Financial Accounting
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
Accounting
Providing information to external users.
External Users
Lenders (creditors), Shareholders (investors), External auditors, Non Managerial and non executive and labor unions, regulators, voters, gov officials, contributors, suppliers, customers.
Internal Users
managers
Financial accounting
Needs of external users
Managerial accounting
focus on needs of internal users
Tax accounting
focus on tax filing, planning, and compliance
Financial Accounting opportunities
Financial, Managerial, Taxation, Accounting related.
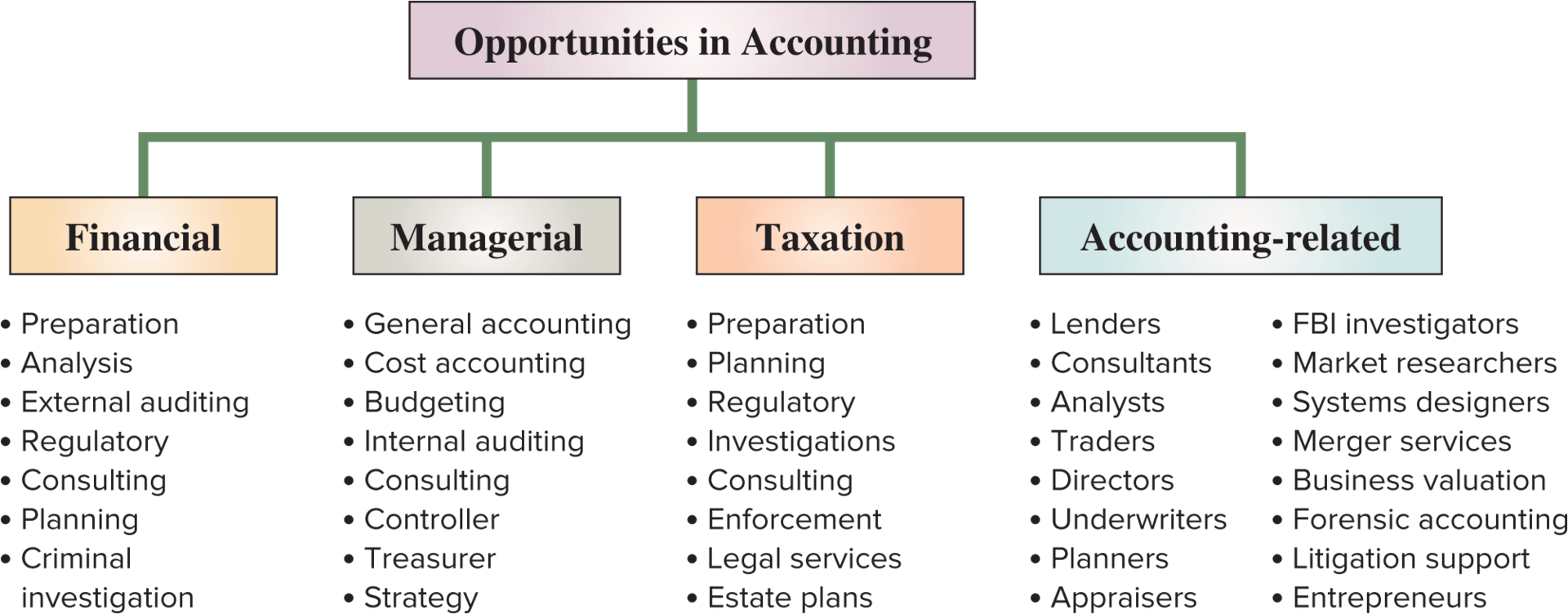
Private accounting
Employees working businesses, internal users.
Public accounting
auditing, taxation, and advisory services. External users.
CPAs (Certified Public Accountants)
Accountants that must meet education and experience requirements, pass an exam, and be ethical.
Data analytics
A process of analyzing data to identify meaningful relations and trends.
There are four types of analytics.
Descriptive, Diagnostic, Predictive, Prescriptive
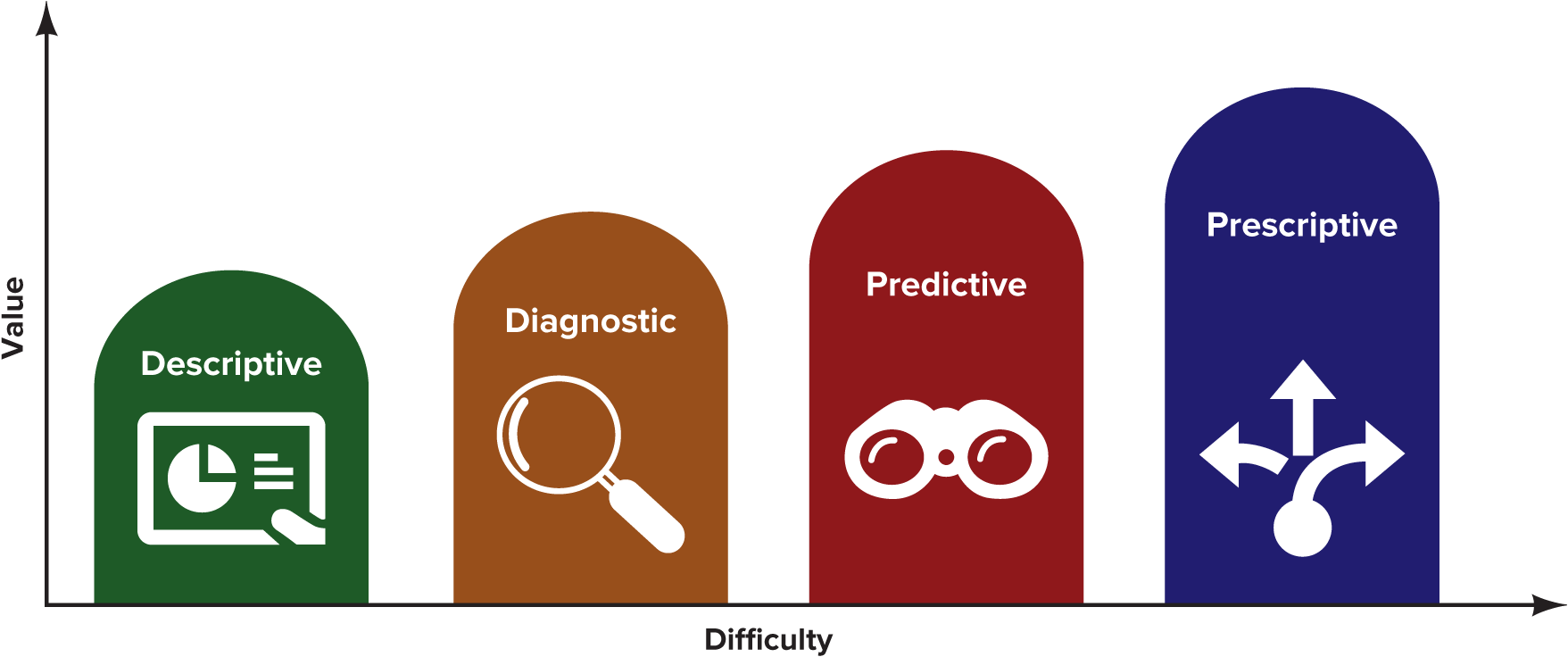
Descriptive analytics
Summarizes and describes events from the past
Diagnostic analysis
reveals causes of events from the past
Predictive analytics
predicts likely events for the future
Prescriptive analytics
creates action plans to achieve a desired future
Data visualization
A graphical presentation of data to help people understand its significance and draw reliable inferences.
Ethics
Codes of conduct by which actions are judged as right or wrong, fair or unfair, honest or dishonest.
Three step process in making ethical decisions?
Identify ethical concerns, analyze options, and make a ethical decision.
Fraud triangle
(ORP)
Opportunity: must be able to commit fraud with a low rish of getting caught
Pressure: person must feel pressure or have incentive to commit fraud
Rationalization: person justifies fraud or doesn’t see it’s criminal behavior.
To help companies prevent fraud, companies set up…
internal controls
Internal controls or internal control system
All policies and procedures used to protect assets, ensure reliable accounting, promote efficient operations, and urge adherence to company policies.
Auditors
Individuals hired to review financial reports and information systems. Internal auditors of a company are employed to assess and evaluate its system of internal controls, including the resulting reports. External auditors are independent of a company and are hired to assess and evaluate the “fairness” of financial statements (or to perform other contracted financial services).
Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP)
Rules that specify acceptable accounting practices.
Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)
Independent group of full-time members responsible for setting accounting rules (GAAP).
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
Federal agency Congress has charged to set reporting rules for organizations that sell ownership shares to the public. They oversee proper use of GAAP
Audit
Analysis and report of an organization’s accounting system, its records, and its reports using various tests.
International Accounting Standards Board (IASB)
Group that identifies preferred accounting practices and encourages global acceptance; issues International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
Set of international accounting standards explaining how types of transactions and events are reported in financial statements; IFRS are issued by the International Accounting Standards Board.
FASB conceptual framework (aka how they prep financial statements for external users)
Objectives, Qualitative characteristics, Elements, and Recognition/Measurement
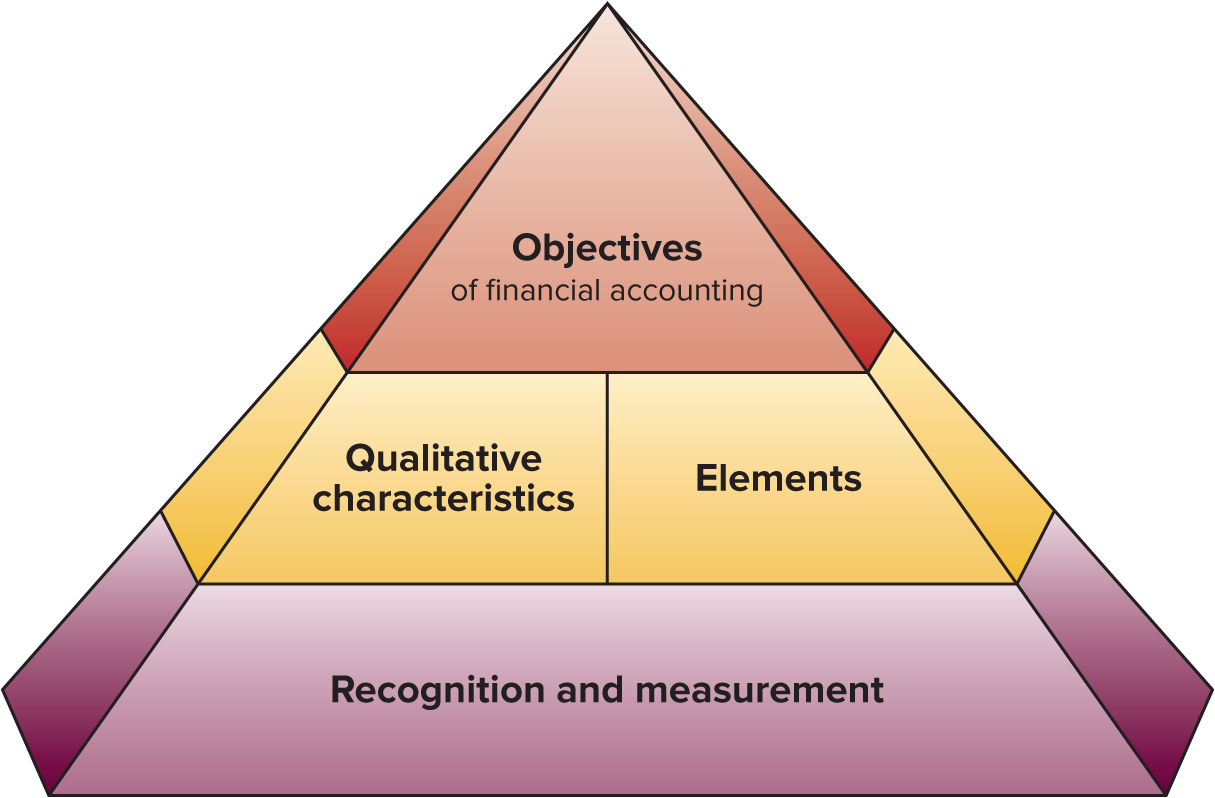
Objectives in FASB framework
to provide into useful for investors, creditors, and others.
Qualitative characteristics for FASB framework
to require info that has relevance and faithful representation
Elements in FASB framework
to define items in financial statements
Recognition and measurement in FASB framework
to set criteria for an items to be recognized as an element; and how to measure it.
General principles vs Specific principles
General: the assumptions, concepts, and guidelines for preparing financial statements.
Specific: detailed rules used in reporting business transactions and events; they are described as we encounter them.
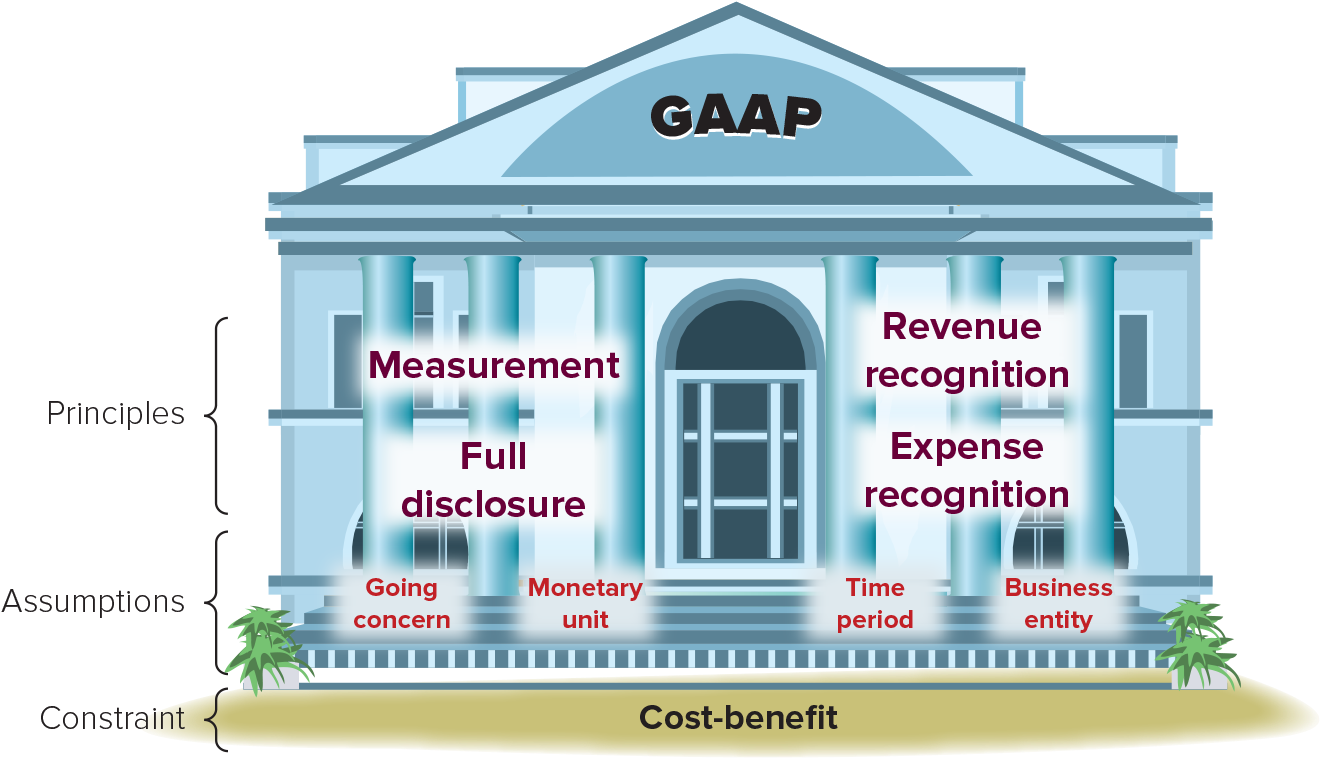
What are the four types of accounting principles?
Measurement (Cost), Revenue recognition, Expense recognition, and full disclosure principle.
Measurement principle
Principle that prescribes financial statement information, and its underlying transactions and events, be based on relevant measures of valuation; also called the cost principle.
Revenue recognition principle
The principle prescribing that revenue is recognized when goods or services are delivered to customers.
Expense recognition (or matching) principle
Prescribes expenses to be reported in the same period as the revenues that were earned as a result of the expenses.
Full disclosure principle
Principle that prescribes financial statements (including notes) to report all relevant information about an entity’s operations and financial condition.
What are the four types of accounting assumptions?
Going-concern assumption, Monetary unit assumption, Time period assumption, and Business entity assumption.
Going-concern assumption
Principle that prescribes financial statements to reflect the assumption that the business will continue operating.
Continuity
Goes with going-concern.
Monetary unit assumption
Principle that assumes transactions and events can be expressed in money units.
Time period assumption
Assumption that an organization’s activities can be divided into specific time periods such as months, quarters, or years.
Business entity assumption
Principle that requires a business to be accounted for separately from its owner(s) and from any other entity.
Cost-benefit constraint
The notion that the benefit of a disclosure exceeds the cost of that disclosure.
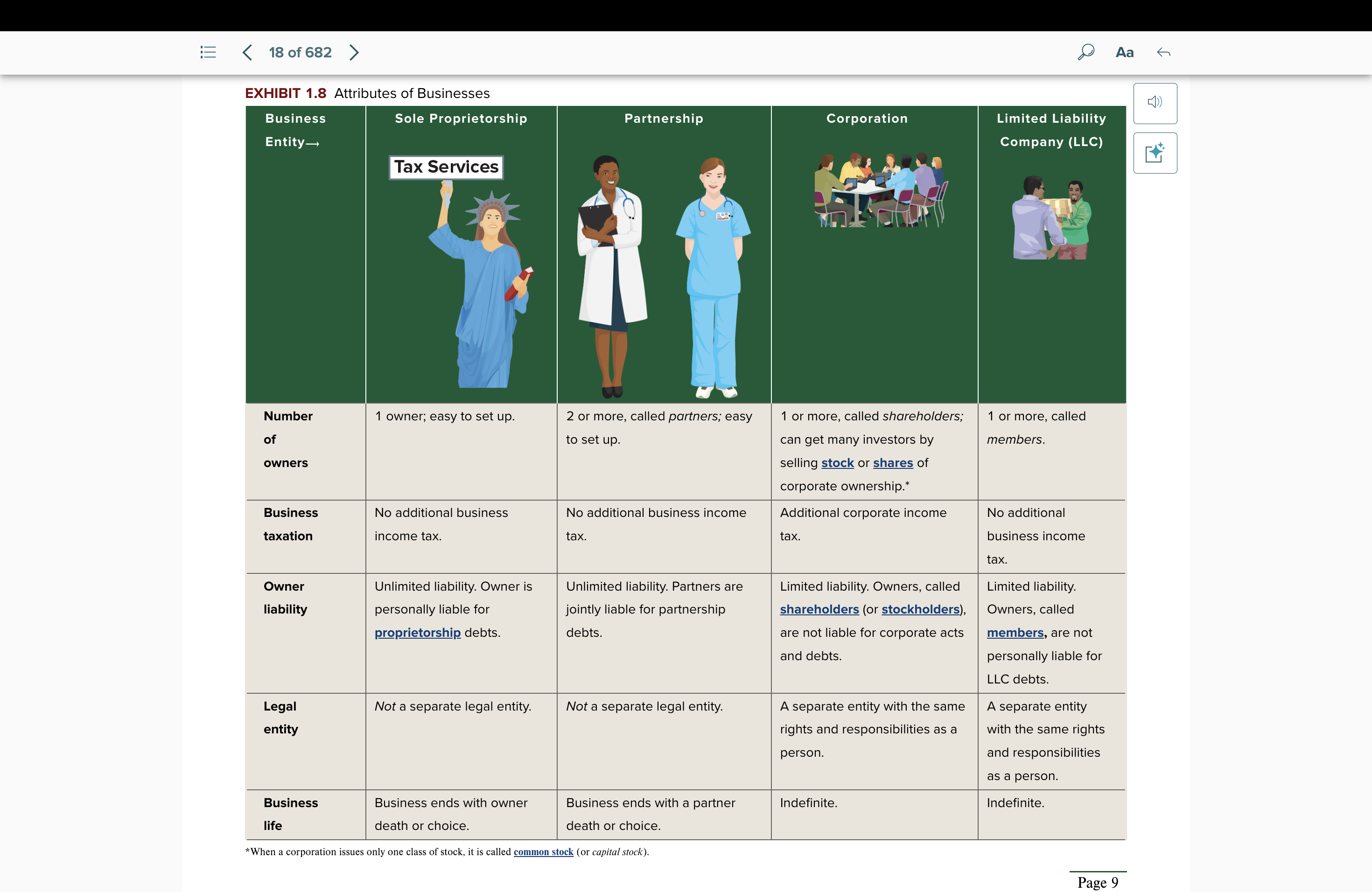
Attributes of Businesses: Sole Proprietorship
no. of owners: 1 owner, ez to set up
business tax: none
owner liability: unlimited liability. personally liable.
legal entity: not a separate legal entity
business life: ends with owner’s death or choice
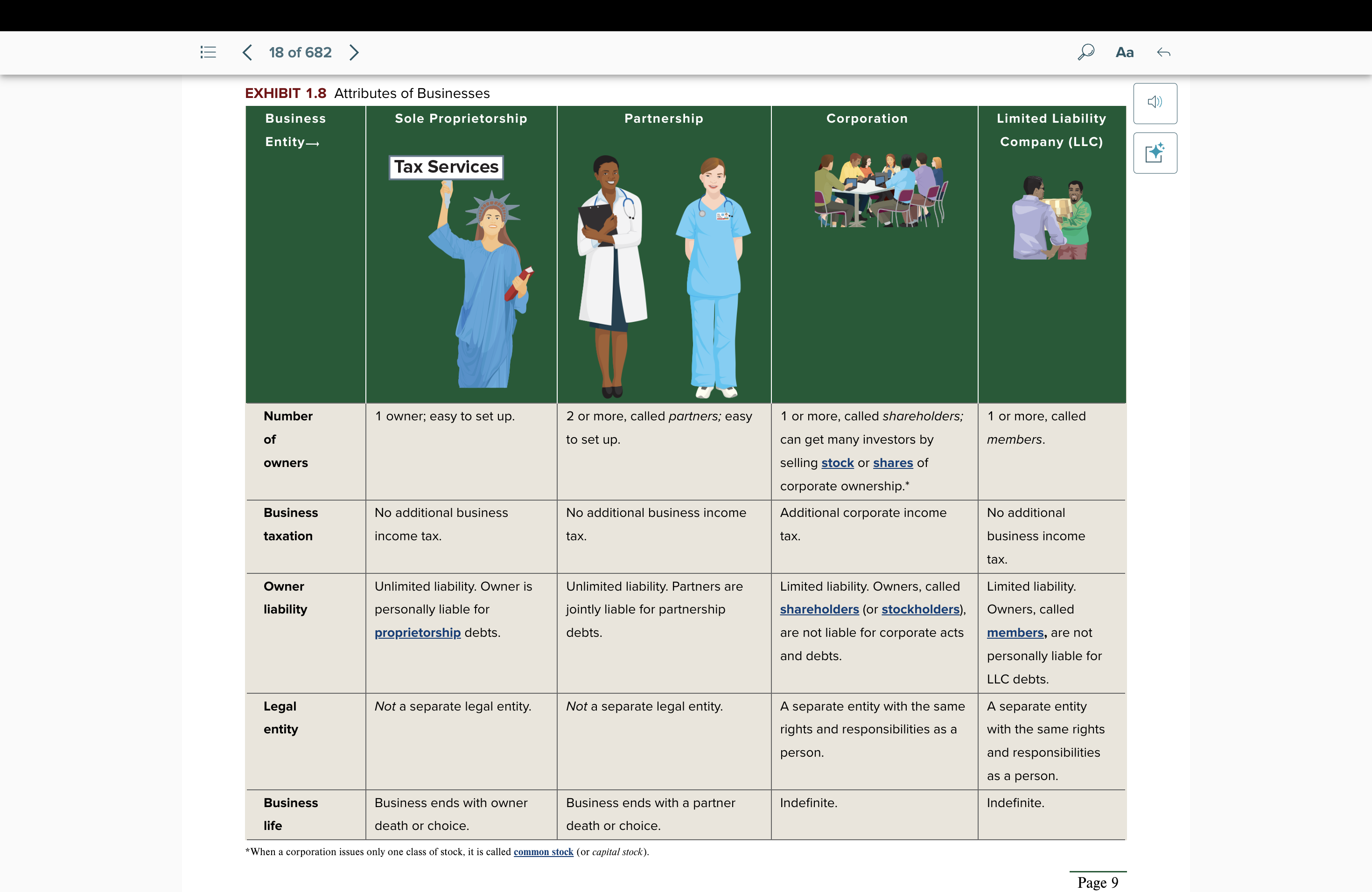
Partnership
no. of owners: 2 owners or more, ez to set up
business tax: none
owner liability: unlimited liability. joint liableness.
legal entity: not a separate legal entity
business life: ends with a partner death or choice
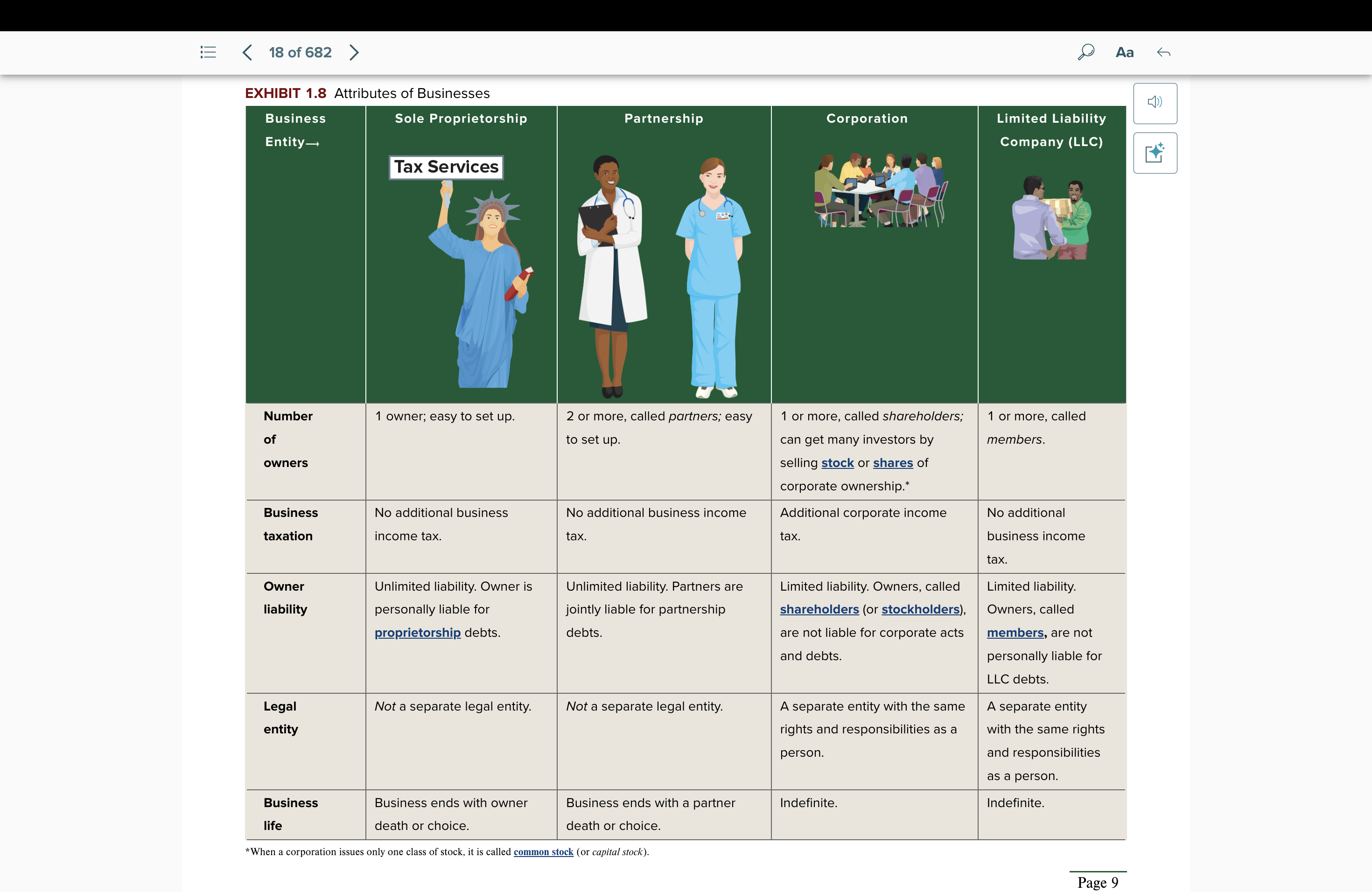
Corporation
no. of owners: 1 or more, shareholders; can get many investors by selling stock or shares of corporate ownership
business tax: additional corporate income tax
owner liability: limited liability. not liable.
legal entity: a separate legal entity
business life: indefinite
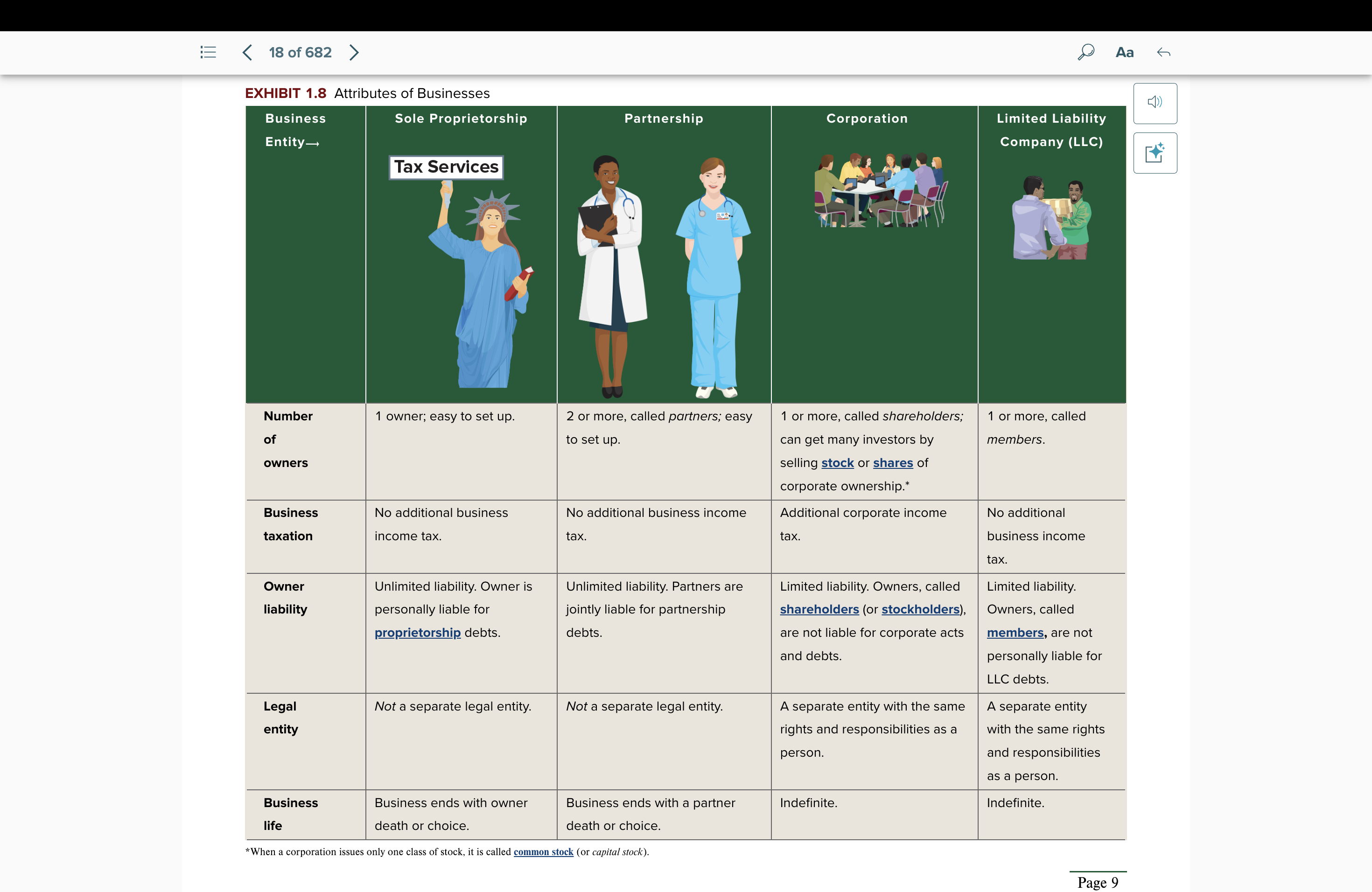
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
no. of owners: 1 or more, members
business tax: no additional business income tax
owner liability: limited liability. not liable.
legal entity: a separate legal entity
business life: indefinite
Assets
Resources a business owns or controls that are expected to provide current and future benefits to the business.
Recievable
an asset that promises a future inflow of resources.
Liabilities
Creditors’ claims on an organization’s assets; involves a probable future payment of assets, products, or services that a company is obligated to make due to past transactions or events.
Equity
Owner’s claim on the assets of a business; equals the residual interest in an entity’s assets after deducting liabilities; also called net assets or owner’s equity.
Accounting equation
Equality involving a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity; Assets = Liabilities + Equity; also called balance sheet equation.
Expanded accounting equation
Expanded version of: Assets = Liabilities + Equity. For a noncorporation: Equity = Owner’s capital − Owner’s withdrawals + Revenues − Expenses. [For a corporation: Equity = Contributed capital + Retained earnings + Revenues − Expenses − Dividends.]
Owner investments
Assets put into the business by the owner.
Whats in a Income statement
Revenues - Expenses = Net income.
Net income
Amount earned after subtracting all expenses necessary for and matched with sales for a period; also called income, profit, or earnings.
Net loss
Excess of expenses over revenues for a period.
Retained Earnings
Retained earnings, start date.
+ Net income
- Dividends
Retained earnings, end date
Balance sheet
Assets and total assets, Liabilities and total liabilities, and Equity: Common stock, Retained earnings, Total equity, and total liabilities and equity.
Cash flows
operating activities, investing activities and financing activities
Source documents
Source of information for accounting entries that can be in either paper or electronic form; also called business papers.
Account
Record where increases and decreases are entered and stored in a specific asset, liability, equity, revenue, or expense.
General ledger
Record containing all accounts (with amounts) for a business; also called ledger. You post your info for each account here.
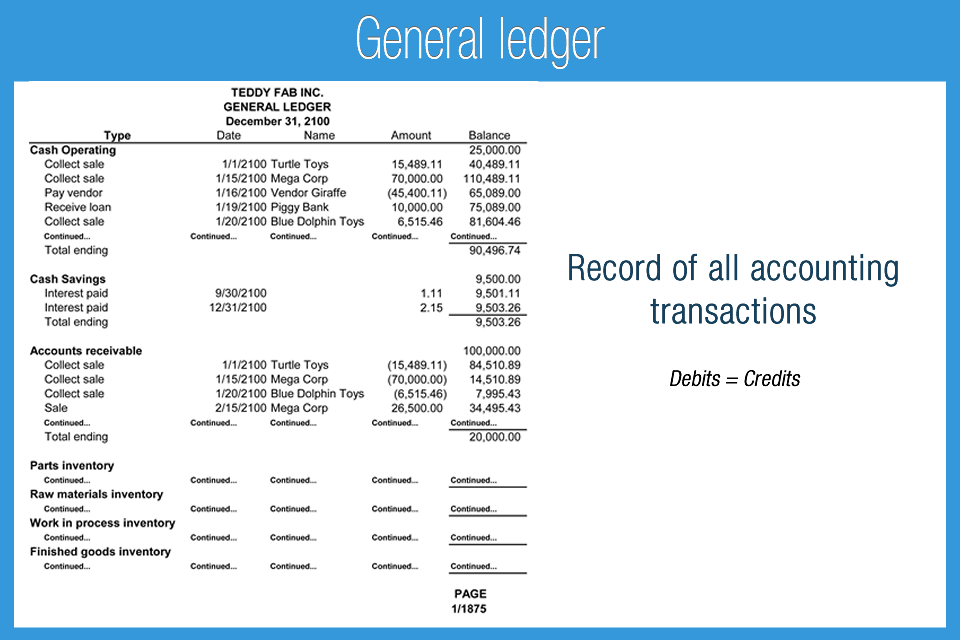
Most accounting systems include ____ accounts for assets, liabilities, equity.
separate
Notes recievable: assets
a written promise of another entity to pay a specific sum of money on a specified future date to the holder of the note. Usually require interest, whereas accounts receivable doesn’t.
Prepaid Accounts (expenses): assets
assets from prepayments of future expenses. (prepaid rent, insurance, etc.)
unearned revenue: liability
Liability created when customers pay in advance for products or services; earned when the products or services are later delivered.
Accrued liabilities
amounts owed that are not yet paid
Owner Investments are…
Common stock
Owner Distributions is…
Dividends
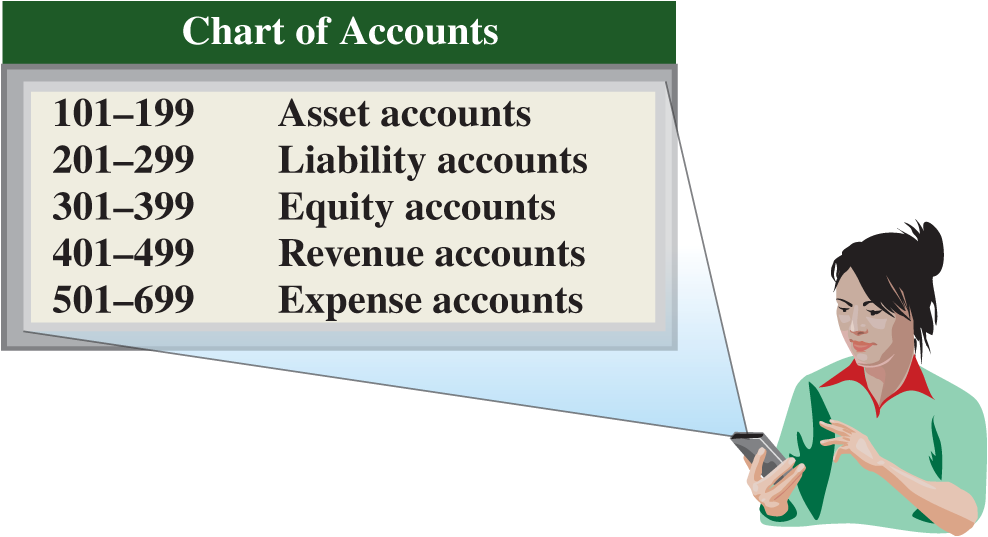
Chart of accounts
List of accounts used by a company; includes an identification number for each account.
Key words: Prepaid, Recievable
Asset
Key words: Payable, Unearned
Liability
T-Account
Tool used to show the effects of transactions and events on individual accounts; shaped in the form of a T.
T-Account: Debit side
Recorded on the left side; an entry that increases an asset or expense account, or decreases a liability, revenue, or equity account; abbreviated Dr.
T-Account: Credit side
Recorded on the right side; an entry that decreases an asset or expense account, or increases a liability, revenue, or equity account; abbreviated Cr.
Account balance
Difference between total debits and total credits (including the beginning balance) for an account. There’s debit and credit balance.
Double-entry accounting
Accounting system in which each transaction affects at least two accounts and has at least one debit and one credit. Both should be equal.
Assets increase on the…
left
Liabilities and Equity increase on the…
right
Posting
Process of transferring journal entry information to the ledger; computerized systems automate this process.
General journal
All-purpose journal for recording the debits and credits of transactions and events.
Posting reference (PR) column
A column in journals in which individual ledger account numbers are entered when entries are posted to those ledger accounts.
Trial balance
List of ledger accounts and their balances (either debit or credit) at a point in time; total debit balances equal total credit balances.
Periodicity
We break time down into specific periods.
Annual financial statements
Financial statements covering a one year period; often based on a calendar year, but any consecutive 12-month (or 52-week) period is acceptable.
Interim financial statements
Financial statements covering periods of less than one year; usually based on one-, three-, or six-month periods.
Fiscal year
Consecutive 12-month (or 52-week) period chosen as the organization’s annual accounting period.
Accrual basis accounting
Accounting system that recognizes revenues when goods or services are provided and expenses when they happen; the basis for GAAP.
Cash basis accounting
Accounting system that recognizes revenues when cash is received and records expenses when cash is paid. Doesn’t account for prepaid or unearned things.
Adjusting entry
Journal entry at the end of an accounting period to bring an asset or liability account to its proper amount and update the related expense or revenue account.
Deferred expenses equals…
prepaid expenses/assets
Plant assets
Tangible long-lived assets used to produce or sell products and services; also called property, plant and equipment(PP&E) or fixed assets.
Depreciation
Expense created by allocating the cost of plant and equipment to periods in which they are used; represents the expense of using the asset.
Accumulated depreciation
Cumulative sum of all depreciation expense recorded for an asset.
Contra account
Account linked with another account and having an opposite normal balance; reported as a subtraction from the other account’s balance.
Ex: Accumulated Depreciation