DC to AC - Inverters
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is the main function of an inverter?
To convert DC into AC.
Two main inverter categories?
Voltage-source (VSI) and current-source inverters (CSI).
What is a square-wave inverter?
An inverter that switches DC polarity to produce a square AC waveform.
What is a PWM inverter?
An inverter that uses Pulse-Width Modulation to approximate a sine wave.
Advantages of PWM inverters?
Lower harmonic distortion and controllable output voltage.
Typical devices in modern inverters?
MOSFETs or IGBTs.
Why are SCRs rarely used in PWM inverters?
They cannot be turned off by gate control and are slow for high-frequency PWM.
What is a pure sine wave inverter?
An inverter whose output closely matches a true sine wave.
What is a modified sine wave inverter?
A stepped approximation of a sine wave with higher harmonics.
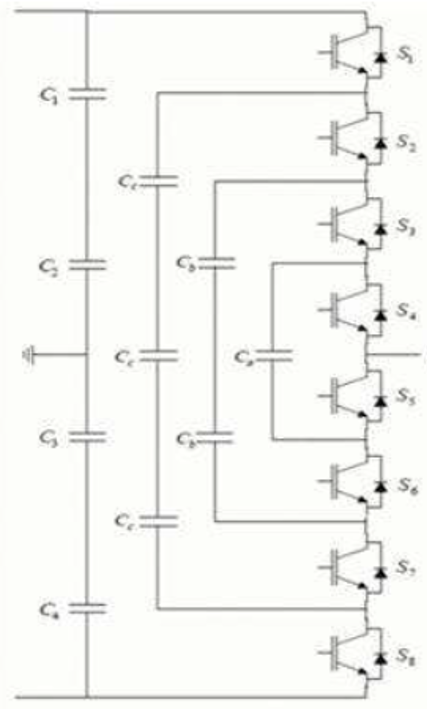
What is a multilevel inverter?
Inverter synthesizing AC from multiple DC levels for smoother output.
List three multilevel inverter types.
Diode-clamped (NPC), Flying capacitor, Cascaded H-bridge.
Advantage of multilevel vs two-level?
Lower dv/dt, reduced harmonics, better efficiency.
How is PWM generated?
Compare high-frequency triangular carrier with sinusoidal reference; switch when reference exceeds carrier.
Inverter applications?
UPS, renewable energy systems, motor drives.
Describe PWM control waveforms.
Triangular carrier compared with sine reference; pulses widen near peaks and narrow near zero crossings.

Describe three-phase inverter output.
Three 120-degree-shifted PWM phase voltages; line-to-line voltage forms stepped near-sine.

Describe multilevel inverter output.
Multiple small voltage steps per half-cycle produce a near-sinusoidal waveform.

The output voltage waveform is controlled using switches (e.g., MOSFETs or IGBTs).
It is the most common inverter type, used in variable-speed drives and grid-tied systems.

The output current waveform is controlled, making it suitable for current-driven loads such as induction heating or certain motor drives.


It divides the DC bus into multiple voltage steps, producing a stepped waveform with reduced harmonics.
It’s common in medium-voltage, high-power industrial drives.

Each bridge generates three voltage levels (+V, 0, −V).
It provides modular design and scalability but requires isolated DC supplies.

Each level is created by charging or discharging specific capacitor combinations.
Advantages include redundant switching states and better voltage balancing, but control is more complex.
• Reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI)
• Higher efficiency at lower switching frequencies
• Can handle higher voltage with standard devices #