organic evolution - CH 6
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What did Darwin believe about variation and inheritance?
Darwin suggested that use and disuse of traits could lead to heritable variation, though he lacked a molecular mechanism.
Who was Conrad Waddington?
A biologist (1905–1975) who performed experiments suggesting inheritance of acquired characteristics.
What is genetic assimilation?
A process where a trait originally produced by environmental stress becomes genetically fixed through selection.
Describe Waddington’s fly experiment
Flies exposed to heat stress lost wing veins. After selecting these flies for several generations, offspring showed the trait without heat exposure.
What did Waddington’s experiment demonstrate?
Environmentally induced traits can become heritable without continued environmental exposure.
Why is the plant inheritance considered non-genetic?
No DNA sequence change occurred; inheritance occurred through epigenetic marking.
What is non-genetic inheritance?
Inheritance not coded in DNA sequence (e.g., cytoplasmic effects, mutualism, epigenetics, culture).
Define epigenetics
Inheritance via molecular marking of DNA or chromatin that alters gene expression without changing DNA sequence.
What does cross-genus cloning in fish show?
Egg cytoplasm can influence phenotype independent of nuclear DNA.
What does the cross-genus cloning in fish imply about inheritance?
Traits can be influenced by cellular environment, not just genes.
Name the three major epigenetic mechanisms
DNA methylation
Histone modification
Non-coding RNA regulation
What is DNA methylation?
Addition of methyl groups to DNA bases that alters gene expression and is heritable.
What effect does DNA methylation usually have?
Gene silencing or reduced expression.
Example of DNA methylation affecting phenotype
Agouti gene regulation via transposon methylation.
What is histone modification?
Chemical modification of histone amino acids that alters chromatin structure and gene expression.
Why are histone modifications complex?
Many amino acids can be modified in different ways, producing varied expression outcomes.
What is non-coding RNA regulation?
Regulation of gene expression by RNAs that do not code for proteins (e.g., small RNAs, lncRNAs).
Can non-coding RNAs be heritable?
Yes.
What is the Weismann barrier?
Separation of somatic cells from germ cells, preventing inheritance of acquired traits.
Why may plants lack a strict Weismann barrier?
Germline cells arise from somatic tissue in plants.
Describe the Arabidopsis methylation experiment
A methylation gene knockout produced offspring with identical DNA but different epigenetic markings.
How many hybrid lines were created in the Arabidopsis methylation experiment?
Over 500.
What did the Arabidopsis methylation experiment demonstrate?
Epigenetic variation alone can generate phenotypic diversity.
Which traits varied in the hybrids in the the Arabidopsis methylation experiment?
Flowering time and plant height.
How should the hybrid clonal descendants of the parent lines vary phenotypically in the Arabidopsis methylation experiment?
A. They should not vary at all.
B. They should vary in a small way in a few traits.
C. They should vary considerably in virtually all traits.
They should vary in a small way in a few traits.
How may epigenetics explain variation in Darwin’s finches?
Epigenetic differences may explain phenotypic variation better than DNA sequence differences.
What is an epigenetic macromutation?
A large phenotypic change caused by epigenetic modification rather than DNA mutation.
Example of epigenetic macromutation
Peloric toadflax caused by methylation of the Lcyc gene.
Does epigenetics suggest evolution is Lamarckian?
Partially, but not fully.
Why is epigenetics not fully Lamarckian?
Epimutations are not produced intentionally in response to environmental challenges.
Can epigenetic traits be inherited?
Yes, in some species, depending on stability across generations.
Define cultural transmission
Inheritance of traits via social learning rather than genes.
What are traditions?
Socially learned behaviors shared by a community across generations.
Which organisms show cultural inheritance?
Social animals.
What is nixtamalization?
Soaking corn in lime to release niacin and improve nutrition.
What happened when Europeans skipped nixtamalization?
A widespread pellagra epidemic occurred.
Describe the monkey food-color experiment
Monkeys avoided bitter food of a certain color and developed a preference for the non-bitter color.
Was the color preference inherited?
Yes — both adults and infants preferred the same color.
What happened when monkeys migrated to new groups?
Most adopted the food preference of the new group (peer pressure).
What is gene–culture coevolution?
Interaction between cultural practices and genetic evolution (e.g., lactose tolerance).
List all sources of heritable variation
genetic mutation
Sex & horizontal gene transfer
Transposons
Mutualism
Epigenetics
Culture
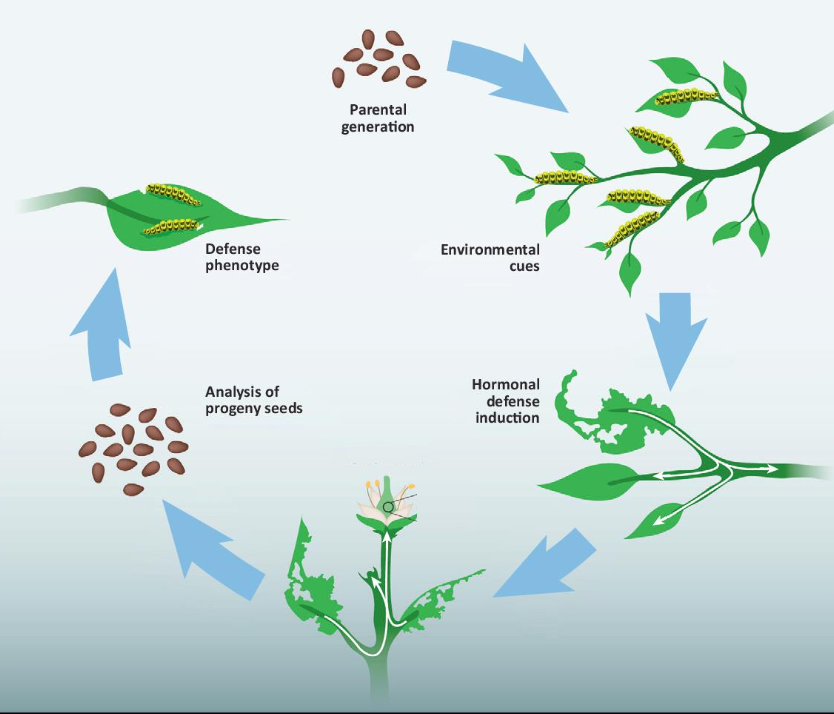
Discuss this example of inheritance of acquired characters
How did the defense trait originate?
How was it passed on to the next generation?
the trait must have already existed within its genes
epigenetics