HE305 Final Lecture Notes (PPTs)
1/846
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
847 Terms
What are fractures?
Any break or disruption in the bone
What are the causes of fractures?
-Accidental falls
-Repetitive injuries
-Sports related
-Secondary conditions (i.e. osteoporosis)
Are fractures always caused by trauma?
No, not all fractures are trauma based
What is a bone bruise?
Blood trapped under bone
What is a sprain?
Stretched or torn ligament
How are fractures classified?
By:
-Pattern: shape of a break or what it looks like.
-Cause: what caused the break in the first place
-Body part: where in your body your broke a bone
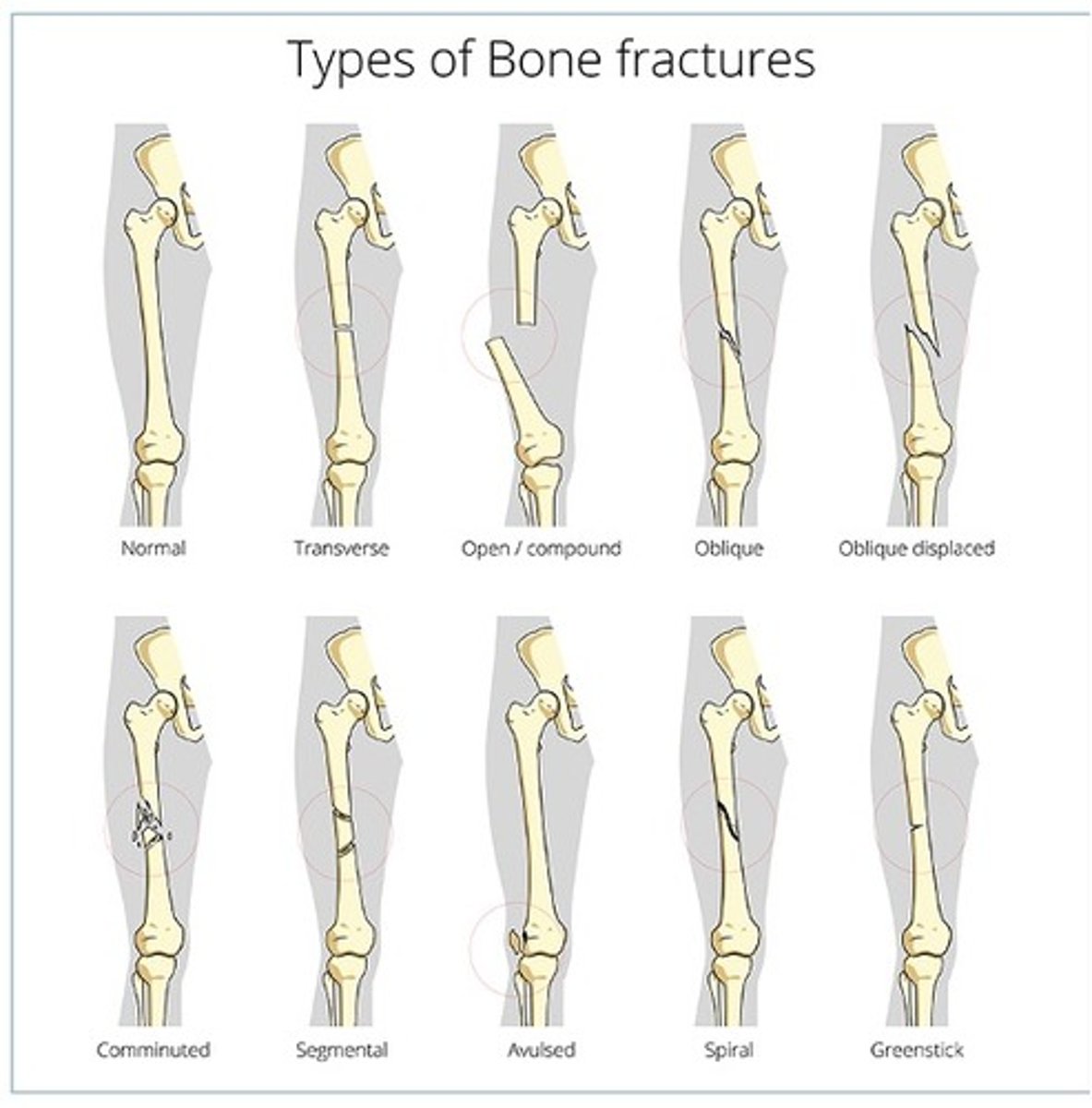
What are the different types of fractures based off pattern?
-Closed
-Open
-Complete
-Incomplete
-Transverse
-Oblique
-Spiral
-Impacted
-Comminuted
-Displaced
-Complicated
-Compression
-Pathological
-Colles
-Stress
Why are compression and pathological fractures different from other types of fractures?
They tend to be related to a diagnosis rather than trauma
What is the golden rule when treating fractures?
Put broken pieces back into position and then prevent them from moving out of place until 100% healed
What are the different types of treatment for fractures?
-Cast
-Splint
-Brace or functional cast
-TRom brace
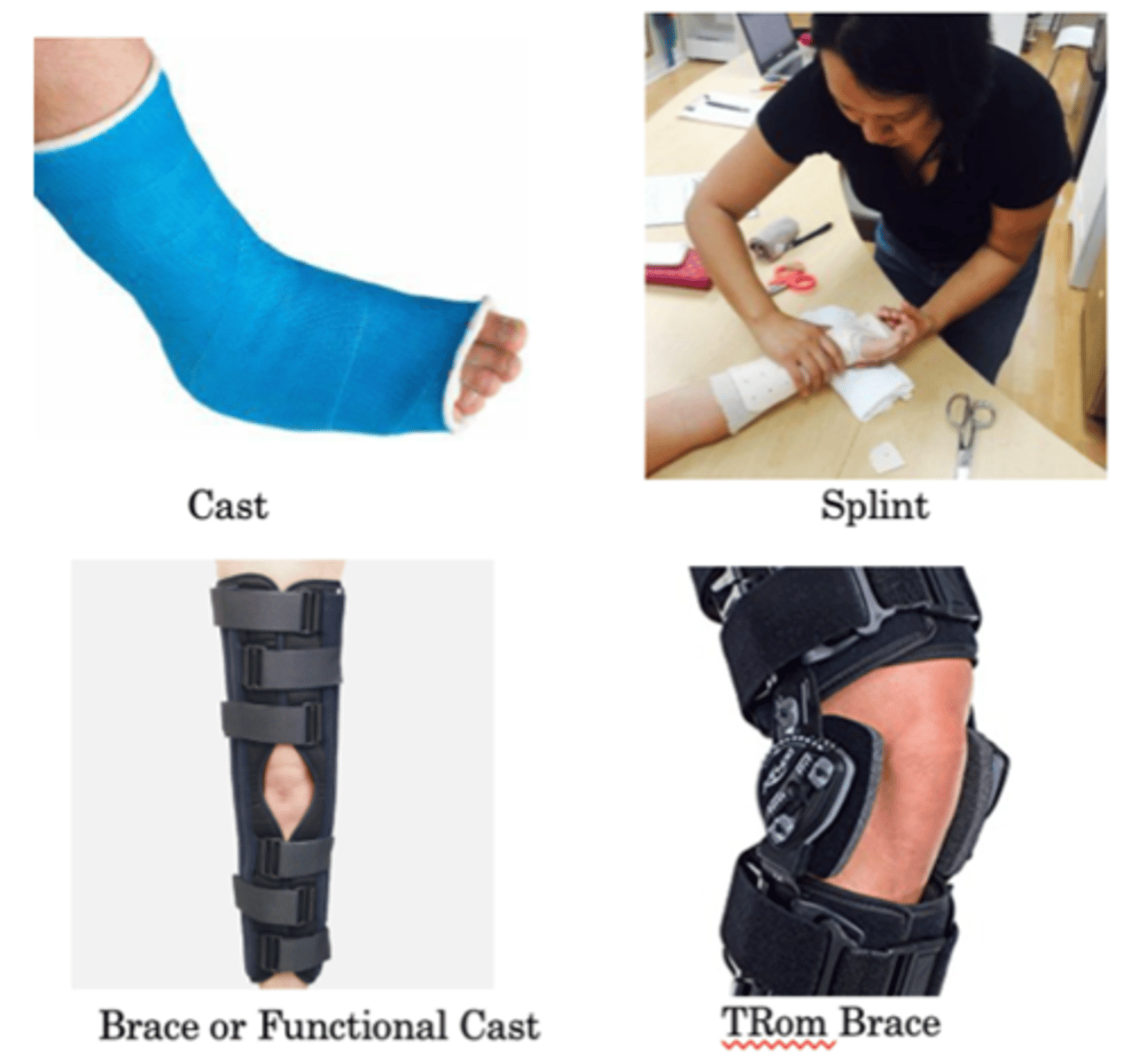
What does a TRom brace do?
It limits ROM
What is reduction treatment for fractures?
Doctor restores the broken bone back into original place
How does a bone heal?
Bone ends heal by knitting back together with new bone formed around edges of broken part
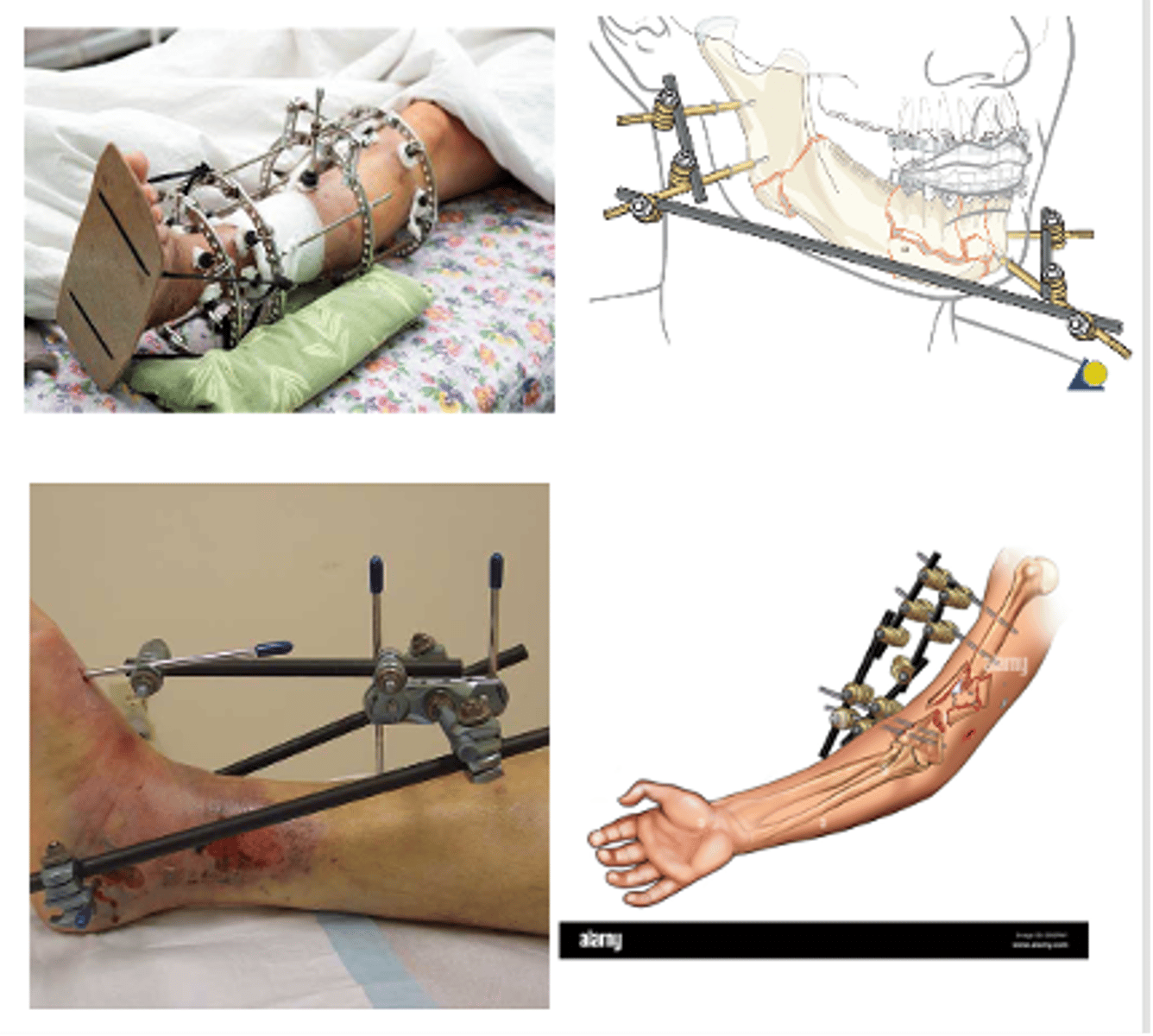
What are the different types of fixators?
-Open reduction and internal fixations (ORIF)
-External fixator
What are open reduction and internal fixations (ORIF)?
Bone was outside skin, so they did surgery to fix it and put rods and fixators are internal
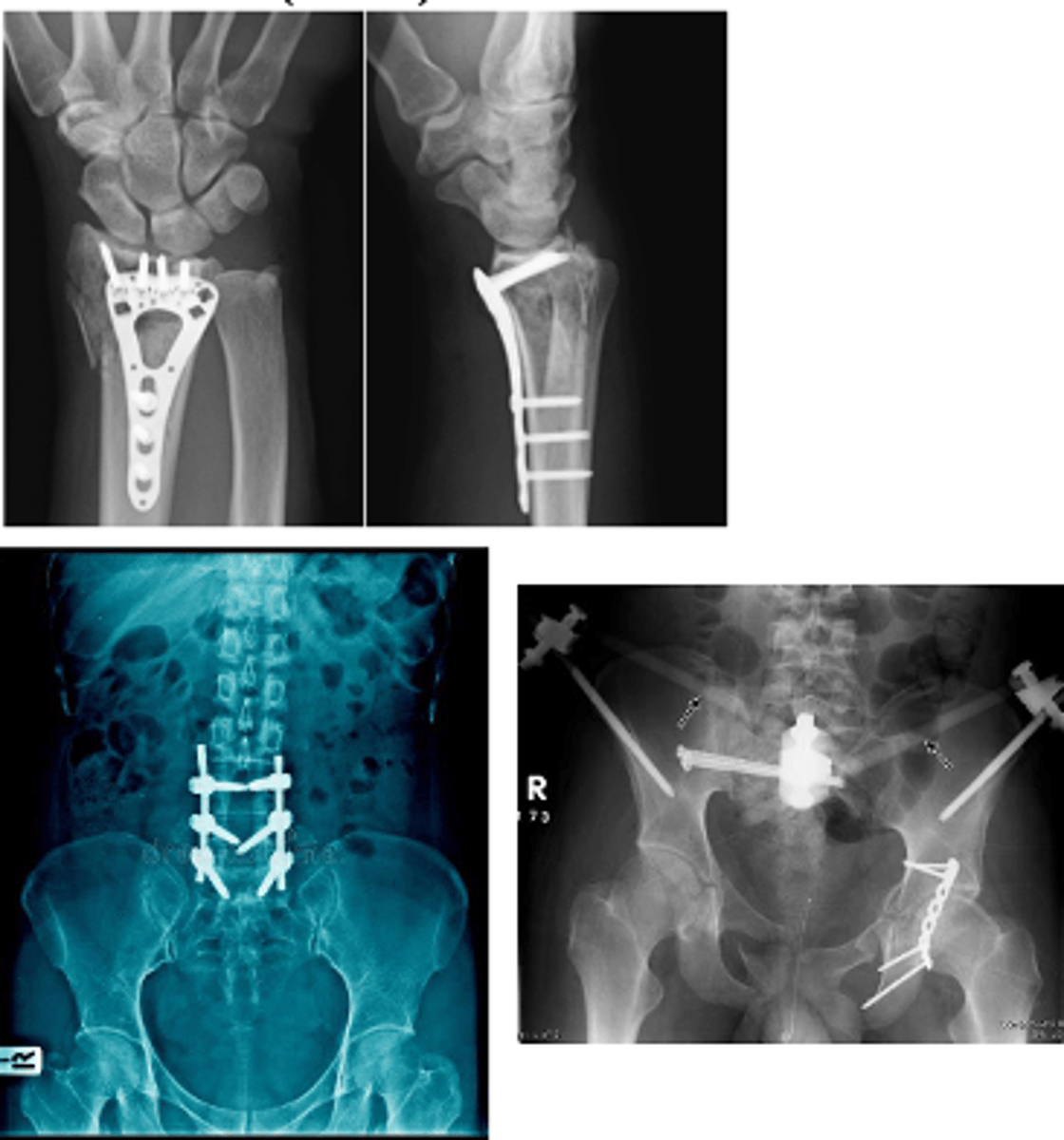
What are external fixators?
External devices used to keep fractured bones stabilized and in alignment
What is carpal tunnel syndrome?
Compression of the median nerve or repetitive, overuse of hand with few rest breaks (repetitive strain injury
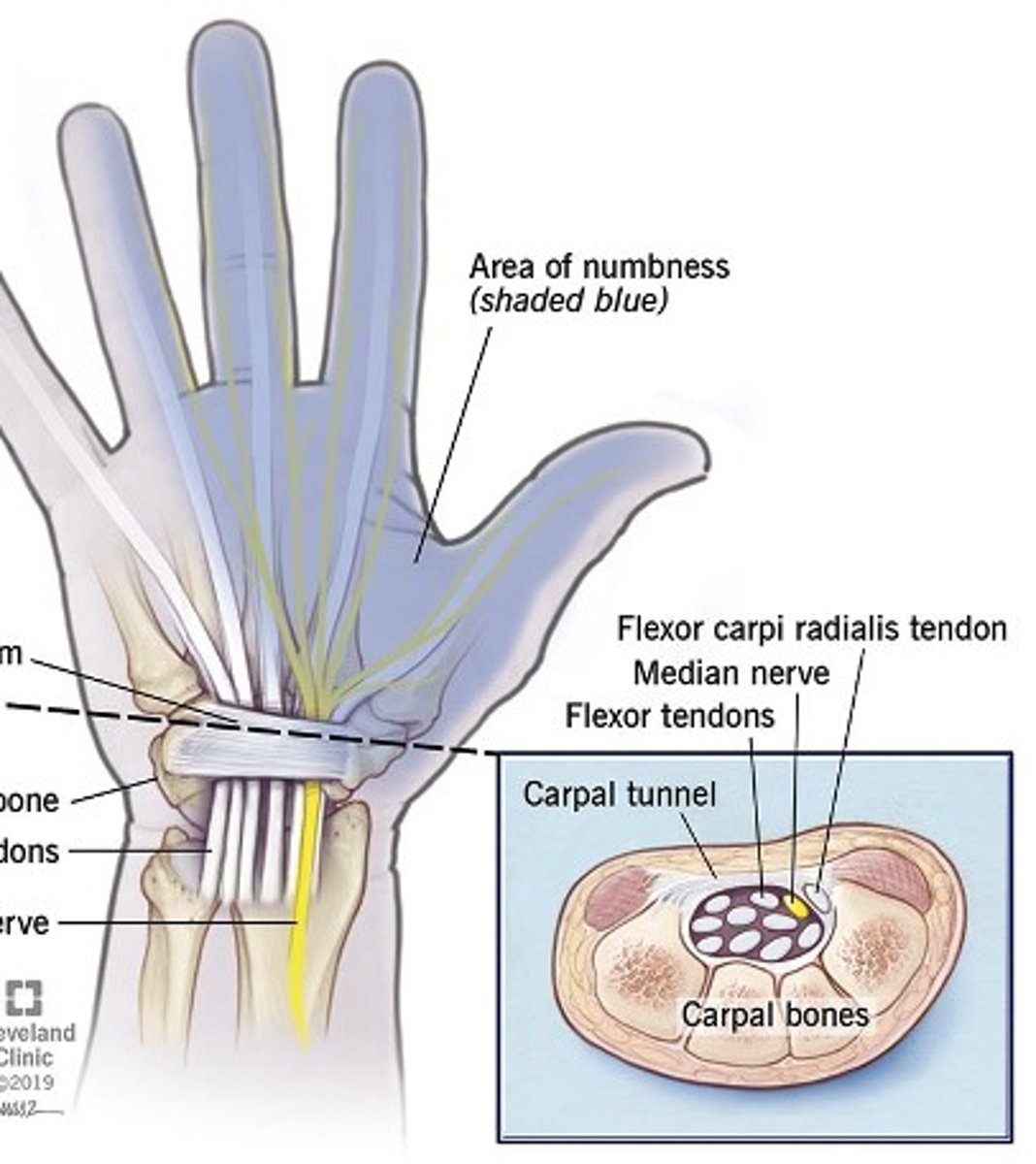
What are some common associated diagnoses with carpal tunnel syndrome?
-Metabolic conditions
-Heredity conditions
-Obesity
-Pregnancy
What is carpal tunnel syndrome common with?
It is common with vocations that overuse the hand
What causes carpal tunnel syndrome?
Compression or entrapment neuropathy
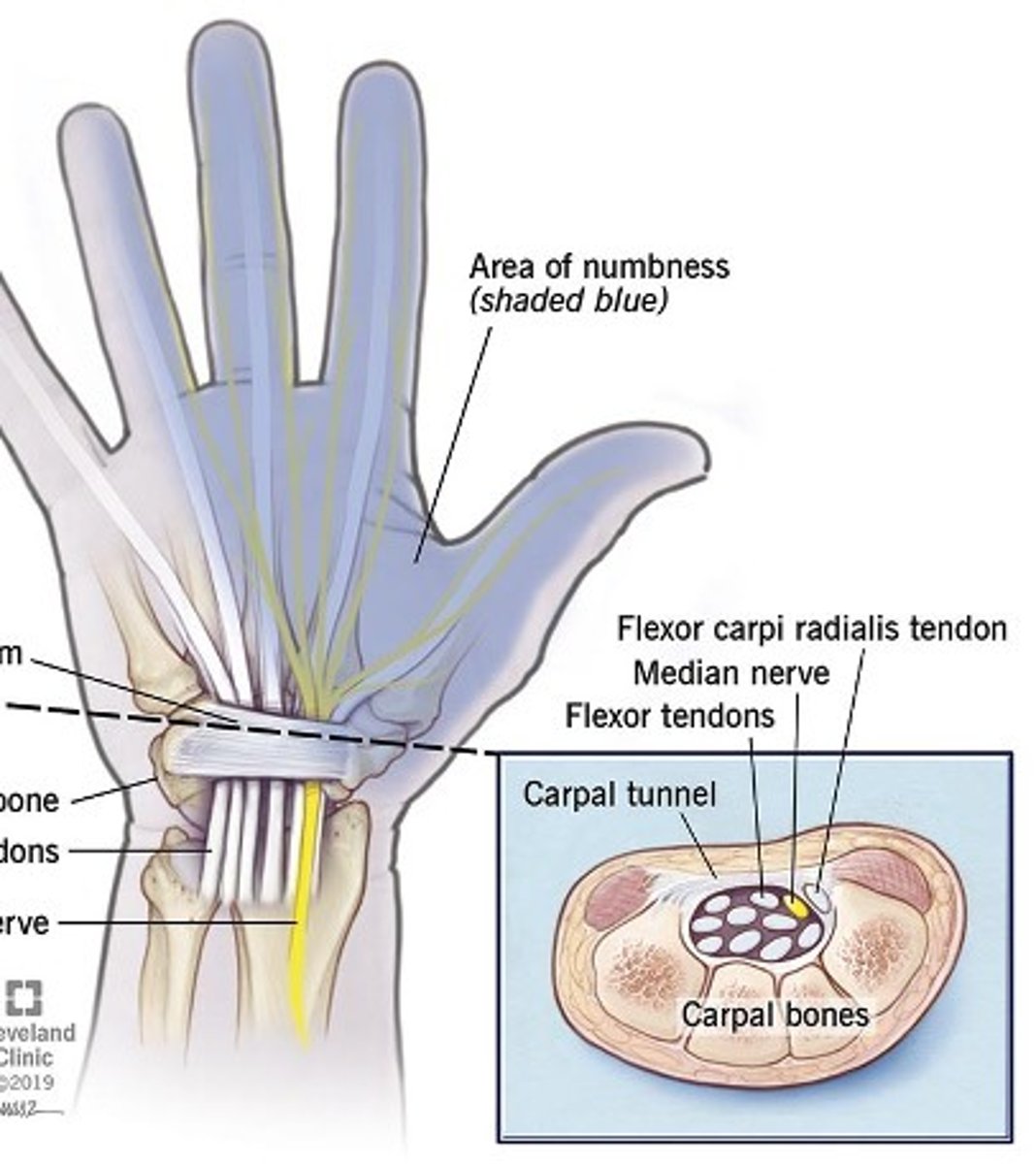
What does carpal tunnel syndrome cause?
Pain and paresthesis (tingling, pricking feeling) in hand
How is carpal tunnel syndrome managed?
-OT
-Ergonomic training
-Night wrist splint in a different day wrist splint
-NSAIDS; corticosteroids
-Surgery
What is another name for osteoarthritis (OA)?
Degenerative Joint Disease (DJD)
When is osteoarthritis more common?
More common in people over the age of 65
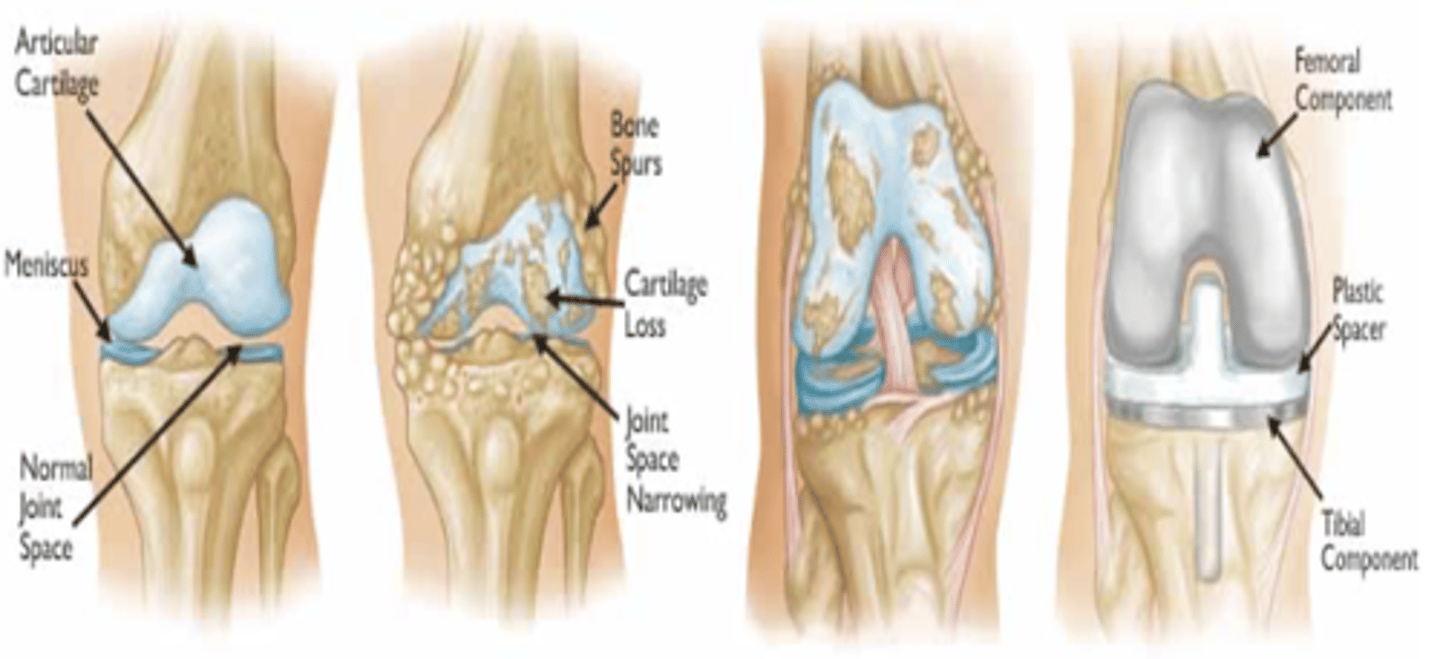
What is osteoarthritis?
The most common chronic condition of the joints (wear and tear of cartilage)
What are the most common locations of osteoarthritis?
-Knees
-Hips
-Lower back
-Neck
-Smaller joints
-Fingers
-Thumb
Osteoarthritis is a localized condition in its beginning stage. What does this mean?
It only affects one joint or localized area. It is typically seen in the beginning of the condition, but the condition often spreads to other joints due to compensation and causes severe OA
What are the potential risk factors for osteoarthritis?
-Obesity
-Joint overuse
-Prior injury
-Age
-Genetics
When does osteoarthritis lead to getting an arthroplasty?
If progression is severe, bone on bone, it develops spurs first and then all cartilage is gone. Surgery is then the only option
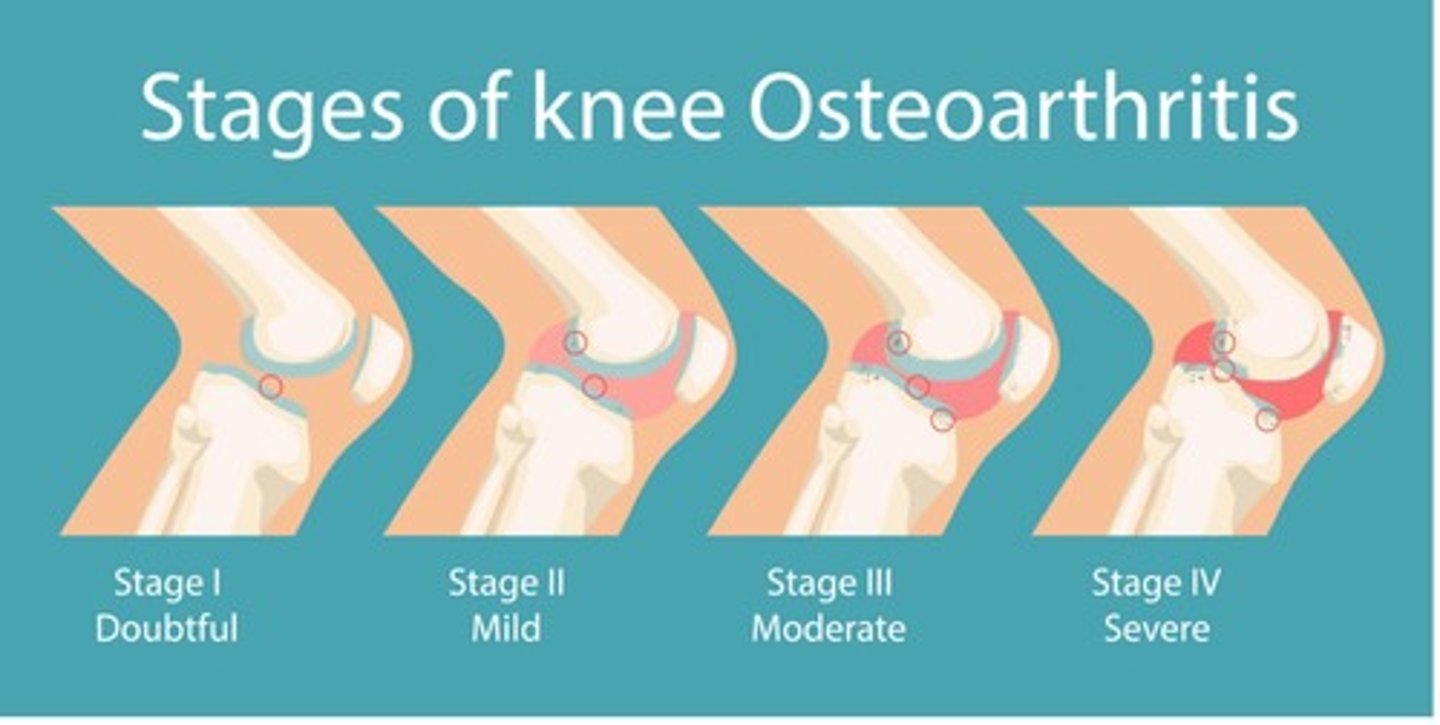
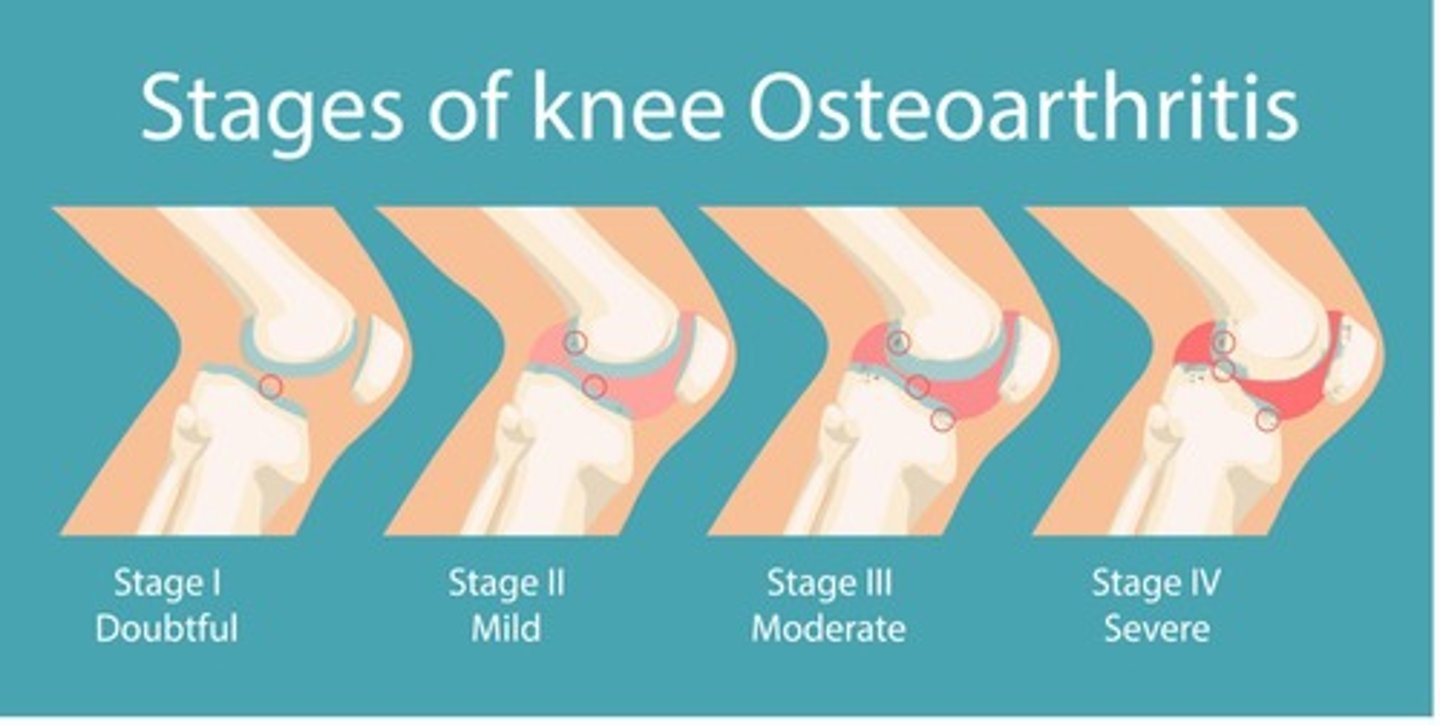
What are the stages of osteoarthritis?
-Stage 1: Doubtful
-Stage 2: Mild
-Stage 3: Moderate
-Stage 4: Severe
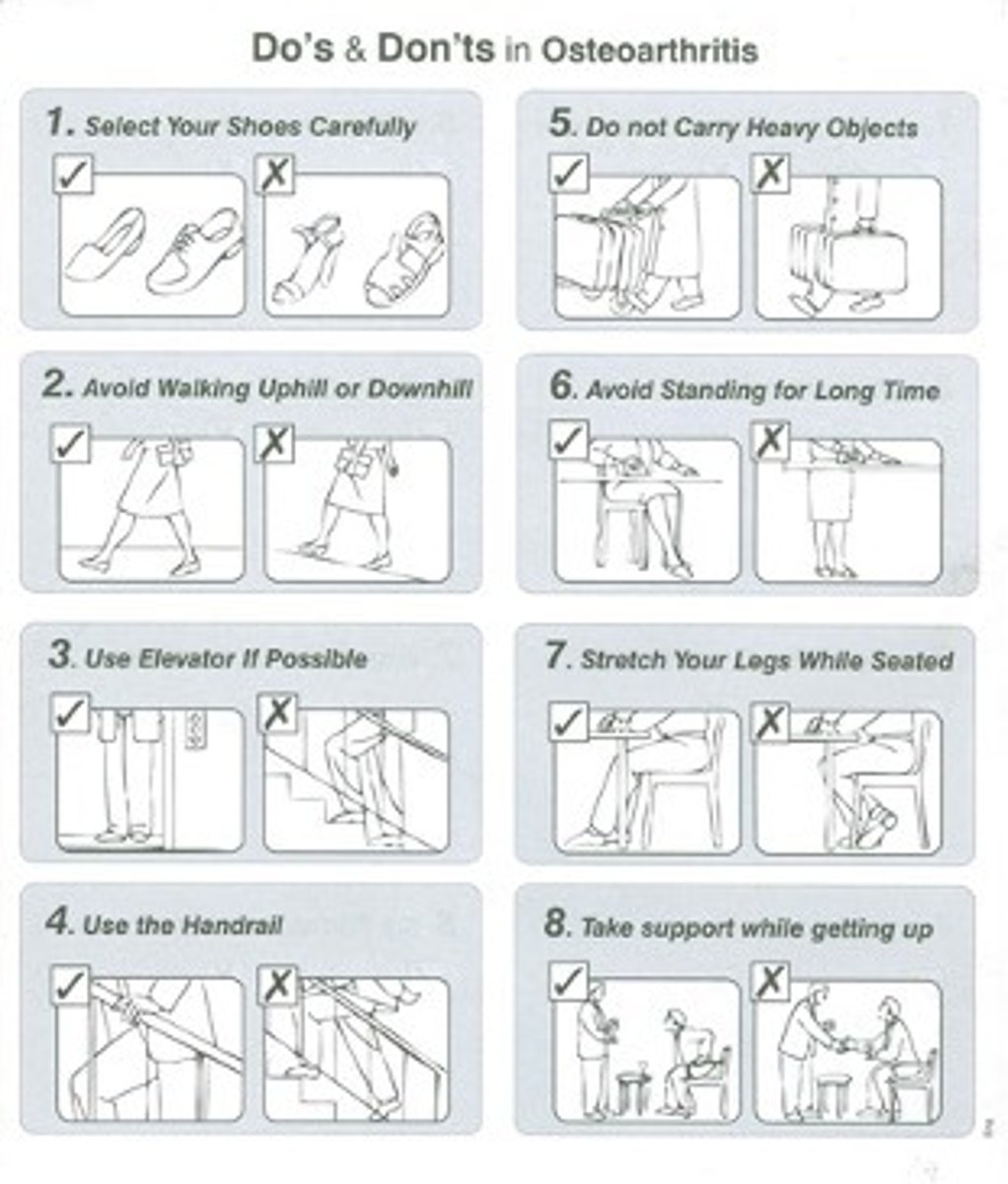
What are some of the tips (Do's and Don'ts) in osteoarthritis?
-Select your shoes carefully
-Avoid walking uphill or downhill
-Use elevator if possible
-Use the handrail
-Do not carry heavy objects
-Avoid standing for a long time
-Stretch your legs while seated
-Take support while getting up
What is osteomyelitis?
Bacterial infection in the bone that leads to bone destruction. It can be an acute and/or chronic condition
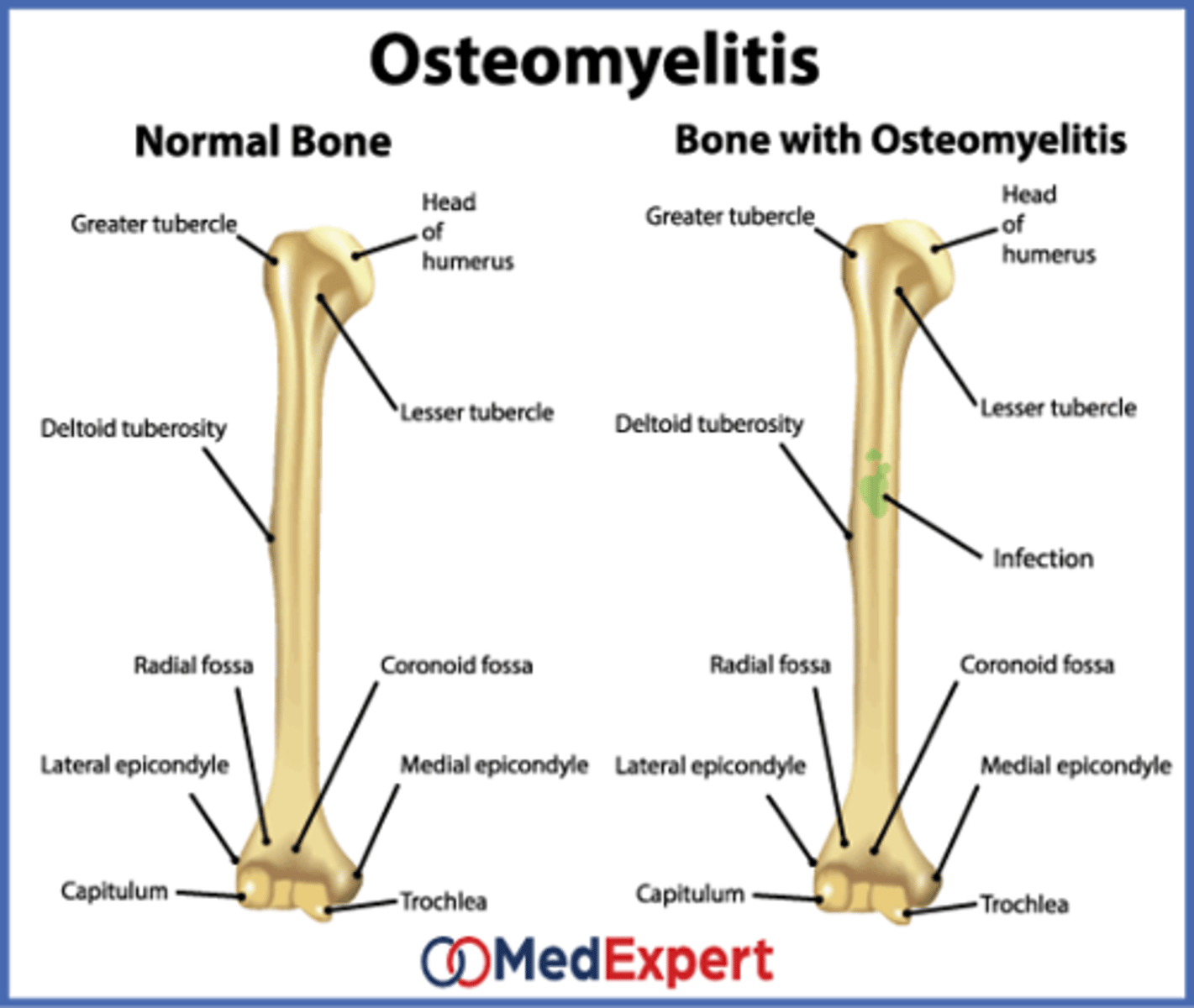
What does osteomyelitis manifest as?
It manifests as edema and reddening (erythema)
When is a total hip replacement (THR) performed?
It is performed as a last resort, used only if patient has already tried medications, therapy and other conservative measures and pain is still severely affecting daily activities and quality of life
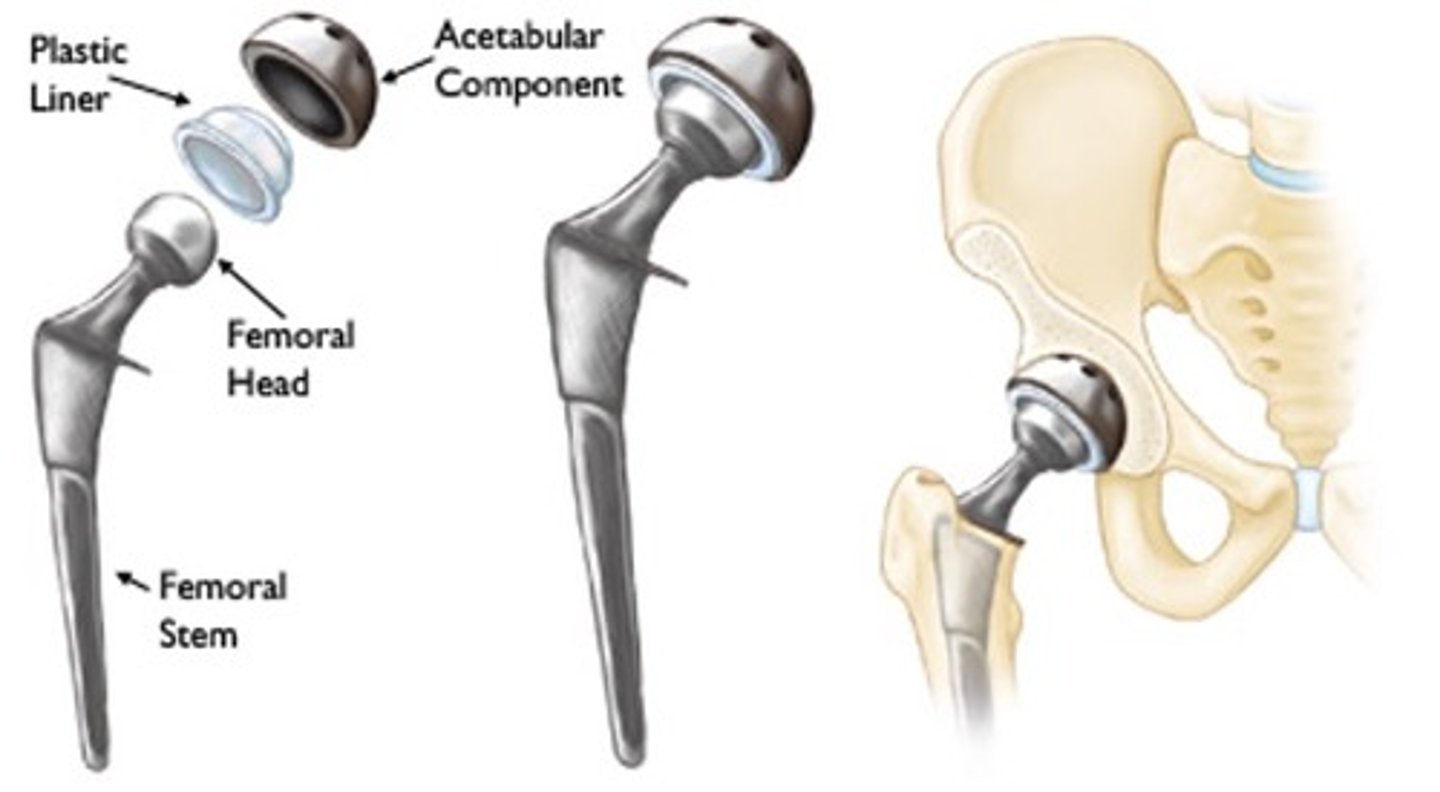
What is a total hip replacement?
Surgery to restore a damaged hip to full function. During the surgery, a plastic lining is fitted into the acetabulum to restore a smooth surface. The head of the femur is removed and replaced with a metal ball attached to a metal shaft that is fitted into the femur
Why are there total hip precautions (THPs) in place?
Keeps new hip from popping out
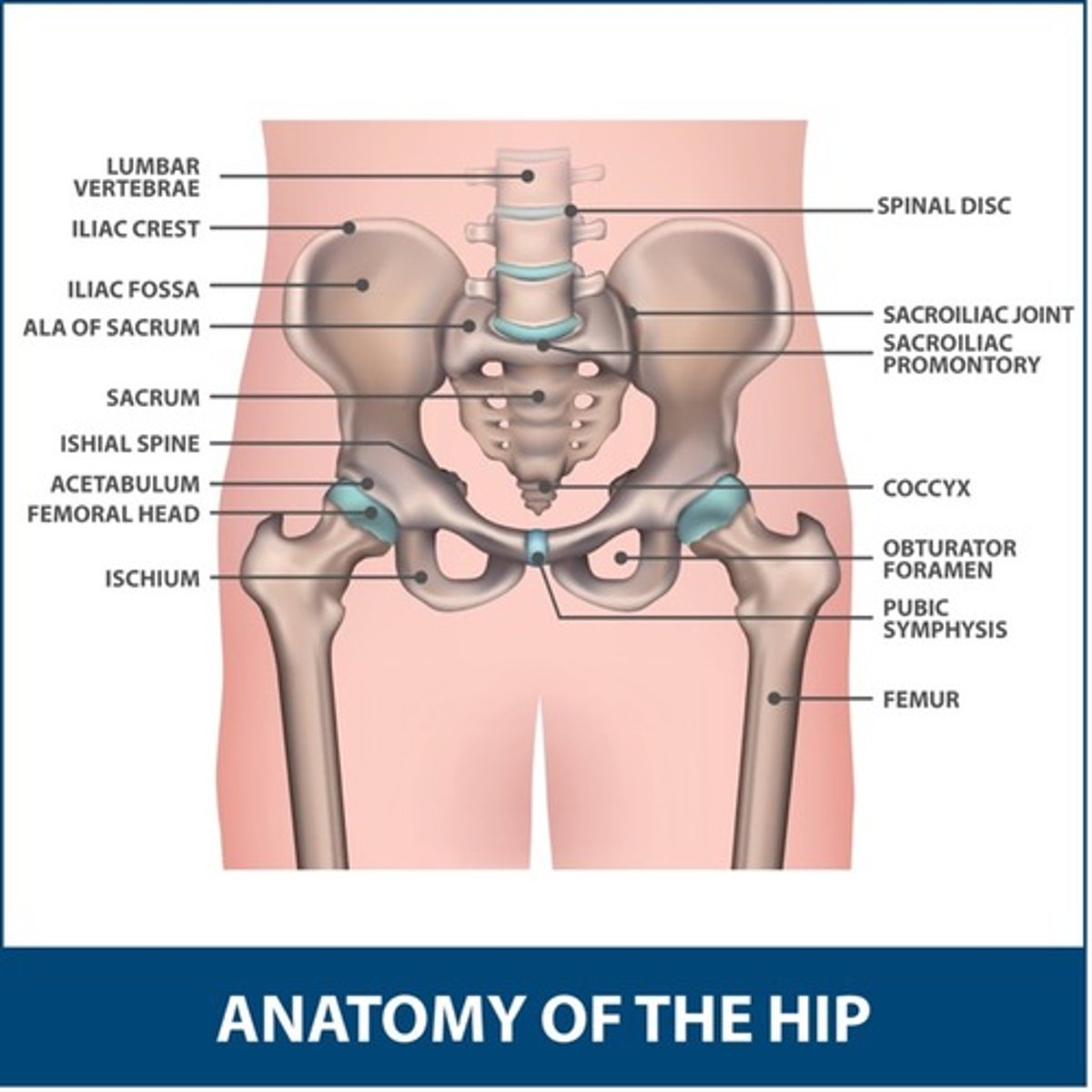
What are the THPs for posterior hip replacement?
-No bending past 90 degrees
-No crossing legs
-No twisting on operated hip (turning toes in/out)
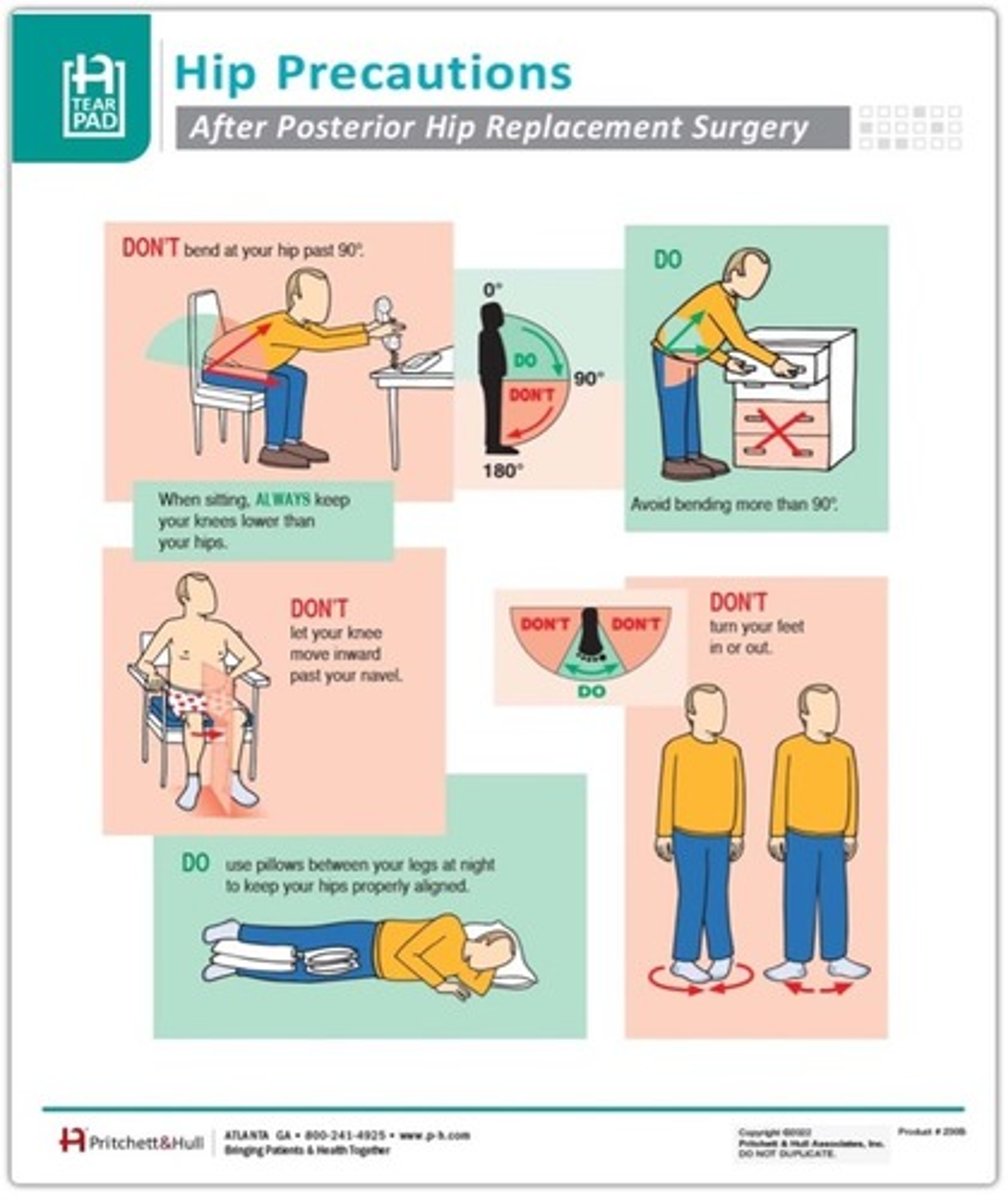
What are the THPs for anterior hip replacement?
-No extreme hip extension
-No extreme hip abduction
-No external rotation (think figure 4 sitting)
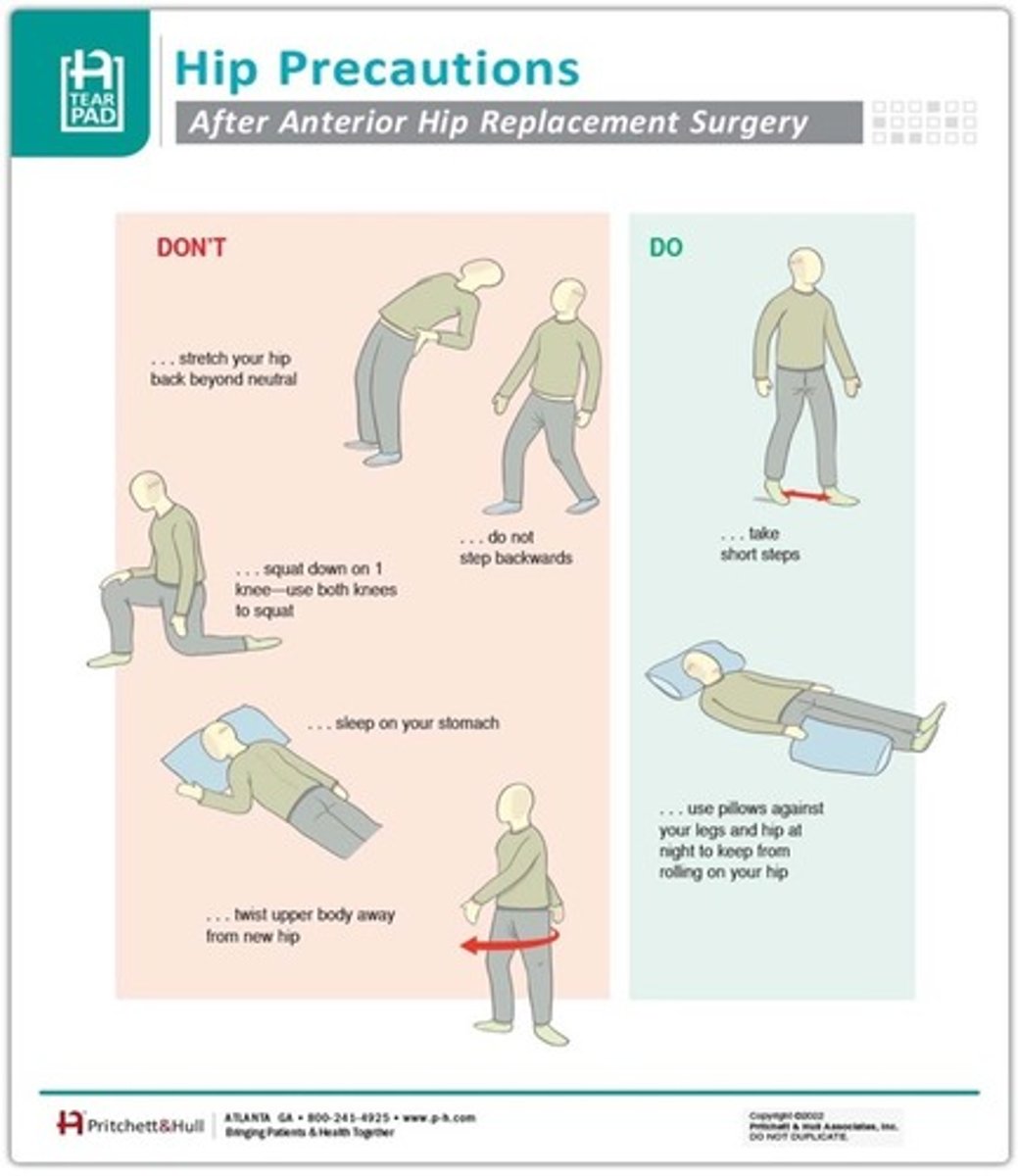
What are some of the possible complications of hip replacements?
-Blood clots
-Blood loss
-Hip dislocation
-Leg length difference
-Hip implant loosening or wearing
-Infection of a joint replacement
-Implant rejection
What are some examples of THR interventions to help lower the risk of complications?
-Education on THP and Safety
-Securely fastened safety bars or handrails in your shower or bath
-Secure handrails along all stairways
-A stable chair for your early recovery with a firm seat cushion (that allows your knees to remain lower than your hips), a firm back, and two arms
-A raised toilet seat
-A stable shower bench or chair for bathing
-A long-handled sponge and shower hose
-A dressing stick, a sock aid, and a long-handled shoehorn for putting on and taking off shoes and socks without excessively bending your new hip
-A reacher that will allow you to grab objects without excessive bending of your hips
-Firm pillows for your chairs, sofas, and car that enable you to sit with your knees lower than your hips
-Removal of all loose carpets and electrical cords from the areas where you walk in your home
Where may blood clots form?
Blood clots may form in one of the deep veins of the body. While blood clots can occur in any deep vein, they most commonly form in the veins of the pelvis, calf, or thigh
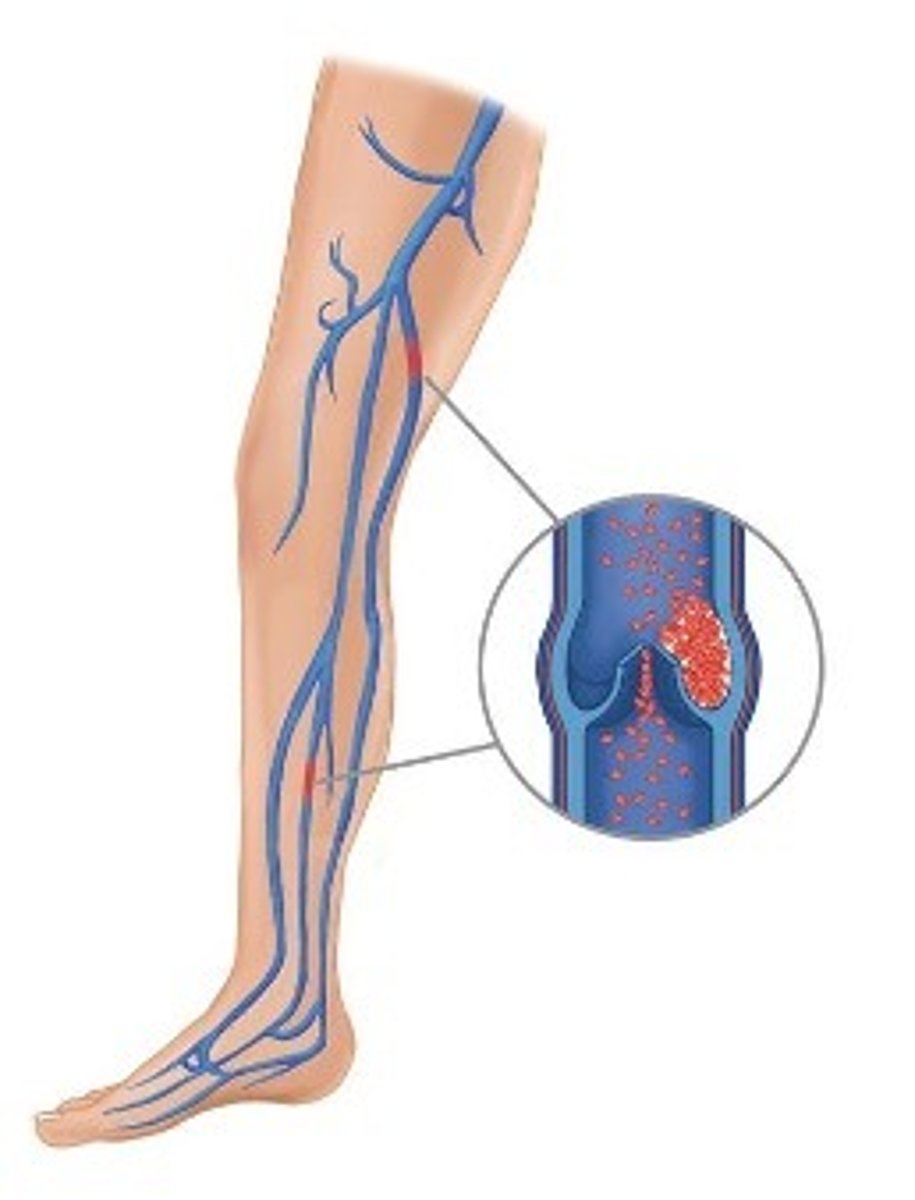
What are some warning signs of a blood clot?
-Pain in your calf and leg that is unrelated to your incision
-Tenderness or redness of your calf
-New or increasing swelling of your thigh, calf, ankle, or foot
What are some signs of a pulmonary embolism?
-Sudden shortness of breath
-Sudden onset of chest pain
-Localized chest pain with coughing
What are some signs of an infection after a THR?
-Persistent fever (higher than 100°F orally)
-Chills
-Increasing redness, tenderness, or swelling of the hip wound
-Drainage from the hip wound
-Increasing hip pain with both activity and rest
What are some precautions to take for a total knee replacement (TKR)?
Don't twist or pivot
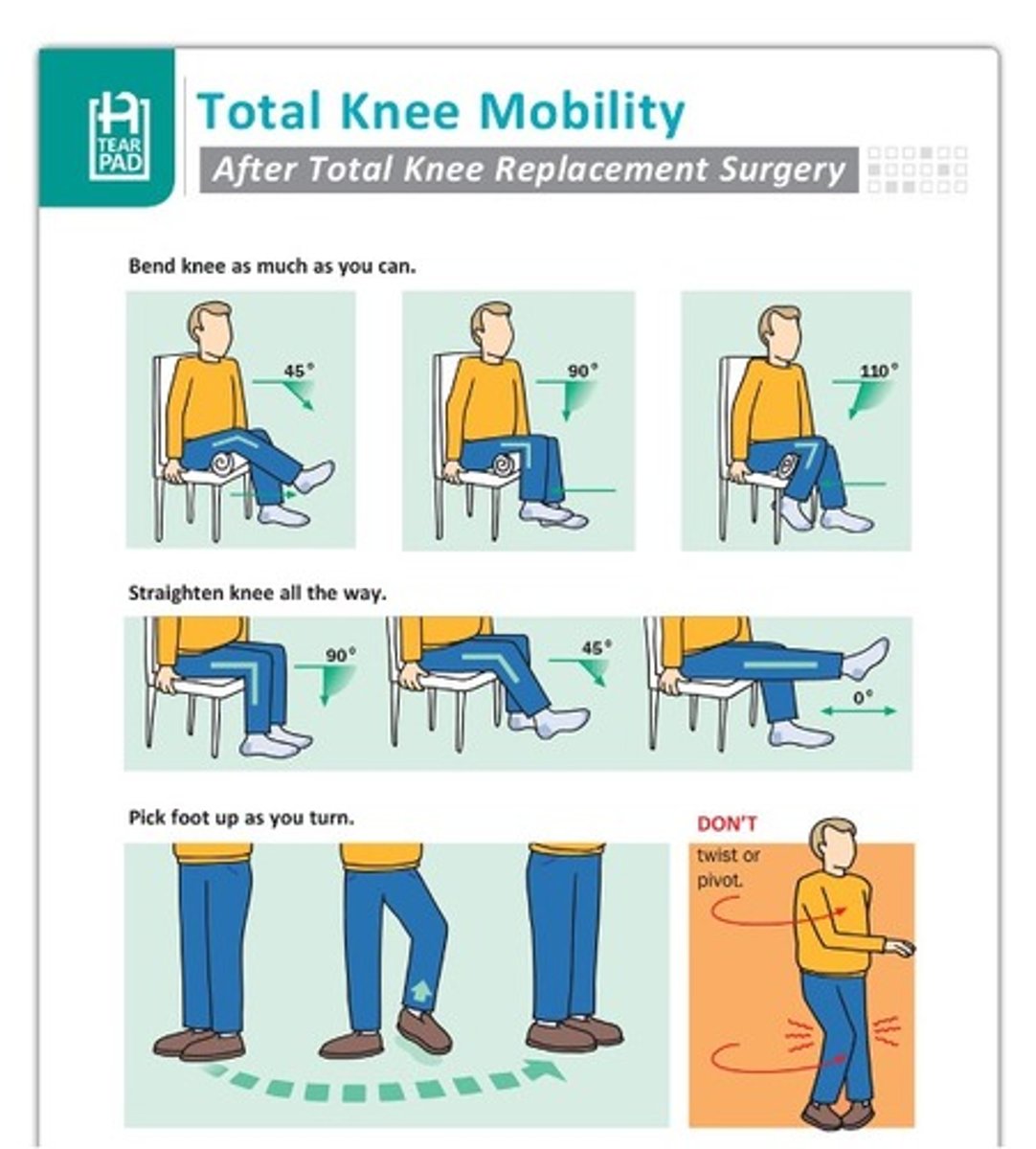
What are some interventions for a TKR?
-Compensatory Strategies for ADL's such as dressing and bathing, for IADLS's
-Using walker
-How to safely monitor knee and surgical site
-Encourage as much extension of knee as possible
-Weight bear according to doctors' recommendations
-No crutches until cleared
-Education on how to functional and safe mobility aka turn without rotating
-Safe positioning of knee (no pillows)
What are some of the causes of total shoulder replacement (TSR)?
-OT
-Rheumatoid Arthritis
-Trauma or severe injury
-Rotator cuff Injury
-Loss of ROM or overall weakness
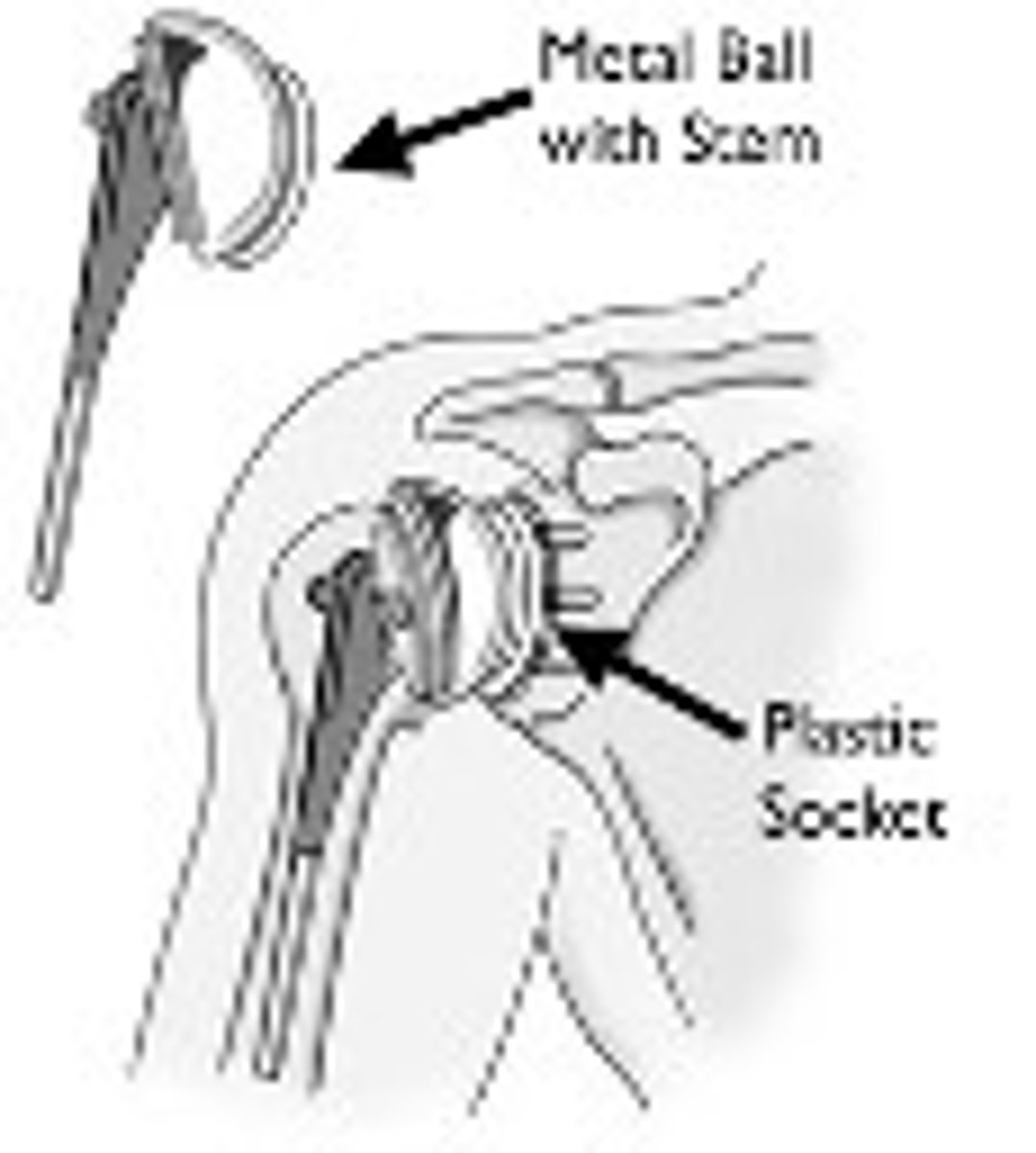
What are some of the rehab considerations of a TSR?
-Generally, NWB (non-weight bearing) and immobilized immediately after surgery
-If in Rehab, there are compensatory strategies for ADL, IADL, Mobility Tasks
-Limited ROM
What are some exceptions to limited ROM in a TSR?
-Pendulums
-Elbow flexion/extension
-Wrist flexion/extension
-Finger flexion/extension
What are some of the different types of spine/back pain?
-Low back pain
-Chronic back pain
-Herniated or ruptured disk
-Spondylolisthesis (one vertebra slips over the other)
-Scoliosis
What are some causes of spine/back pain?
-Tumor
-Injury
-Poor body mechanics
-Arthritis
-Osteoarthritis
-Narrowing of spinal canal (stenosis)
-Degenerative conditions (i.e. congenital conditions, injury, cancer, infection)
How do spinal surgery procedures vary?
They will vary based on what part of the spine is damaged
What are the different types of spinal surgery?
-Laminectomy
-Diskectomy
-Fusion
What is a laminectomy?
Surgery that removes lamina to create space and enlarge spinal canal (aka decompression surgery)
What is a diskectomy?
Surgery that removes herniated disk and any pieces that have broken loose
What is a fusion?
Surgery that connects 2+ vertebra via graphs or metal rods and screws to support/stabilize
What is the typical duration of spinal precautions taken after spine surgery?
6-8 weeks post op
What is the "BLT" strategy for spine precautions?
-B: No bending over @ back
-L: No heavy lifting (> 5 lbs)
-T: No twisting
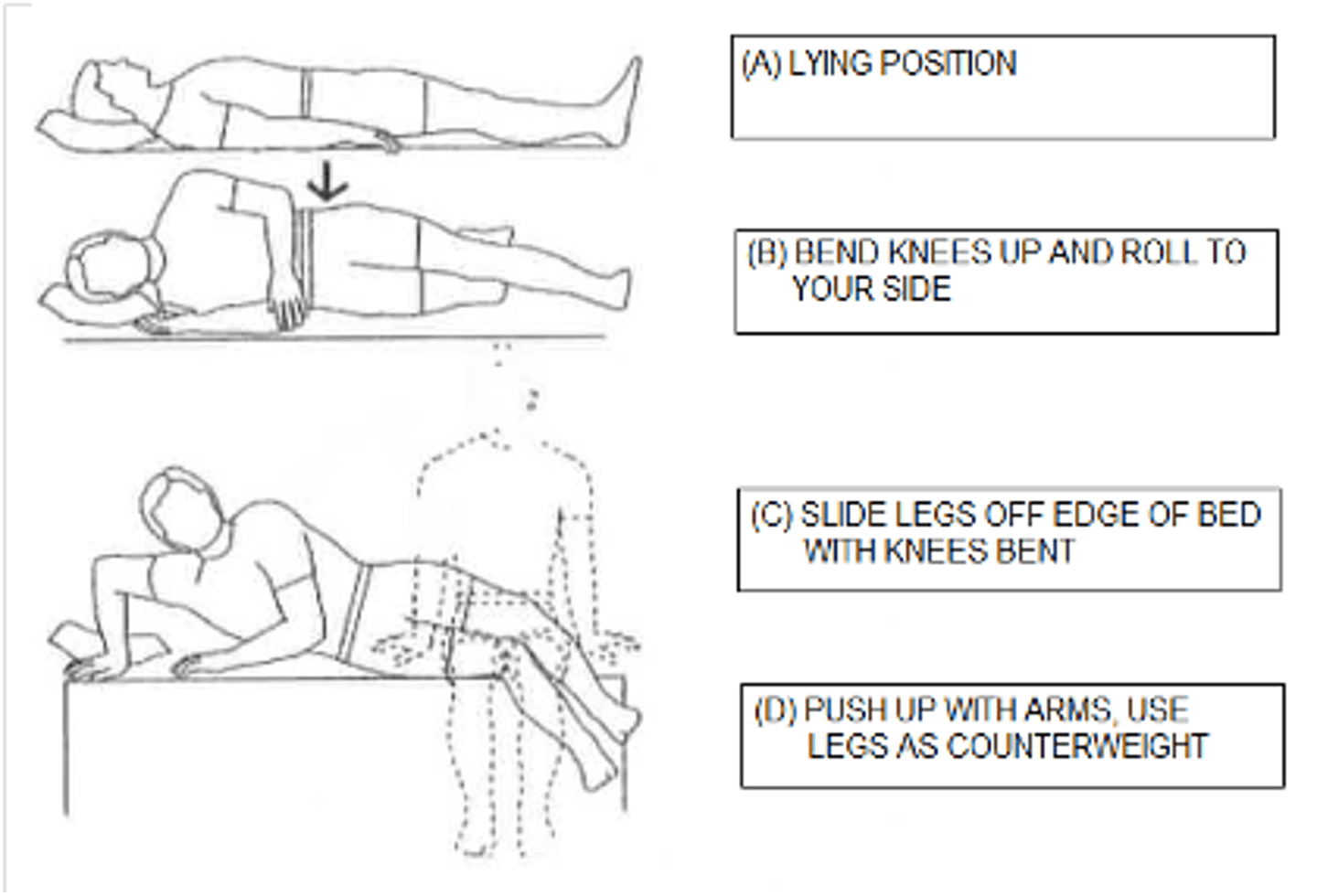
What are some different types of back braces?
-Turtle or clam shell (TLSO)
-Lumbar sacral orthosis (LSO)
-Cervical collar or neck collar
-TLSO with cervical extension
-HALO
-Thoracolumbar (TLSO)

How many Americans have osteoporosis?
54 million Americans have osteoporosis and low bone mass, placing them at increased risk for osteoporosis. Studies suggest that approximately one in two women and up to one in four men age 50 and older will break a bone due to osteoporosis
What does osteoporosis mean?
Porous bone
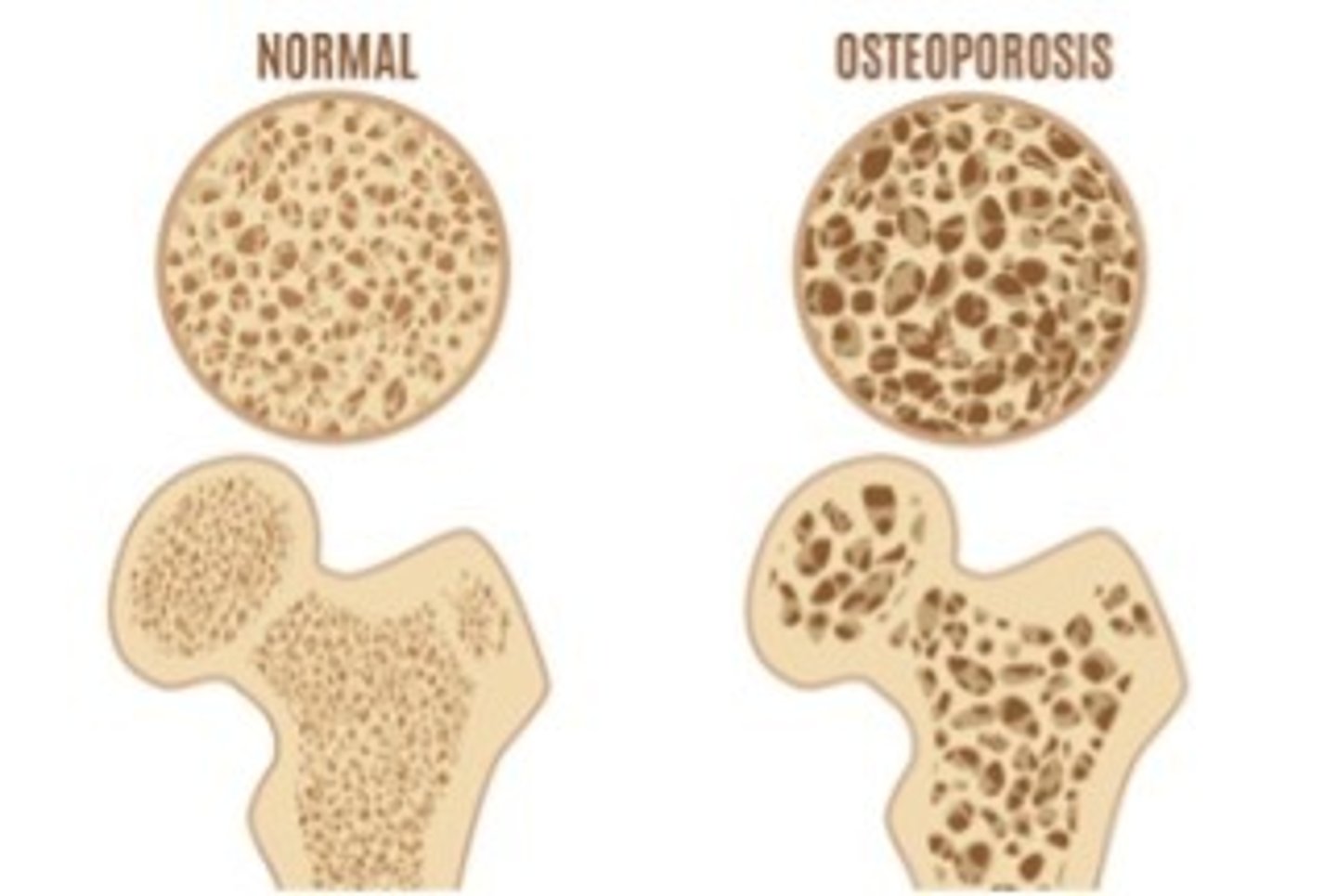
Whatis osteoporosis?
A metabolic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone density which causes weakening and increased susceptibility to fracture
What are the most common places for osteoporosis?
-Spine (thoracic)
-Hips
-Wrists
What percentage of bone mass must be lost for it to be classified as osteoporosis?
30-50% loss in bone mass = osteoporosis
How does osteoporosis develop/occur?
It occurs when there is a disruption of the remodeling process of bone occurs where osteoclasts dominate and dissolve the bone
What is resorption?
Bone dissolves
What is formation?
New bone forms
In osteoporosis, bones become brittle and fragile. What are some potential causes for this imbalance in bone?
-Decrease in essential hormones
-Decrease in vitamins and minerals
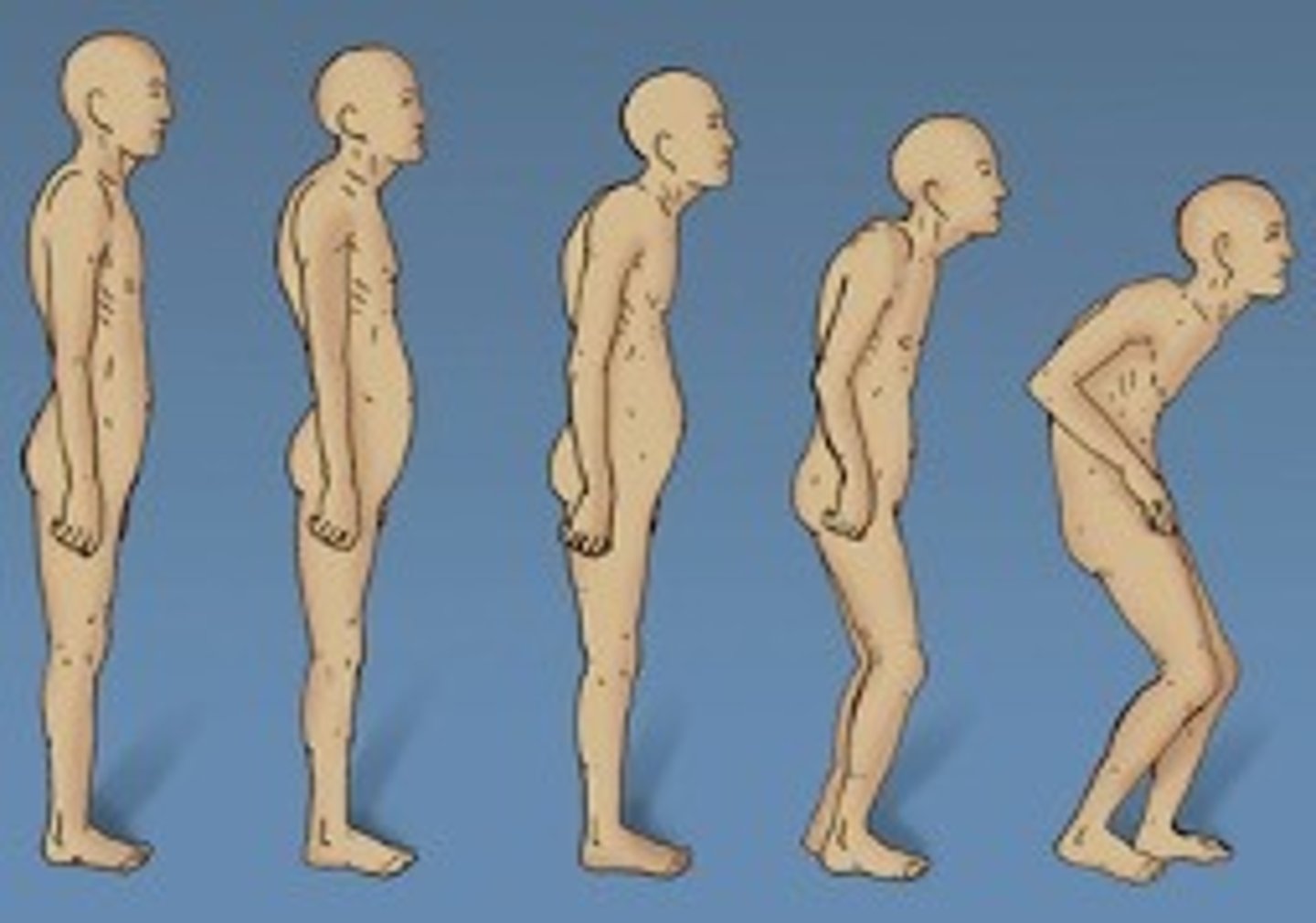
In this picture, which person has osteoporosis?
All of them. You cannot see osteoporosis
What are the different types of osteoporosis?
-Primary
-Secondary
What are the characteristics of primary osteoporosis?
-Uncertain cause
-Seen more frequently in post-menopausal women and the elderly
-Most often osteoporosis is primary
When does secondary osteoporosis occur?
It occurs as a result of another condition
What are some of the risk factors for osteoporosis?
-Genetics
-Age
-Heredity
-Small boned/frame
-Hormone irregularities
-Diet
-Activity level
-Smoking/alcohol abuse
-Medications
What are the risk factors for secondary osteoporosis?
-Autoimmune disorders
-Medical procedures
-Bleeding disorders and cancers
-Thalassemia
-Digestive and gastrointestinal disorders
-Endocrine/hormonal disorders
-Neurological conditions
-Mental illness
What are some medications that increase the likelihood of osteoporosis?
-Corticosteroids/ glucocorticoids
-Anti-convulsants
-Cancer drugs
-Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH)
-Blood thinners
-Lithium
-Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
-Certain cholesterol medications
-Antacids with aluminum
-Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
-Thyroid medications
What is typically the first sign of osteoporosis?
Typically, 1st sign is a broken Bone without any real trauma
What is the bone mineral density (BMD) test or DEXA scan?
They are tests that measure bone density and amount of minerals in bone. They provide a diagnosis BEFORE a fracture occur (less density = higher risk of fracture)
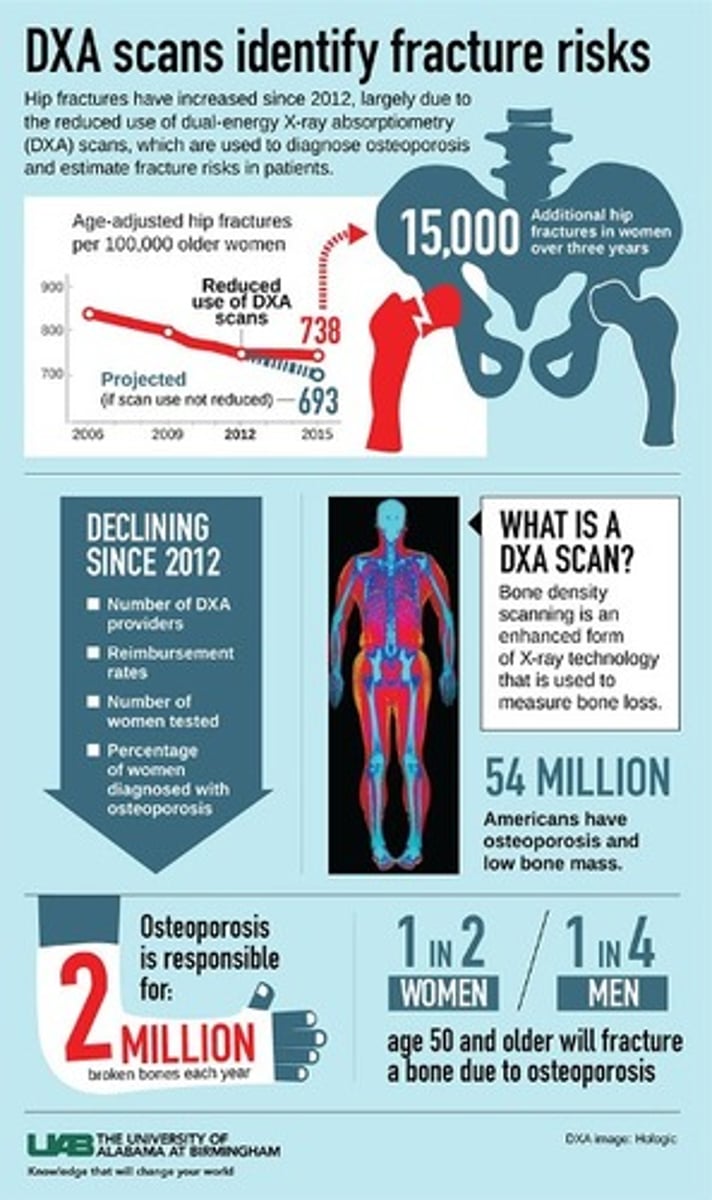
What are the 2 types of BMD tests or DEXA scans?
-Localized scan
-Entire body scan
What are some recommendations for getting BMD testing?
-Females age 65 or older
-Males age 50-69 with risk factors
-Males aged 70 or older
-X-rays confirming fractures or bone loss in spine
-Fractures that happen after age 50
-Unexplained back pain
-Females of menopausal age with risk factors
-Height loss of 1/2 inch or more within 1 year
-Post-menopausal females under age 65 with risk factors
-Total height loss of 1 1/2 inches from your original height
What are some universal precautions/recommendations with osteoporosis?
-Adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D
-Regular weight-bearing exercise and strengthening
-No high impact activities
-Fall prevention (enviro or home visits)
-Good posture and safe movements during ADLs/IADLs
-Avoidance of tobacco use and excessive alcohol intake
What does good posture and safe movement during ADLs/IADLs look like?
-Avoid flexion at wrist, twisting, or other resistance activities
-Walking is the best exercise
-Goal is to increase posture and good body mechanics
What are some bracing considerations for osteoporosis in thoracic spine?
"Spinomed brace" provides extra stability and helps to strength abs (increases posture)
You are working with Suzy, a 55 y/o female who has just undergone a R THR with posterior THPs. Suzy is currently using a walker for mobility, and expresses her 3 main areas of concern as the following:
-Feeding her dog and cleaning the bowls
-Getting up from a chair
-Retrieving items from the fridge, including lower shelves
Simulate some of the above mentioned activities. What are the potential challenges she might face? Why will these be challenging?
-Bending down for the dog and fridge
-Twisting to get off of chair
You are working with Suzy, a 55 y/o female who has just undergone a R THR with posterior THPs. Suzy is currently using a walker for mobility, and expresses her 3 main areas of concern as the following:
-Feeding her dog and cleaning the bowls
-Getting up from a chair
-Retrieving items from the fridge, including lower shelves
How might you adapt some of these tasks so she can more easily participate?
-Getting a higher chair so she doesn't have to bend as low/with arms
-Raised dog bowl
-Reacher for fridge
You are working with Suzy, a 55 y/o female who has just undergone a R THR with posterior THPs. Suzy is currently using a walker for mobility, and expresses her 3 main areas of concern as the following:
-Feeding her dog and cleaning the bowls
-Getting up from a chair
-Retrieving items from the fridge, including lower shelves
Are there any other additional potential participation restrictions? Home, work, community, etc?
-Home environment (small home)
-Work environment
What is an amputation?
The general term used to describe loss of all or a portion of a body part
What are some of the causes for lower extremity amputations?
-Trauma/burn (typically in younger male population, MVA, military, industrial accidents)
-Peripheral vascular disease (condition where there is poor circulation. Most common cause of LE amp., commonly associated with DM, from poor oxygen supply to the LE’s)
-Diabetes Mellitus (DM) (wounds, lack of healing from poor blood supply)
-Infections (osteomyelitis, gangrene, to prevent septicemia)
-Non-healing fractures
-Tumors (cancer of the bone to prevent metastasis)
-Congenital
-Thermal injuries (heat or cold causing tissue damage)
-Elective amputation (previous injury which limits function)
What are some of the causes of upper extremity amputations?
-Trauma (accidents, burns, explosions)
-Malignancies
-Contractures
-Congenital deformities
-PVD
-Infections
-Neurological disorders
1.8 million people live with lower limb amputations. What percentage of these people live with each type of amputation?
-54% to PVD
-50% to DM
-45% to trauma
-1% other (tumor, infections, congenital)
How many lower limb amputations are performed every year?
185,000 amp/year. This number is expected to more than double by year 2050 to 3.6 million
How many upper extremity amputations are performed a year?
6,000 to 10,000 per year
What percentage of upper extremity amputations are trauma related?
70% of UE amp. are trauma related between the ages of 15-45
What are the different types of lower extremity amputations?
-Hemipelvectomy
-Hip Disarticulation
-Above knee or transfemoral
-Knee Disarticulation
-Below knee or transtibial
-Syme's
-Partial Foot/transmetatarsal
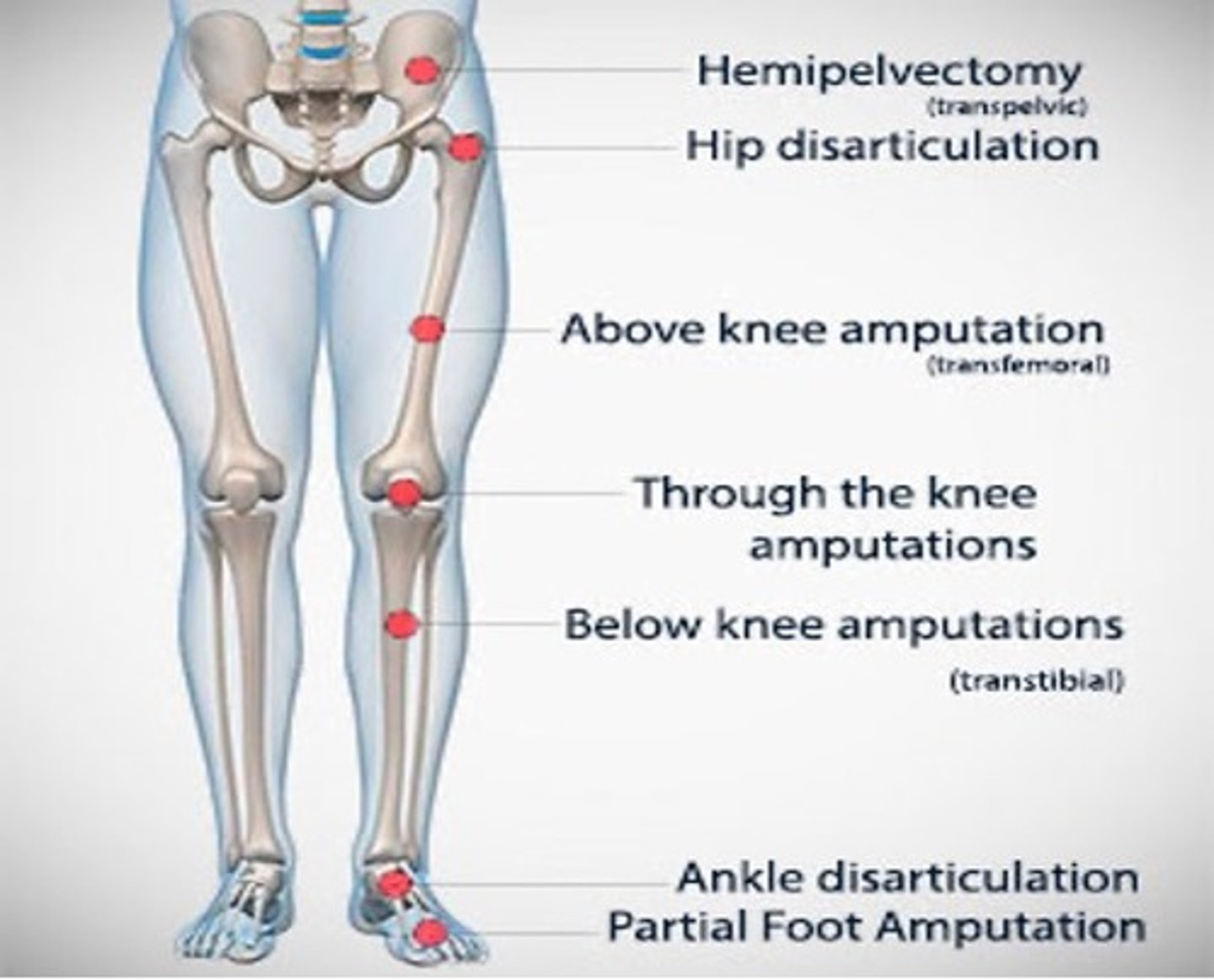
What is a hemipelvectomy?
Entire lower limb and half of the pelvis are removed
What is a hip disarticulation?
Removal of the leg at the hip joint
What is an above knee or transfemoral amputation?
Amputation between the hip and knee joints
What is a knee disarticulation?
Amputation at the knee joint
What is a Syme's amputation?
Removal of the foot at the ankle
What is a partial foot/transmetatarsal amputation?
Amputation of a portion fo the foot
What is the ratio between above the knee amputations (AKAs) and below the knee amputations (BKAs)?
-In the 1960s, it was 70 AKAs to 30 BKAs
-Currently, it is 30 AKAs to 70 BKAs