Unit 7
5.0(1)Studied by 24 people
0%Unit 7 Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/67
Last updated 11:53 PM on 4/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
1
New cards
Industry
any economic activity using machinery on a large scale to process raw materials into products
2
New cards
Raw materials
any metals, wood or other plant products, animal products, or other substances that are used to make intermediate or finished goods
3
New cards
Industrialization
the process in which the interaction of social and economic factors causes the development of industries on a wide scale
4
New cards
The Industrial Revolution
The change in manufacturing methods from small-scale, hand-crafted, muscle-powered production, to power-driven mass production
5
New cards
How were goods produced prior to the industrial revolution?
High quality craft goods were made in isolated, independent, small scale operations.
6
New cards
Cottage Industry
A form of manufacturing in which members of families spread out through rural areas and worked in their homes to make goods.
7
New cards
Where did the Industrial Revolution start?
The Industrial Revolution began in the 18th century in Britan, partially due to their access to natural resources.
8
New cards
What was the first Industry affected by Industrialization?
Textiles
9
New cards
What was the significance of the coal-powered steam engine?
It allowed for machines to produce massive amounts of a product. It also allowed iron workers to generate more heat, creating new ways to fashion iron.
10
New cards
How did industrialization diffuse through Europe and North America?
Relocation: The British textile manufacturer moved to the US in 1789, and his technology became the 1st center of industrial production in the US
11
New cards
What is the relationship between industrialization and the location of coal resources?
Where there was coal, industrialization was able to happen faster. Coal was the basis of the revolution, so the countries that had access to it industrialized
12
New cards
The first industrial revolution
When: 18th century
Powered By: Coal, Steam, and waterpower
Industries: Textiles, iron, and coal
Key Innovations: Spinning jenny, water frame, power loom, steam engine
Powered By: Coal, Steam, and waterpower
Industries: Textiles, iron, and coal
Key Innovations: Spinning jenny, water frame, power loom, steam engine
13
New cards
The second industrial revolution
When: Late 19th century
Powered By: Electricity and internal combustion engine
Industries: Steel, automobiles, airplane, chemical, and consumer appliance
Key Innovations: Assembly line and machine tools
Powered By: Electricity and internal combustion engine
Industries: Steel, automobiles, airplane, chemical, and consumer appliance
Key Innovations: Assembly line and machine tools
14
New cards
The third industrial revolution
When: After WWII (1945ish)
Powered By: Advances in computerization and miniaturization
Industries: Computer manufacturing, software engineering, telecommunications, banking, and insurance
Key Innovations: Computer changes
Powered By: Advances in computerization and miniaturization
Industries: Computer manufacturing, software engineering, telecommunications, banking, and insurance
Key Innovations: Computer changes
15
New cards
How did industrialization expand the middle class?
There was a rise in the amount of factories, which gave more people jobs. This lead to wealth being a marker of class.
16
New cards
What is the fourth industrial revolution?
The growth of robotics, information, and biomedical industries.
17
New cards
economic sector
Collections of industries engaged in similar economic activities based on the creation of raw materials, the production of goods the provision of services or other activities
18
New cards
primary sector
Jobs consisting of extracting, processing, producing an packaging raw materials and basic foods from the Earth.
19
New cards
secondary sector
Manufacturing, processing, and constructing finished goods by transforming raw materials
20
New cards
tertiary sector
Services for the general population and businesses to acquire and use finished goods
21
New cards
Quaternary sector
Knowledge and skills for complex processing and handling of information and environmental technology
22
New cards
quinary sector
High-level economic and social decision making through responsible institutions
23
New cards
relationship between urbanization and industrialization
Industrialization provides a city with more jobs, firstly typically working in factories. This causes more people to come to the cities for stable jobs, causing urbanization.
24
New cards
postindustrial economy
An economic pattern marked by predominant tertiary sector employment with a good share of quaternary and quinary jobs
25
New cards
What is happening in each of the sectors in a postindustrial economy?
Primary: Very low employment, many farmers moved to cities
Secondary: relatively low employment, workers must learn new skills in other fields
Tertiary: predominant employment
Quaternary: rising amount of jobs available
Quinary: rising amount of jobs available
Secondary: relatively low employment, workers must learn new skills in other fields
Tertiary: predominant employment
Quaternary: rising amount of jobs available
Quinary: rising amount of jobs available
26
New cards
Features of a postindustrial economy
Women get more advanced educations and make up more of the workforce; AI and IT have developed.
27
New cards
GDP
The total value of all goods and services produced by a country’s citizens within the country in a year
28
New cards
dual economy
Economies with two distinct distributions of economic activity across the economic sectors (ex. Brazil)
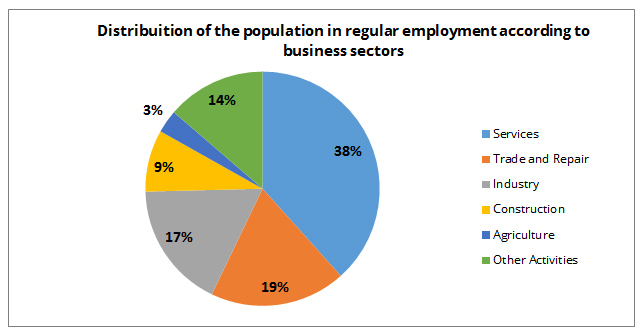
29
New cards
why do dual economies develop?
There are multiple theories some of which are resistance is due to tradition or agricultural workers don’t see enough benefit to moving to the secondary sector
30
New cards
Least-cost theory
A theory suggesting that business locate their facilities in a particular place because that location minimizes production cost.
31
New cards
3 factors of the least-cost theory
Transportation, Labor, and Agglomeration
32
New cards
Agglomeration
The tendency of enterprises in the same industry to cluster in the same area
33
New cards
break-of-bulk point
A place where goods are transferred from one kind of transport to another
34
New cards
Assumption of the least-cost theory
Ignore political or economic systemic influence; There are fixed amount of raw materials; workers who make up a labor force won’t move; There is a uniform transportation cost.
35
New cards
Bulk reducing industry
An industry where the raw material weighs more then the finished good
36
New cards
Bulk gaining industry
An industry where the raw material weighs less than the finished good
37
New cards
Bulk gaining/reducing influence on location
\
38
New cards
Limitations of the least cost theory
Ignores political and economic influence; only works in capitalism systems; market is not located at a singular point
39
New cards
What has changed in manufacturing since the least-cost theory was proposed in 1909?
Use of airplanes, ships, and supertankers; Use of shipping containers; Higher labor cost; Many goods weigh less
40
New cards
Industrial park
A collection of manufacturing facilities in a particular area
41
New cards
Human Development
The process involved in the improvement of people’s freedoms, rights, capabilities, choices, and material conditions
42
New cards
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The total value of the goods and services produced by a country’s citizens within the country in a year
43
New cards
Gross National Product (GNP)
Per capita, the total value of goods and services globally produced by a country in a year divided by the country’s population
44
New cards
Formal Sector
Businesses, enterprises, and other economic activities that have government supervision, monitoring, and protection, and are taxed
45
New cards
Informal Sector
Any part of a country’s economy that is outside government monitoring or regulation, sometimes called the informal economy
46
New cards
Human Development Index
A measurement of LE at birth, education access, and GNI per capita to indicate level of development
47
New cards
Three Key Dimensions of HDI
LE at Birth - health dimension
Access to education, measured in years of schooling - education dimension
GNI per capita - economic dimension
Access to education, measured in years of schooling - education dimension
GNI per capita - economic dimension
48
New cards
Limitations of the HDI
Doesn’t reflect poverty, gender equality, environmental quality or sustainability; Doesn’t take into account lack of equal access to income, education, and healthcare; doesn’t consider political aspects
49
New cards
Gender Parity
A balance between the genders
50
New cards
Gender equality
When everyone has the same level of resources and opportunities for everyone, regardless of gender
51
New cards
Gender equity
The acknowledgment of how the lack of access to opportunities and resources affects people of different genders.
52
New cards
Gender Development Index (GDI)
A measure that calculates gender disparity taking knowledge and standard of living into account
53
New cards
Gender Inequality Index
A measure that calculates inequality based on reproductive health, empowerment, and labor market participation
54
New cards
microloan
A very small short-term loan with low interest indented to help people in need
55
New cards
Key strategies for investment in girls and women
Ensure that financial assets are in the hands of women; Keep girls in school; Improve reproductive health and access to family planning; Support women’s leadership
56
New cards
Sectors of economic growth
A model that suggests that all countries can be categorized on a spectrum from traditional to modern and to become modern, countries need to pass through defined stags of economic growth
57
New cards
Dependency Theory
A theory that explains the development challenges poorer countries face, it also explains the political and economic relationships between richer and poorer countries
58
New cards
Commodity dependence
When a country’s economy is reliant in the export of 1 or 2 resources
59
New cards
Comparative advantage
The ability to produce a good or service at a lower cost than others
60
New cards
Complementarity
When a country has the income, goods or services that another country desires
61
New cards
Neoliberalism
the belief that open markets and free trade across the globe will lead to economic development everywhere and also result in less political conflict or more democracy
62
New cards
Free trade
laws that encourage trade
63
New cards
How can government policies impact trade?
Policies can either encourage or discourage trade. Tariffs can be put in place to decrease dependent on foreign goods or to influence another country
64
New cards
Trading bloc
A group of countries that agree to acommon set trade rules
65
New cards
IFI
International financial institution - assists struggling countries with financing and provide professional development advice
66
New cards
IMF
An IFI with 190 member states that aids countries in need of financial assistance and promotes economic stability and provides loans.
67
New cards
Outsourcing
contracting work to non company employees or other companies
68
New cards
trans/multinational companies
Businesses that operate in multiple countries