Psych 454 exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/125
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:26 PM on 2/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
1
New cards
There is more sodium...
outside the cell
2
New cards
There is more potassium
inside the cell
3
New cards
What is membrane potential?
the voltage difference across a membrane
4
New cards
At resting membrane potential...
more negative inside cell (-70mV)
5
New cards
What causes sodium channels to briefly open?
Na+ influx
6
New cards
What is depolarization?
the inside of the membrane becomes less negative
7
New cards
What is hyperpolarization?
the inside of the membrane becomes more negative
8
New cards
When potassium channels open...
K+ rushes out; Na+ channels become refractory until membrane reaches resting potential
9
New cards
What are the two types of neural codes?
Spike rate code and spike timing code
10
New cards
what is spike rate code?
number of spikes in a given interval
11
New cards
What are the two types of spike timing code?
spike pattern code and spike-phase code
12
New cards
single-unit recording
an invasive technique for studying brain function, permitting the study of activity in single neurons
13
New cards
Which brain recording methods are invasive?
Single unit and LFP
14
New cards
Which brain recording methods have good spatial resolution?
Single unit and LFP
15
New cards
Which brain recording methods have good temporal resolution?
Single unit, LFP, and EEG
16
New cards
Which brain recording method has poor spatial resolution
EEG and FMRI
17
New cards
Which brain recording method has poor temporal resolution?
FMRI
18
New cards
What are the peripheral sensory organs?
eyes, ears, skin
19
New cards
What are first-order thalamic areas?
Thalamic areas that receive input directly from the sensory periphery
20
New cards
Which system bypasses the thalamus?
olfactory system
21
New cards
What are feedforward pathways?
pathways directed from posterior to anterior cortical areas (info about sensory enviroment)
22
New cards
What are feedback pathways?
pathways directed from anterior to posterior (goals, attention priorities, predictions)
23
New cards
What do direct pathways between cortical areas carry?
Detailed information about sensory stimuli
24
New cards
What is the role of the indirect pathways between cortical areas via the higher-order thalamus?
Indirect pathways facilitate processing of only the behaviorally relevant info in the cortex
25
New cards
Where is the "how" pathway located?
across the dorsal cortex
26
New cards
Where is the what pathway located?
across the ventral cortex
27
New cards
How many layers are in the neocortex?
six layers
28
New cards
What layer do pyramidal cells have their soma?
layer 5
29
New cards
What do excitatory cells do?
Depolarize and increase activity of post-synaptic cells
30
New cards
What do inhibitory cells do?
Hyperpolarize and inhibit activity of post-synaptic cells?
31
New cards
What type of cells are excitatory?
pyramidal
32
New cards
Layer 4
receives feedforward input from thalamus or another cortical area
33
New cards
Layer 2/3
sends feedforward output to another cortical area
34
New cards
Layer 5
sends feedforward output to subcortical areas
35
New cards
Layer 6
sends feedback output to the thalamus or another cortical area
36
New cards
layer 1
receives feedback input from another cortical area (and thalamus)
37
New cards
Frontal lobe
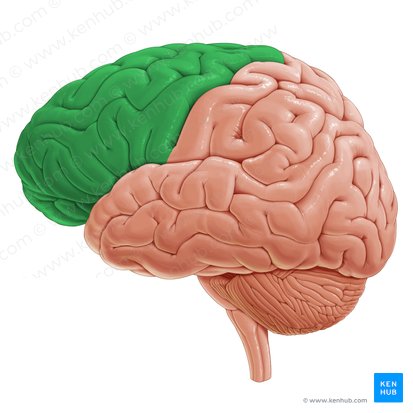
38
New cards
Central sulcus
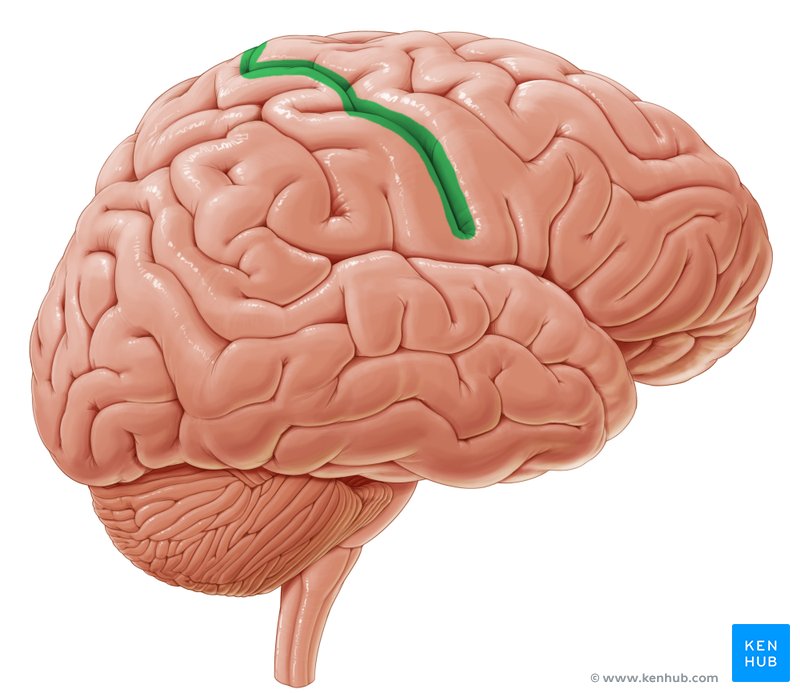
39
New cards
parietal lobe
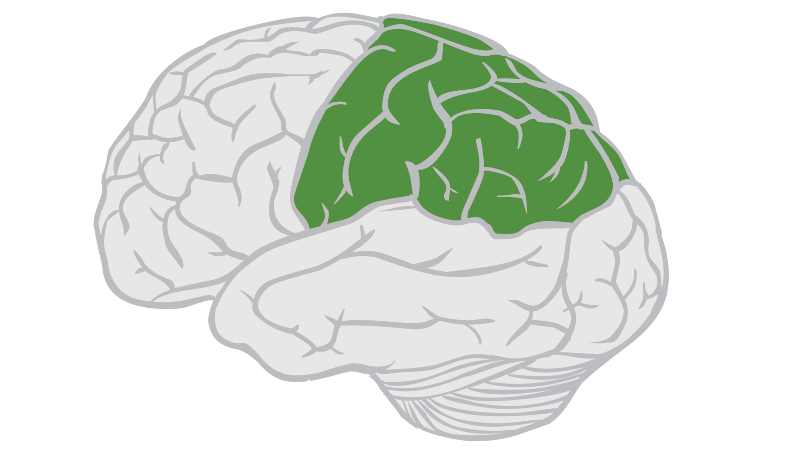
40
New cards
occipital lobe
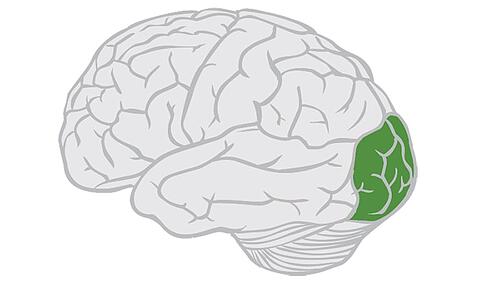
41
New cards
temporal lobe
42
New cards
function of basal ganglia
action selection and reinforcement learning
43
New cards
Which functional territories do not have pathways to the striatum?
Primary visual cortex and primary auditory cortex
44
New cards
Increased striatal activity can \_______ thalamus (via direct pathway)
disinhibit
45
New cards
hyperdirect pathway
cortex to subthalamic nucleus
46
New cards
direct pathway
striatum to GP internal segment
47
New cards
indirect pathway
striatum to GP external segment to subthalamic nucleus to GP internal segment
48
New cards
What does GP stand for?
globus pallidus
49
New cards
What is the cerebellum's function?
motor and cognitive functions
50
New cards
What is the hippocampus's function?
episodic memory and spatial navigation
51
New cards
What is a node degree?
number of connections that link a node to the rest of the network
52
New cards
what is a clustering coefficient?
Number of connections that exist between nearest neighbors of a node (as a proportion of the maximum number of possible connections)
53
New cards
what is path length?
minimum number of edges to go from one node to another
54
New cards
what is a module?
subset of nodes with high within-module connectivity and low inter-module connectivity
55
New cards
what is a rich node?
Node with a large number of connections (i.e. high-degree node (called network hub))
56
New cards
what is a rich club?
Rich nodes that are well connected with each other, forming a tight subgraph (yellow box)
57
New cards
what is a rich-club organization?
Greater likelihood of high-degree nodes forming clubs than low-degree nodes
58
New cards
What are tracer studies?
an invasive procedure where tracer molecules are injected into brain and travel along axons
59
New cards
What is diffusion MRI?
allows visualization of the diffusion process of molecules, mainly water, in biological tissues, in vivo and non-invasively
60
New cards
Section a?
Precuneus
61
New cards
Section b
Posterior Cingulate Cortex (PCC)
62
New cards
Section c?
anterior cingulate cortex
63
New cards
Section d?
superior frontal cortex
64
New cards
Section f?
insular cortex
65
New cards
Section i?
lateral parietal cortex
66
New cards
Section J?
thalamus
67
New cards
Visual receptive field
Covers area of visual space
68
New cards
Somatosensory receptive field
mapped along dimensions of body surface
69
New cards
Visual area in left hemisphere
right visual field
70
New cards
reference frame
a coordinate system from which the positions of objects are described
71
New cards
egocentric reference frame
eye-centered, body-centered
72
New cards
allocentric reference frame
object-centered, world-centered
73
New cards
Visual cortex uses...
eye-centered reference frame
74
New cards
Motor cortex uses
body centered reference frame
75
New cards
hippocampus uses...
allocentric reference frame
76
New cards
Posterior parietal cortex (PCC) is important for...
coordinate transfomations
77
New cards
Hippocampus contains...
allocentric cells
78
New cards
Parietal cortex contains...
egocentric cells
79
New cards
Retrosplenial cortex contains...
both allocentric and egocentric cell
80
New cards
Transmitter diffuses across\___ and binds to \_____ on post-synaptic neuron
synaptic cleft; receptors
81
New cards
Opening of the transmitter-gated ion channels leads to...
post synaptic potential
82
New cards
Excitatory post-synaptic (EPSP) is produced by
glutamate
83
New cards
Inhibitory post-synaptic potential (IPSP) produced by
GABA
84
New cards
Long-term potentiation (LTP)
increased magnitude of EPSP after pre-synaptic activity
85
New cards
long-term depression (LTD)
decreased magnitude of EPSP after low pre-synaptic activity
86
New cards
Increase in pre-synaptic calcium leads to...
transmitter release
87
New cards
Large increase in post-synaptic calcium \=
LTP
88
New cards
Small increase in post-synaptic calcium \=
LTD
89
New cards
axo-dendritic synapse
axon terminal synapses on a dendrite
90
New cards
axo-somatic synapse
axon terminal synapses on the cell body (soma)
91
New cards
axo-axonic synapse
synapse between two axons
92
New cards
Synaptic cleft
The narrow gap that separates the presynaptic neuron from the postsynaptic cell.
93
New cards
synaptic vesicle
storage site for neurotransmitters
94
New cards
main inhibitory neurotransmitter
GABA
95
New cards
main excitatory neurotransmitter
glutamate
96
New cards
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers sent across synapse
97
New cards
Neuromodulators
modulate effectiveness of other neurotransmitters (amines)
98
New cards
Step one in neurotransmitter release
synaptic vesicle docked at pre-synaptic "Active zone"
99
New cards
Step 2: Neurotransmitter Release
action potential leads to increased pre-synaptic calcium
100
New cards
step 3 of neurotransmitter release
calcium triggers neurotransmitter release