path 1/2- hypothalamus/pit
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
adenohypophysis
anterior lobe of the pituitary gland
neurohypophysis
posterior lobe of the pituitary gland
blood supply to the anterior lobe of the pituitary is mostly
venous --> portal system
blood supply to the posterior lobe of the pituitary is mostly
arterial
which lobe of the pituitary is more vulnerable to hypoperfusion
anterior
somatotrophs release
GH
lactotrophs secrete
prolactin
thyrotrophs release
TSH
corticotrophs release
ACTH
gonadotrophs release
FSH and LH
lactotrophs are stimulated by
TRH
lactotrophs are inhibited by
dopamine
2 functions of oxytocin
uterine contraction
milk ejection
Functional pituitary adenoma
hormonal excess
assocaited clinical s/s
Nonfunctional pituitary adenoma
non-hormone producing
no clinical s/s
invasive adenomas
not encapsulated
infiltrating neighboring tissues (cavernous and sphenoid sinuses)
describe what bitemporal hemianopsia looks like
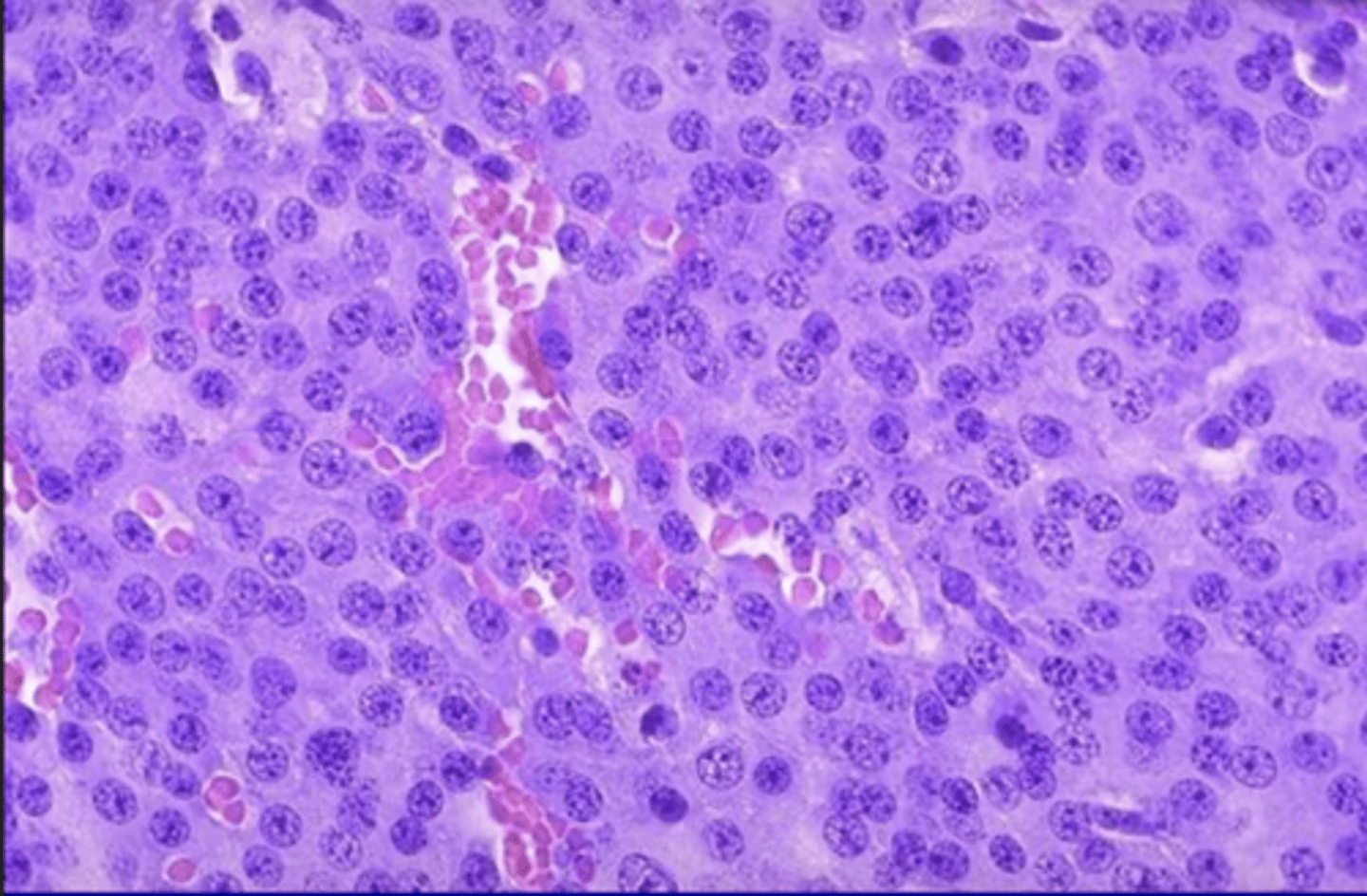
what is seen in microscopy for pituitary adenoma
monomorphic polygonal cells arranged in sheets/cords
prolactinomas have a tendency to
calcify
atypical adenomas
brisk mitotic activity
Ki-67 +
P53 +
peak incidence for pituitary adenomas
35-60
most common hyper functioning pituitary tumor
prolactinoma
s/s of prolactinoma in women
amenorrhea
galactorrhea
infertility
s/s of prolatinoma in men
dec libido
impotence
galactorrhea (rare)
physiologic causes of hyperprolactinemia
pregnancy
breastfeeding
stress
drugs than can cause hyperprolactinemia
birth control
haloperidol
alpha methyl dopa
reserpine
____thyroidism can lead to hyperprolactinemia
hypo
bc of inc TRH
2nd MCC of pituitary adenoma
GH adenoma
functions of GH
IGF-1 synthesis in liver
gluconeogenesis + aa uptake in muscle
functions of IGF-1
stimulates growth of bone (linear and lateral), cartilage, soft tissue
IGF-1
insulin-like growth factor 1
acromegaly can cause what other disease
diabetes mellitus
MSK findings for acromegaly
weakness
carpal tunnel
lumbar canal stenosis
lab findings for acromegaly
inc GH
inc IGF-1
definitive test for acromegaly
oral glucose tolerance test
pos = failure of GH to dec after ingesting glucose
microscopic findings for acromegaly
densely granulated acidophilic monomorphic cells (strong + for GH)
sparkly granulated chromophobic pleomorphic cells (weak + for GH)
treatment for acromegaly
surgery
somatostatin analog
GH R antagonist
Cushing syndrome
too much cortisol
Cushing disease
too much cortisol due to ACTH secreting pituitary adenoma
Nelson's syndrome
pituitary adenoma discovered years after BL adrenalectomy for chushings syndrome
due to loss of inhibitory effect of cortisol of a preexisting corticotroph adenoma
S/S of nelson syndrome
hyperpigmentation
is there high cortisol w/ nelson syndrome
no (adrenals removed)
most important sign of pituitary carcinoma
craniospinal or systemic metastasis
are pituitary carcinoma or metastatic tumors more common
metastatic tumors
MCC of SIADH
Small cell carcinoma of the lung
hypofunction of the AP happens when ___% or more of the parenchyma is lost
75
Causes of hypopituitarism
tumors/lesions
brain trauma
subarachnoid hemorrhage
ablation of pituitary (surgery/radiation)
pituitary apoplexy
Sheehan
pathogenesis of Sheehan syndrome
AP enlarges in pregnancy w/o inc in blood supply --> relative anoxia
further blood less due to obstetric bleeding/shock = infarction of AP
s/s of sheehan syndrome
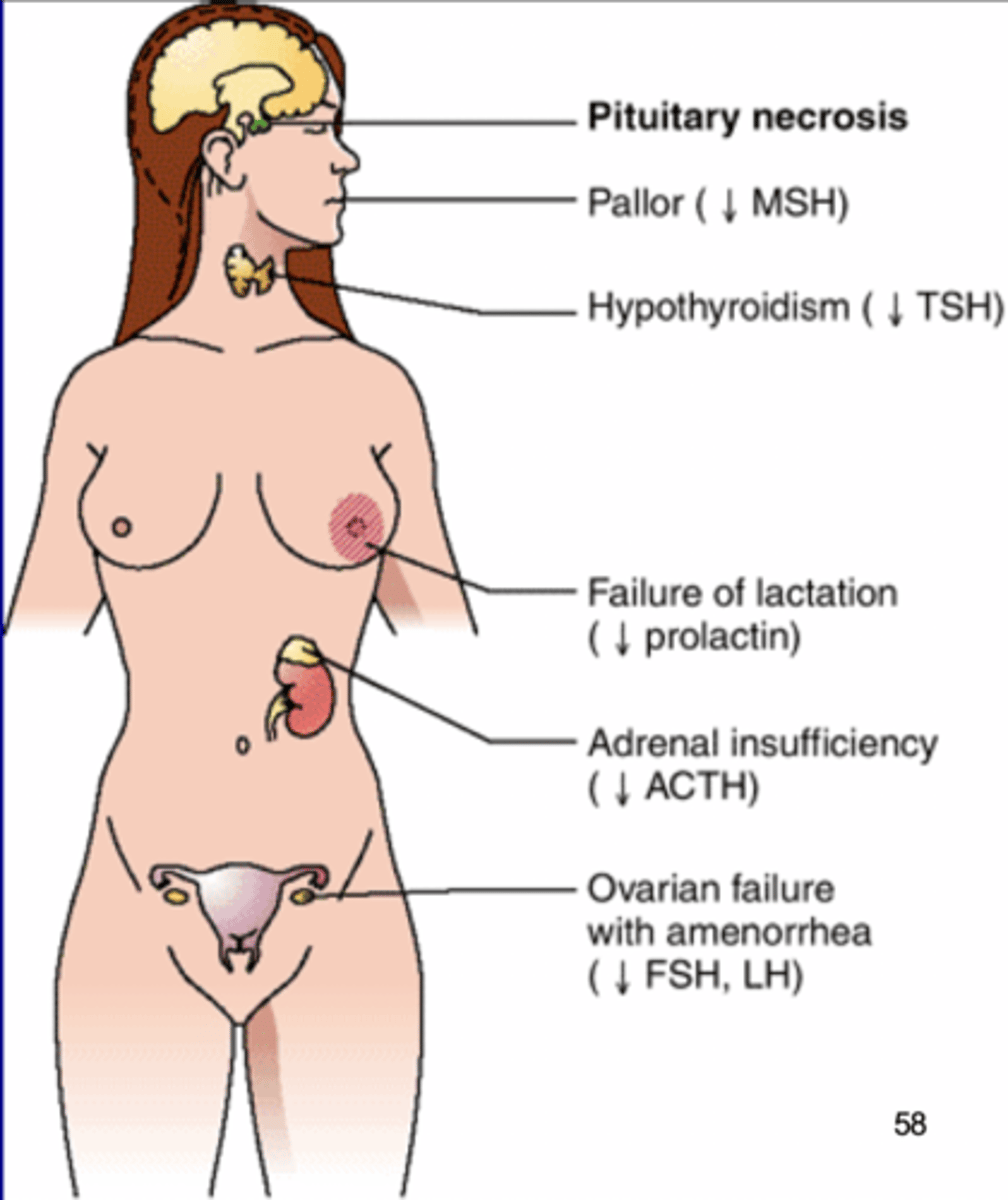
empty sella syndrome causes
hypopituitarism
empty sella syndrome
congenital sella defect
herniation of arachnoid & CSF into the sella compresses & destroys pituitary gland
pituitary gland is "absent" on imaging
hypothalamic lesion in children that causes hypopituitarism
craniopharyngioma
MCC of hypopituitarism in children
Craniopharyngioma
craniopharyngioma is derived from
Rathke's pouch
age for craniopharyngioma
bimodal
5-15
60-70
s/s of craniopharyngioma
headache
endocrine def
mass effect
central DI
what craniopharyngioma variant is MC in kids
adamantinomatous
what craniopharyngioma variant is MC in adults
papillary
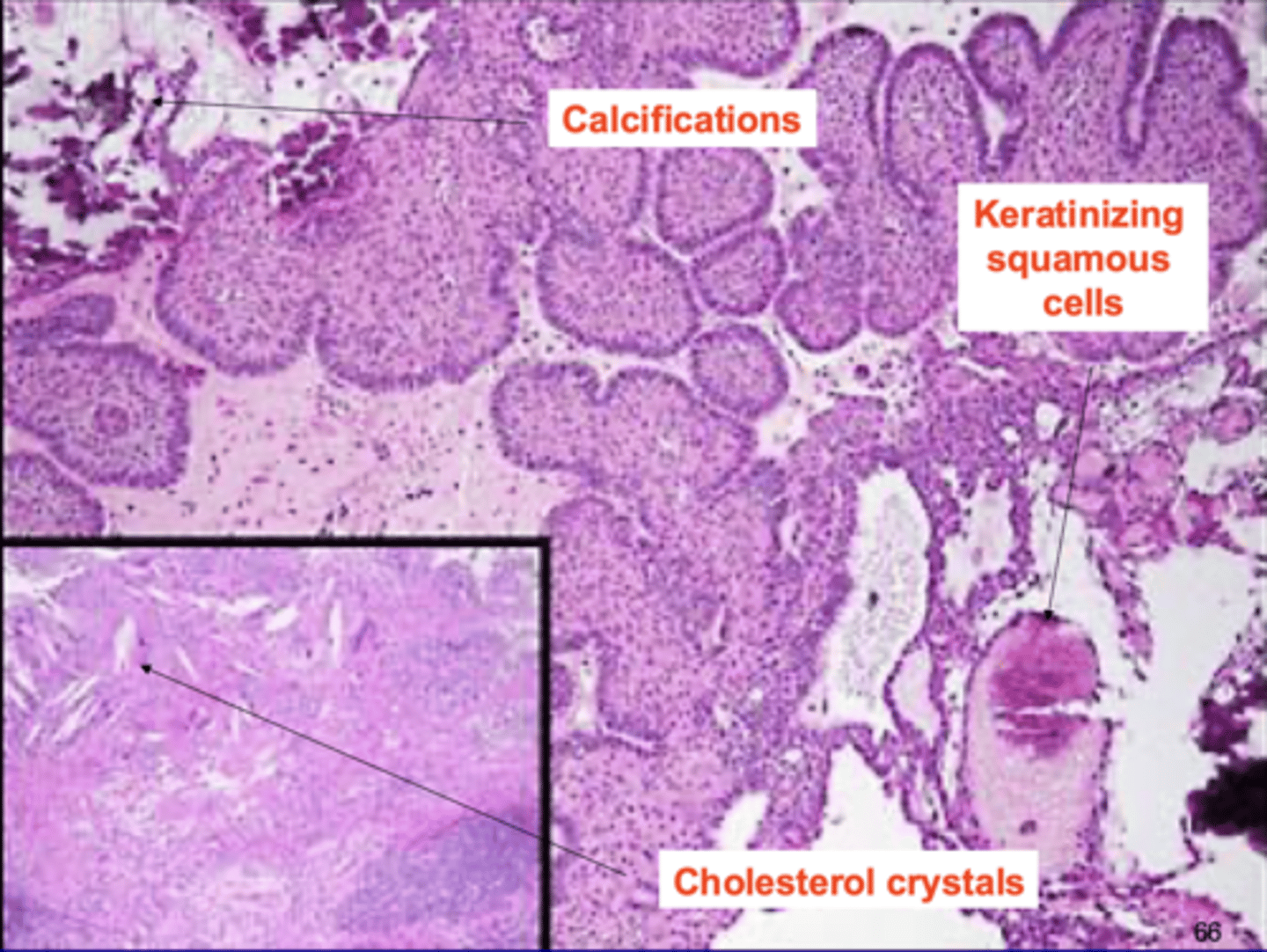
appearance of craniopharyngioma
cystic, "motor-oil" fluid filled
areas of calcification
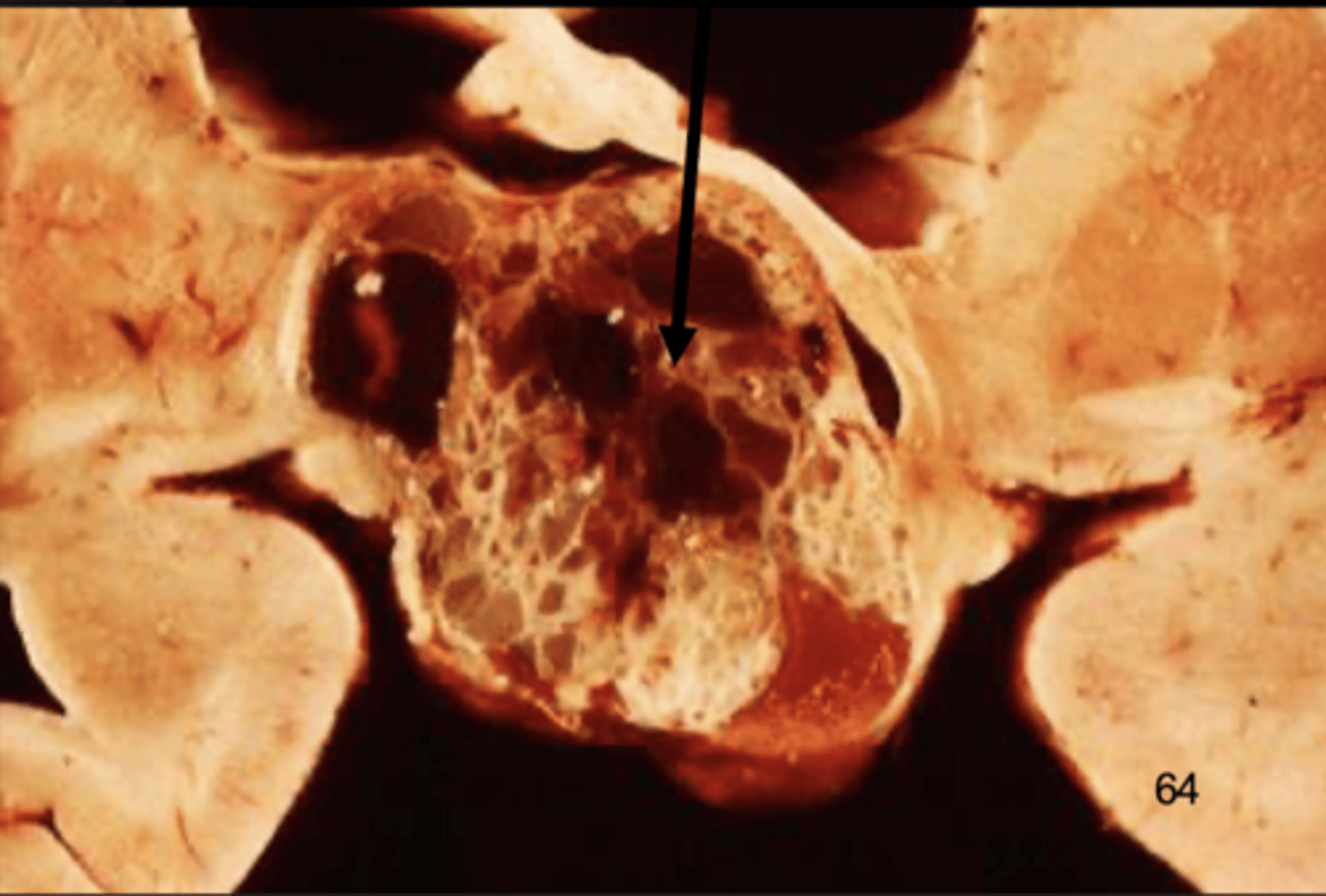
histo of craniopharyngioma
cholesterol crystals
keratinizing squamous cells
calcifications
s/s of dec gonadotropins in men
low libido
impotence
testes shrink
s/s of dec gonadotropins in women
low libido
dyspareunia (painful sex)
breast atrophy
s/s of GH def in infants
hypoglycemia
TSH deficiency
secondary hypothyroidism
dec T4 and TSH
ACTH def
secondary adrenal insufficiency
hypoglycemia
prolactin def
failure of lactation in post-partum pts
MSH def
pallor due to loss of stimulatory effects of MSH on melanocytes
ADH and oxytocin are synthesized in the
neurons of the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei in hypothalamus
causes of central DI
transection of pituitary stalk
hypothalamic disease
posterior pituitary disease
what part of the nephron is affected in nephrogenic DI
collecting tubules
causes of nephrogenic DI
hypokalemic nephropathy
drugs
nephrocalcinosis
drugs that can cause nephrogenic DI
Lithium, demeclocycline
what can be done to differentiate DI from other causes
fluid deprivation test
urine concentrated in normals, not in DI
what can be done to differentiate pituitary from renal causes of DI
desmopressin stimulation or administration of ADH
CDI --> inc urine concentration
NDI --> no urine conc
principle secretory product of pineal gland
melatonin
pineal gland tumor commonly take the form of
germinomas