Topic 2 - Genes and health
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
what is ficks law

what are the 2 types of epithelial cells and where are they in the body
pavement- alveoli and capillary lining
Cilated- tranchea and bronchi lining
What is cilia and what does it do to mucus
Cilia is a hair like structure which moves mucus (produced by the globlet cells ) up and out of the lungs
What do goblet cells do ?
Produces mucus which traps pathogens. This protects the epithelial layer
How are lungs adapted for gas exchange?
Large surface area from alveoli
Large concentration gradient from the greater level of oxygen in the lungs to the blood in the capillaries
Thin exchange surface from alveoli through blood capillary ( 2 cells thick)
hat if the structure of a protein and its 3 groups?
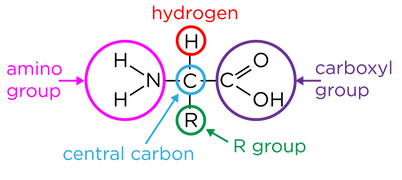
what are amino acids linked by?
peptide bonds from condensation reactions
define a primary structure
sequence if amino acids joined together by peptide bonds
define tertiary structure and lost its bonds
further folding of a polypeptide chain into a 3D globular shape
bonds: hydrogen, covalent, ionic, disolphite
define quaternary structures
more than one polypeptide chain joined together
define secondary structure
sequence of amino acids joins by hydrogen bonds
give some features of a globular structure and an example
soluable, ball structure, metabolic, active site, e.g. haemoglobin/enzyme
give some features of a fibrous protein and some examples
insoluable, thin strands, tough, no active site, e.g. collagen
describe the structure of a phospholipid

whats in the fluid mosaic model
cholesterol, makes it more fluid, glycolipds, glycoprotein, channel protein
What js endocytosis?
it takes substances into cell and requires energy.
name all types of transportation in the cell membrane
Diffusion, facilated diffusion ( proteins involved ), Active transport, osmosis, endocytosis, exocytosis.
What makes Active transport difference from osmosis and diffusion?
Requires energy ATP and its active
What are the features of induced fit hypothesis
Enzyme molecule changes shape slightly at the active site to fit the substrate
Only works for specific shaped substrates
What are the features of the lock and key hypothesis
enzyme remains unchanged
reduces activtiin energy if an enzyme
What is transcription?
Dna unwinds from dna helicase, complimentary bases come in. RNA polymerase forms bonds between coding strand and mRNA and then mRNA leaves nucleus through nuclear pores and the dna and hydrogen bonds are reformed between the dna
Describe Translation
mRNA moves into cytoplasm and attaches to the starting codon of the ribosome. tRNA anticodon reads each triplet code on mRNA. A second tRNA carrying the next amino acid comes in and forms hydrogen bonds with the mRNA and peptide bonds with the other tRNA amino acid. the first trna then detaches and leaves the amino acid and the ribosome continues along thr chain of mRNA where tRNA continues to bring in amino acids forming a amino acid chain which creates a protein.
What does a CFTR Protein do?