Plant Systematics - Exam 1
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Synapomorphy
shared derived trait that’s present in a group of organisms and their common ancestor
Whorled leaves
more than two leaves per node
Basal leaves
leaves that grow at the base of the plant/stem

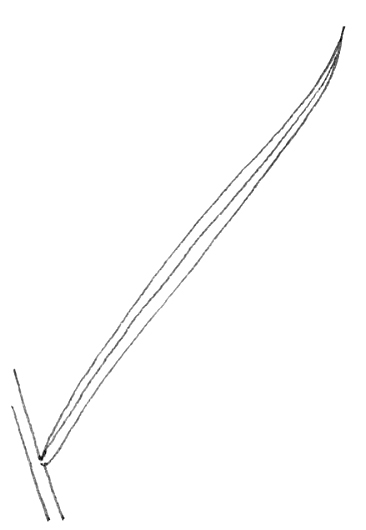
describe the leaf shape
elliptical
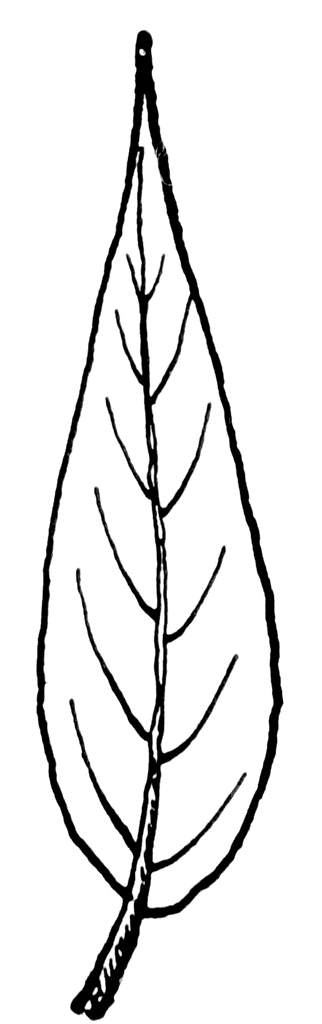
describe the leaf shape
linear
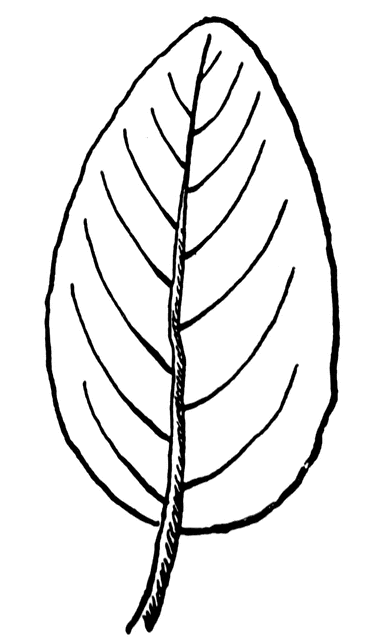
describe the leaf shape
lanceolate
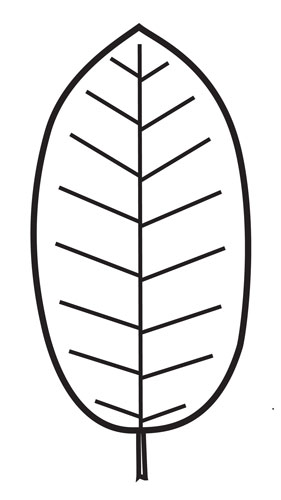
describe the leaf shape
ovate
describe the leaf shape
oblong
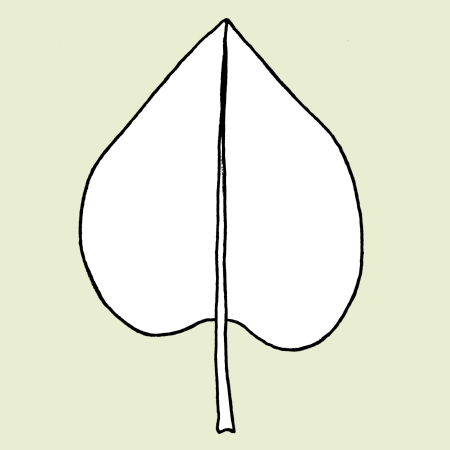
describe the leaf shape
cordate
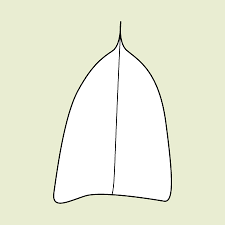
describe the leaf apex
acuminate
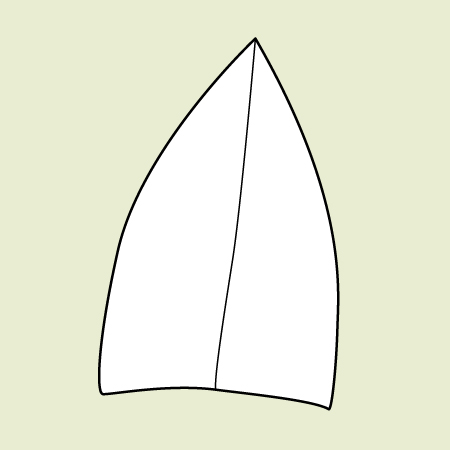
describe the leaf apex
acute

describe the leaf apex
obtuse

describe the leaf margin
crenate

describe the leaf margin
denate
Indument
hairs on a plant
Stipules
paired or sheathing (wrapped around stem). Little flaps of tissue near the base of the petiole
Tendrils
modified stem or leaf used for climbing
Thorns
modified branch, come out from auxiliary buds and at the node
Spines
modified leaves or stipules, usually paired
Prickles
outgrowth of epidermis, can be anywhere on the plant
Rhizome
horizontal stem, usually underground
Bulb
compact underground stem
Tuber
thickened stem or roots, usually full of starches for storage
Liana
a woody vine
Carpel
female reproductive unit of a flower
Sepal
1st whorl: the green, leaf-like part of a flower (isn’t always green), protects developing flower
Calyx
what sepals are collectively called. All sepals on a flower
Petals
2nd whorl: brightly colored to attract pollinators
Corolla
what petals are collectively called. All petals on a flower
Perianth
term used to describe both calyx and corolla together
Stamen
3rd whorl: pollen producing structure. 2 parts: anther and filament
Androecium
what stamen are collectively called. All stamen in a flower
Pistil
4th whorl: seed producing structure, comprised of carpel(s).
Gynoecium
what pistils are collectively called. All the pistils in a flower
Stigma
part of carpel that’s the landing pad for pollen
Style
part of carpel where the pollen tube passes down
Ovary
enlarged basal part of carpel, contains one or more ovules (which will eventually become seeds)
What is the order that pollen travels?
stigma→style→ovary
Perfect flowers
flower has both stamens and pistil(s)
Imperfect flowers
flowers that have the stamens or pistils that are highly reduced so they don’t function. Only one of the two works
Monoecious
A single plant has staminate and pistillate flowers
Diecious
Male or female plants, will only have either staminate or pistillate flowers
Connate fusion
when parts of the same whorl are fused together
Adnate fusion
when parts of adjacent whorls are fused together (stamens + petals, or pistil + stamens)
Hypanthium
fusion of sepals, petals, and stamens, can form a cup-like structure
Radially symmetrical/actinomorphic
can be cut anywhere and folded in half and be symmetrical
Bilaterally symmetrical/zygomorphic
can be cut in half in only one spot and be symmetrical
Superior ovary
ovary is above the other whorls, sepals “below” the fruit
Half-inferior ovary
ovary is in the middle of the whorls, between superior and inferior
Inferior ovary
ovary below the other whorls, sepals “above” the fruit
Inflorescence
the arrangement of flowers
Indeterminate inflorescence
oldest growth towards the base of the stem, youngest growth at the tip
Determinate inflorescence
youngest growth towards the base of the stem, oldest towards the tip

What type of inflorescence is this?
receme, flowers of pedice
Peduncle
axis that stems all the flowers
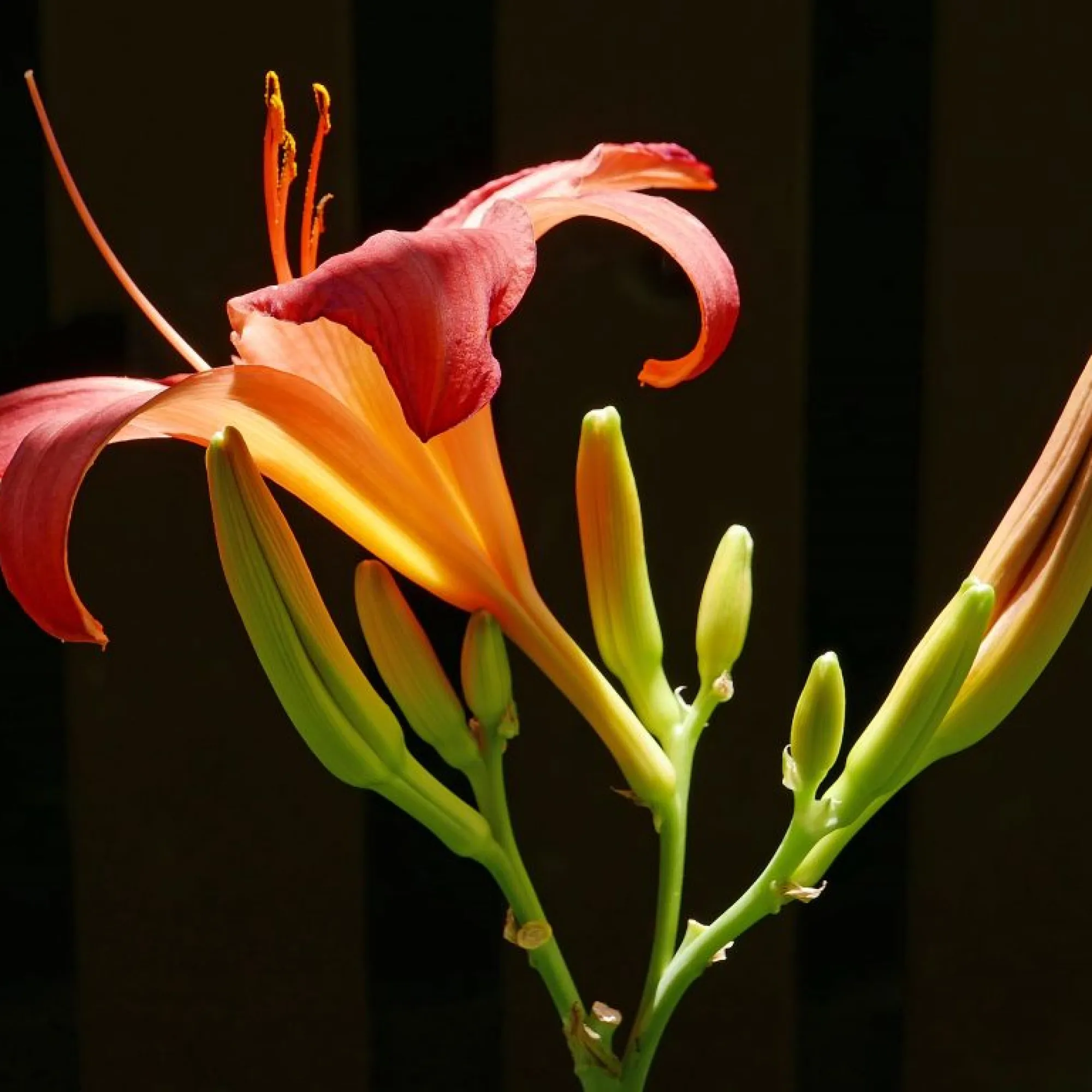

What type of inflorescence is this?
cyme, indeterminate. Central flower develops firs
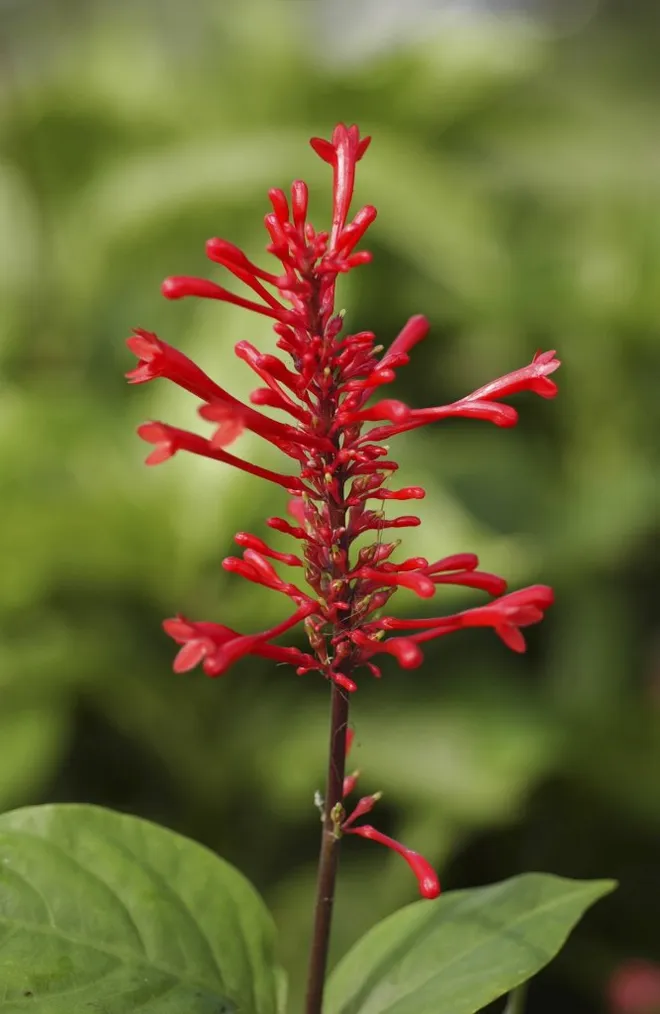

What type of inflorescence is this?
spike, flowers are sessile (no pedicels)

What type of inflorescence is this?
Panicle, branched lateral axis
Sessile
flowers that lack a pedicel (a little stem)

What type of inflorescence is this?
Umbel, flat-topped, pedicels attach at one point
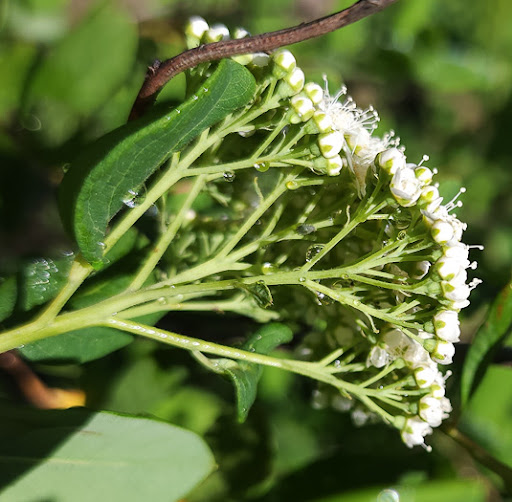

What type of inflorescence is this?
Corymb, pedicels attach at more than one point
Fruit
seed bearing structure derived from an ovary/ovaries
Pericarp
what the endocarp, mesocarp, and exocarps are collectively called
Simple fruit
fruits that come from one pistil (can be simple pistil or compound pistil)
Aggregate fruit
fruit that come from many simple pistils together (that are all from the same flower)
Multiple fruit
fruit that come from many flowers
Accessory fruit
aggregate or multiple fruit embedded in non-ovary tissue
Dehiscent fruits
splits open along seam to release seeds
Indehiscent fruits
fruit that doesn’t split open to release seeds
Follicle
derived from simple pistil, has one locule, splits open along one seam
Legume
derived from simple pistil, splits open along two seems
Loment
legume that breaks into one-seeded pieces
Capsule
derived from compound pistil, multiple locules, opens along joined seams
Schizocarp
one seed per locule, splits apart into one-seededunits
Locule
chamber within an ovary/fruit
Achene
single-seeded indehiscent fruit, seeds held loosely within hardened pericarp
Nut
single-seeded indehiscent fruit, seed is fused to a hardened pericarp, usually with involucer
Involucer
cup-like structure derived from bracts
Berry
has one or more seeds, has fleshy pericarp, usually has “skin” or “rind”
Drupe
has one seed that’s surrounded by a “pit” (hardened endocarp)
Marginal placentation
seeds attached along a single line along the ovary wall, fruits w/ simple pistil and one locule
Parietal placentation
seeds attached along several lines along the ovary wall, fruits w/ compound pistil and one locule
Axile placentation
seeds attached along the central column, fruits w/ compound pistil and multiple locules
Free-central placentation
seeds attached along the central column, fruits w/ compound pistil and one locule
Basal placentation
a single seed attached at the base of the ovary
Monocots
leaf venation parallel, flower parts in multiples of 3, never woody
Water lilies, magnolias, and relatives
not monophyletic, flower whorls poorly differentiated (spiraled), strong odors
Dicots
leaf venation netted, flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5
Rosids (dicots)
petals not fused, stamen # greater than petal #, stamens not fused to petals
Asterids
petals connate, stamen # equal or less than petal #, stamen adnate to petals
Bract
modified leaf in an inflorescence
Araceae
rhizome or tuber, huge variation in size, inflorescence is a spathe and spadix, flowers tinyP(a)4-6(or 0), A 1-6, G 1-3 (g is circled and underlined)
Alismataceae
rhizomes, basal leaves, latex, inflorescence is receme or panicle, radially symmetrical, fruit aggregate of achenes. Ca3, Co(a)3, A6-infinity, G6-infinity
Juncaceae
rhizomes, rush family, leaves basal and round, inflorescence: congested cyme, flowers bisexual. P(a)6, A6, (G3) (circle and line under)
Cyperaceae
sedge family, sometimes rhizomatous, stems solid and triangular, leaves in 3 ranks and sheaths closed, often monoecious
Poaceae
grass family, stem internodes hollow, leaves in 2 ranks, sheaths open, leaves with ligules. A3, G2
Spikelet
one or more flowers and bracts
Glumes
bracts at the base of the spikelet
palea and lemma
bracts at the base of each flower