Bio 151. UW Madison. Exam 1
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
ATP stands for...
adenosine triphosphate
Macromolecules
polymers built from monomers
long molecule consisting of similar or identical building blocks
-typer of bonding: covalent
polymer
true or false: lipids are chain like molecules
false
Dehydration rxn
-synthesizing a polymer
removes H2O molecule , forms a new bond
Hydrolysis
-breaking down a polymer
-adds H2O molecule, breaks bond
Important macromolecules
-sugars
-lipids
-proteins
Sugars
-monosaccharides
-disaccharides
-polysaccharides
example of monosaccharides
glucose
galactose
fructose
disaccharides are two monosaccharides joined together by
glycosidic linkage
glycosidic linkage
a covalent bond formed by dehydration rxn.
cite polysaccharides
-starch
-glycogen
-cellulose
-chatin
-Little to no branching, stored in plants, slower energy but lasts longer
-stores glucose
starch
structure
function
-a lot of branching
-faster energy
-stores glucose for energy
glycogen
-straight fiber
-structure of plant cell walls
cellulose
-animals and fungi
-strengthens cell wall
chatin
Fats are constructed by
glycerol and fatty acids
glycerol is a
an alcohol each of its 3 Cs has a hydroxyl group
3 types of lipids
-triglycerols
-phospholipids
-steroids
energy source
one glycerol and 3 fatty acids
triglycerols
bilayers of membrane
head of P with 2 fatty acids
phospholipids
-component of cell membranes,
-signal molecules that travel through body
-fused rings
steroids
saturated fats and why are they worse for you?
because its trans structure they pack together, they form a solid and clog arteries.
unsaturated fats
they don't pack together because of their cis-configuration
function of protein
-enzymatic
-defensive
-Storage of amino acids
-transport
-hormonal
-receptor: stimuli
-motor
-structural
Polypeptides are made out of
peptide bonds
peptide bonds
amino acids joined together. COOH group is adjacent to amino group
protein structure 1
-long chain of amino acids
protein structure 2
1. Interactions of nearby amino acids
2. a helix and B sheet
3. Stabilized through hydrogen bonding
protein structure 3
1.interactions between side chains
2. 3D shape of protein
protein structure 3 bonds
-disulfide bonds
-vandeer waals
-ionic and H bonding
protein structure 4
-many polypeptide chains together
Chaperonin
-helps protein shape into right shape (denaturation)
-slow folding
-hydrophobic environment when the protein goes in
two types of nucleic acids
RNA, DNA
Gene expression
DNA directs RNA synthesis and controls protein synthesis
Components of nucleic acids
-Nitrogenous base
-sugars
-phosphate group
Nitrogenous bases in nucleotide
- (C)ytosine
- (T)hymine---(DNA)
-(U)racil---- (RNA)
-(A)denine
-(G)uanine
Sugars (nucleotides)
-Deoxyribose
-Ribose
DIfference between Deoxyribose and Ribose
Deoxyribose lacks an oxygen atom
Thin section of specimen
Reveals internal structure
Cross sections
TEM
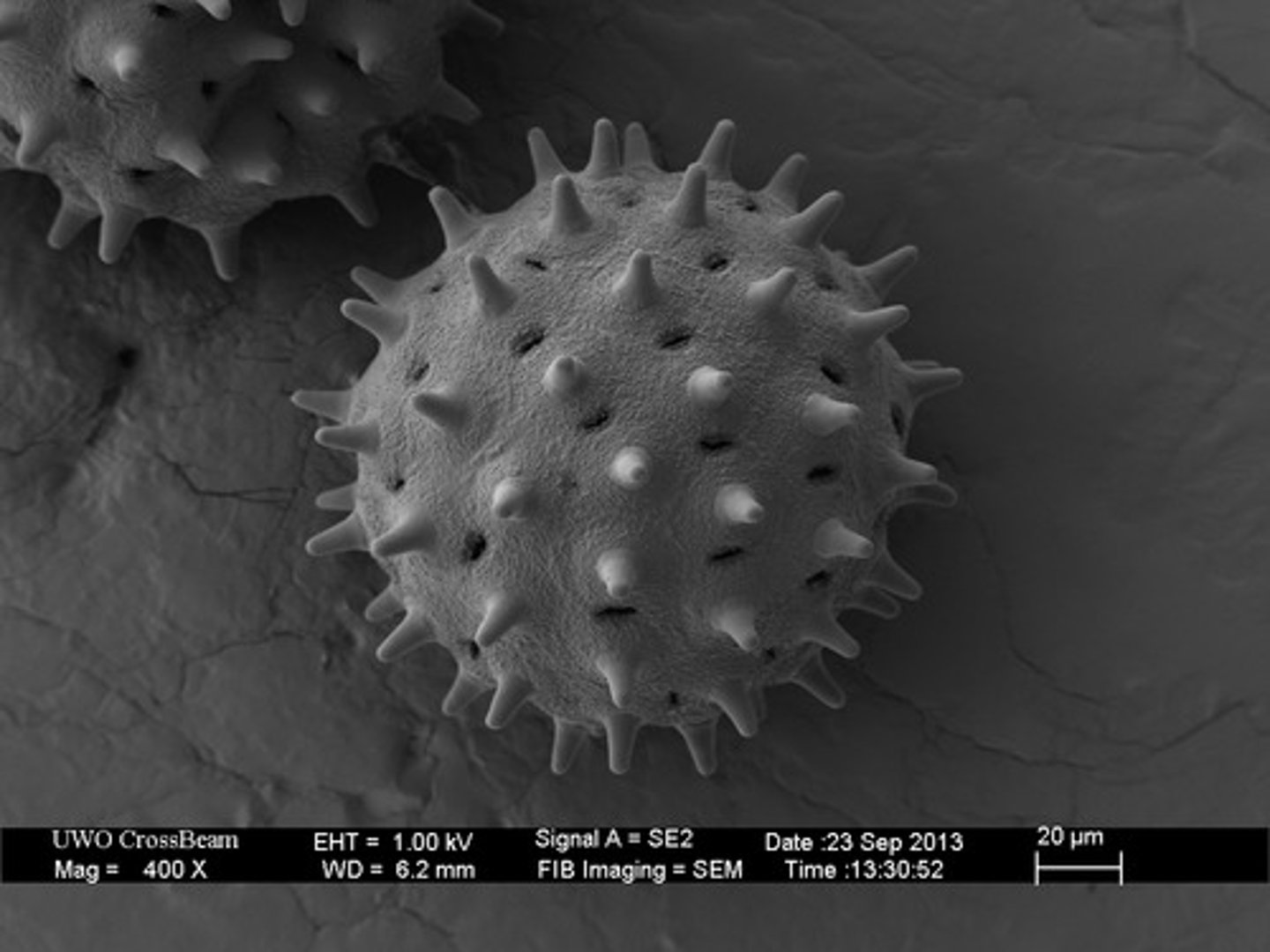
3D image of the surface of a specimen
SEM
SEM

TEM
Differences between Eukarytic and prokaryotic cells
eu: nucleus
pro: nucleoid
Nucleus size, structure, function
5micrometers, nuclear envelope double membrane, lamina
- information central : DNA
Chromatin:
complex of DNA and proteins making up chromosomes
Ribosomes
-Protein factory
-No membrane
-can be floating, bound to ER or nucleus envelope
Endoplasmatic reticulum
smooth: -detox
-synthesis of lipids/ metabolism of carbs
-store calcium ions
rough: -make secretory proteins
- membrane factory of cell
Golgi apparatus
-Shipping and receiving
- proteins are modified and store and sent to other destinations
-makes macromolecules
secreation
explain the making of membrane proteins
nucleus->nuclear pore->RER (ribosome)->cis golgi->leave thru trans golgi->membrane
what happens to "waste proteins"
lysosomes "Eat them"
difference between lysosomes and peroxysomes
-digestion
lysosomes: has proteases that only works on low ph
peroxisomes: uses redox reactions
mitochondria
-own DNA
-Double membrane
-ribosomes (so that it can make their own proteins)
-function: celular respiration (makes ATP)
-electro chemical gradient
what happens when trying to make actin?
Detour from the nucleus to the cytoplasm into the free ribosome floating around.
3 types of cytoskeleton
-microtubules
-microfilaments
-intermidiate filaments
Function of microtubules
-motility
-mantains cell shape
-can both push and pull. but main function: push
-strength
-no flexibility
-cell division
microfilaments
-what are they made of?
-function
-what do they use?
-made out of actin
-muscle contraction!!!
-can push and pull
-uses ATP
what makes microtubules?
tubulin
true or false
microtubules start at centrosome
true
What are microfilaments made out of
2 strands of actin
microfilaments functions
-cell shape
-muscle contraction
-cytoplasmatic streaming
-cell motility
Intermidiate filaments
Made out of fibrous proteins
functions
-cell shape
-anchorage of nucleus
-formation of nuclear lamina
Motion of flagella and motion of cilia
microtubules
How are membranes held together
hydrophobic interactions
what makes membrane fluid
unsaturated (cis) fats
functions of cholesterol
-reduces membrane fluidity
-reduces phospholipid movement
-Hinders solidification (low temps)
Functions of lipids and proteins in the membrane
-Transport
-Enzymatic
-signaling
-cell-cell recognition
-intercellular joining
-attachment to cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix
Pathway for making membrane
Nucleus->nucleus pore->RER (proteins and lipids syntehsized), glycogen is formed-> Cis golgi-> leaves thru trans golgi as glycolipids-> glycolipids are transported with vesicles ->membrane and release of secretory proteins
What is difussion?
-Movement of any particle into available space
-equilibrium
osmosis
difussion of free water across permeable membrane
Concentration gradient
the region along which the density of a chemical substance increases or decreases
type of solution that makes the cells lyse, swell and burst... little to no water...
hypotonic solution
type of solution that doesn't change the cell.
Isotonic solution
makes the cell shrivel/ more water
hypertonic solution.
Passive transport divides in:
-Difussion
-Facilitated difussion
-Transport proteins, serve as pumps
- Move things against concentration
- Energy supplied by ATP
Active transport
Steps of active transport
1. Na+ binds to pump
2. phosphorylation by ATP
3.change in protein shape. Na+ released outside 4. K+ binds on the side. P leaves
5. since P leaves, K leaves
6. K leaves and Na+ is high again
types of signaling
1. Paracrine
2. synaptic
3. endocrine (hormones)
Paracrine signaling acts on
-nearby target cell (it's a local regulator)
Synaptic signaling happens when
A nerve cell releases neurotransmitter molecules into synapse..
Endocrine signaling
Hormones reach all body cells.
Stages of signaling
1. Reception
2. Transduction
3. Response
G- protein coupled steps
1. Ligand binds to receptor (change of shape)
2. inactive G-protein binds receptor and switches for GTP
3. GTP binds to it and activates it
4. Enzyme activates proteins
True or false
G protein works for unlimited time
False
intracellular receptor
steps
1. pass thru membrane
2. bind to receptor proteins
3. receptor binds to gene in nucleus
4. transcription into mRNA
5. Translation
Secondary messenger
-non protein h2o molecules
-initiated by both tyrosine kinase and g protein
-example: cyclic amp
-leads to cellular activity
Receptor tyrosine kinase steps
1. ligand binds TK and activates it
2. Dimer creation
3. each tk add a Phosphate from ATP in the tail of a monomer
4. binding to phosphorulated tyrosine/ structural change.
Ion channel receptors steps
1. Ligand binds to receptor
2. ions flow thru and change concentration of ions
3. ligand dissociated and gate closes.
outcome of glycolysis
2ATP, 2NADH, 2pyruvate
Pyruvate oxidation outcome
Acetyl CoA
Krebs cycle net
2ATP
8NADH
6CO2
2 fadh2
Causes H to move outside of the mitochondrial matrix
stores energy as proton motor force
NADH is transformed into NADH+
ETC
H goes back into matrix
ATP synthase
adp->ATP
chemiosmosis
opening K+ channels in a resting neuron causes
hyperpolarization
hyperpolarization makes the inside of the membrane more...
negative
if a depolarization shifts the membrane potential sufficiently, the result of the massive change in membrane voltage is called
graded potential
Graded potential happens in the...
dendrites
action potential happens in...
the axon
What does action potential cause?
Na+ gates to open