Heart sound 1
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
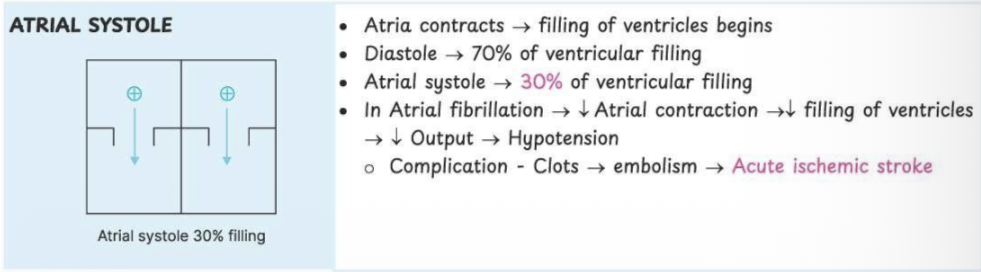
Atrial systole
Phase where atria contract and fill ventricles
Isometric contraction

Timing of S1
at End of atrial systole /at start of isovolumetric contraction
Mnemonic for S1
M1T1
Valve bulge after isovolumetric contraction
Slight bulge in mitral and tricuspid valves
Ventricular systole

Ventricular contraction pattern in ventricular systole
Both ventricles contract simultaneously with equal force
Ejection click is seen in
Normal
Aortic stenosis
Isovolumetric relaxation

Rapid ventricular filling phase
Initial phase of diastole where blood flows rapidly into ventricles

Maximum filling occur in which phase of cardiac cycle
rapid ventricular filling
Gap between second heart sound
splitting of 2nd heart sound
Time lag between A2P2 splitting
30 msec
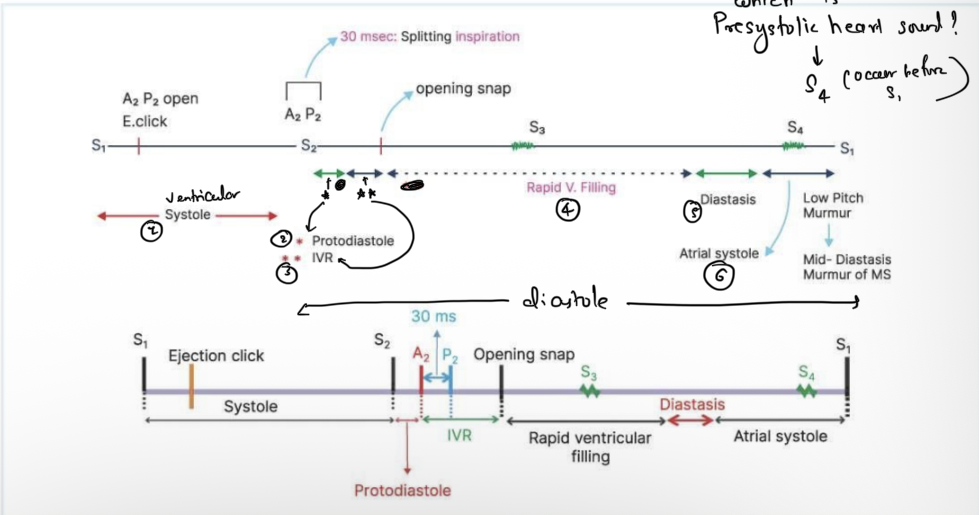
Full linear diagram of sound, systole, diastole
Between s1 and s2
ventricular systole
What is protodiastole?
period between end of systole to closure of A2P2 ( valve need some time to close )
Phase just after s2
protodiastole
Period between s2/protodiastole till opening snap
IVR (isovolumetric relaxation)
Phase after IVR
rapid ventricular filling
Sound in rapidventricular filling
S3
Other name of 3rd heartsound
ventricular gallop rhythm
Diastasis
Phase of minimal ventricular filling
Least movement of heart present in
diastasis
Systole phase present between
S1 to S2
Phases in diastole
Protodiastole
IVR
Rapid ventricular filling
Diastasis
Atrial systole
All events chart in video
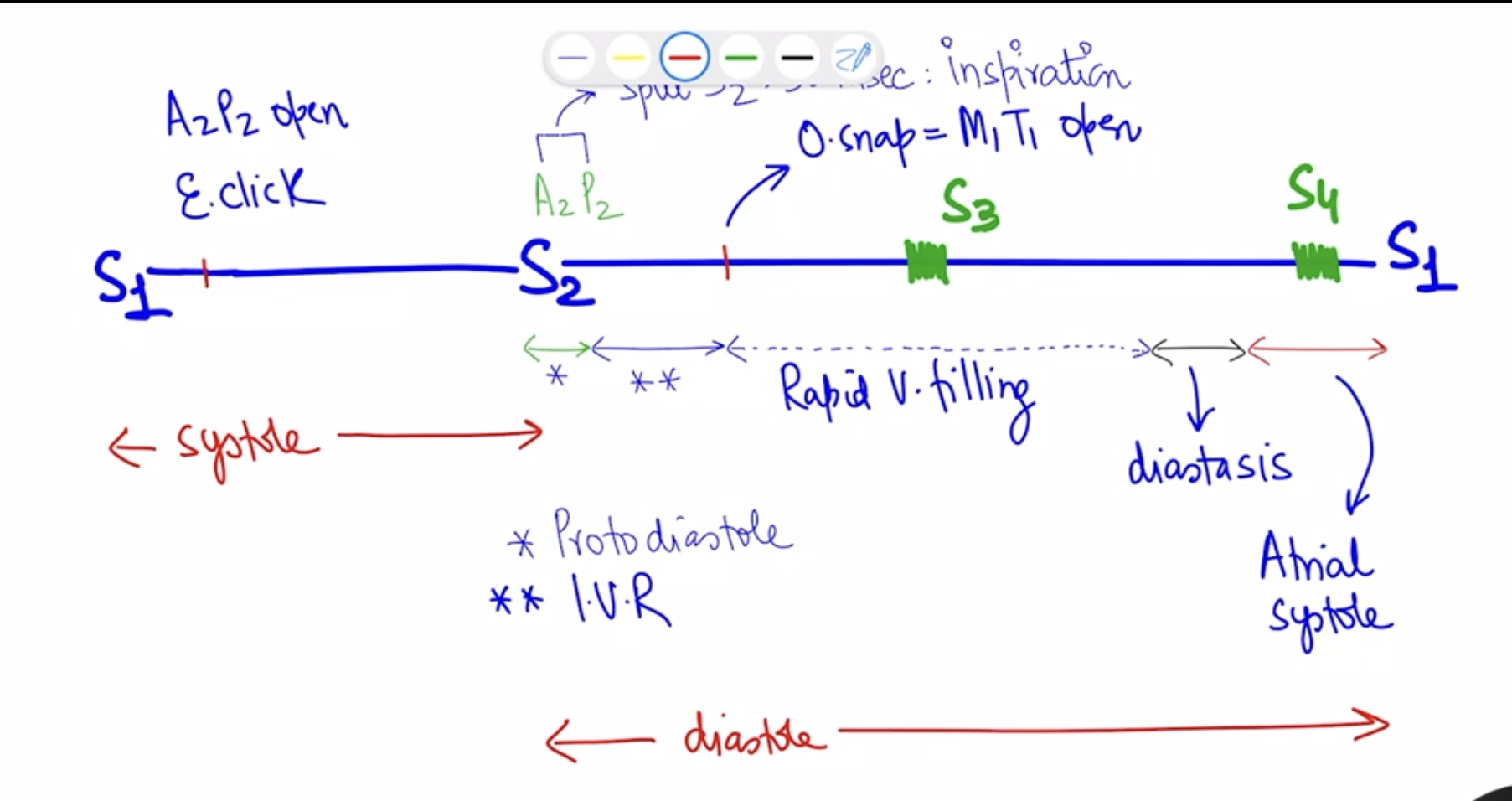
Splitting of S2 more prominent in
inspiration
Other name of 4th heart sound
atrial gallop rhytm
Which heart sound present before S1
s4
High piched heart sound
(Heard by diaphragm)
S1
S2
Opening snap
Low pitched heart sound include
Heard through bell
S3
S4
Tumor plop sound (in cardiac tumor e.g atrial myxoma)
Low pitch murmer
mid diastolic murmer
Is murmer heart sound?
no, it is due to turbulence of blood
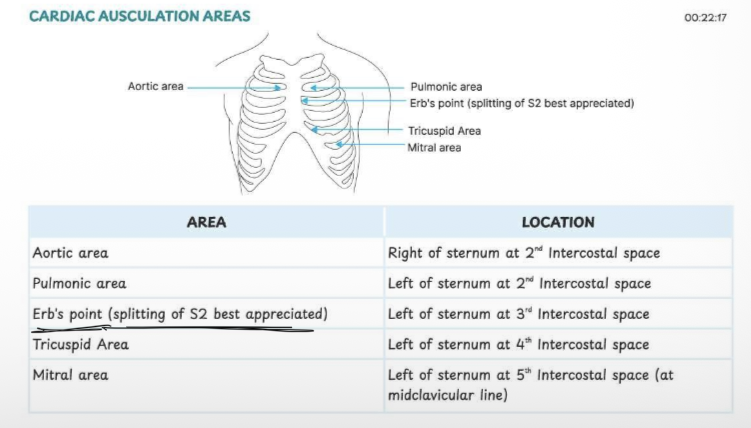
Cardiac auscultation areas
Five standard areas
Site of atrial myxoma
Left atrium ( attached by stalk to wall)
Sound mechanism in atrial myxoma
tumor obstacle →blood hit tumor →swinging of tumor →hit mitral valve leaflet → produce sound
Big sized atrial myxoma cause
mitral stenosis
Cause of platypnea in atrial myxoma
Tumor obstructs valve in upright position (gravity)
Clinical features of atrial myxoma
young female
Dyspnea on exertion
Platypnea ( breathlessness while sitting → resolve on lying)
Transient ischemic attacks ( embolism of platelet plug, embolism of tumor cell)
Examination finding in atrial myxoma
Pallor
Tumor plop
Mid-diastolic murmer
Mitral regurgiattion ( damage to mitral leaflets )