AC to AC - Converters
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What is the main function of an AC-AC converter?
To convert AC at one voltage or frequency to AC at another voltage or frequency.
Why are AC-AC converters used?
To control AC motor speed and for soft starting by adjusting voltage and frequency.
Two main AC-AC converter types?
AC voltage controllers and cycloconverters.
What is an AC voltage controller?
A circuit that varies RMS output voltage via phase control of the AC waveform.
What is an AC chopper?
An AC-AC converter that chops the input waveform to control output voltage and frequency.
What is a cycloconverter?
Directly converts input AC to a lower-frequency AC without a DC link.
Typical devices used?
Thyristors or TRIACs.
What is integral cycle control?
Turning devices on or off for entire cycles to control average power.
Common AC-AC applications?
Induction motor control, variable AC supplies, lighting dimmers.
Main advantage of a cycloconverter?
Smooth low-frequency output suitable for large motor drives.
Describe AC voltage controller output.
Phase-cut AC where only part of each half-cycle is applied based on firing angle.
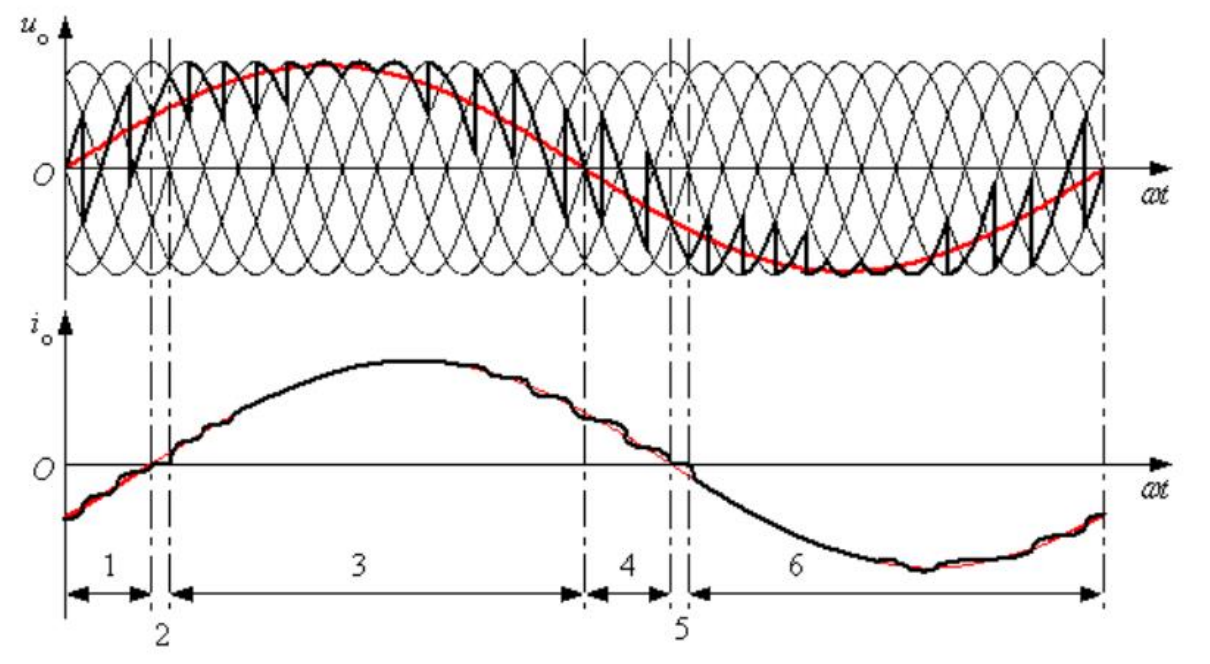
Describe integral cycle control waveform.
Several whole AC cycles delivered followed by several cycles of zero, controlling average power.
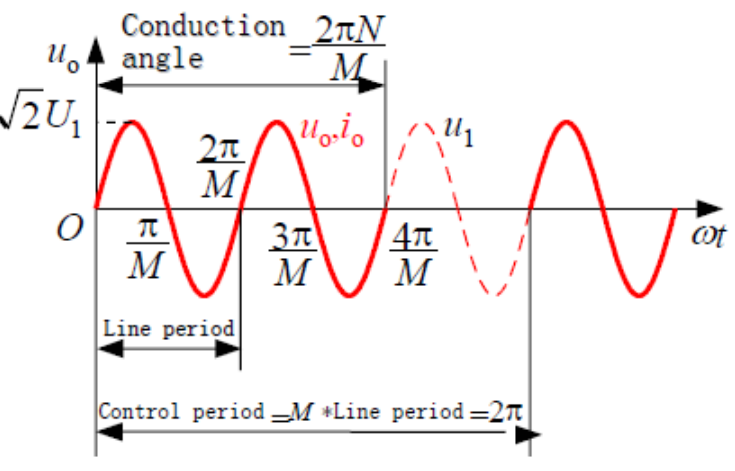
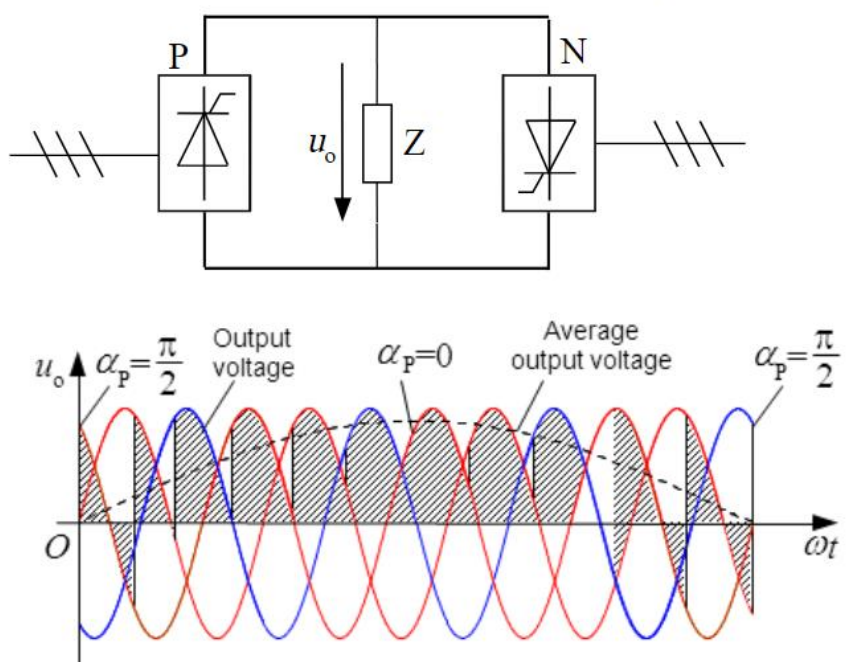
Describe cycloconverter waveform.
Recombined segments of input create a lower-frequency, stair-stepped near-sine output.