ME 240: Final Review (Hopefully)
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Specifications of Metals
Strong, Ductile, High Thermal and Electrical Conductivity, Opaque, Reflective
Specifications of Semiconductors
Covalent bonding (share electrons), depends on contaminants
Specifications of Polymers/plastics
Covalent bonding, Soft, Ductile, low strength, low density, thermal and electrical insulators, optically translucent or transparent
Specifications of Ceramics
Ionic bonding, brittle, glassy, elastic, non-conducting
Electron Configuration for Carbon (6)
1s²2s²2p²
Electron Configuration for Neon (10)
1s²2s²2p^6
Electron Configuration for Aluminum (13)
1s²2s²2p^6 3s²3p^1
Electron Configuration for Argon (18)
1s²2s²2p^6 3s²3p^6
Specifications of Ionic bonding
Pos. and Neg. ions naturally attract each other, Non-directional, Pos. Valence Electrons must have Neg. Valence Electrons, Strong Resistance to mechanical force and experiences plastic deformation
Specifications of Covalent Bonding
Equal sharing of valence electrons, directional bonds, strength of covalent bonds varies widely, backbone of polymer chains, hard and brittle.
Specifications of Metallic Bonding
Valence electrons detach from atoms and spread, non-directional, very good conductors of electricity and heat
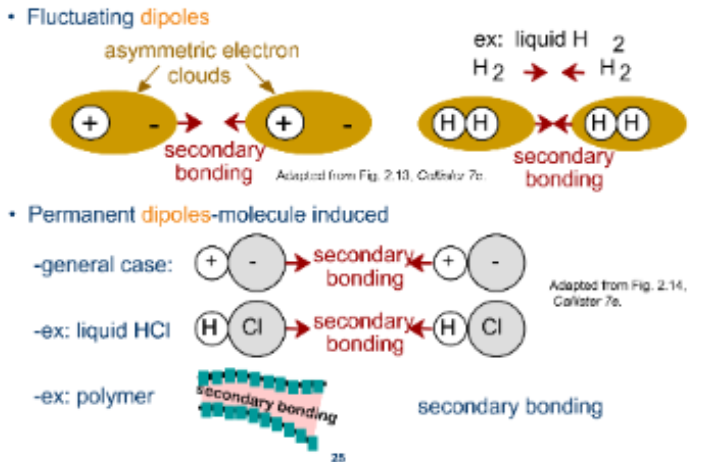
Specifications of Secondary Bonding
Between Dipoles
Iron has a BCC crystal structure, an atomic radius of 0.124 nm, and an atomic weight of 55.85 g/mol. Compute and compare its theoretical density with the experimental value (7.87 g/cm³)
7.90 g/cm³

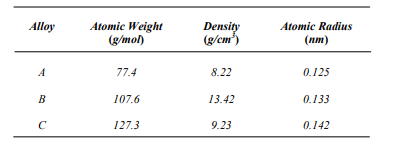
Determine whether its crystal structure is FCC, BCC, or simple cubic, and then justify your
determination.

List the point coordinates for all atoms associated with the FCC unit cell

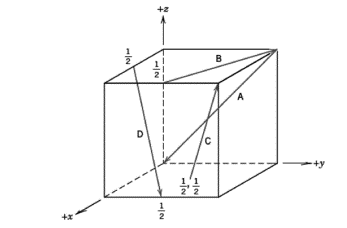
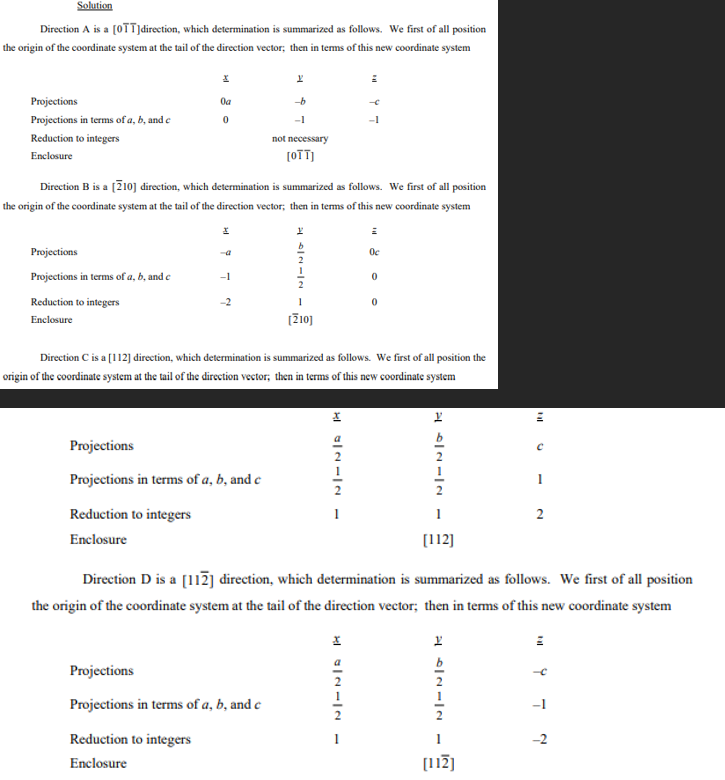
Determine the indices for the directions shown in the following cubic unit cell
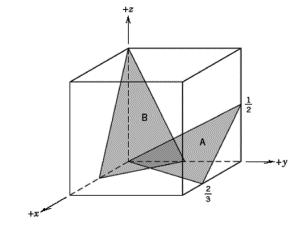
Determine the Miller indices for plane B only

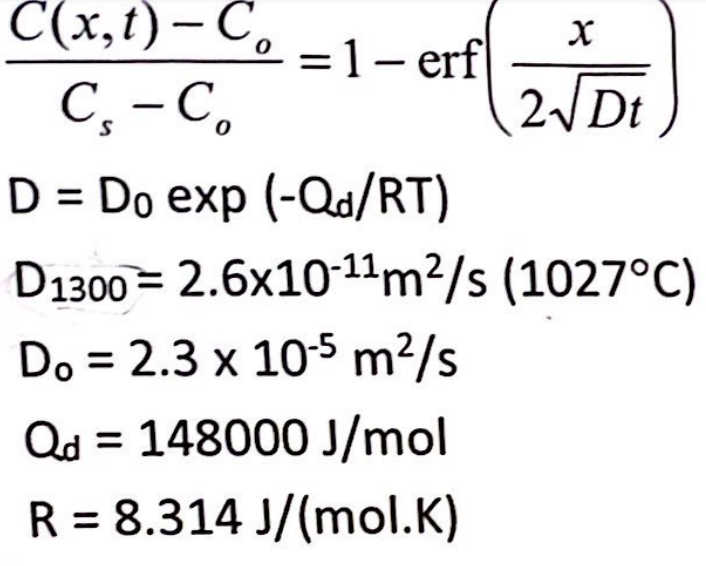
Calculate the diffusion coefficient at 1250 C if you are given the following information
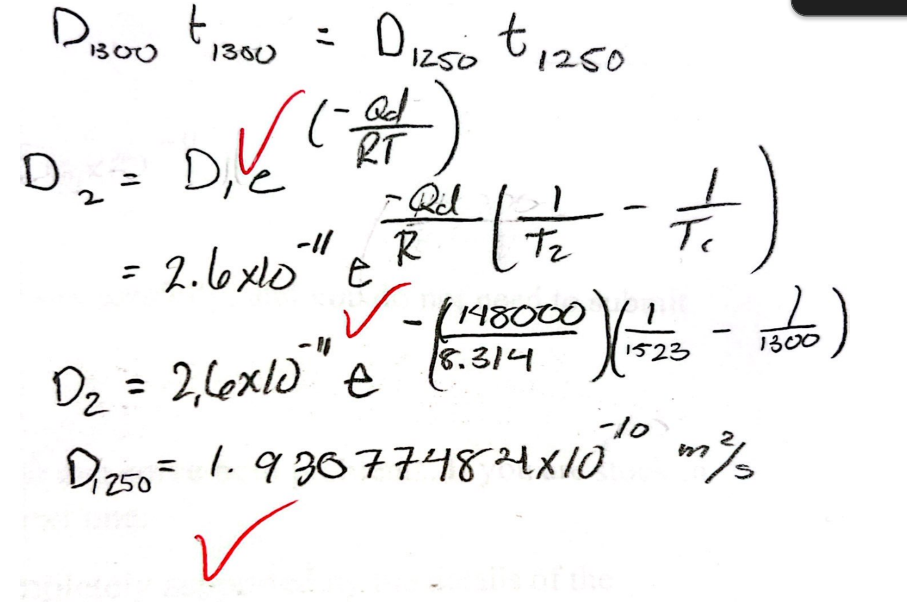
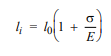
For a bronze alloy, the stress at which plastic deformation begins is 275 MPa (40,000 psi), and the modulus of elasticity is 115 GPa (16.7 × 106 psi).
(a) What is the maximum load that may be applied to a specimen with a cross-sectional area of 325 mm2 (0.5 in.2 ) without plastic deformation?
89,375 N

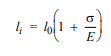
For a bronze alloy, the stress at which plastic deformation begins is 275 MPa (40,000 psi), and the modulus of elasticity is 115 GPa (16.7 × 106 psi).
(b) If the original specimen length is 115 mm (4.5 in.), what is the maximum length to which it may be stretched without causing plastic deformation?
115.28 mm
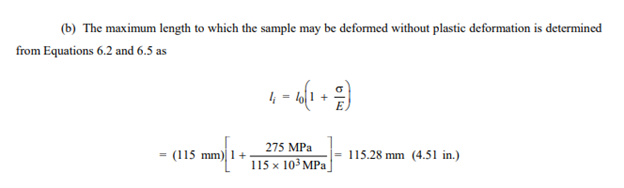
A cylindrical rod 100 mm long and having a diameter of 10.0 mm is to be deformed using a tensile load of 27,500 N. It must not experience either plastic deformation or a diameter reduction of more than 7.5 × 10-3 mm. Of the materials listed as follows, which are possible candidates? Justify your choice(s).

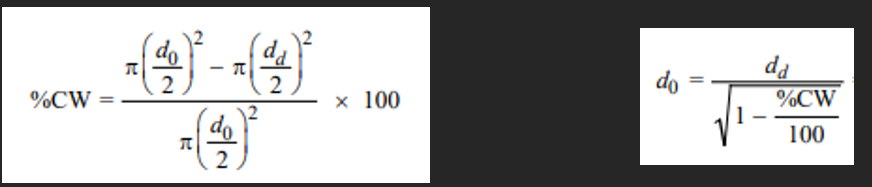
A cylindrical 1040 steel rod having a minimum tensile strength of 865 MPa (125,000 psi), a ductility of at least 10%EL, and a final diameter of 6.0 mm (0.25 in.) is desired. Some 7.94 mm (0.313 in.) diameter 1040 steel stock, which has been cold worked 20% is available. Describe the procedure you would follow to obtain this material. Assume that 1040 steel experiences cracking at 40%CW.

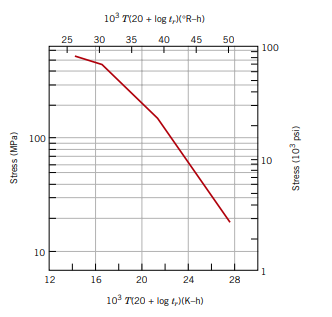
Consider an 18-8 Mo stainless steel component (Figure 8.35) that is exposed to a temperature of 500°C (773 K). What is the maximum allowable stress level for a rupture lifetime of
a) 5 years
260 MPa

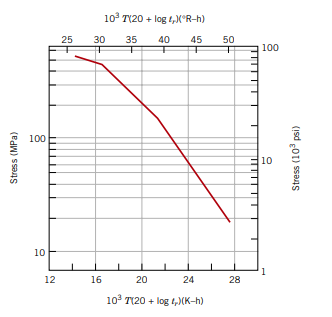
Consider an 19-8 Mo stainless steel component that is exposed to a temperature of 773K. What is the maximum allowable stress level for a rupture lifetime of
b) 20 years
225 MPa

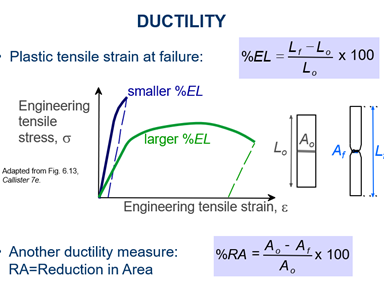
Explain Ductility
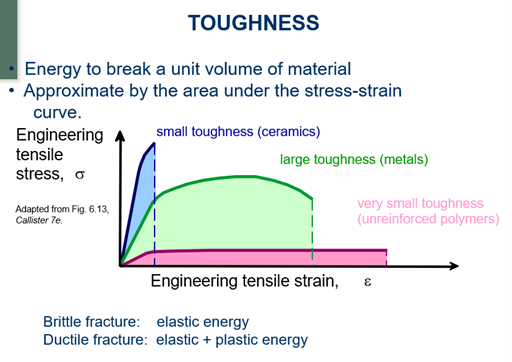
Explain Toughness
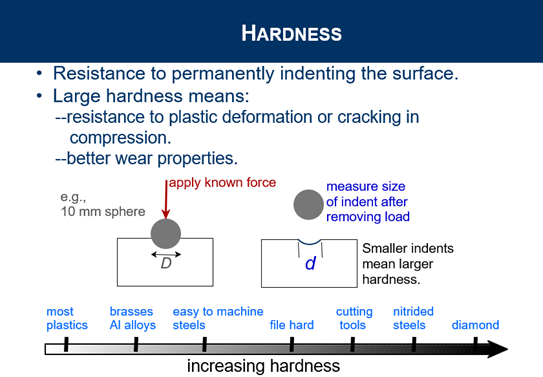
Explain Hardness
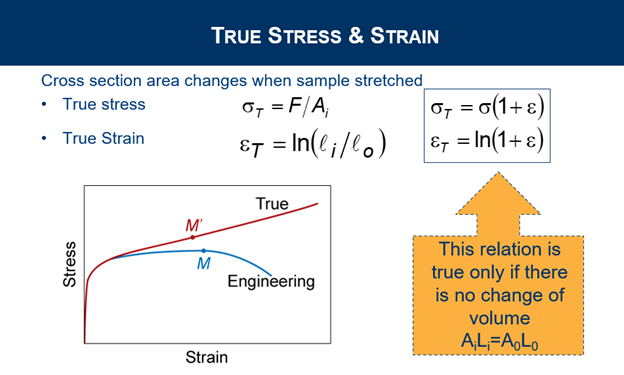
Explain True Stress and Strain
Explain three Strategies for strengthening
Strengthening by grain size reduction, Solid-Solution, Strain hardening
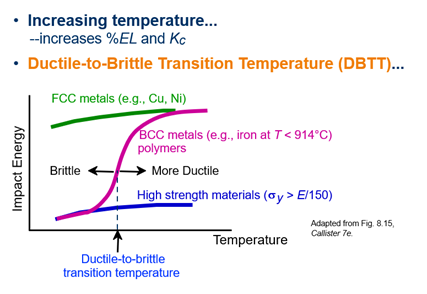
Explain Ductile to Brittle Transition Temperature
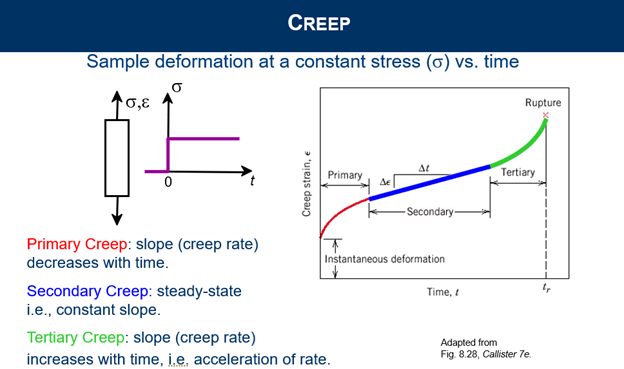
Explain three stages of creep
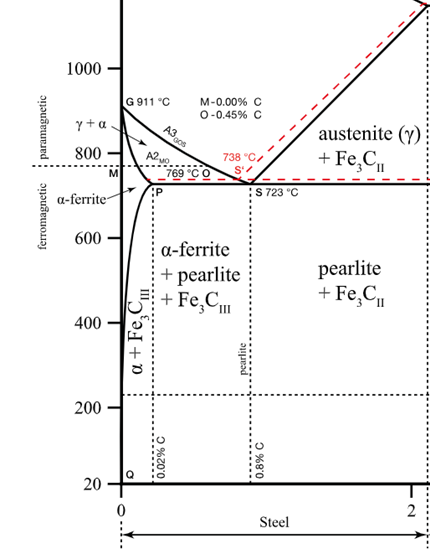
Consider 2.5 kg of austenite containing 0.65 wt% C, cooled to below 727°C (1341°F).
(a) What is the proeutectoid phase?
Ferrite

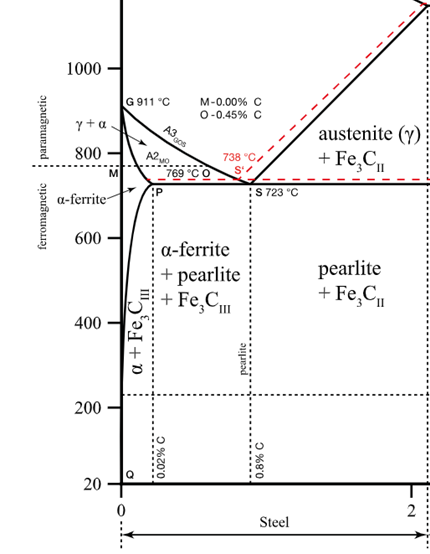
Consider 2.5 kg of austenite containing 0.65 wt% C, cooled to below 727°C (1341°F).
(b) How many kilograms each of total ferrite and cementite form?
2.27 kg of Ferrite, 0.23 kg of total cementite
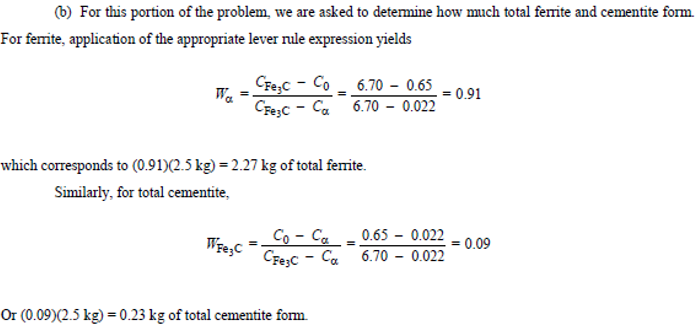
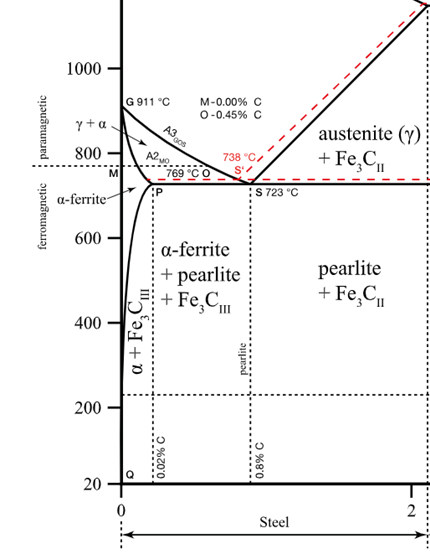
Consider 2.5 kg of austenite containing 0.65 wt% C, cooled to below 727°C (1341°F).
(c) How many kilograms each of pearlite and the proeutectoid phase form?
2.12 kg of pearlite, 0.38 kg of proeutectoid ferrite
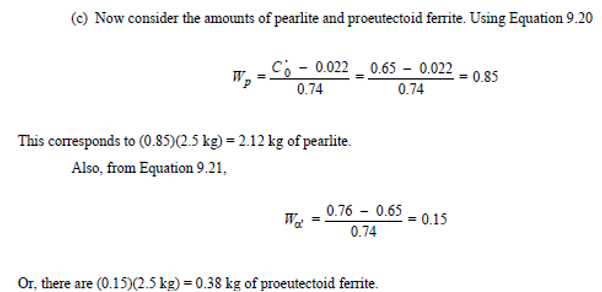
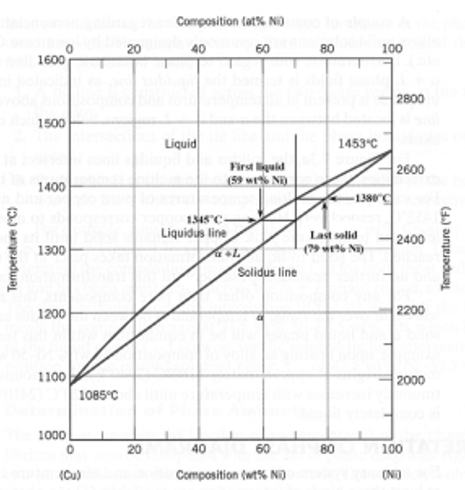
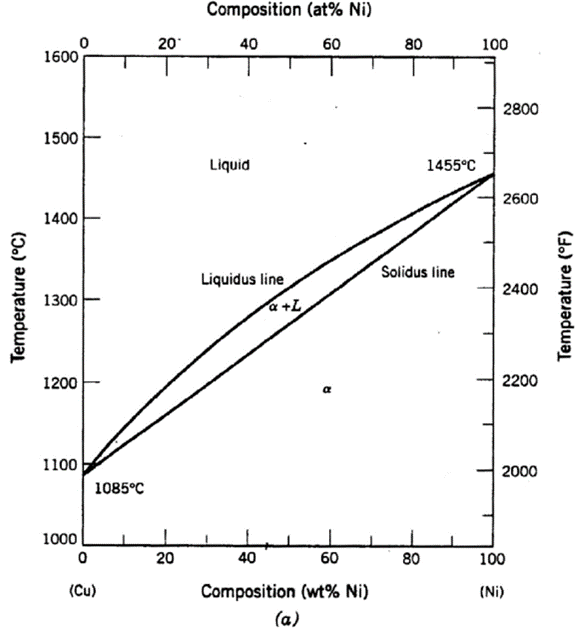
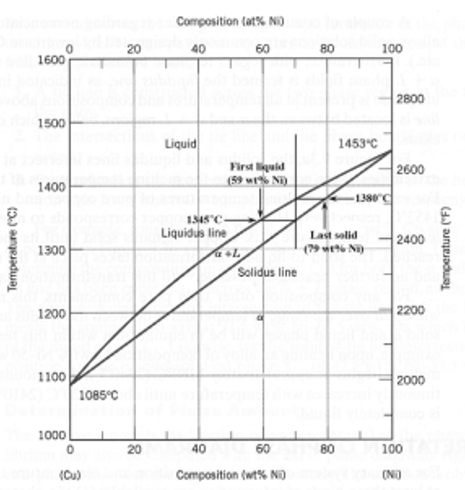
A copper-nickel alloy of composition 70 wt% Ni-30 wt% Cu is slowly heated from a temperature of 1300°C (2370°F).
At what temperature does the first liquid phase form?
About 1345 C
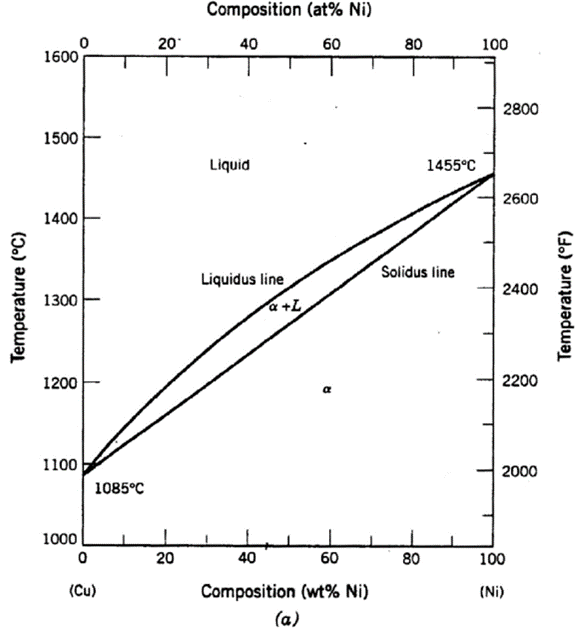
A copper-nickel alloy of composition 70 wt% Ni-30 wt% Cu is slowly heated from a temperature of 1300°C (2370°F).
What is the composition of the first liquid phase?
59 wt% Ni
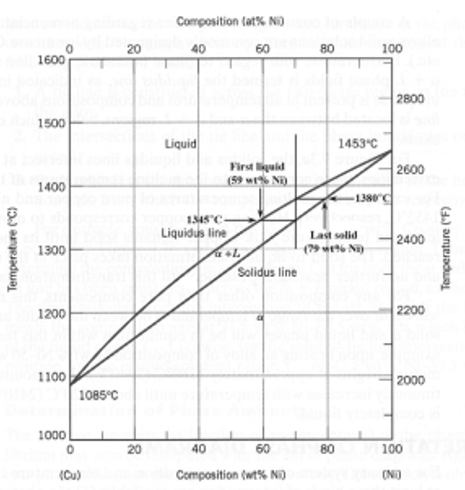
A copper-nickel alloy of composition 70 wt% Ni-30 wt% Cu is slowly heated from a temperature of 1300°C (2370°F).
At what temperature does complete melting of the alloy occur?
about 1380 C
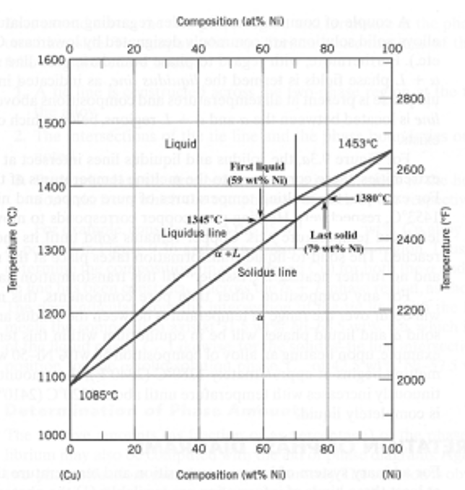
A copper-nickel alloy of composition 70 wt% Ni-30 wt% Cu is slowly heated from a temperature of 1300°C (2370°F).
What is the composition of the last solid remaining prior to complete melting?
about 79 wt% NI
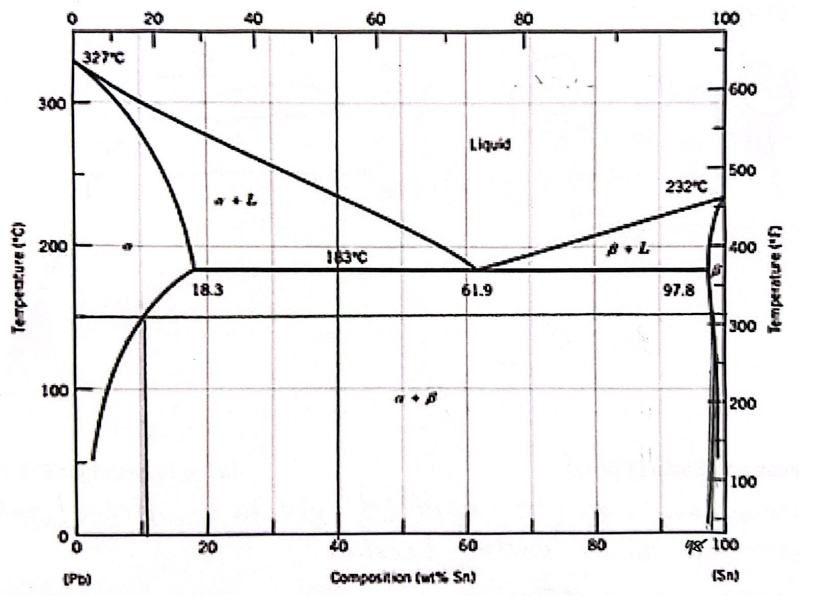
For a 40 wt% Sn-60 wt% Pb alloy at 150 C, find the phases that are present
Pb & Sn
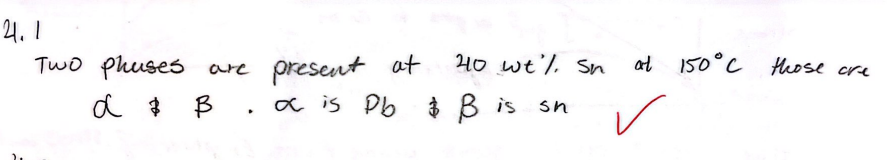
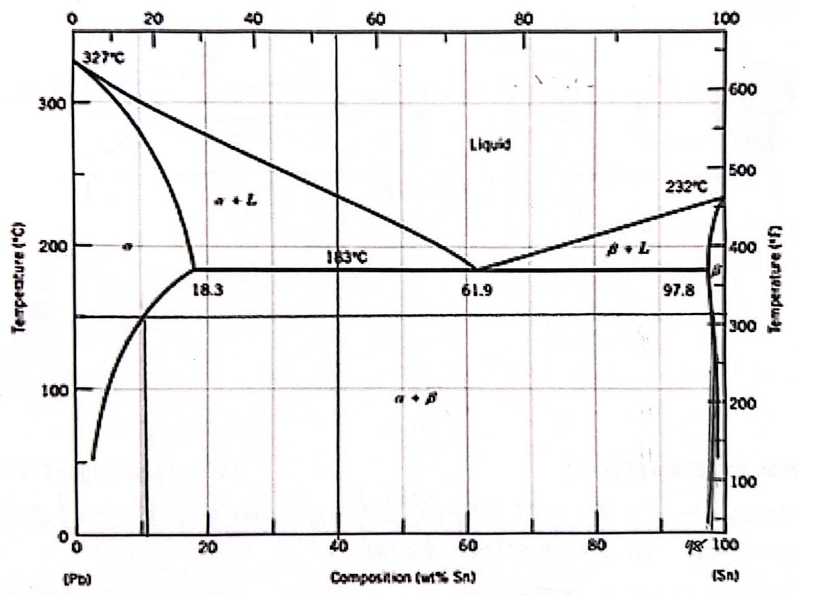
For a 40 wt% Sn-60 wt% Pb alloy at 150 C, find the compositions of each existing phase
Alpha - 11 wt% Sn
Beta - 98 wt% Sn
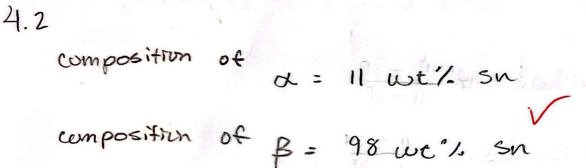
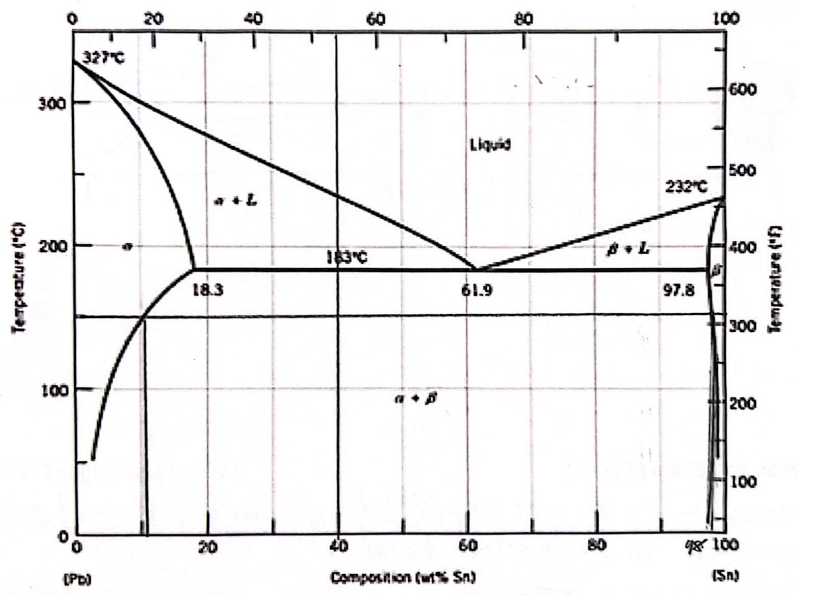
For a 40 wt% Sn-60 wt% Pb alloy at 150 C, find the relative (%) amount of each phase
Alpha - 0.66 wt% Sn
Beta - 0.33 wt% Sn
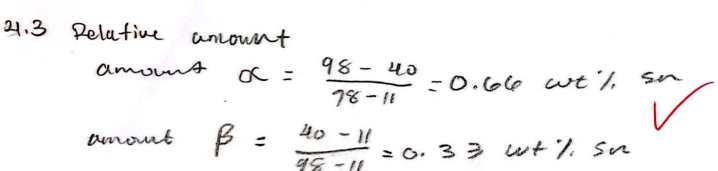
What are the three main components of whiteware ceramic such as porcelain?
Quartz, Clay, Flux
Describe the role of Quartz in forming and firing procedures
Quartz acts as a filler material
Describe the role of Clay in forming and firing procedures
Clay facilitates the forming operation and maintains shape of the piece.
Describe the role of Flux in forming and firing procedures
Flux facilitates the formation of glass having a relatively low melting temperature.
Name 3 glass forming fabrications methods
Pressing, Blowing, Fiber Drawing
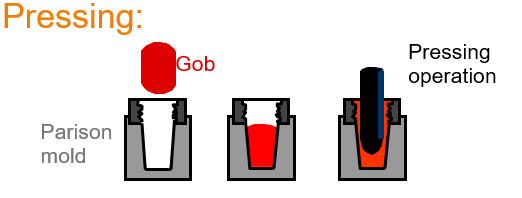
Explain the Pressing glass forming method
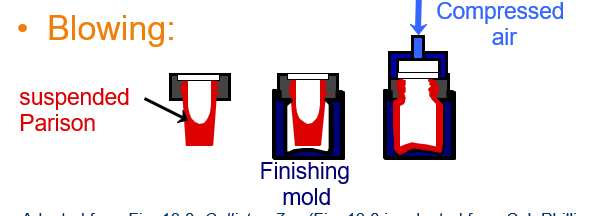
Explain the Blowing glass forming method
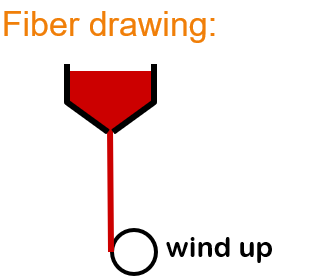
Explain the Fiber Drawing glass forming method
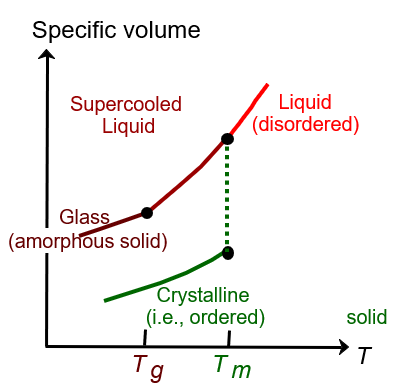
Draw the specific volume changes with temperature in crystalline materials versus amorphous glasses and explain with words the characteristics of each one

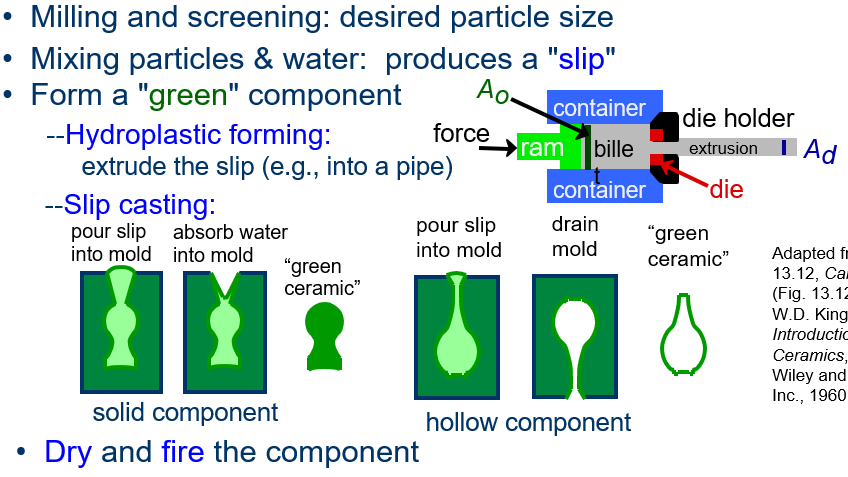
Explain the steps in the particulate forming fabrication method for ceramics
What are the advantages of using ceramics for heat engine?
Run at higher temperature, Excellent Wear & Corrosion resistance, Low Frictional Losses, Ability to operate without a cooling system, low density
What are the disadvantages of using ceramics for heat engine?
Brittle, Easy to have voids-weaken the engine, Difficult to machine
Name 2 examples candidates for ceramics for heat engines
Si3N4, SiC, & ZrO2

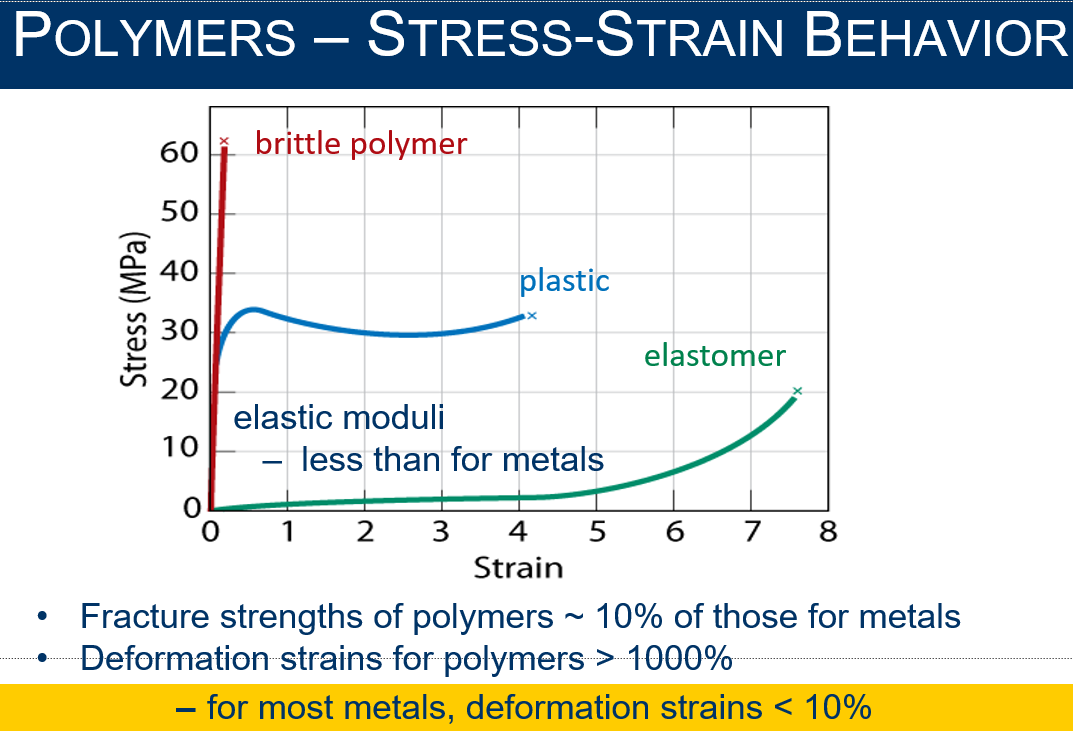
Draw the stress-strain graph for brittle, plastic, and elastomer polymers
Explain fiber-reinforced Polymers
Fibers are very strong in tension, provide significant strength improvement to the composite
Provide examples of fiber-reinforced polymers and properties
Fiber-glass - continuous glass filaments in a polymer mix
Glass Fibers: strength and stiffness
Polymer matrix: holds fibers in place, protects fiber surfaces, transfers load to fibers


L = 1254 nm
r = 15.4 nm
