Developing Fuels
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
define: enthalpy, enthalpy change, standard conditions(ΔH°)
enthalpy- measure of heat content of a substance
enthalpy change-change in heat content at constant pressure
standard conditions((ΔH°)- 100kPa (1atms) and a stated temperature (usually 0c)
how do you go from celcius to kelvin
+273
define standard enthalpy change of reaction, formation, combustion, neutralisation
standard enthalpy change of reaction(ΔrH°)- enthalpy change for a reaction with the quantities shown in the equation
standard enthalpy change of formation(ΔfH°)-enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance is formed from its constituent elements with all reactants and products in standard states, under standard conditions
standard enthalpy change of combustion(ΔcH°)-enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance is completely burned in oxygen with all reactants and products in standard states under standard conditions
standard enthalpy change of neutralisation(ΔneutH°)-enthalpy change when 1 mole of water is formed in areaction between an acid and alkali in standard states under standard conditions
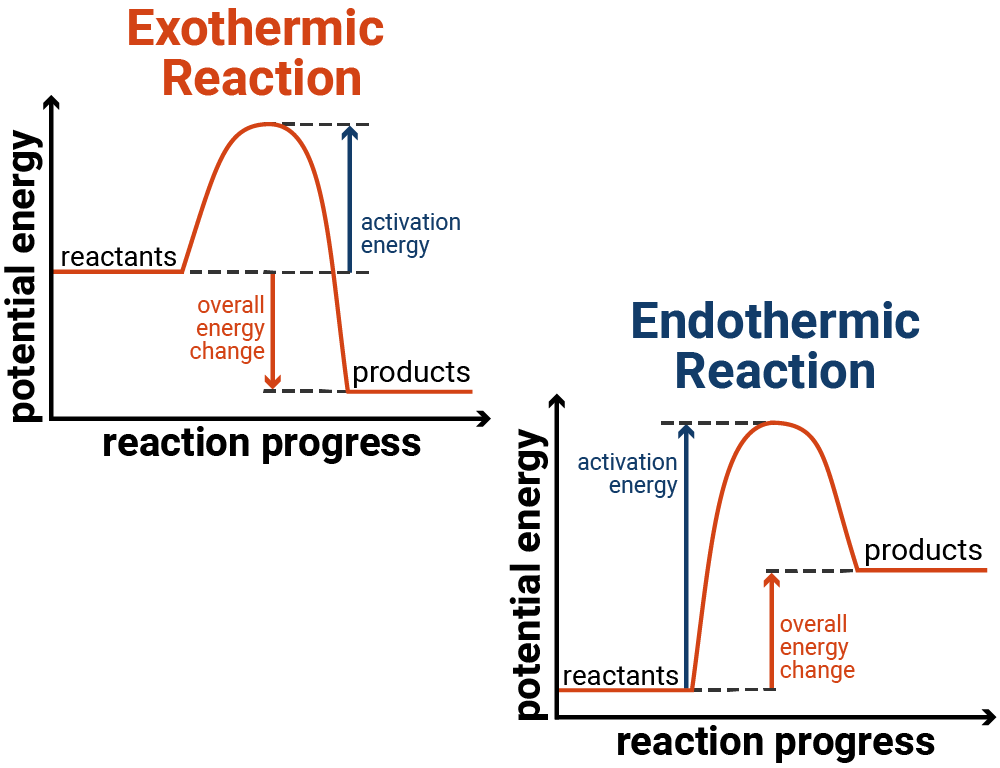
reaction profiles
exothermic e.g. combustion of a fuel
chemical energy→heat energy released so environment gets hot
energy change is negative
more energy released making new bonds than absorbed to break existing bondsendothermic
heat energy absorbed→chemical energy so environment gets colder
energy change is positive
more energy absorbed to break existing bonds than released making new bonds
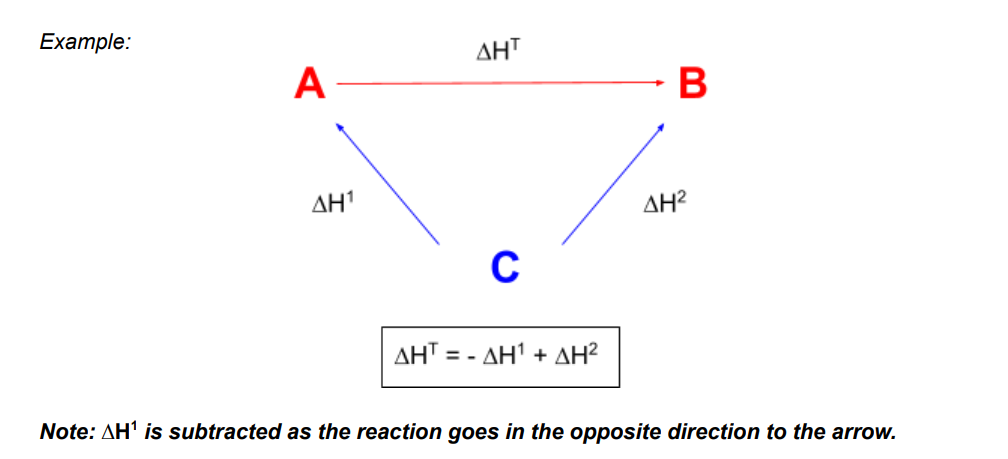
Enthalpy cycles and Hess’s law
Hess’ law is that the overall enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of the route that it takes
sometimes it is measured it is used to measure enthalpy change indirectly if the reaction is too slow, more than one product is formed, or the reaction has a very high activation enthalpy
coffee-cup calorimetry to determine enthalpy of neutralisation

bond enthalpy
bond enthalpy-energy needed to break one mole of a bond to give it separate atoms, all in gaseous states. average bond enthalpy-energy needed to break one mole of a bond to five separate atoms in gaseous state, averaged over a number of different compounds
when covalent bonds form, the atoms move together bc of attractive forces between the nuclei and electrons. There are also repulsive forces between both atoms’ nuclei that get bigger as the atoms approach, until the atoms stop moving together. The distance between them is now the equilibrium bond length.
The shorter the bond length, the stronger the attraction between the atoms so the shorter the bond, the higher the bond enthalpy.
triple>double>single in terms of bond enthalpy
△H=bonds broken-bonds made
bond enthalpies may be different to official values if the method doesn’t use standard conditions(bond enthalpies only apply to gaseous states) or if it uses the average bond enthalpy which may be different to the value for a bond in a particular compound
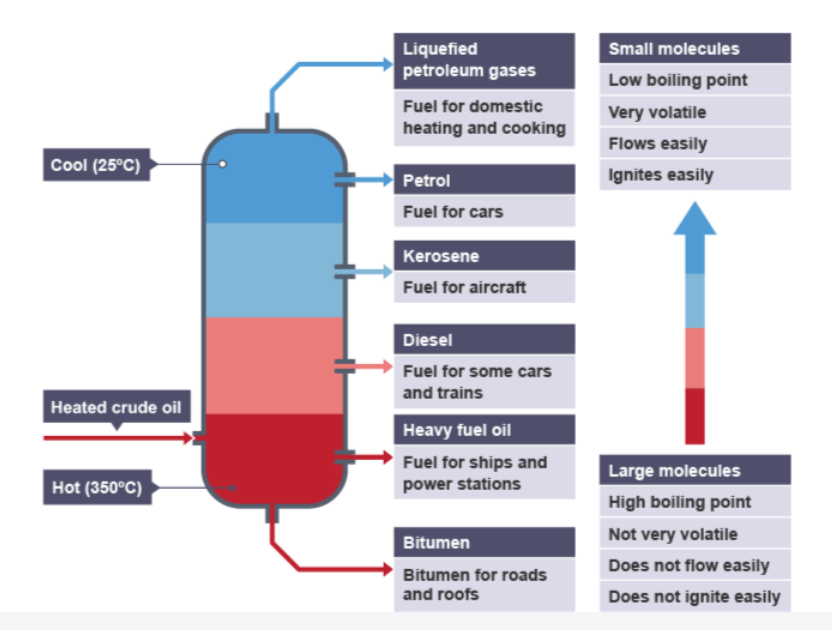
fractional distillation
heated crude oil enters a tall fractionating column, which is hot at the bottom and gets cooler towards the top
vapours from the oil rise through the column
vapours condense when they become cool enough
liquids are led out of the column at different heights
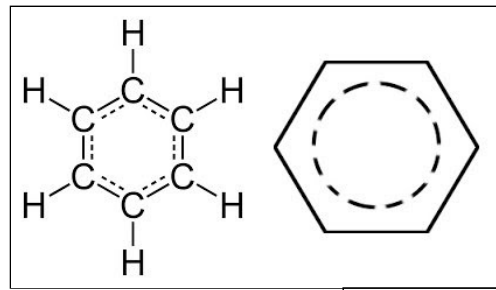
define aromatic compound, aliphatic compound, arene, cycloalkane functional group, homologous series
aromatic- contains one or more benzene rings. A benzene ring is a ring of six carbons each bonded to one hydrogen atom, so it also has a ring of delocalised electrons
aliphatic- does not contain any benzene rings
Cycloalkane- saturated, non polar ring of carbons
Arene- unsaturated(contains double bonds), aromatic ring w delocalised electrons
functional group- modifiers responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of molecules
homologous series- family of organic compounds that share the same functional group, general formula and similar chemical properties
alchools, alkenes and alkanes, and how to test for alkenes
alkanes:
saturated hydrocarbons-all carbon atoms are full of hydrogen bonds
general formula CnH2n+2
alkenes:
unsaturated hydrocarbons w at least one C=C
general formula CnH2n
the carbon double bond is an area of high electron density so it attracts electrophiles more. This means alkenes are more reactive than alkanes
alcohols:
general formula- CnH2n+1OH
functional group is OH
test for alkenes:
Alkenes cause bromine water to change from orange-brown to colourless because the C=C bond can break to accept bromine atoms and become saturated. The production of this reaction is a dibromo compound.
volumes of gases
one mole of any gas at room temperature and pressure will take up the same volume. moles * 24dm3 =gas volume at STP, 22.4= gas volume at RTP
RTP(room temp and pressure 25c, 1atm) STP(standard temp and pressure 0c 1atm)
for gases and volatile liquids pressure is proportional to temperature, volume is proportional to temp, pressure and vol are inversely proportional
m3 ×1000=dm3
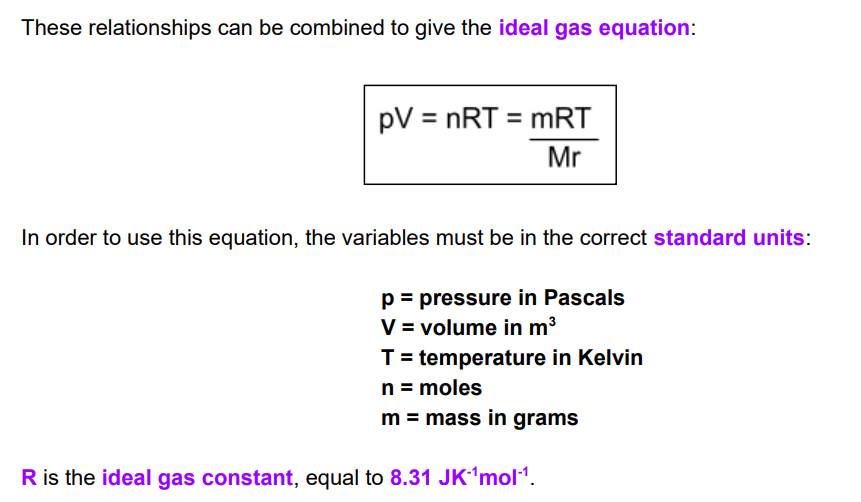
experimental techniques to measure gas volume
method 1: use a gas syringe to measure the volume of gas produced
method 2: measure the mass lost on a weighing balance and calculate the moles of gas produced from this
method 3: collect the gas released from a reaction in an upturned test tube filled with water. The water is displaced by gas, allowing its volume to be found.
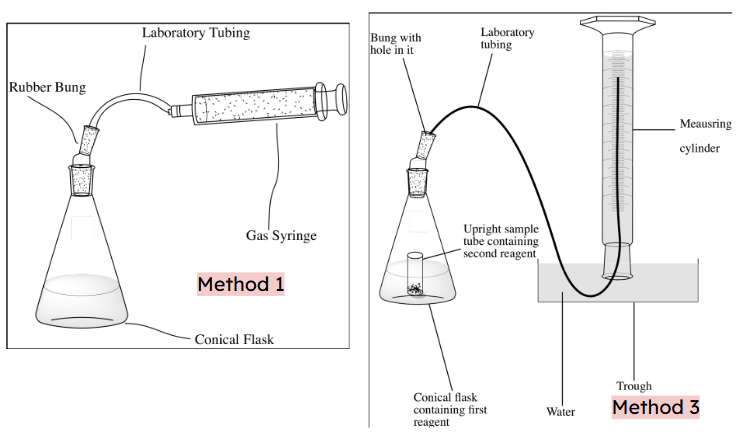
what are double bonds
single bonds are called σ bonds. The axial overlap of orbitals is directly between the two atoms and there is free rotation around the σ bond.
Double bonds consist of a σ bond and a π bond. The σ bond is formed by lateral overlap of p-orbitals above and below the plane
In a double bond the pi bond is weaker bc the electrons are above and below the plane of the molecule so experience a less strong attraction to the nuclei than the electrons in the sigma bond which are directly between the nuclei
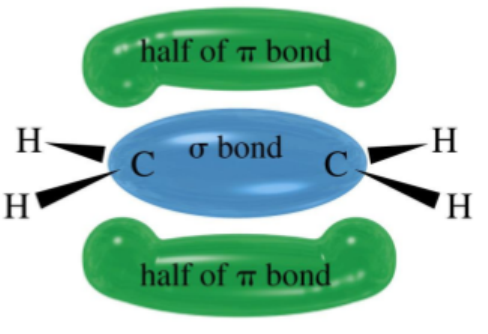
calorimetry
the experimental method for finding enthalpy change by measuring temperature change over time as reaction occurs
when recorded and plotted on a graph data can be extrapolated to give an accurate value for the change in temperature at the beginning of a reaction
q=mcΔT and ΔH= q/moles
q-energy change, m-mass, ΔT-temp change(C), c-specific heat capacity(J g-1°C-1), ΔH-enthalpy change- J mol-1
specific heat capacity- the energy required to raise the 1g of a substance by 1K without a change of state
4.18 for water
why may calorimetry/enthralpy values be innacurate
heat loss to surroundings- use insulating materials and lids, polystyrene cups(not for combustion bc it will burn)
incomplete combustion
non-standard conditions
in combustion- evapouration of fuel leading to incorrect mass being measured if you dont put a lid on the fuel burner instead of blowing it out
how does boiling point change as chain length of organic compounds increases, in pentant vs methylbutan which has a higher melting point
as organic chain length increases, boiling point also increases
pentane bc it is less branched so the molecules can pack closer together making the intermolecular forces stronger and require more energy to break
catalysts
catalysts lower the activation energy of a reaction by providing an alternative reaction route
heterogenous catalysts are catalysts that are ina different state/phase to the species in the reaction
how they work:
reactants are adsorbed(sticks to surface, not absorb) onto the surface of the catalyst active site
the active sites increase the proximity of molecules and weaken the covalent bonds in the molecules to allow reactions to occure more easily and reduce the activation enregy required, leading to a faster rate of reaction so new bonds can form
products then desorb from the catalyst surface
catalyst poisoning:
molecules e.g carbon monoxide irreversibly bond all around the catalyst so reactants cannot adsorb onto the surface
solutions- replace the catalyst but this is expensive and wasteful, react the catalyst in substances to remove poison but this is usually toxic, so the most common method is to mechanically remove a layer of catalyst and the poison
cracking
process used to convert long-chain hydrocarbons into shorter, more useful hydrocarbons by breaking bonds between carbons
thermal cracking- uses high temp and pressure
catalytic cracking- produced aromatic compounds w carbon rings. lower temps around 720K are used, and normal pressure is used, so a catalyst is needed to compensate for the less harsh conditions. The hydrocarbon vapour is passsed over heated catalyst such as zeolyte
nomenclature rules
prefix/stem tells you the length of the longest unbroken chain of carbon atoms
1-meth-, 2-eth-, 3-prop-, 4-but-, 5-pent-, 6-hex-, 7-hept-, 8-oct-, 9-non-, 10-dec-suffix/ending tells you the functional group
alkane -ane, alkene -ene, alcohol -olif a halogen is present it is also represented with a prefix
flourine fluoro-, chlorine chloro-, bromine bromo-, iodine iodo-side chains are branches from the longest carbon called alkyl groups. they use the stems (meth ect.) depending on how many carbons they have + the suffix -yl
additional rules:
functional group and side chains are given w the number corresponding to the carbon they are attached to
numbers are separated by commas
numbers and words are separated by hyphens
if multiple side chains or functional groups are present then the prefix di(2), tri(3) or tetra(4) are added
the carbon chain is numbered so that it adds up to the smallest number
if multiple prefixes are present, they are included in alphabetic order
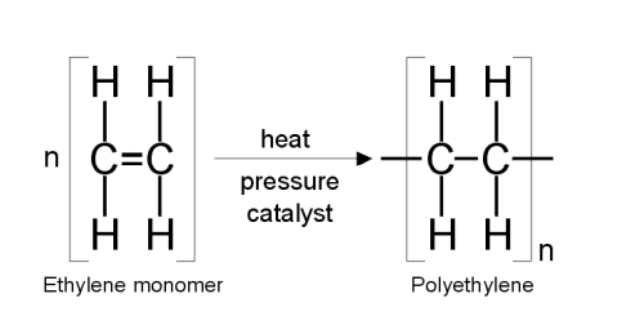
addition polymers
addition polymers are produced from alkenes when the double bond is broken to form a repeating unit. Either side of the double bond extends to connect 2 more monomers to it
an addition reaction is a reaction that joins two molecules together to make one product
formulae
molecular- actual number of atoms of each element in a compoiund
structural-shows the structural arrangement of atoms within a molecule
displayed-shows every atom and every bond
skeletal- shows bonds, vertices are carbon atoms, hydrogen is assumed to be bonded unless otherwise, goes in a zigzag
stereoisomers
stereisomers have the same structural formula but different spatial arrangement of atoms and bonds
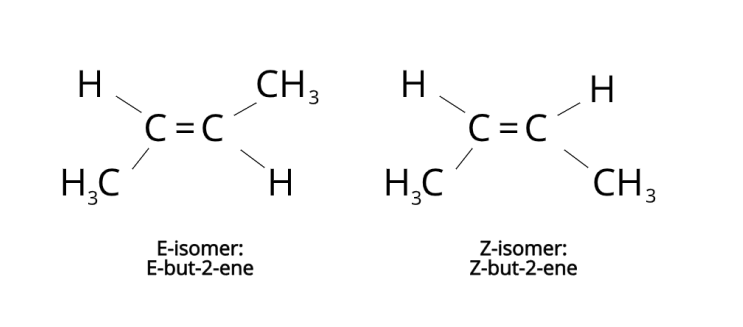
E-Z isomerism:
E-Z isomerism is in compounds with carbon double bonds bc there is no rotation around the double bond. Each carbon of the double bond must also be bonded to a hydrogen and one other atom/group
count the mr on each of the 4 parts
if the highest 2 parts are on the same line horizontally it is Z/cis isomer ‘zame zide’
if the highest 2 parts are across the double bond diagonally it is an E/trans isomer
if 2 parts vertically are the exact same than it is not an E-Z isomer bc there is no free rotation
optical isomers are an different stereoisomer
structural isomers
structural isomers have the same molecular formula but the atoms are bonded together in a different order
chain isomerism: when the carbon chain arrangement differs, only possible with 4 or more carbons in a chain e.g butane and 2-methylpropane
position isomerism: occurs when the functional group is situated in different positions in the molecules. e.g propan-1-ol, vs propan-2-ol
functional group isomerism: when compounds have the same molecular formula but different functional groups
emissions and sustainability
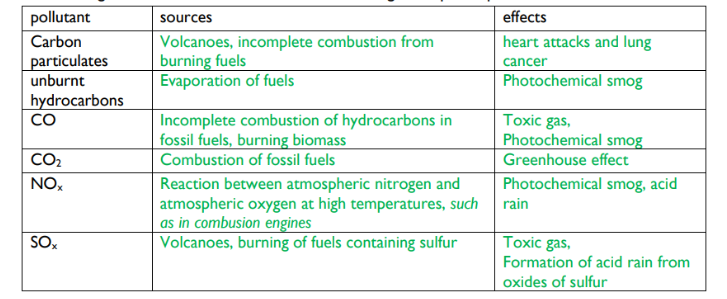
hydrocarbons: release lots of energy when burned. Produce carbon dioxide and water when they undergo complete combustion-with excess oxygen. Produce carbon monoxide and water or carbon and water in incomplete combustion-insufficient oxygen
carbon monixide: toxic gas that is colourless and oudorless. It replaces oxygen in blood and causes suffocation
oxides of nitrogen and sulfur: produced from reactions with air in hot car engines. In clouds they can react with water to form acids, resulting in acid rains that erods limestone buildings and statues and makes rivers and lakes acidic, killing marine life
carbon particulates: small fragments of unburned hydrocarbons from incomplete combustion, that cause respiratory problems and global dimming
photochemical smog: when primary pollutants such as nitrogen oxides react with sunlight to create secondary pollutants such as ozone O3, it causes respiratory problems
catalytic converters: remove unburnt hydrocarbons and oxides of nitrogen from systems. They use a rodium catalyst to convert harmful products into more stable products such as CO or C→CO2 and H2O and NO→N2
biofuels: biofuels are sustainable so their supply can be maintained at the rate it is being used
ethanol-common biofuel that is carbon neutral bc the carbon it releases when burn=carbon taken in by crops during growing process
hydrogen-carbon neutral as only product of its combustion is water
electrophillic additon
alkenes react w electrophiles and undergo electrophilic adddition about the double bond
electrophiles are electron acceptors that are attracted to areas of high electron density e.g HBr, Br2
halogen(Br2) + alkene=dihalogenoalkene
electrophillic addition is the reaction mechanism that shows how electrophiles attack the double bond in alkenes. When the double bond is broken, a carbocation forms-a carbon atom w only 3 bonds and has a + charge
when the double bond breaks, the atom goes to the carbon which already has the most hydrogens connected to it in the chain
curly arrows are used in mechanism to show the movement of a pair of electrons
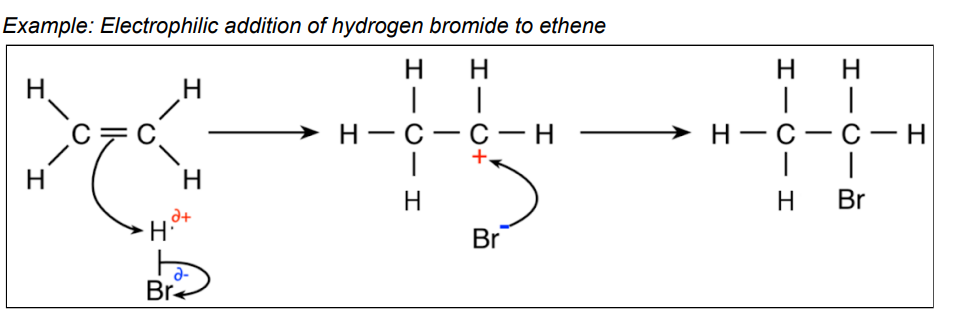
curly arrow rules
arrow must start where electrons come from- either the middle of a covalent bond, or from a lone pair
arrows finish where the electrons are going:
to an atom-they become an extra lone pair
to the area between 2 atoms, a bond forms between those 2 atoms
to a single bond, then it becomes a double bond
alkene addition reactions with hydrogen and water
reaction w hydrogen to form alkanes : needs a nick catalyst+high temp and pressure or a platinum catalyst+room temp and pressure
water to form alcohols: sulfuric acid and then add water or steam + phosphoric acid+high temp and pressure