Chapter 20: The Limbic System
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
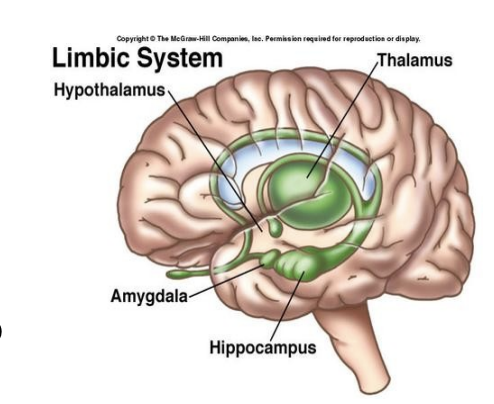
The limbic system and hypothalamus is responsible for what?
The limbic system + hypothalamus = foundation of:
emotional behavior
motivational behavior
drives (hunger, sex, fear, reward)

What are the two cortical structures that makes up the limbic lobe? What are they connected by?
2 cortical structure
Cingulate gyrus
Parahippocampal gyrus
These are interconnected by a subcortical fiber bundle called the cingulum
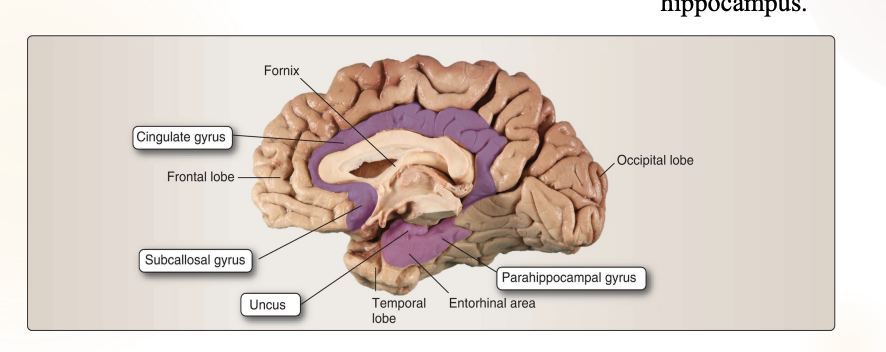
What are the subcortical structures in the limbic system? What are they responsible for?
Hippocampus → learning and memory
Amygdala → emotion + drives
Septal nuclei → reward mechanism
Uncus → over amygdala and anterior of the hippocampus
What is the amygdala responsible for?
important role in emotion and behavior.
Processing of fear- PTSD
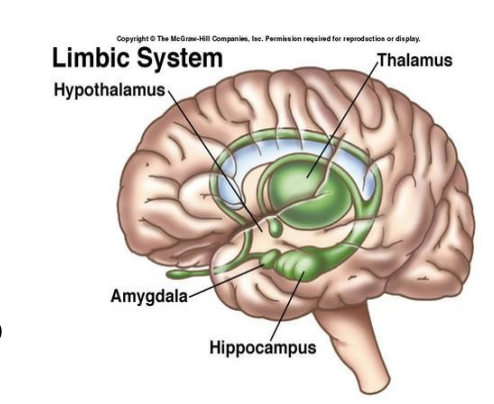
What is the hippocampus responsible for?
embedded deep in the temporal lobe of each cerebral cortex.
Sea-horse shaped, new learning, memory, navigation
HM- the man with no memory
What is the thalamus responsible for?
Gatekeeper” for the cortex.
regulation of sleep, consciousness, alertness.
critical processing station for all sensory information (except olfactory)
helps integrate higher-order cognitive and emotional information,

What is the hypothalamus responsible for?
It is structurally part of the diencephalon but functionally part of the limbic system.
It is coordinating and integrating endocrine, autonomic, and homeostatic functions. (temp, hunger, fatigue, sleep)
What is the subthalamus responsible for?
is part of the basal ganglia and plays an important role in modulating and integrating voluntary movement and muscle tone.
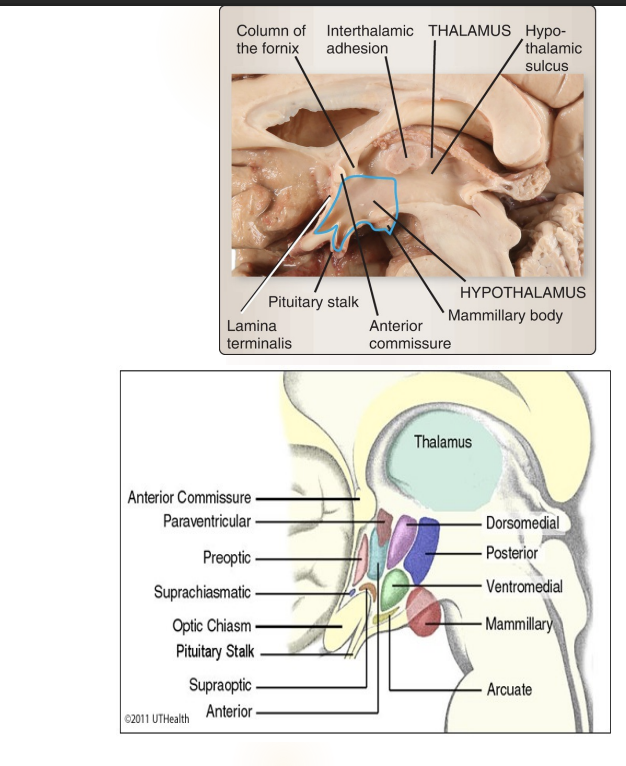
Where is the hypothalamus located, what makes up the anterior and posterior portion?
Small region located directly above the brainstem- about the size of an almond
Found underneath the thalamus and comprises the floor of the third ventricle,
Anterior- optic chiasm and anterior commissure,
Posterior by the mammillary bodies
Extends downward from the brain into a stalk known as the pituitary stalk (or infundibular stalk), which connects it to the pituitary gland- hypothalamus–pituitary complex
What are the three parts of the hippocampus?
Subiculum- transition zone of cortex, between the hippocampus and the parahippocampal gyrus;
Hippocampus proper, also called Ammon horn; grey mater
Dentate gyrus - is a notched or “toothlike” band of gray matter
It is located in the medial surface of the temporal lobe, like a sea horse shaped
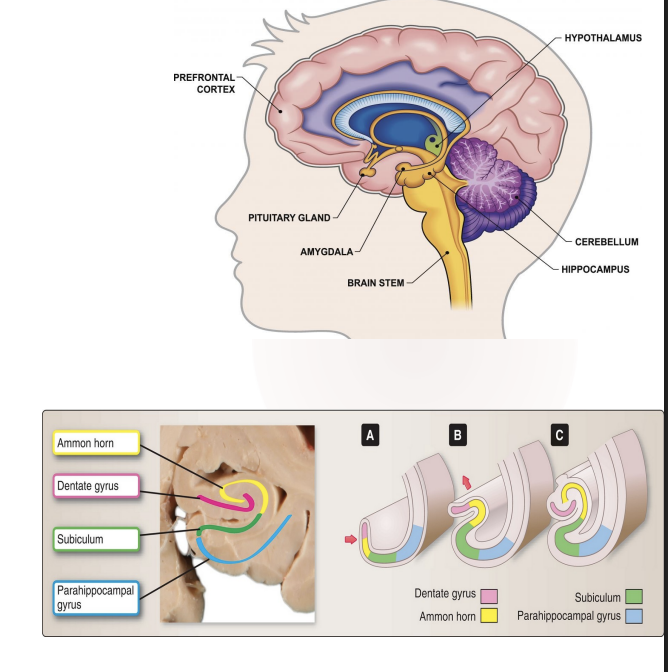
What is the amygala responsible for and where is it located?
Located: an “almond shaped” structure that lies deep the the uncus, rostal to the hippocampus
Integrative center for emotion, emotional behavior, and motivation
Just like with the hippocampus, major pathways communicate bidirectionally and contain both efferent and afferent fibers
This is the part of your brain that reacts without thinking of the consequences or affects.
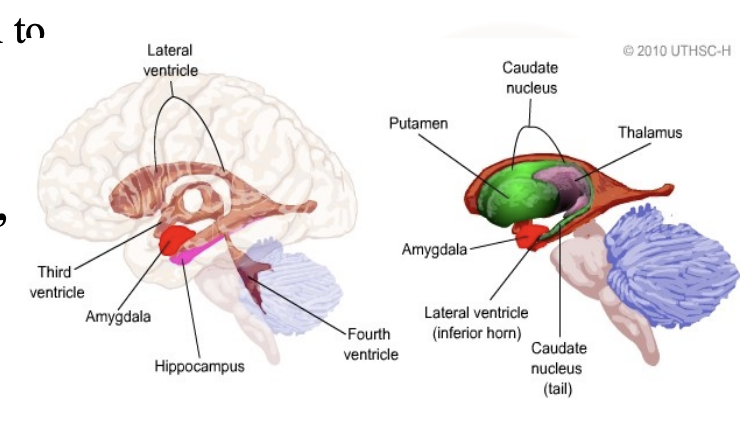
What are the input sources for the amygala?
All senses
Visceral inputs from the hypothalamus, septal area, orbital cortex, and parabrachial nucleus
Olfactory sensory information from the olfactory bulb
Auditory, visual, and somatosensory information from the temporal and anterior cingulate cortices
This explains why emotions can be triggered by sights, smells, memories, or visceral feelings

What is the basolateral nucleus (BLA) responsible for?
One of the three major group in the amygdala nuclei
Attaches emotional meaning to a stimulus
Has reciprocal connections, which means that the BLA both sends information to and receives information from these brain areas, allowing for a constant feedback loop that refines emotional responses and behavior.
These areas are the orbitofrontal, parietal, temporal, cingulate, parahippocampal gyri
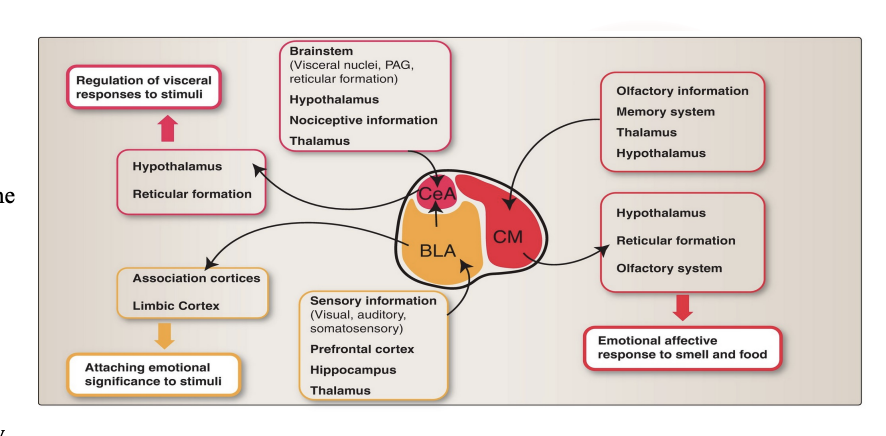
What is the central nucleus (CeA) responsible for?
One of the three major group in the amygdala nuclei
Generate visceral responses to emotional stimuli, & pain
Reciprocal connections mean the CeA can both send signals out to trigger these responses and receive feedback from the body about its current state. This constant communication allows the body to react instantly to perceived dangers or painful situations without conscious thought.
These areas are visceral nuclei of the brainstem and spinal cord, input from the BLA, cholinergic and aminergic neurotransmitter systems of the brainstem

What is the corticomedial nucleus (CM) responsible for?
One of the three major group in the amygdala nuclei
Emotional affective responses to food. This means the CM helps determine the emotional and behavioral response to food based on its smell and taste, influencing whether you feel motivated to eat more or stop eating
Receive olfactory information from the olfactory bulb, gustatory information, and information from the thalamus. Reciprocal connections with the hypothalamus, specifically the ventromedial and lateral areas, which are involved in the regulation of food intake
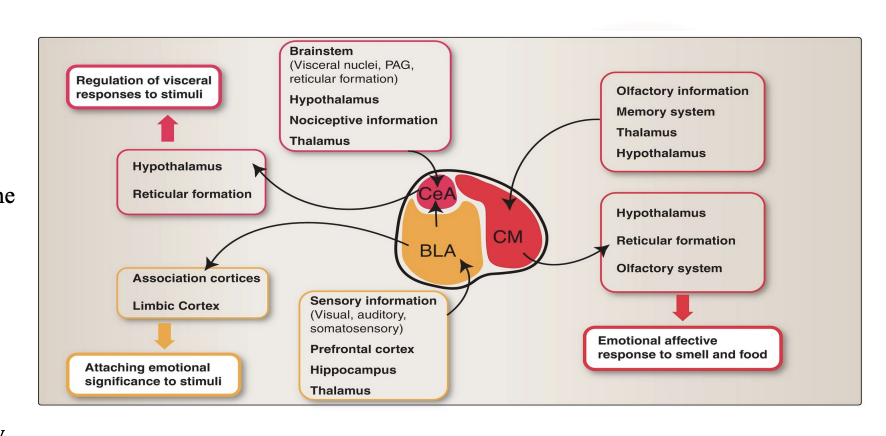
What is the septal nuclei responsible for? Where is it located? What are its reciprocal connections? What is the normal pathway that the septal nuclei will send information?
A small group of nuclei in the medial wall of the frontal lobe
Responsible for pleasure & reward
Reciprocal connections with: the olfactory bulb, hippocampus, amygdala
The septal nuclei have extensive two-way connections (afferents and efferents) with the medial forebrain bundle. This critical pathway carries signals to and from the hypothalamus and reticular formation, which then link to the brainstem and spinal cord to influence visceral (autonomic) and motor (movement) functions.
Electrical simulation in this area have reports of sexual feelings and orgasms
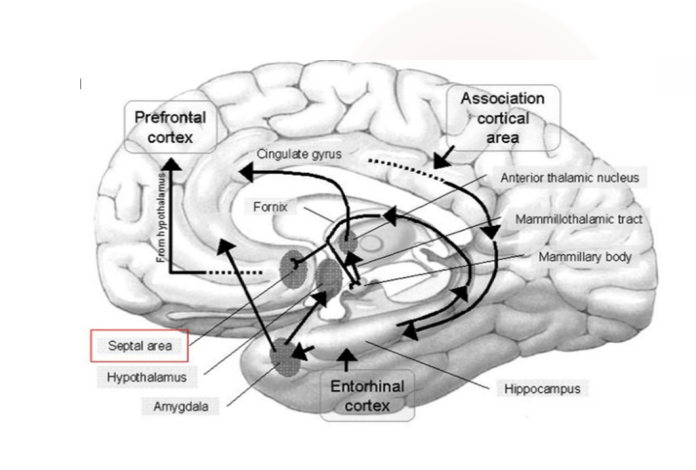
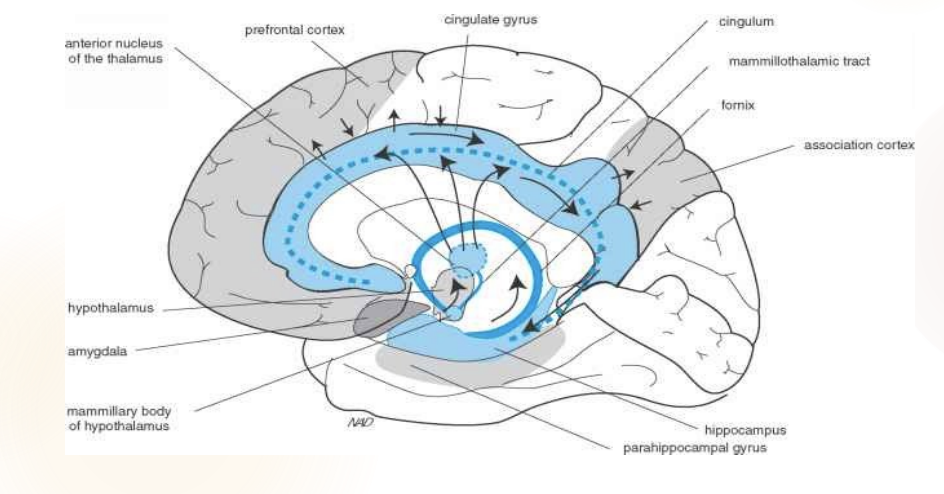
What is the simple circuit for the papez circuit?
Cingulate
Hippocampus
Mammillary bodies
Thalamus
Back to cingulate
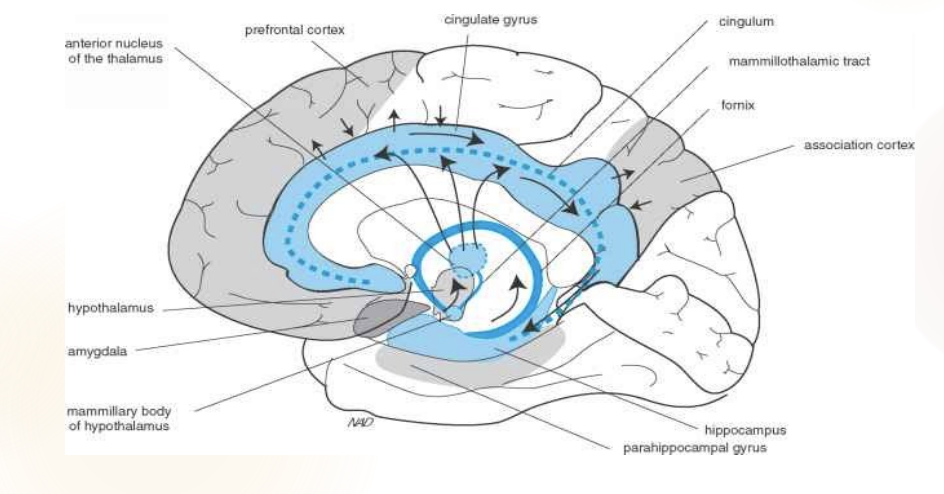
What is the papez responsible for?
The Papez circuit, first proposed by James Papez in 1937, is a circuit believed to control memory and emotions,
What is the expanded version of the papez circuit?
Cingulate
What is the hippocampus responsible for? Tell me about the HM case
Hippocampus allows new memory formation
After removal both of the hippocampus, HM could not form new memories (anterograde amnesia)
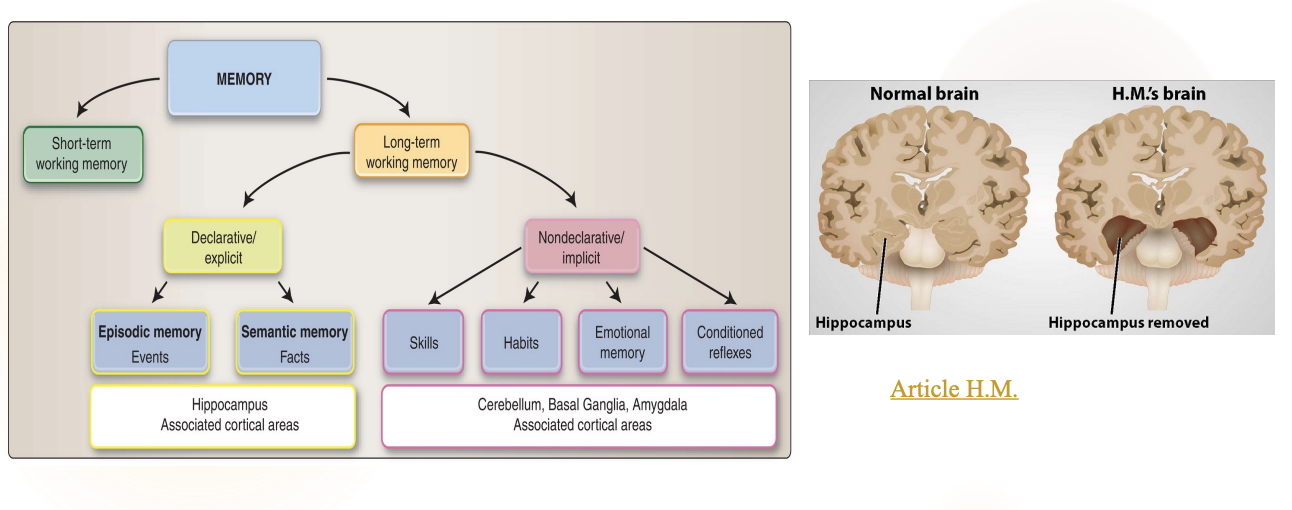
What is the difference between declarative/explicit memories vs. nodeclarative/implicit memories?
Declarative memory (events, facts) requires conscious effort to retrieve, whereas nondeclarative memory (skills, habits, emotional memory, conditioned reflexes) is accessed without conscious thought

What does the amygdala link? How does it relate to fear?
Responsible for emotional learning and memory
It links perception (what we see) with visceral responses and behavioral responses and with memory
Fear and fear conditioning: this is where you learn to be afraid of something.
EX: If a loud noise (unconditioned stimulus) is always paired with a specific room (neutral stimulus), you will eventually become afraid of that room even without the noise.
To actually "feel" fear, you need to recognize and interpret the situation. This involves the amygdala and other parts of the brain working together
Also part of the reward circuitry
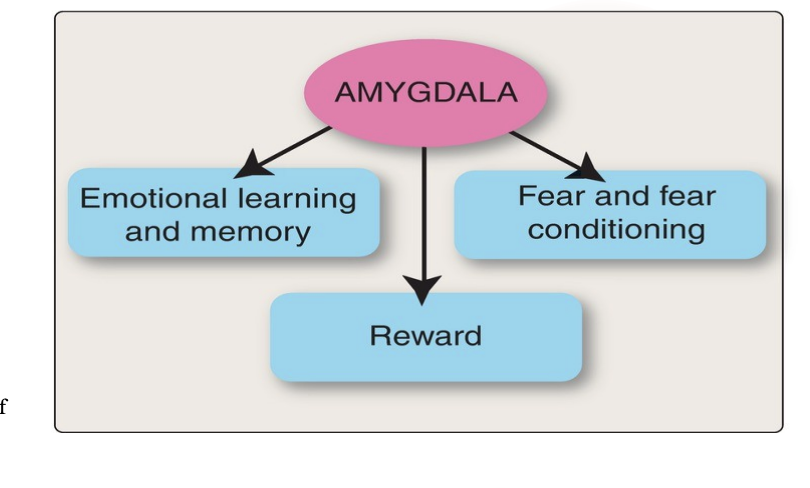
When the amygdala is activated, how does it relate to fear?
Amygdala will detect and responds to threats
Neural activity in the amygdala increases
Results in 2 responses (with fear)
behavioral (freeze or jump back)
physiological (increased heart rate, sweating
Recognizing fear, however, involves the cortex.
Explain what fear conditioning is
A form of emotional learning/ associative learning; a neutral stimulus (the conditioned stimulus) becomes associated with an aversive event (the unconditioned stimulus)
Presentation of the conditioned stimulus alone can elicit defensive behavior and the appropriate visceral and endocrine responses.
EX: PTSD
Basically, fear conditioning is a type of emotional learning done by the amygdala. It explains how we learn to fear things that were originally not scary. Take door slamming for example, this is a neutral stimulus that elicits NO fear. But add door slamming with someone yelling, hitting, etc, now your amygala tries to protect you the next time (neutral thing + something scary happening). Now, the next time a door slams, which is a neutral thing, it ALONE triggers fear. So next time: A door slams → heart races, body freezes, anxiety hits… even though nothing bad is happening
Explain what the reward circuitry is and explain the pathway
Incentive-based learning describes how your brain uses a "reward system," heavily reliant on the neurotransmitter dopamine, to encourage behaviors that lead to positive outcomes
Dopamine is the key player, acting like a chemical "gold star" or "feel-good" messenger. Its release tells your brain that what you just did was good and worth repeating
Pathway:
The medial forebrain bundle is a communication highway for dopamine. It will allow dopamine fibers project to the nucleus accumbens.
It will also project to the hippocampus, amygdala, septal nuclei, prefrontal cortex
The prefrontal cortex will provide feedback to the midbrain either directly or through the nucleus accumbens
They will all communicate with the hypothalamus to initiate neuroendocrine and visceral responses to reward.
In addition, cortical and subcortical structures interact to form a complex network that mediates adaptive behaviors, allowing motivation and reward to be combined with a strategy and action plan for obtaining goal
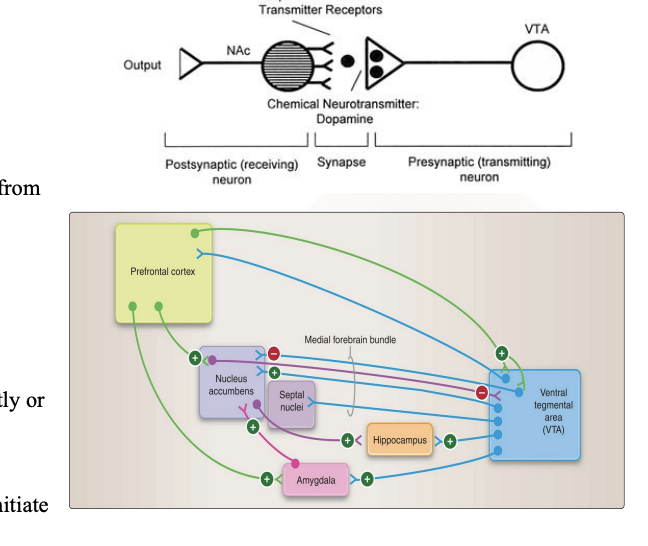
How does drug affect the dopamine pathway? What does it lead to?
Similar to natural rewards drugs will activate and increases the amount of dopaminergic neurons that travel in the medial forebrain bundle from the nucleus accumbens.This creates feelings of pleasure and makes the experience seem very important or salient
With chronic use, the dopaminergic system is impaired. It reduces the number of dopamine D2 receptors, making the system less sensitive to dopamine's effects.
Because of these changes, the substance no longer provides the same intense satisfaction it did initially. The user develops a tolerance and feels a strong want or craving for more of the substance just to feel "normal," which can lead to negative emotions during withdrawal.
