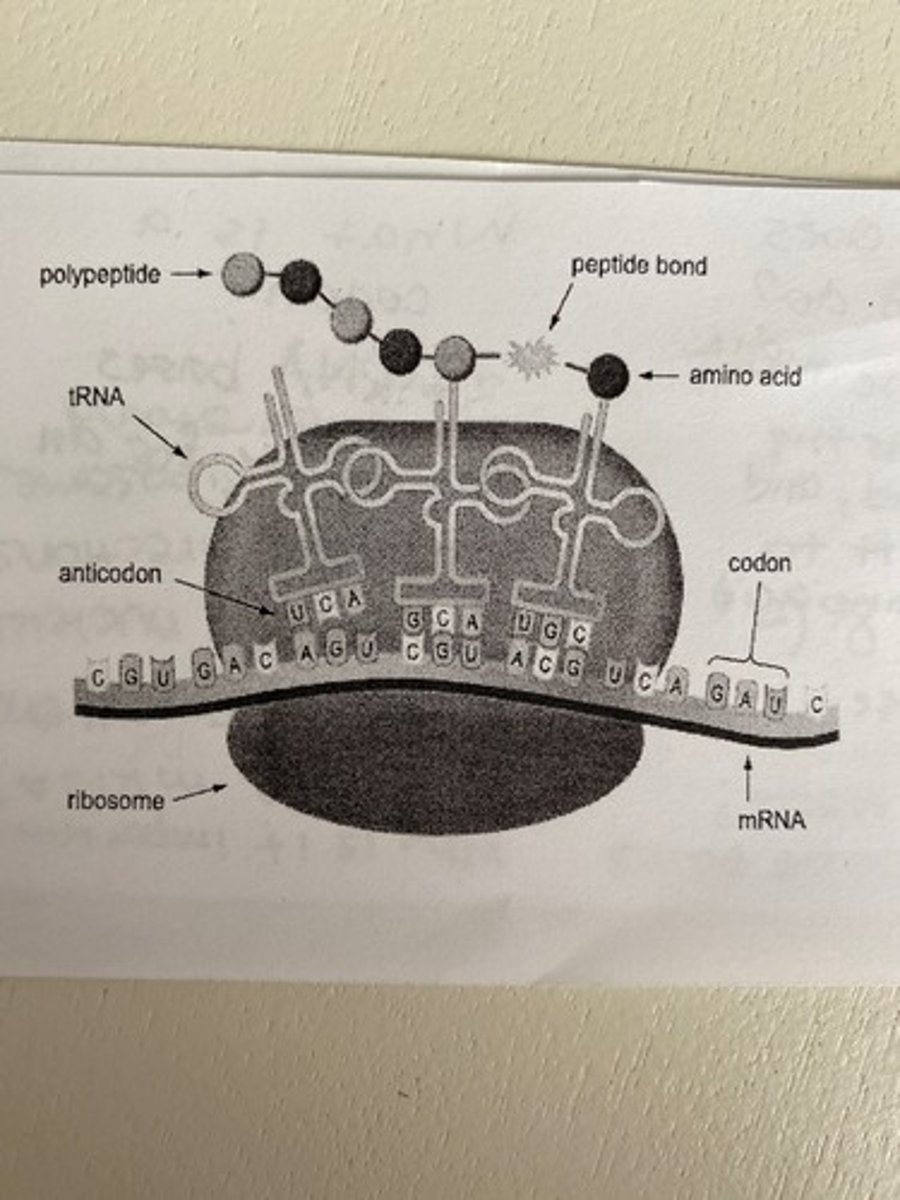
Translation
mRNA--protein, in cytoplasm at ribosome
In protein synthesis, the GENETIC CODE is:
sequence of nitrogen bases along one strand of DNA
Proteins
long chains of amino acids
20
number of different amino acids
Codon
a sequence of 3 bases that provides the code for an amino acid
64
number of different codons in the genetic code
61
number of codons in amino acids in the genetic code
3
number of stop codons in the genetic code
There can be more than one _____ for an _____ _____.
codon; amino acid
The genetic code is UNIVERSAL because:
the codons represent the same amino acids in ALL organisms
In transcription, DNA cannot leave the nucleus, so...:
small parts (genes) are copied (transcription) to create mRNA.
In transcription, the enzyme RNA helicase:
opens a small portion of DNA.
In transcription, RNA nucleotides base pair with:
only one side of the DNA.
In transcription, a single strand of RNA is produced that is called:
mRNA
In transcription, the mRNA carries the copied information to:
the ribosome located in the cytoplasm.
In transcription, ribosomes are made up of:
proteins and ribosomal (rRNA)
Translation is:
the process that converts mRNA into a sequence of amino acids.
In translation, the START codon (AUG) of the mRNA:
attaches to a ribosome
In translation, tRNA brings:
a specific amino acid.
In translation, the tRNA anticodon:
pairs with the mRNA codon.
In translation, the mRNA slides along the ribosome and:
eventually a protein forms.
Translation ends with a:
STOP codon.
DNA Replication occurs so:
it can copy a segment to create mRNA
DNA (can or cannot) leave the nucleus to bring instructions to the ribosomes.
CANNOT
Ribosomes (can or cannot) make the protein without instructions.
CANNOT
Why is transcription so important?
The DNA matches up bases to RNA to send the instructions with the RNA strand because it is smaller and can fit out of the nucleus.
Which comes first, transcription or translation?
transcription
What is translation?
This is when the mRNA brings the instruction to the ribosome to make the protein.
What happens in translation?
The mRNA is read by tRNA (transfer RNA) and the tRNA goes out to find the amino acid that pairs up with the codons in mRNA.
Codon = _______
3 RNA bases like AGC
On a Codon chart:
1st letter is on the left side;
2nd letter is on top;
3rd letter is on the right side
DNA Base Pair Rule:
A--T (Apple is in the Tree)
C--G (Car is in the Garage)
RNA Base Pair Rule:
A--U (Apple is Under the tree)
C--G (Car is in the Garage)
Where can I find the CODON Chart so I can practice?
Bio Workbook!
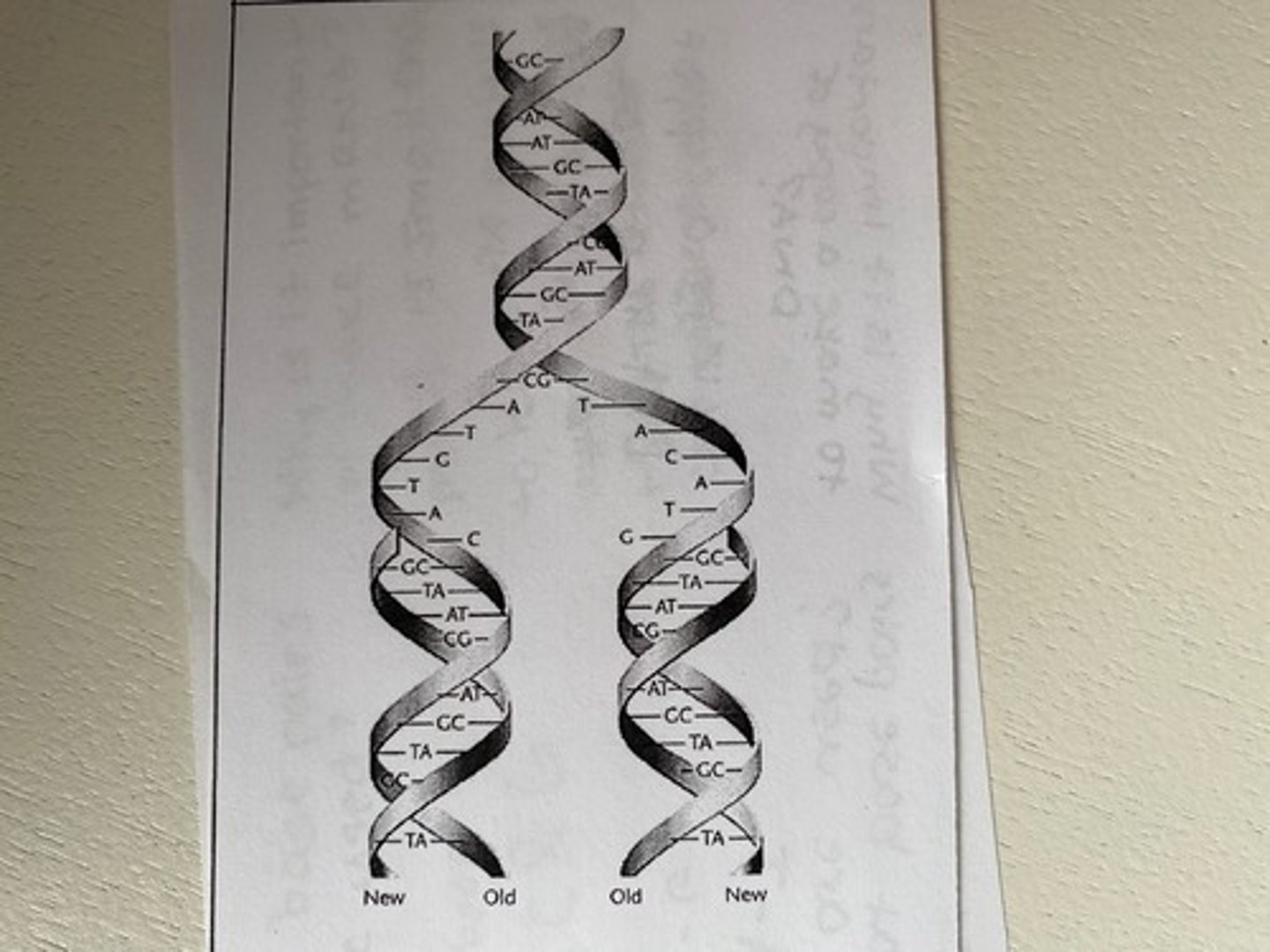
DNA Replication
the process of making a copy of DNA
mRNA (messenger RNA)
Transcription
Protein
Translation
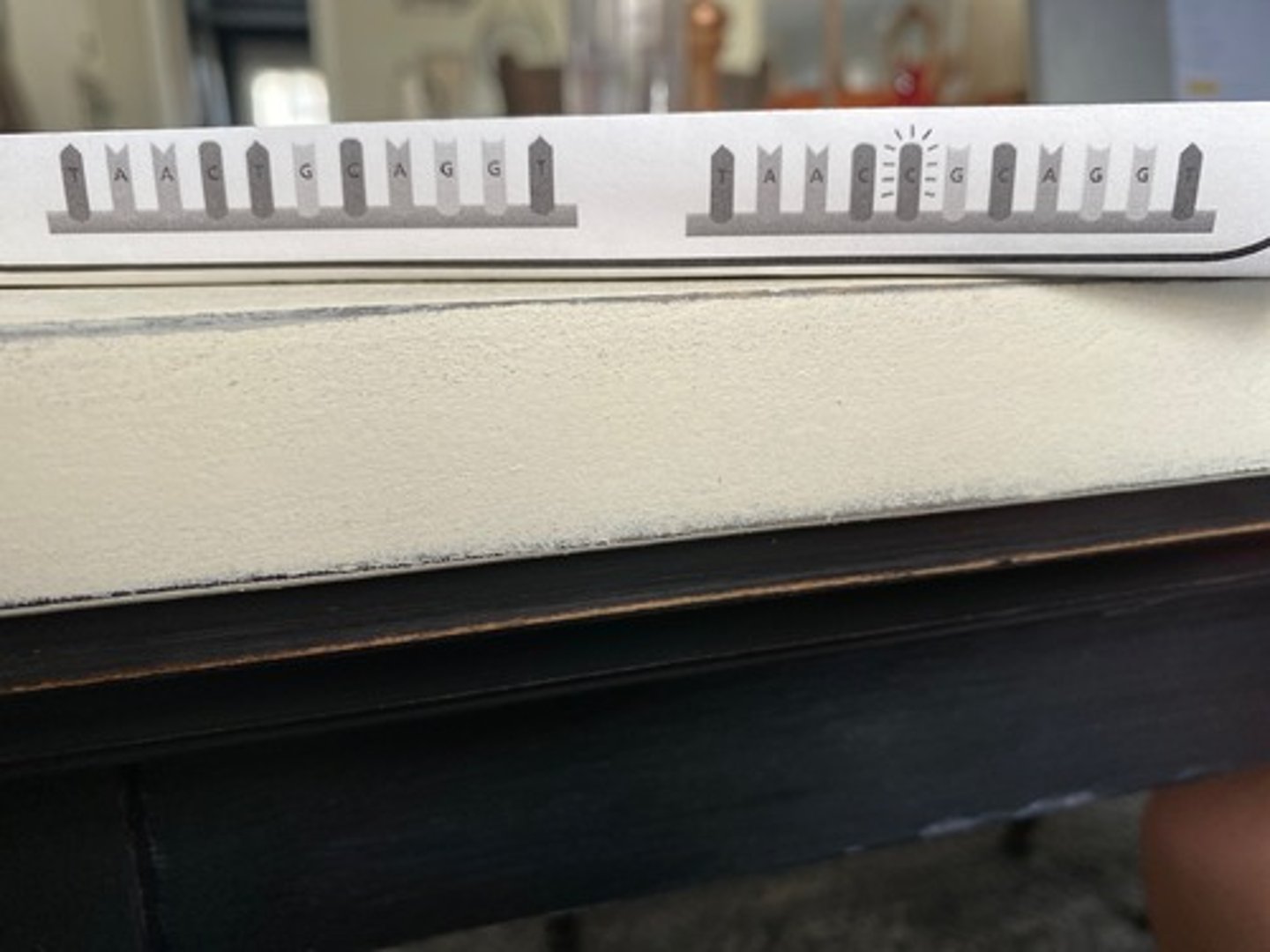
point mutation (substitution)
Mutation where one nucleotide is put in place of the correct nucleotide.

Frameshift mutation
Involves insertion or deletion of a nucleotide in a DNA sequence.
