Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems- Miroshynk
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What are the 3 main transport routes of drugs in transdermal systems?
intracellular/transcellular
intercellular
shunt routes
sweat pores/ hair follicles
What physiological factors affect permeation (movement of the drug)?
body site
race
age
skin condition
skin hydration
“BRASS”
What physiochemical factors affect permeation (movement of the drug)?
MW
Effective dose of a drug
Partition coefficient (log P)

What formulation factors affect permeation (movement of the drug)?
drug conc
pH of vehicle
surface area
larger the TTDS= more drug absorbed
exposure time
What are the advantages of TDDs?
bypass 1st pass metabolism
continuous/controlled drug delivery
avoid GIT
self-administrable
noninvasive/painless
inexpensive
possible transdermal VACCINE delivery (could improve immune response)
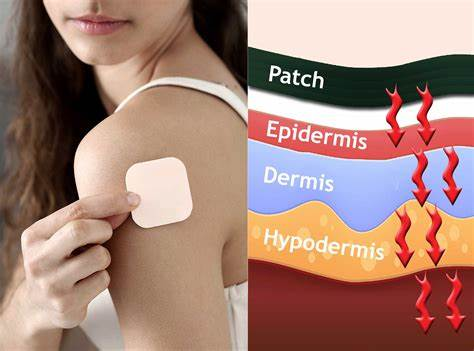
What is a transdermal patch?
dosage form designed to deliver a constant and controlled therapeutic dosage across the skin over extended periods of time for SYSTEMIC therapy
(key words: skin and systemic)
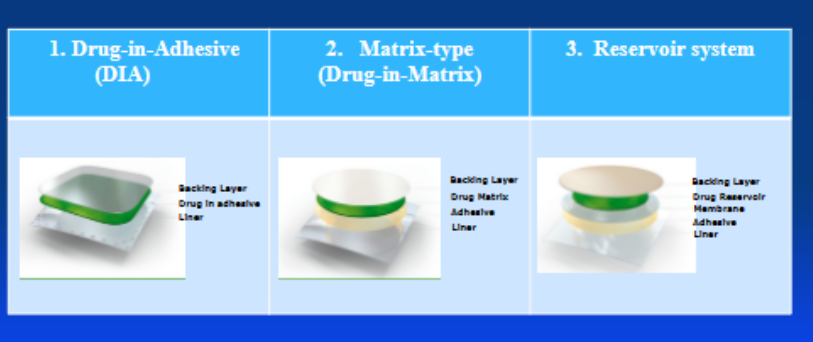
What are the 3 types of transdermal patches?
drug-in-adhesive (DIA)
drug-in-matrix (DIM)
reservoir system
(hint: as you go from 1-3 the patches get more complex. I think of DIA as the simplest, and reservoirs as most complex)
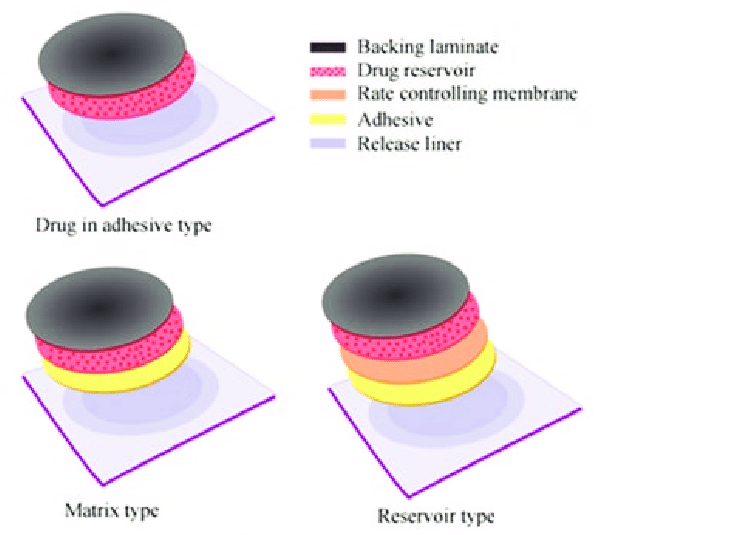
Describe the “anatomy” or each part of a transdermal patch:
protective liner
adhesive
backing layer
drug matrix
drug reservoir
membrane
protective liner- temporary covers adhesive, removed before application
adhesive- part that maintains contact w/ the skin, should be non-irriating/allergic, and compatible, serves as matrix for DIA
backing layer- film, protects the patch from the outside world
drug matrix- ONLY in DIM, a blend of drug+polymer
drug reservoir- ONLY in RESERVOIR systems, isolated drug donor layer, contains a liquid or gel blend of the drug+polymer, viscosity is important
membrane- semipermeable, optional, usually used to separate reservoir and adhesive
For Drug-in-adhesive and drug-in-matrix transdermal patches the drug matrix is a blend of drug+polymer. What polymers are used?
cellulose derivatives
PVP
POVIAC
For each type of transdermal patch, what layer or “part” of the patch contains the drug for administration? (hint: look at the name)
Drug-in-adhesive
Drug-in-matrix
Reservoir
Drug-in-adhesive: ADHESIVE LAYER
Drug-in-matrix: DRUG MATRIX LAYER
Reservoir: RESERVOIR LAYER
True or False: A drug-in-adhesive transdermal patch contains a reservoir.
false
Which of the transdermal patches are considered to have matrix systems and which have membrane controlled systems?
matrix systems- Drug-in-adhesive and drug-in-matrix
even tho DIAs don’t have matrix in the name the “adhesive” layer is considered the matrix layer
membrane controlled release- reservoir systems
What are the disadvantages of matrix systems (DIAs and DIMs)?
low drug loading
What are the disadvantages of membrane controlled systems (reservoir patches)?
only potent drugs can be used
only small, unionized, moderately lipophilic drugs can be used
possibility of site reactions (dermitits)
patches contain lots of residual drugs
What are the advantages of membrane controlled systems (reservoir systems)?
higher drug loading
as long as reservoir full = release rate is constant
Drug Matrix systems can either be infinite or finite dose formulations. What do each of these mean?
Finite- withOUT excess of drug, no drug reserve
Infinite- WITH excess of drug, drug reserve
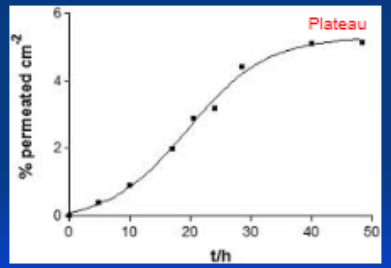
Is this permeation profile, infinite or finite?
finite
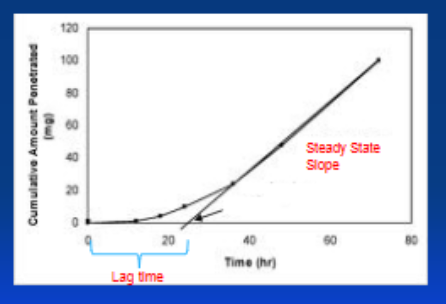
Is this permeation profile, infinite or finite?
infinite
Permeation (movement of the drug) can be enhanced in what 2 ways?
physical OR chemical
How does chemical permeation enhancement work?
increases skin permeability by REVERSIBLY damaging or altering the physicochemical nature of the stratum corneum(skin) to reduce its diffusion resistance
basically: altering the skin so the drug can better absorb
How does physical permeation enhancement work?
enhancing skin penetration through physical means like electroporation, iontophoresis, sonophoresis, and microneedles
What is the MOA of chemical permeation enhancers?
increase skin hydration
expand intracellular lipids and lipoprotein channels
What is the MOA of electroporation? (a physical permeation enhancer)
creates aqueous pores in lipid bilayers by applying short electrical pulses
What is the MOA of Iontophoresis? (a physical permeation enhancer)
passage of a constant electrical current onto the skin through
electromigration
electroosmosis
passive diffusion
What is the MOA of Sonophoresis? (a physical permeation enhancer)
uses low/high frequency ultrasound to produce cavitation, microstreaming, and heating
What is the MOA of Microneedles? (a physical permeation enhancer)
minimally invasive devices that disrupt the stratum corneum by creating microchannels
Examples of chemical permeation enchancers:
water
alcohols
DMSO
fatty acids
surfactants
What is the goal of in vitro release testing and how is it measured?
goal: determine route and amount of drug permeated through skin
measured using DIFFUSION CELLS (Ex: Franx)
PRACTICE
What is the most significant barrier to transdermal drug delivery?
a. molecular size of drugs
b. skin structure
c. patient noncompliance
d. a high cost of TDDS
b
PRACTICE
A patient asks a pharmacist whether or not she can cut her transdermal scopolamine patch in halves and use a half patch for her daughter. What should you, as an attending pharmacist, respond to this patient?
no-you cannot cut it in half
PRACTICE
The passage of a constant electrical current onto the skin is known as ______________________.
a. electroporation
b. iontophoresis
c. sonophoresis
d. microneedles
b
PRACTICE
Which of the following can be used as the chemical permeation enhancers?
Water
Fatty acids
Ethanol
DMSO
Glucose
Surfactants
water, fatty acids, ethanol, DMSO, surfactants