Lab 5 - Axial Skeletal System and Bone Anatomy
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
Body (Miscellaneous)
The largest or principal portion of the bone.
Head (Miscellaneous)
The enlarged and often rounded end of a bone that articulates with another bone.
Neck (Miscellaneous)
The constricted part of a bone lying between the head and the body.
Angle (Miscellaneous)
A pronounced bend in a bone
Facet (Miscellaneous)
A small, smooth articular surface which may be flat, concave, or convex.
Condyle (Projections)
A smooth and rounded knob which articulates with another bone.
Epicondyle (Projections)
A protuberance located above a condyle.
Crest (Projections)
A prominent but narrow ridge.
Spine (Projections)
An elevated narrow ridge.
Process (Projections)
Prominent protuberance on the surface of a bone.
Tubercle (Projections)
A small rounded protuberance.
Tuberosity (Projections)
A moderate protuberance.
Trochanter (Projections)
A very large protuberance on the femur.
Fossa (Depressions)
A shallow, wide, or elongated depression on the surface of a bone.
Notch (Depressions)
A depression on the edge of a bone.
Canal (passageways)
A tunnel that penetrates a bone.
Meatus (passageways)
A large opening that gives way to a canal.
Foramen (passageways)
An often rounded hole that pierces a bone.
Malleus, Incus, and Stapes
What are the three ear ossicles?
Hyoid
What small bone is the muscle under the tongue, behind the lower jaw located below the skull and functions to help support the tongue.
Male
Identify the skeleton:
heavier skull
larger skull
prominent brow-ridge
narrow pelvis
heart-shaped pelvis
sharper angles
Female
identify the skeleton:
smooth brow ridge
rounder angles
smaller skull
broad pelvis
round pelvic opening
Parietal
Forms the roof of the skull and encases the top and lateral sides of the brain.
Temporal
Forms the sides and base of the skull at the temples. It also forms the posterior portion of the cheekbone and articulates with the lower jaw.
Auditory meatus
small openeing in the temporal bone or passes through this bone to form the auditory canal.
Frontal
Forms the forehead, including the brow ridge and upper surface of the eye sockets.
Occipital
Forms the base of the skull, and surrounds the foramen magnum, which is the opening for the spinal cord. It articulates with the atlas (C1) by two occipital condyles.
Foramen magnum
large opening in the occipital bone
Ethmoid
Forms the roof of the nasal cavity and a portion of the medial orbital socket between the sphenoid and lacrimal bones.
Sphenoid
Forms a portion of the base of the skull and is visible on the side of the cranium between the frontal and temporal bones. It forms portions of the posterior and lateral eye socket. It is the location of the pituitary gland.
Lacrimal
Forms part of the medial surface of each eye orbit. The orbits contain a groove that houses the lacrimal canal.
Nasal
Joins to form the base of the nose.
Maxilla
Joins to form the upper jaw and the anterior hard palate, and provides sockets for the upper teeth.
Zygomatic
Forms the cheekbones and connects the maxillary bones to the frontal and temporal bones.
Palatine
Forms the posterior part of the hard palate and a portion of the wall of the nasal cavity.
Inferior nasal concha
Located below the ethmoid bone on the lateral wall of each nasal cavity.
Mandible
Forms the lower jaw and contains sockets for the lower teeth.
Cervical vertebrae
These 7 vertebrae form the neck. They are numbered C1-C7. The two transverse foramina provide a passage for the vertebral arteries, and are found only in this vertebrae.
Atlas (C1)
a modified to articulate with the occipital condyle, which enables vertical, up and down movement of the skull,
Axis (C2)
Is highly modified and has a large medial process called the “dens,” . The dens articulates with the axis, providing a point of rotation that enables the horizontal turning of the skull.
Thoracic vertebrae
These are the 12 vertebrae of the chest, where the ribs attach. They are numbered T1-T12. These vertebrae have long spinous processes which increase in height, inferiorly.
Lumbar
These 5 vertebrae form the lower back. They are numbered L1 - L5. The bodies are large and thick, with long transverse processes, and short, wide spinous processes.
Sacrum
This bone is the result of the fusion of the five sacral vertebrae. It articulates with L5, the coccyx, and the pelvic girdle.
Coccyx
This bone is the result of the fusion of between three to five caudal, or tail, vertebrae. It is often called the tail bone.
Sternum
This is commonly known as the breastbone. It is a flat narrow bone in the center of the upper chest. It articulates with the clavicles (collarbones) and the ribs. Is composed of the manubrium, body and xiphoid process.
True ribs
The costal cartilage attaches these ribs directly to the sternum. These ribs increase in length, inferiorly. There are seven pairs of these ribs.
False ribs
The first three pairs of ribs are indirectly connected to the sternum by cartilage attached to the costal cartilage of the last true rib. These ribs become shorter, inferiorly.
Floating ribs
Are the last two pairs of false ribs. They do not connect to the sternum.
Nasal
Type of Bone: Skull (frontal)
What is A?
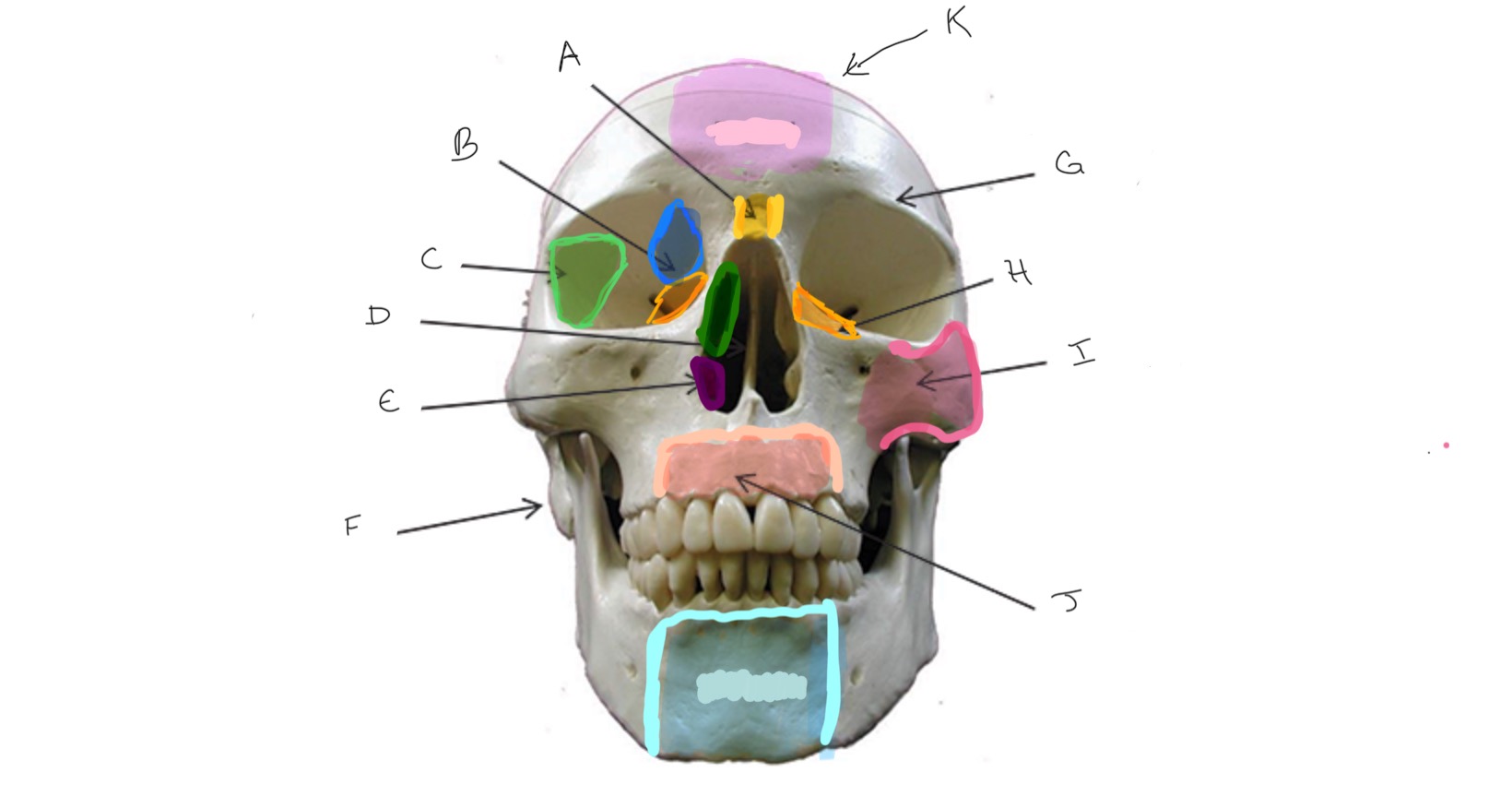
Ethmoid
Type of Bone: Skull (frontal)
What is B?
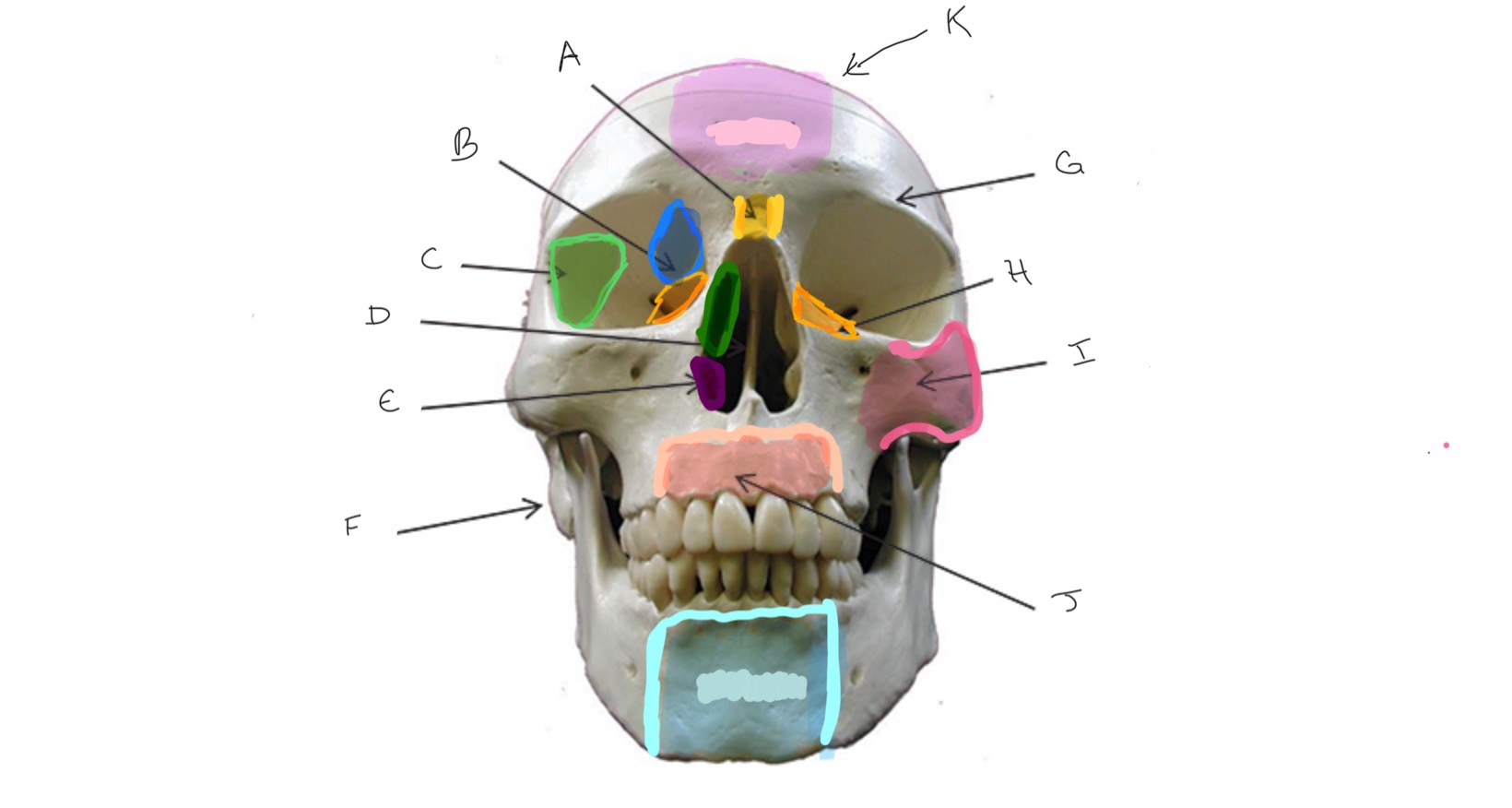
Sphenoid
Type of Bone: Skull (frontal)
What is C?
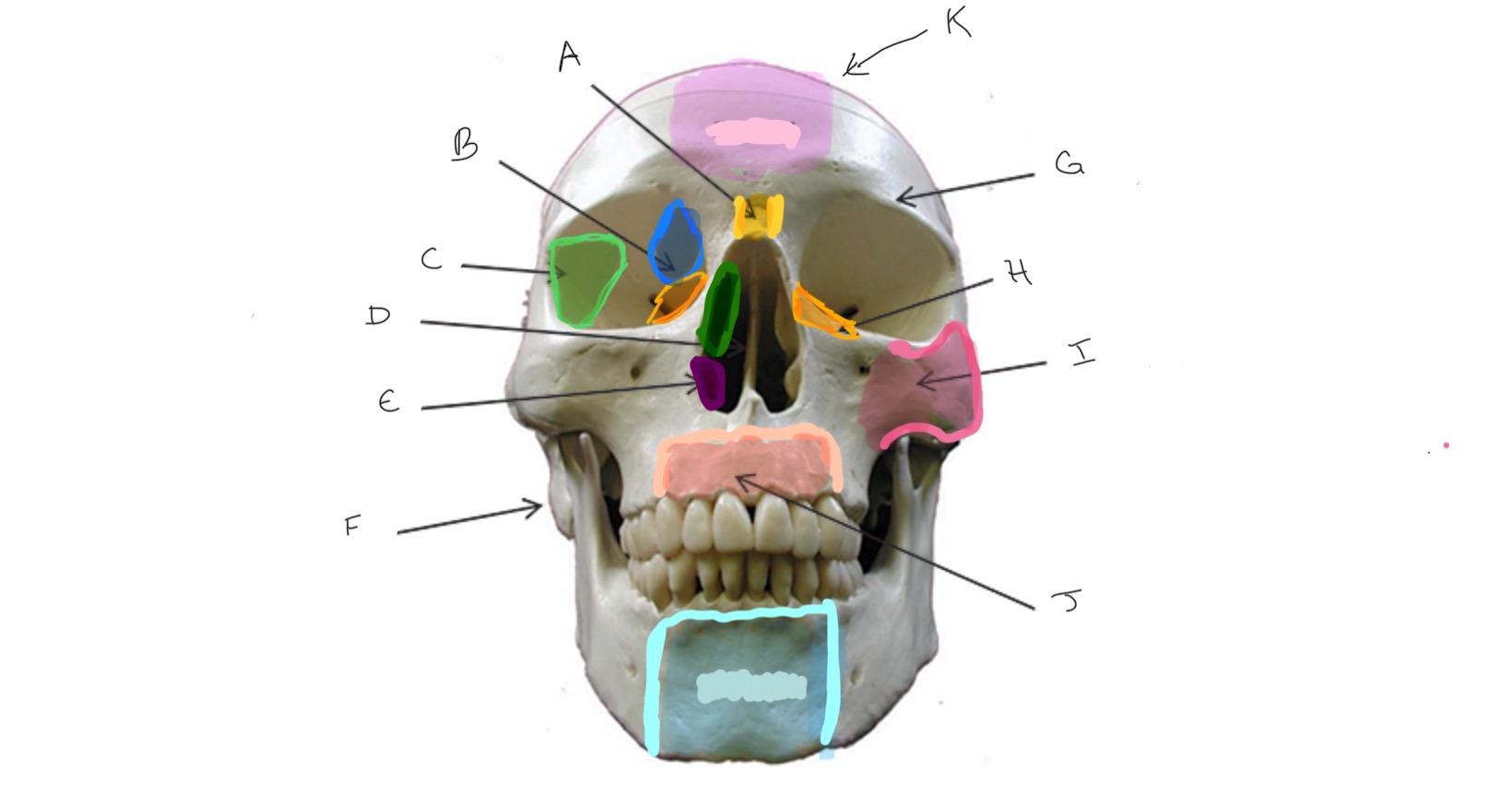
Nasal Septum
Type of Bone: Skull (frontal)
What is D?
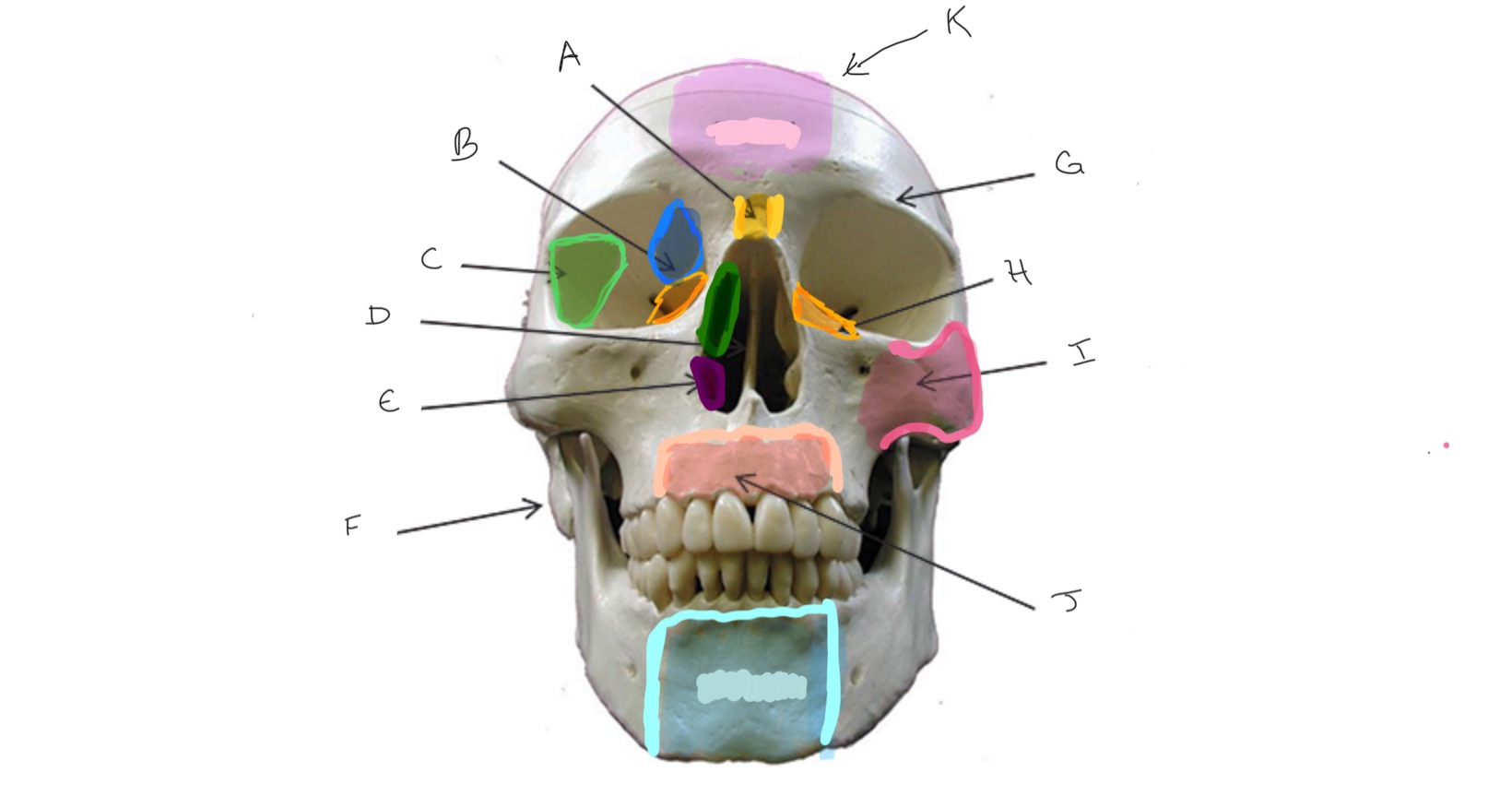
Inferior Nasal Concha
Type of Bone: Skull (frontal)
What is E?
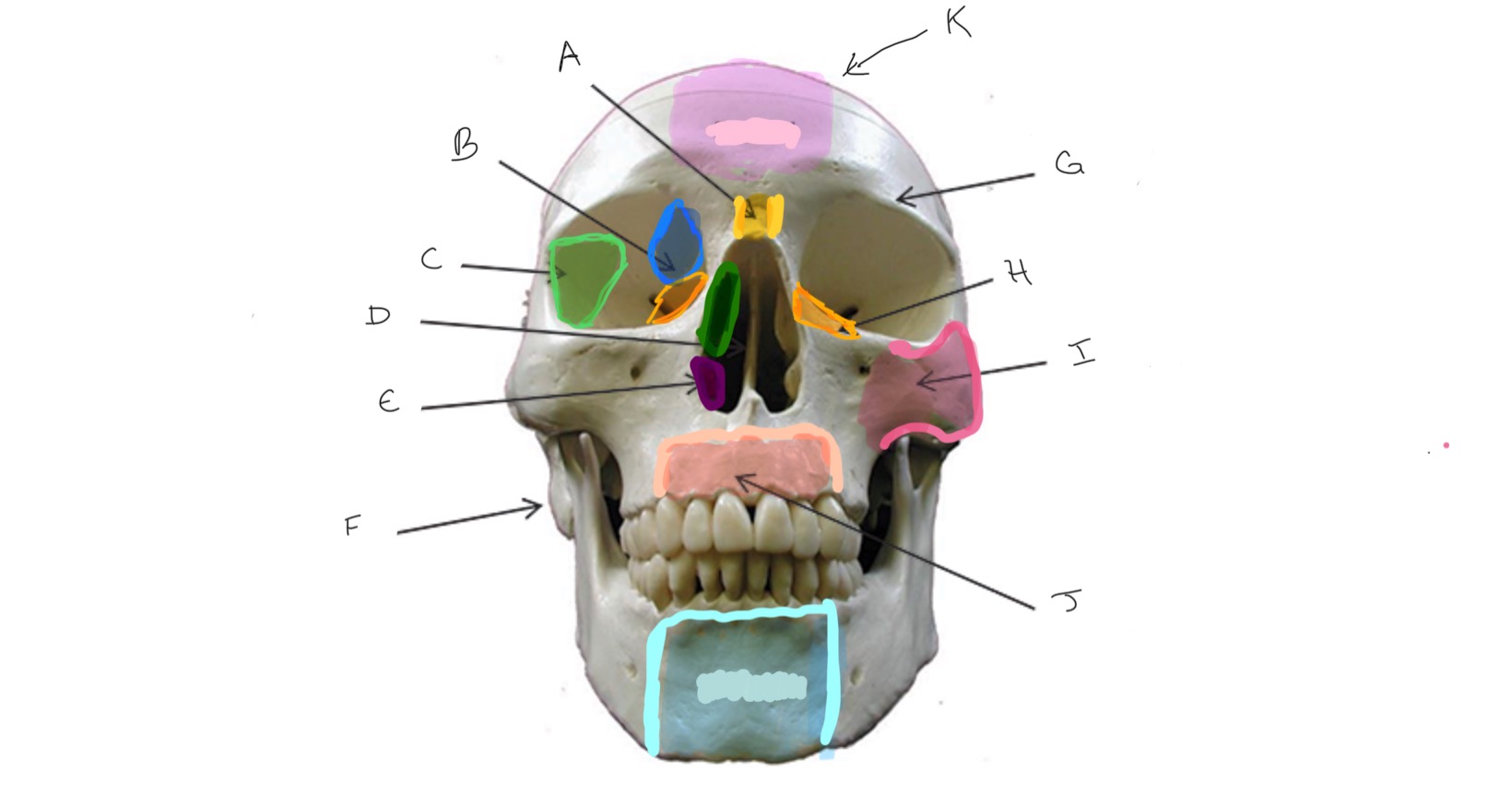
Mastoid Process
Type of Bone: Skull (frontal)
What is F?
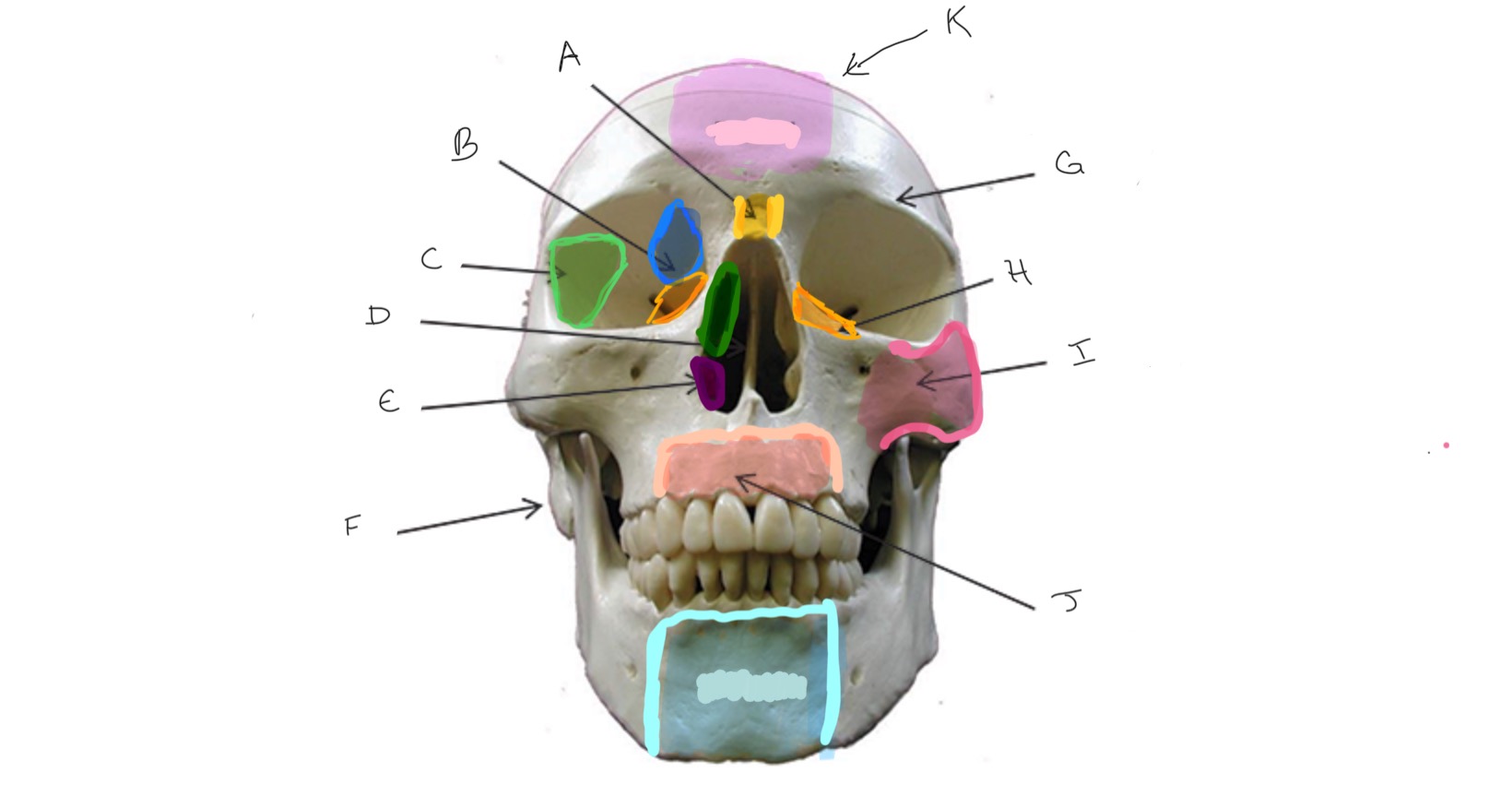
Frontal
Type of Bone: Skull (frontal)
What is G?
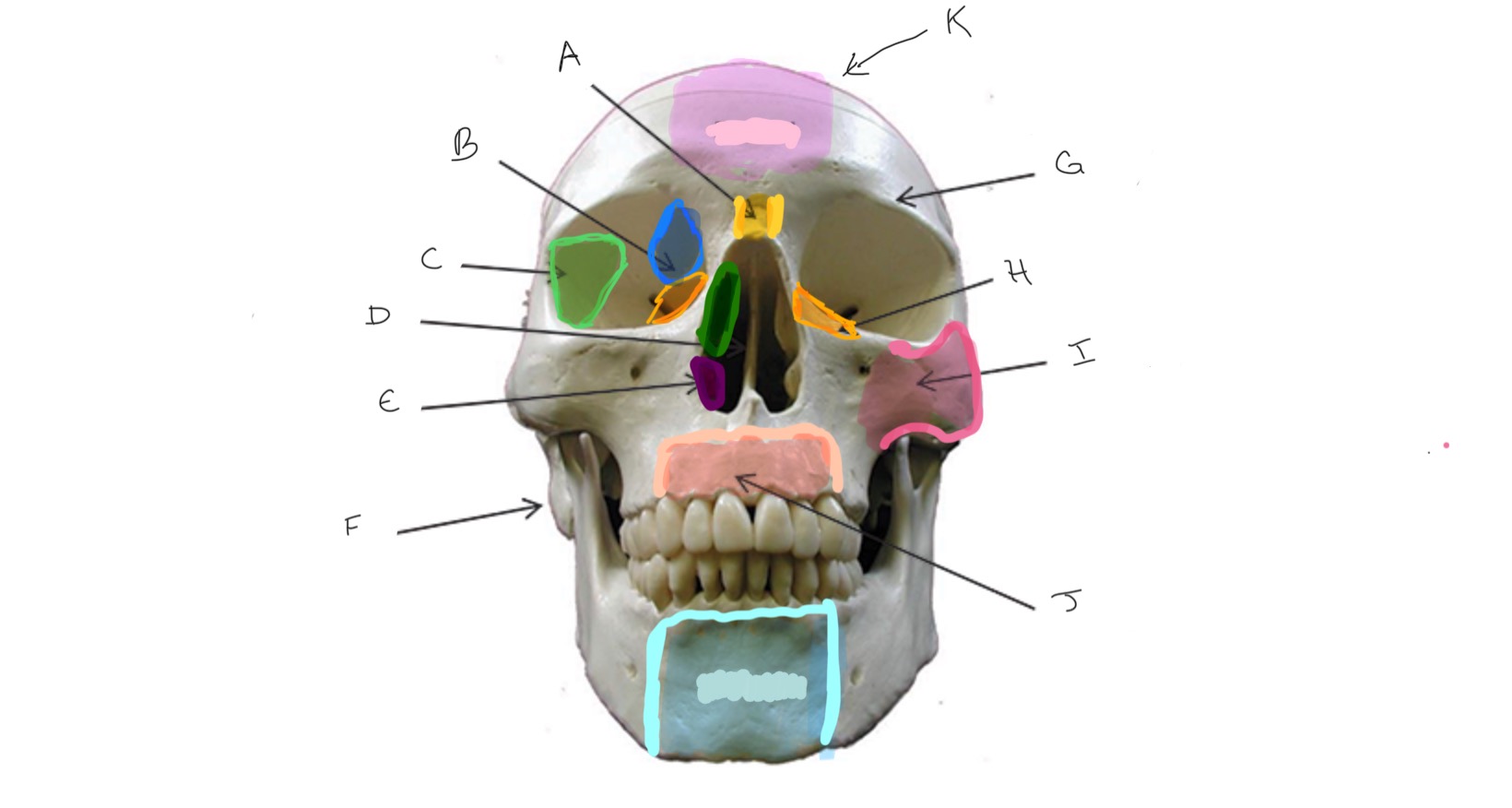
Lacrimal
Type of Bone: Skull (frontal)
What is H?
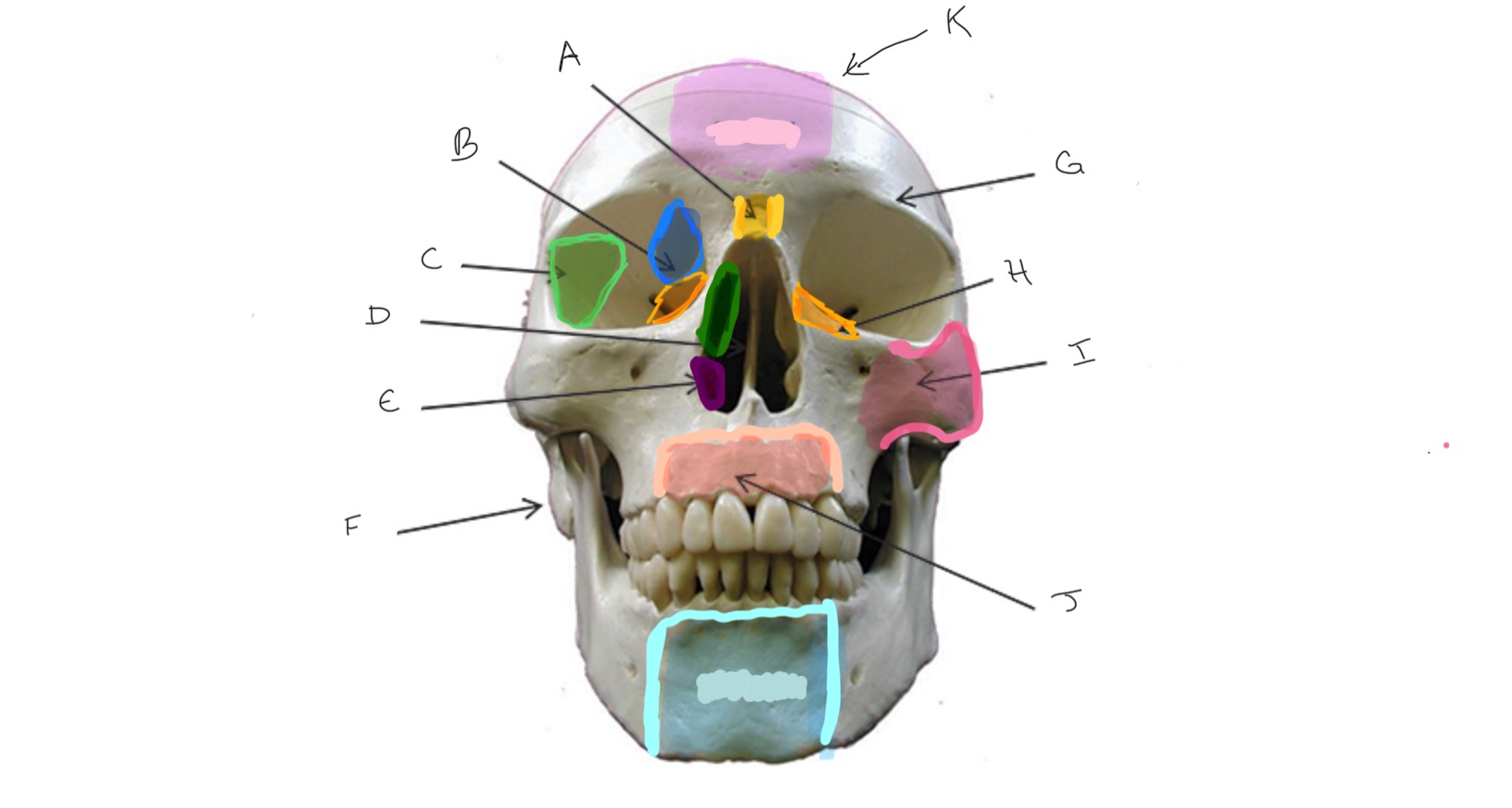
Zygomatic
Type of Bone: Skull (frontal)
What is I?
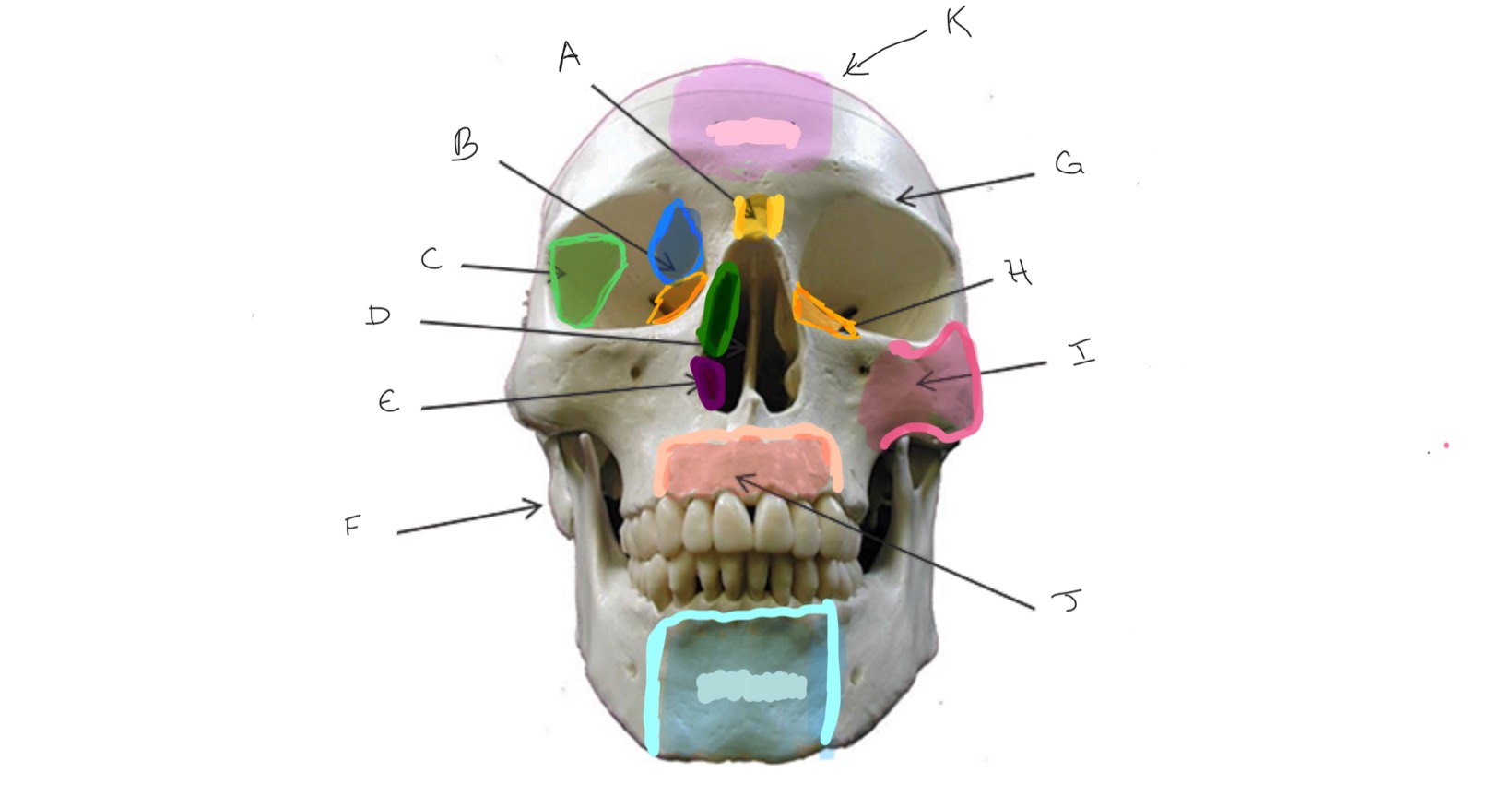
Maxilla
Type of Bone: Skull (frontal)
What is J?
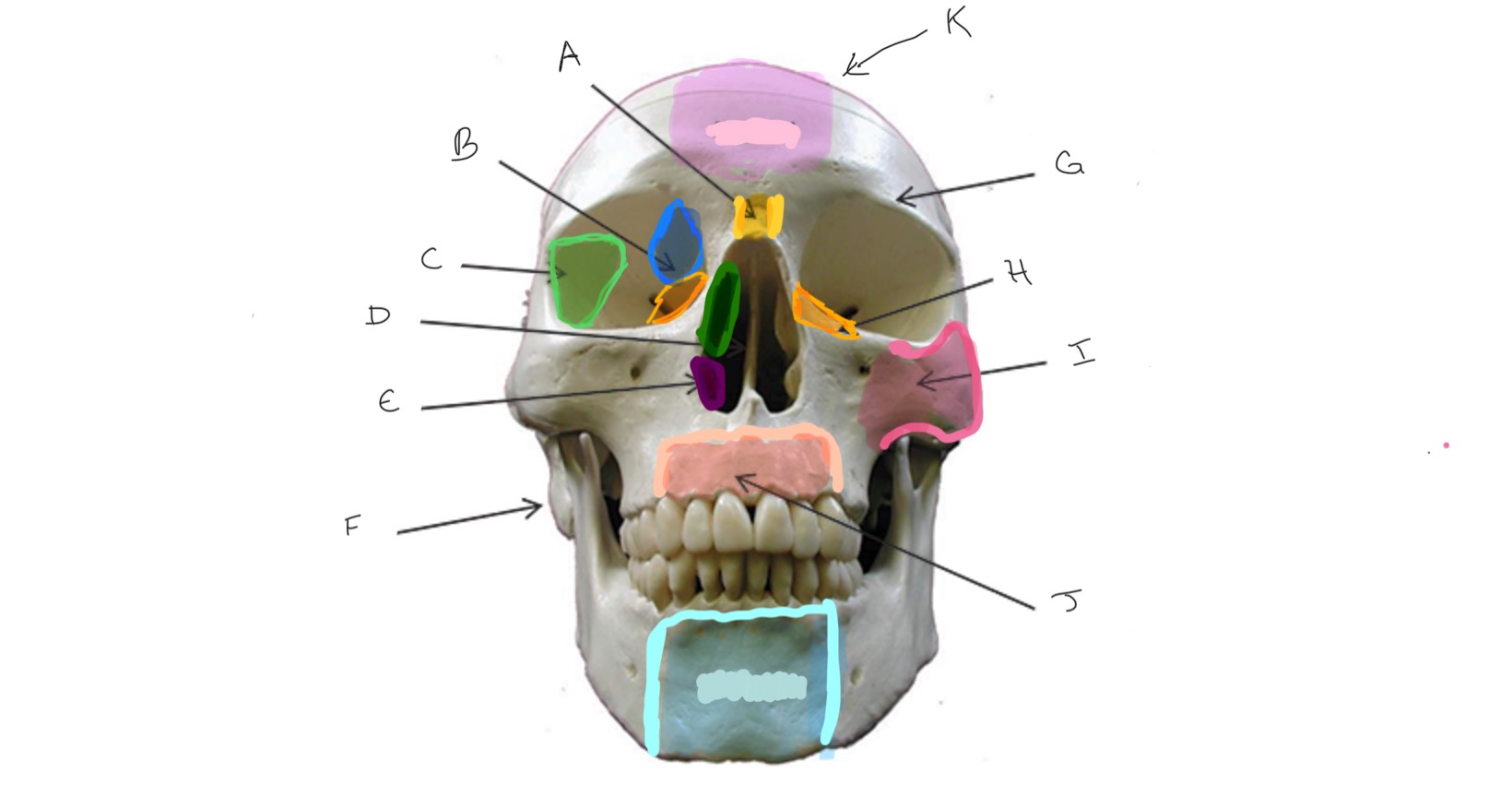
Nasal
Type of Bone: Skull (lateral)
What is A?
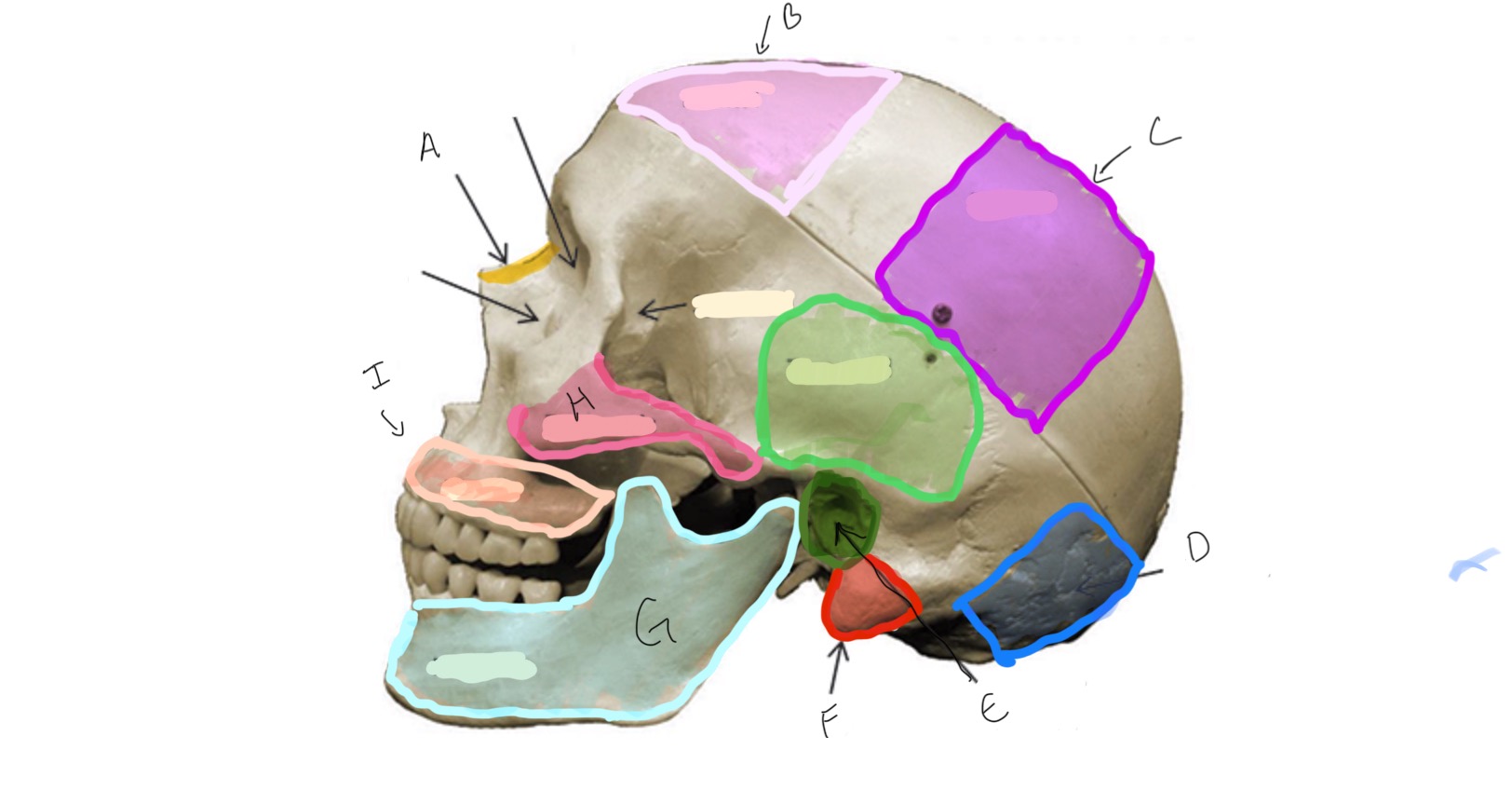
Frontal
Type of Bone: Skull (lateral)
What is B?
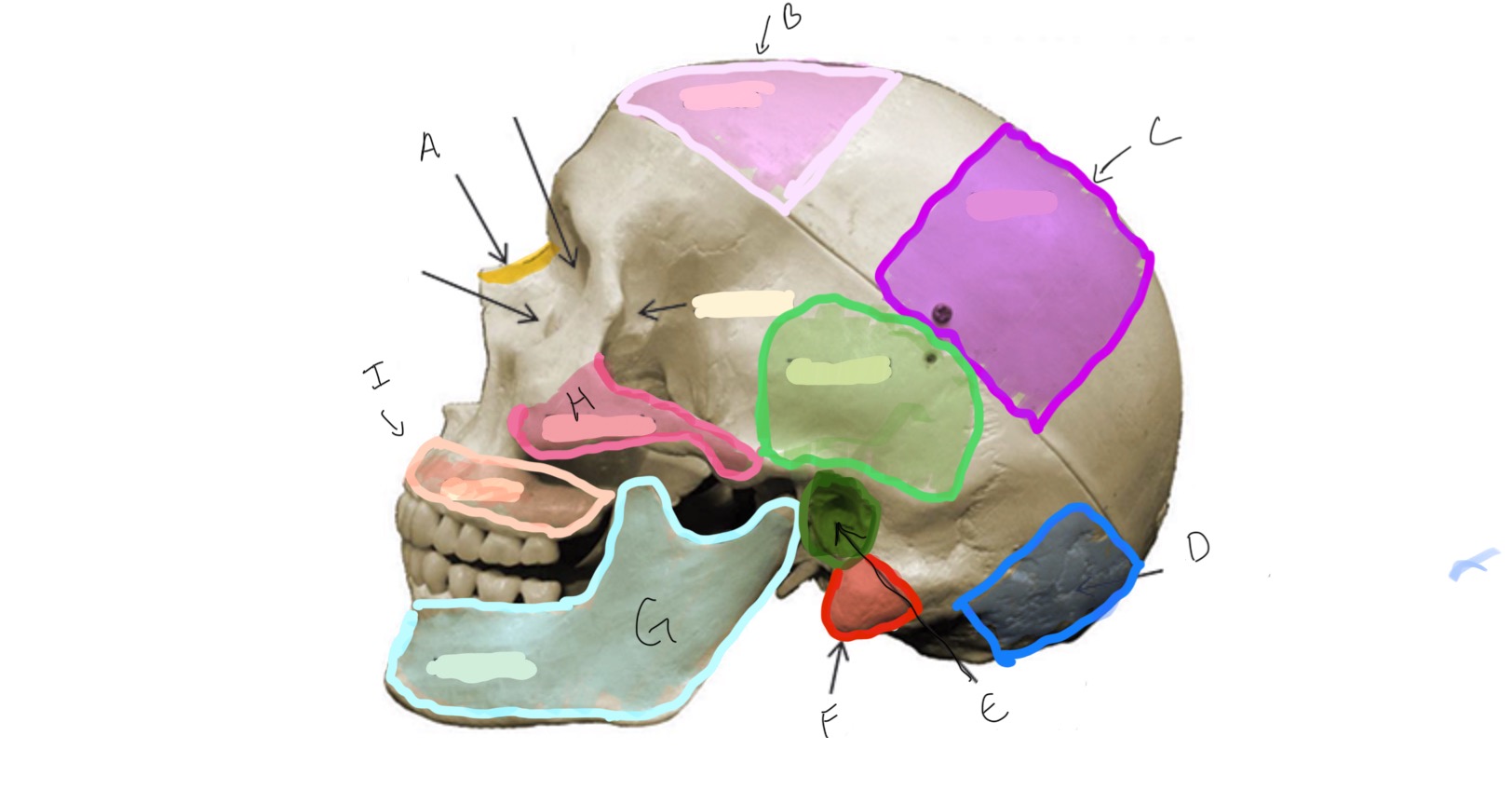
Parietal
Type of Bone: Skull (latera)
What is C?
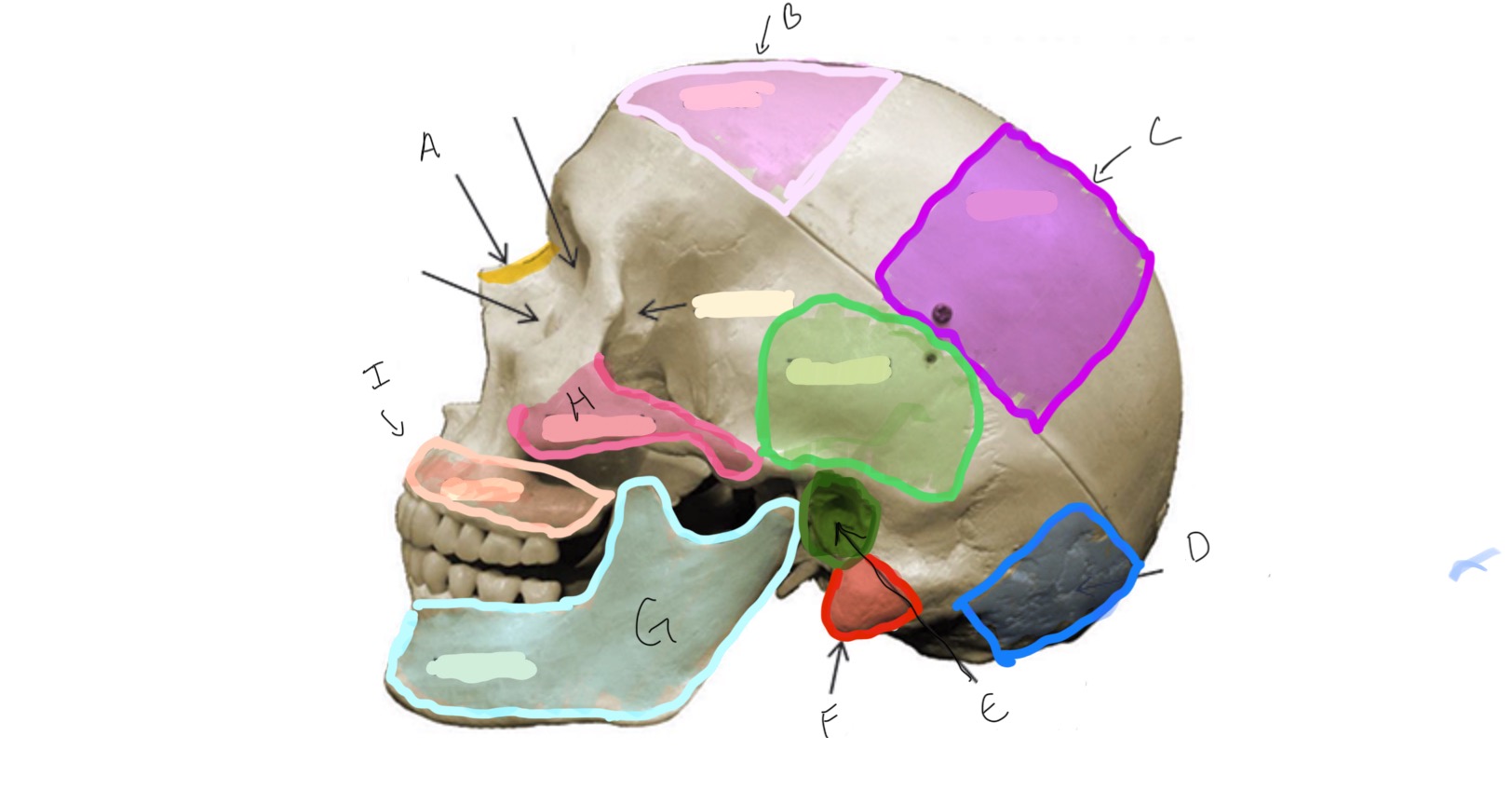
Occipital
Type of Bone: Skull (lateral)
What is D?
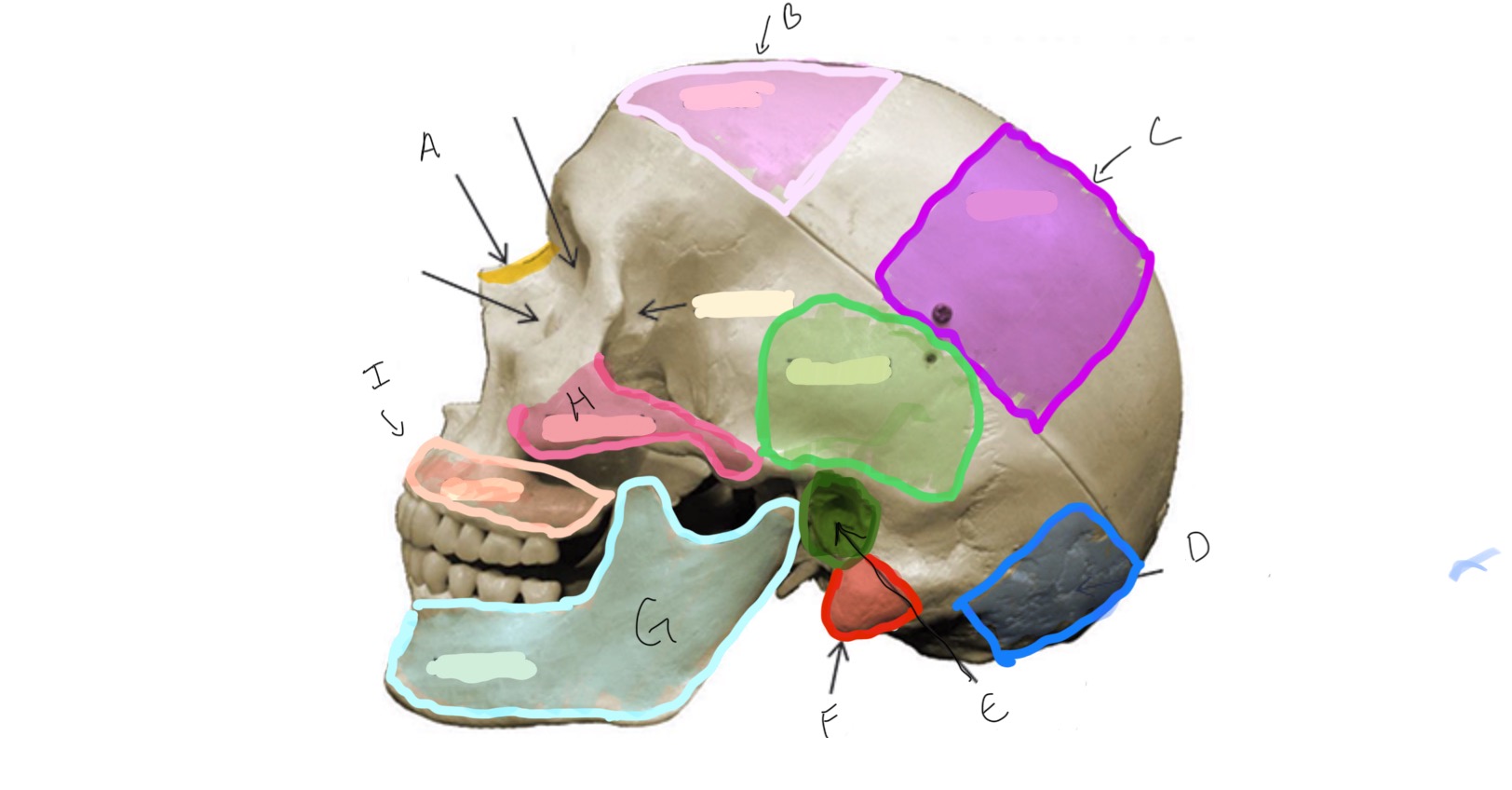
Auditory Meatus
Type of Bone: Skull (lateral)
What is E?
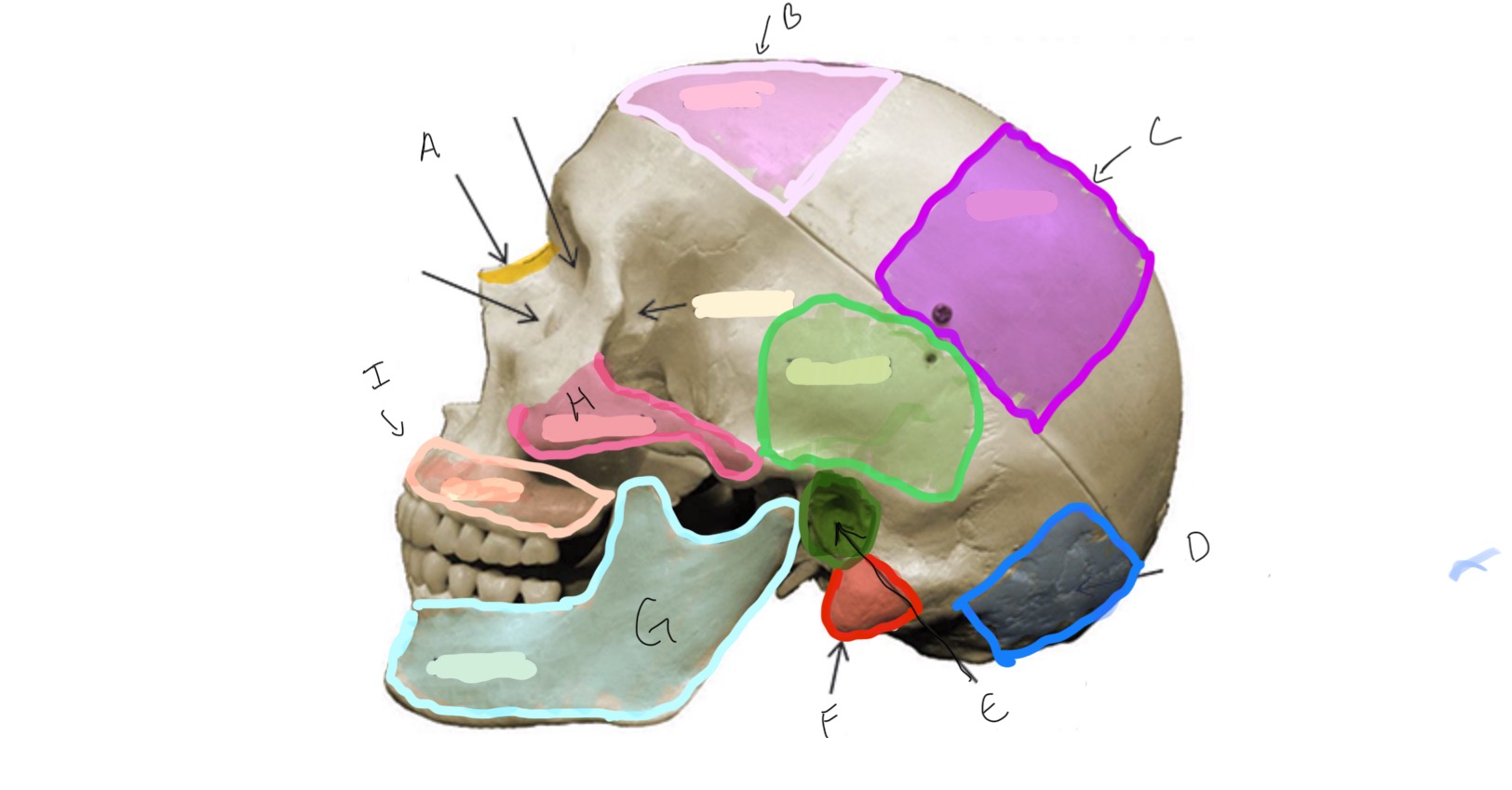
Mastoid Process
Type of Bone: Skull (lateral)
What is F?
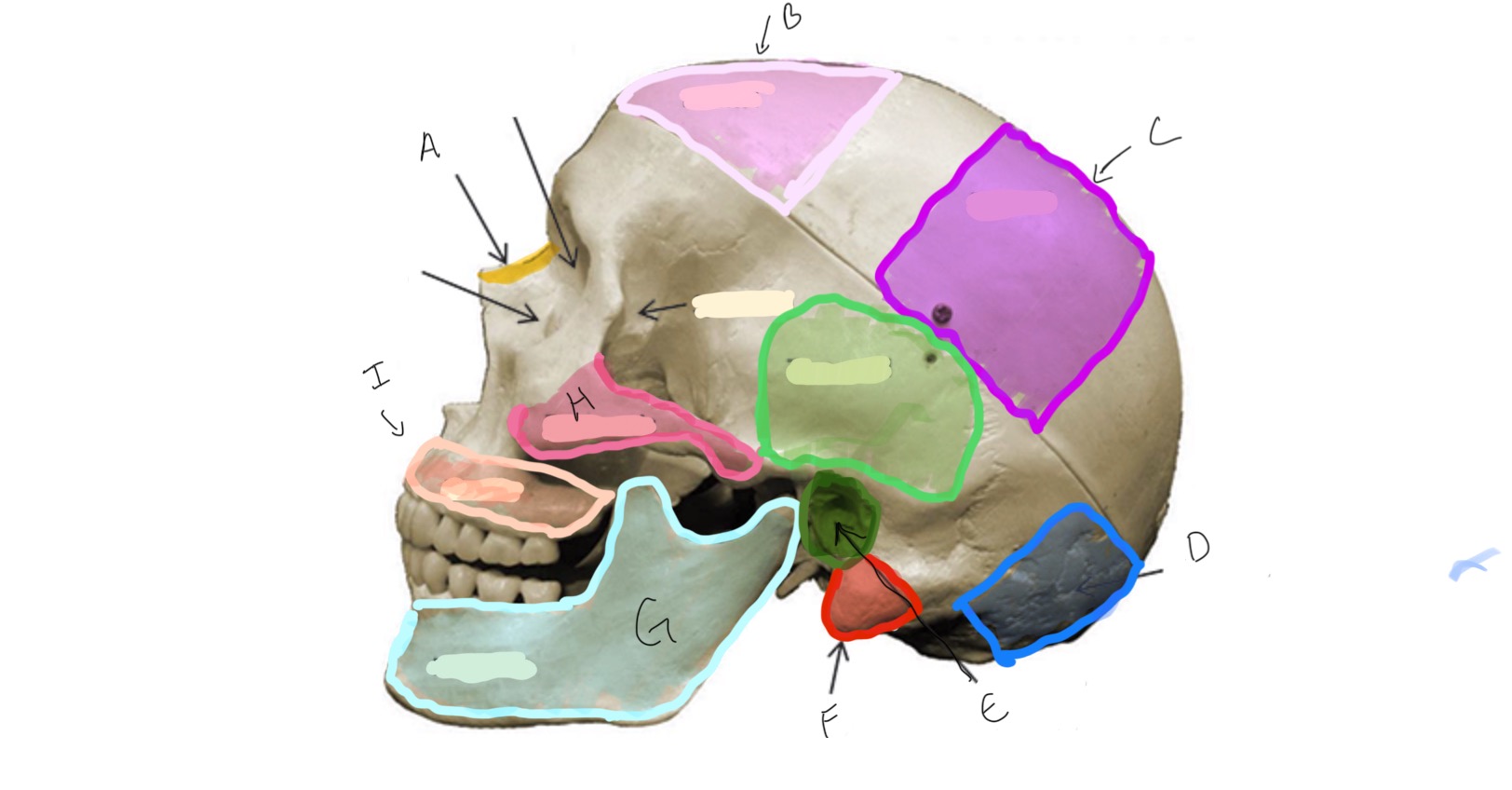
Mandible
Type of Bone: Skull (lateral)
What is G?
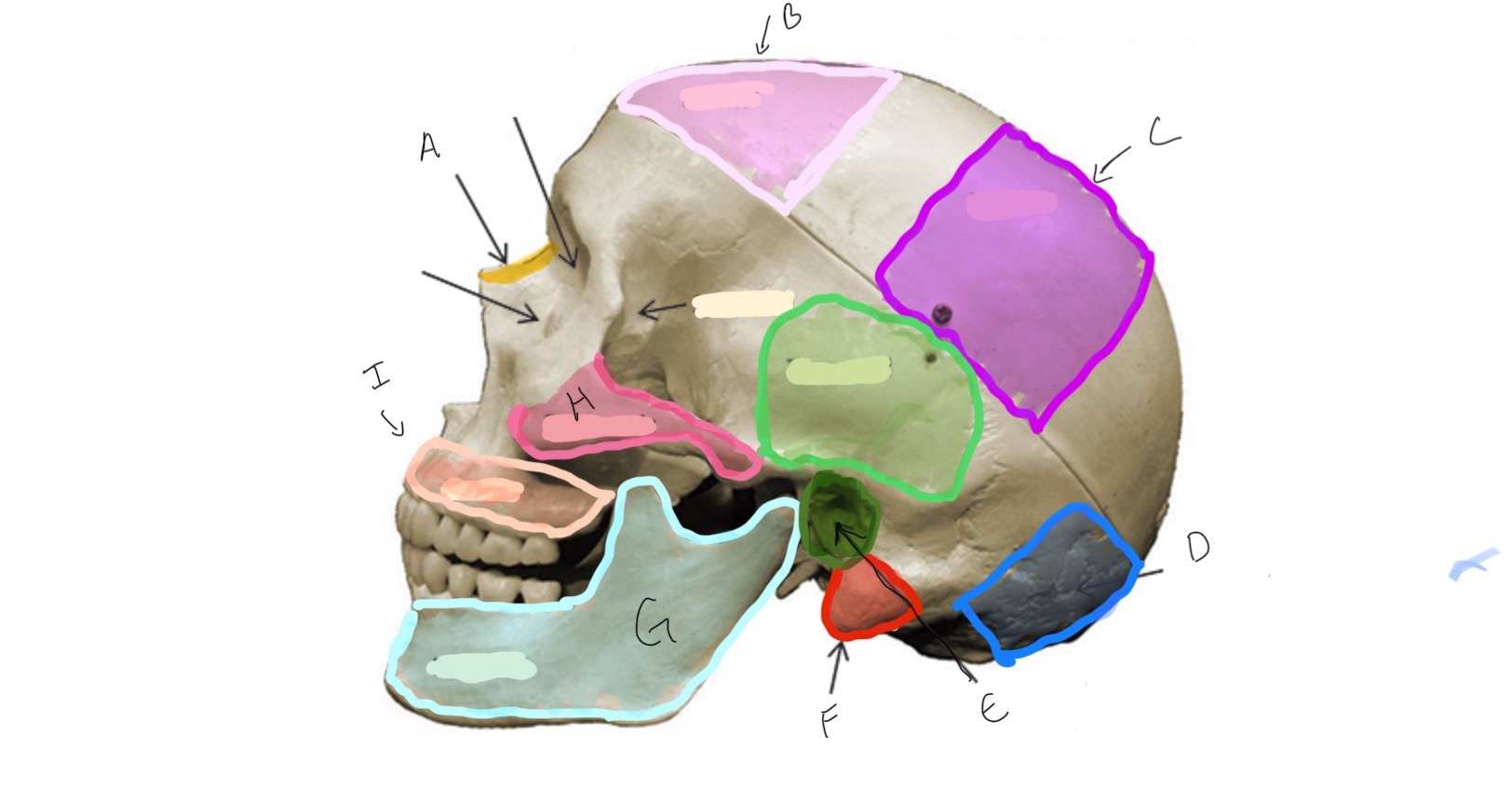
Zygomatic
Type of Bone: Skull (lateral)
What is H?
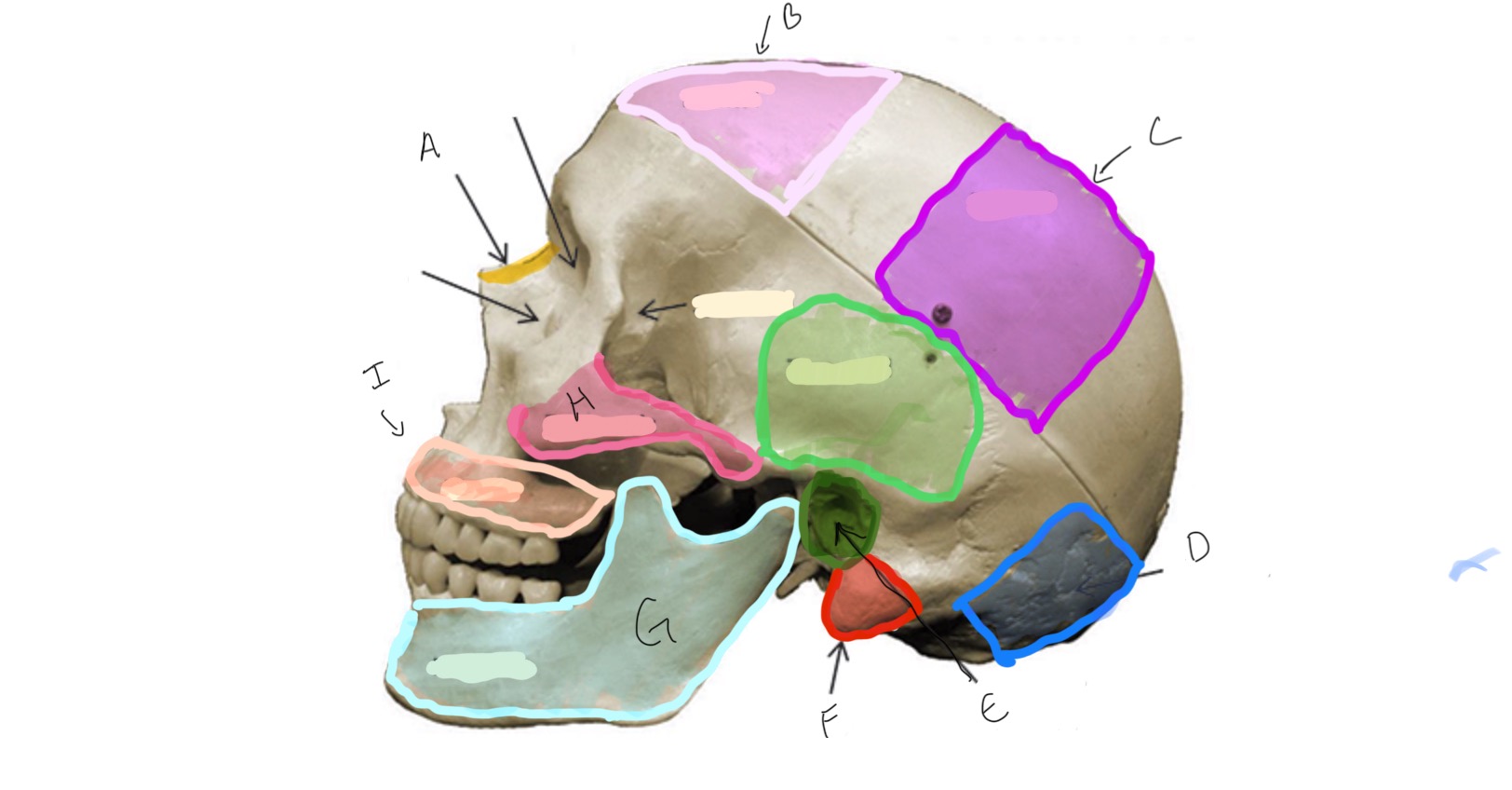
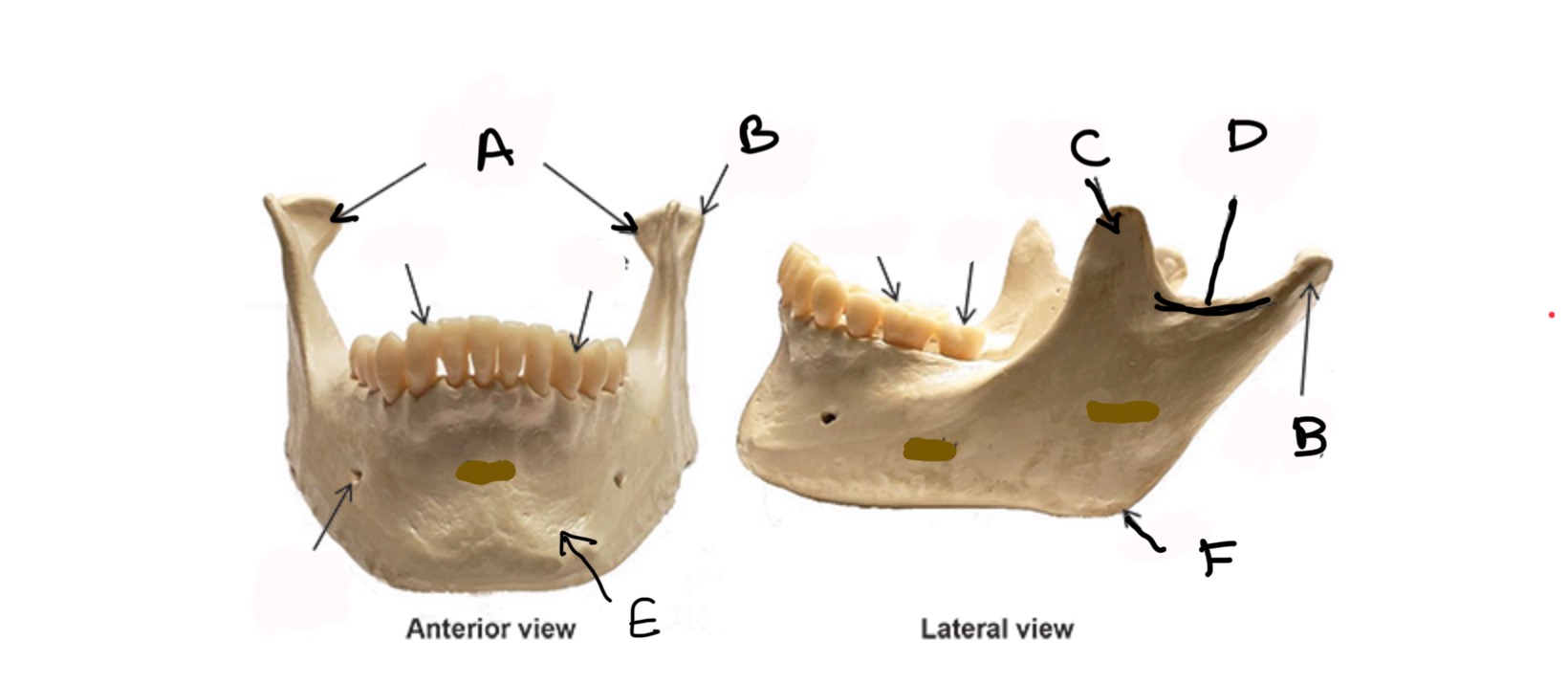
Mandibular Condyle
Type of Bone: Mandible
What is A?
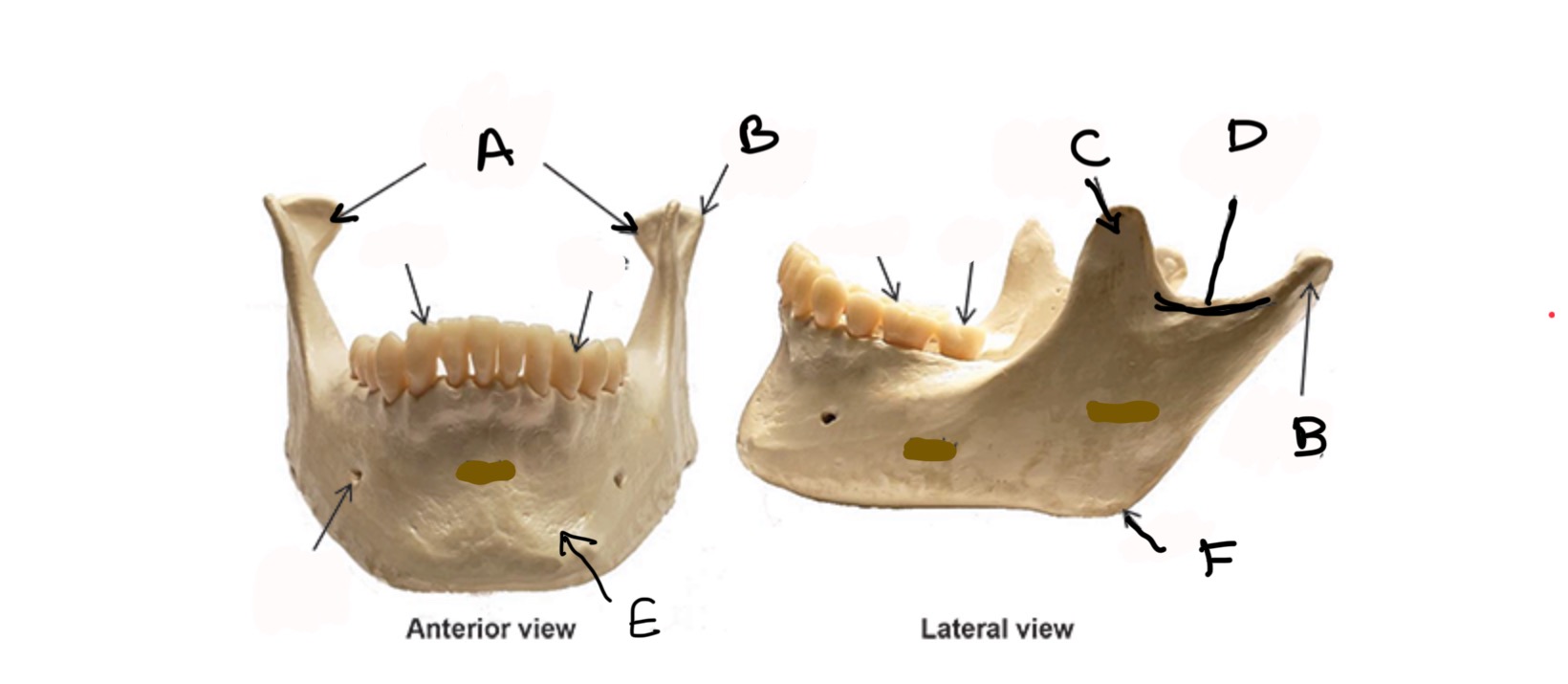
Condylar process
Type of Bone: Mandible
What is B?
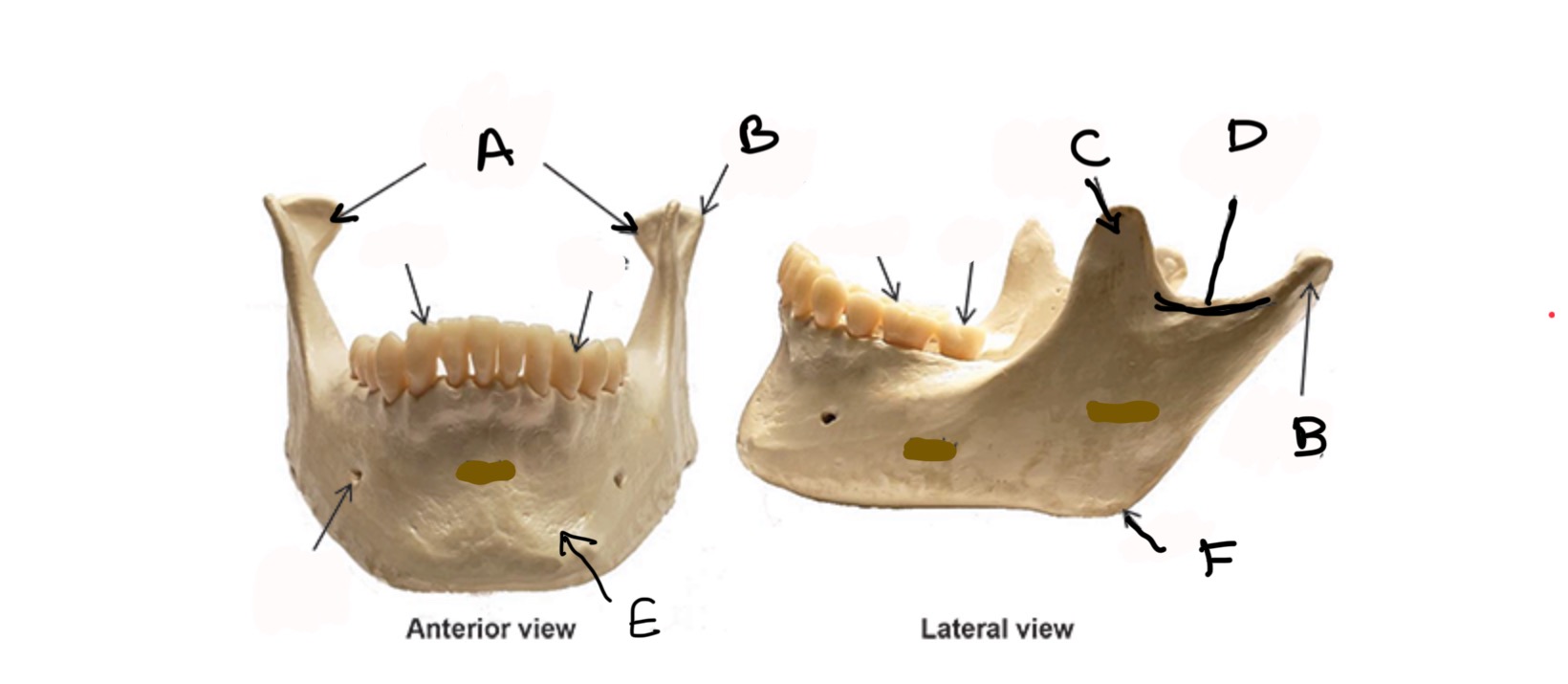
Coronoid process
Type of Bone: Mandible
What is C?
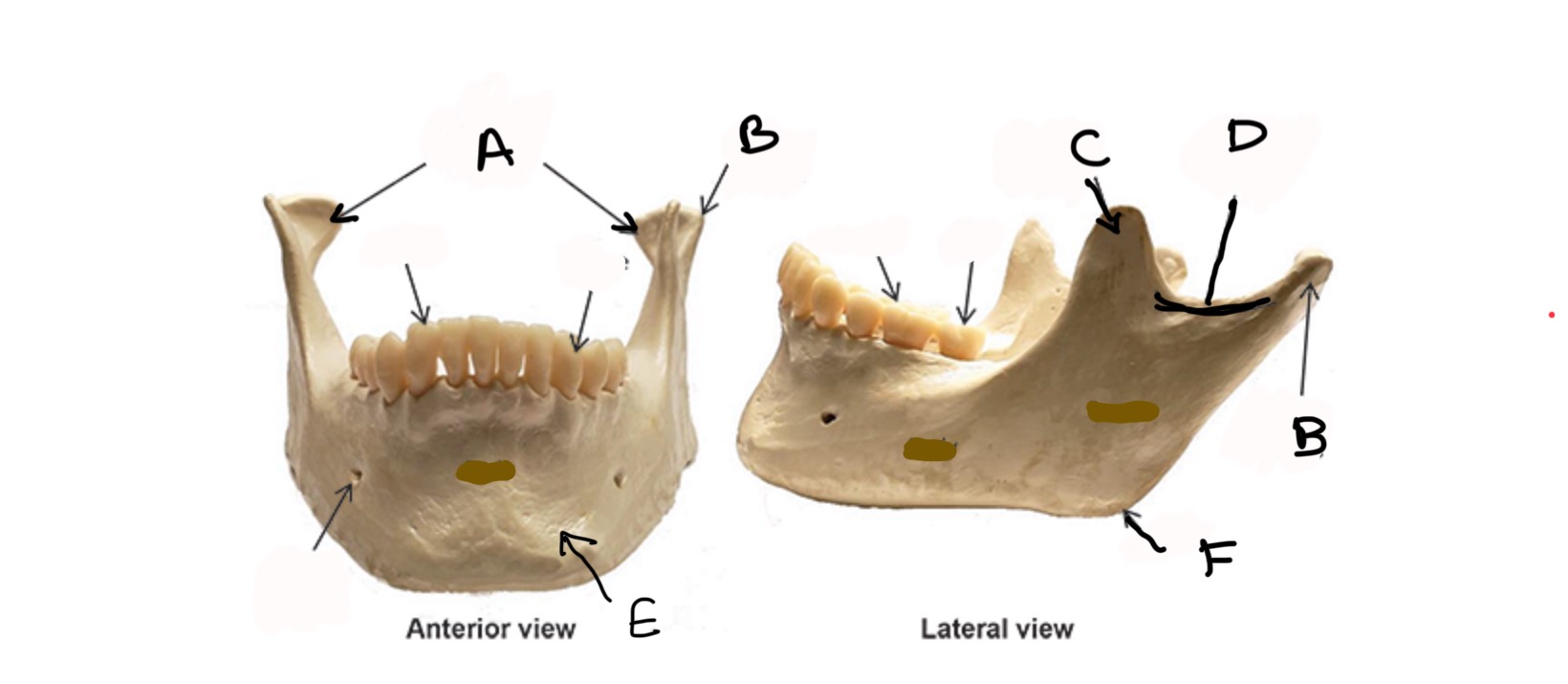
Mandibular Notch
Type of Bone: Mandible
What is D?
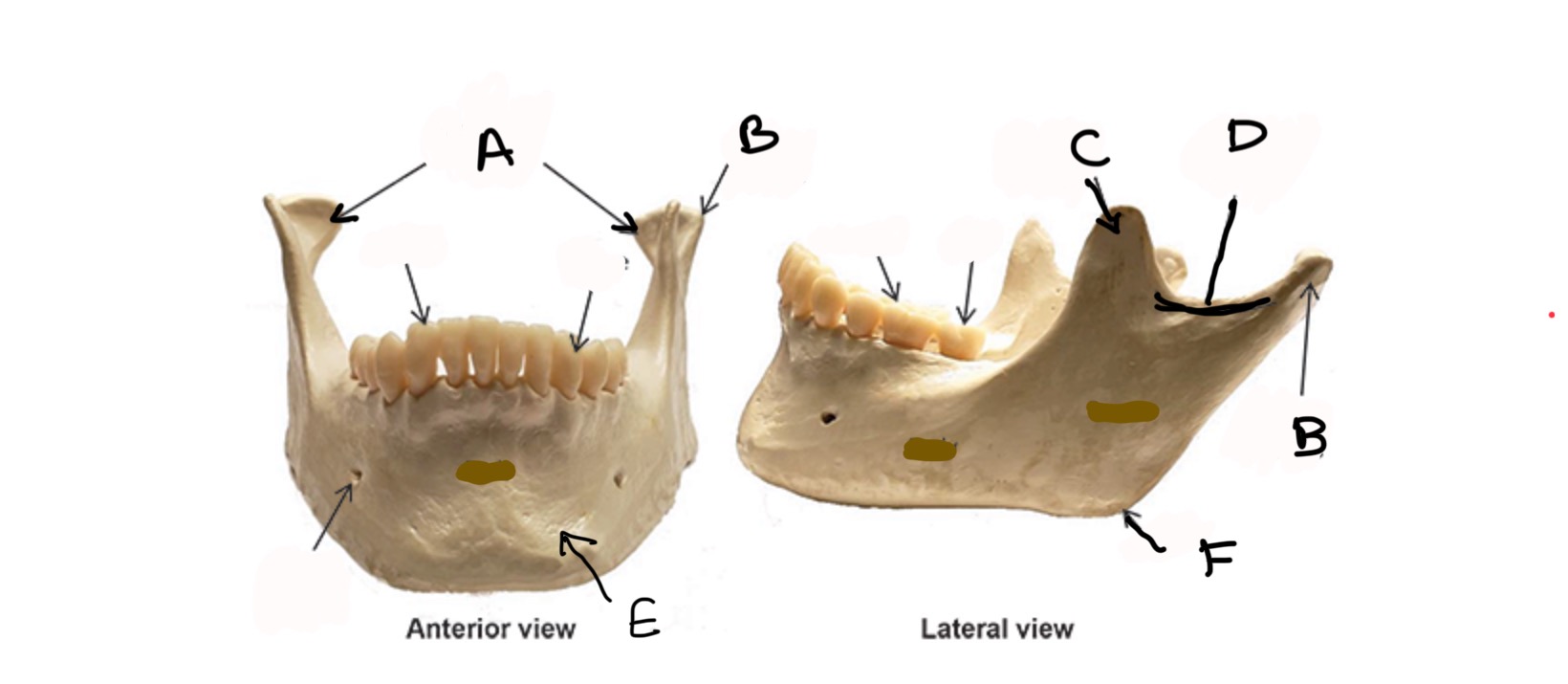
Body
Type of Bone: Mandible
What is E?
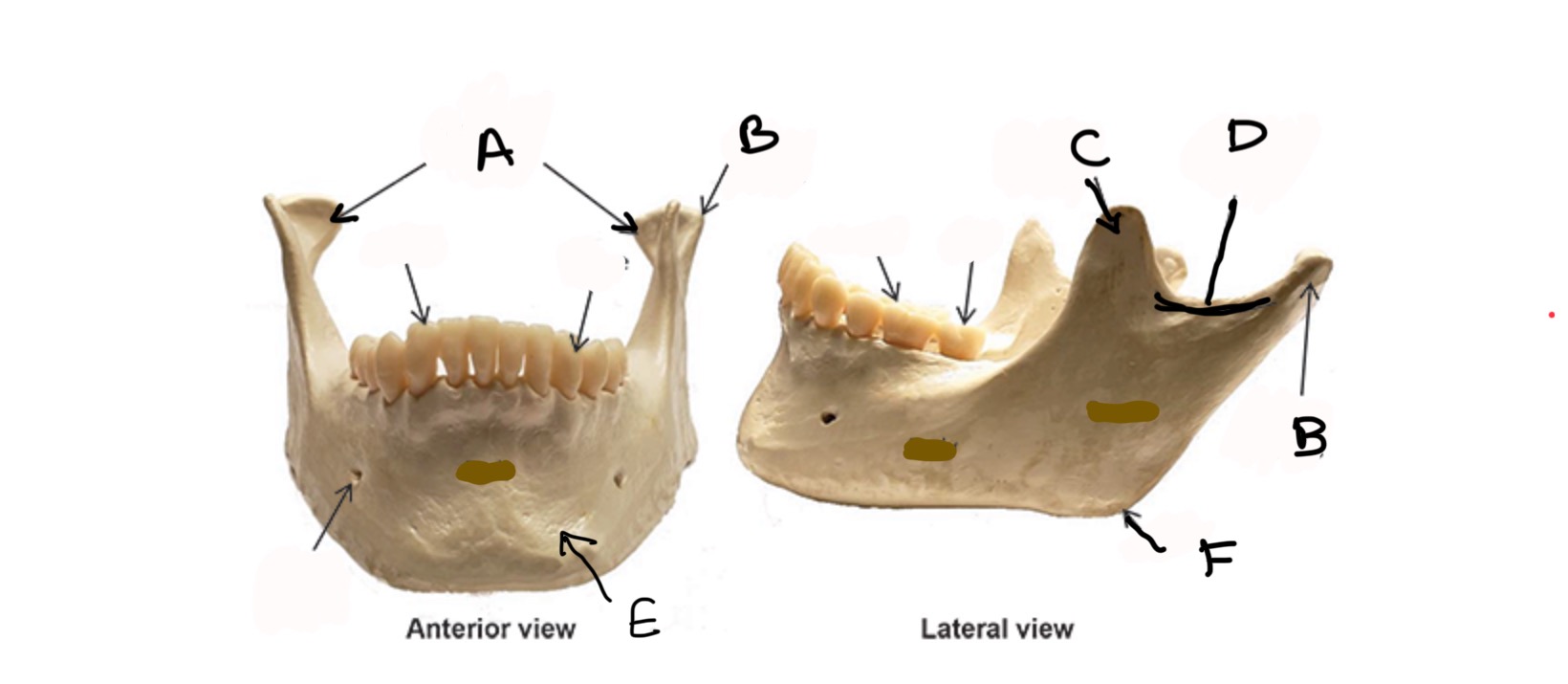
Ramus
Type of Bone: Mandible
What is F?
Body
Type of Bone: Cervical Vertebrae
What is A?
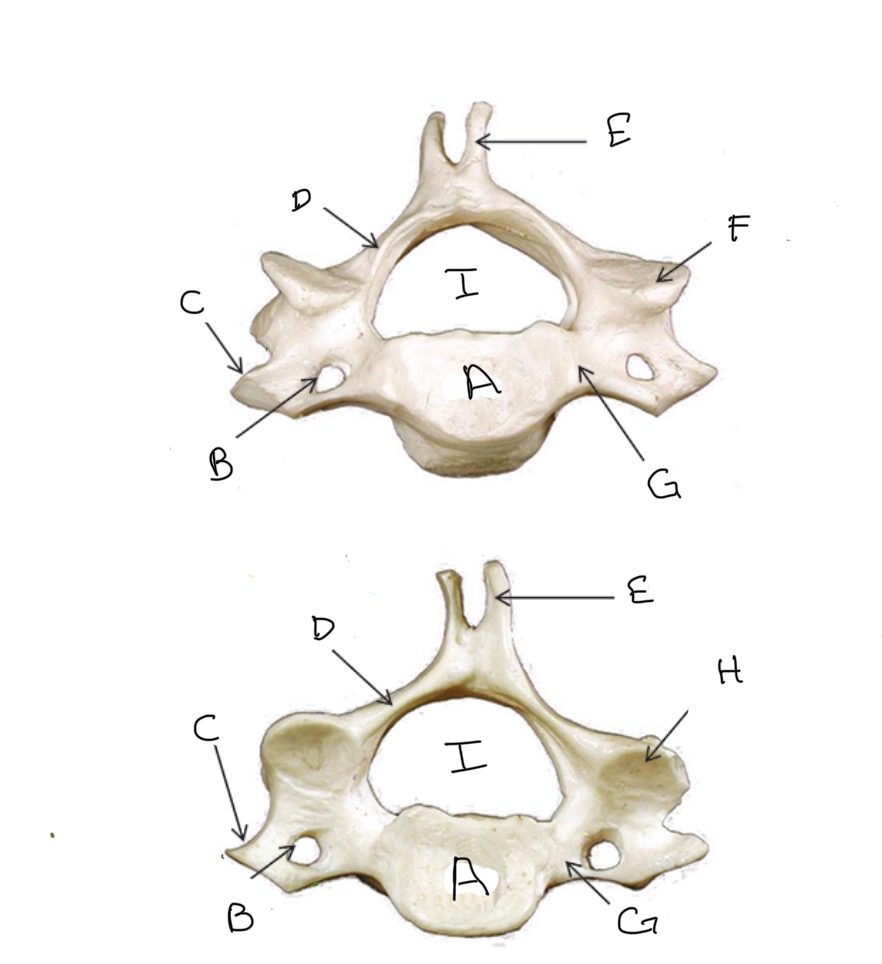
Transverse Foramen
Type of Bone: Cervical Vertebrae
What is B?
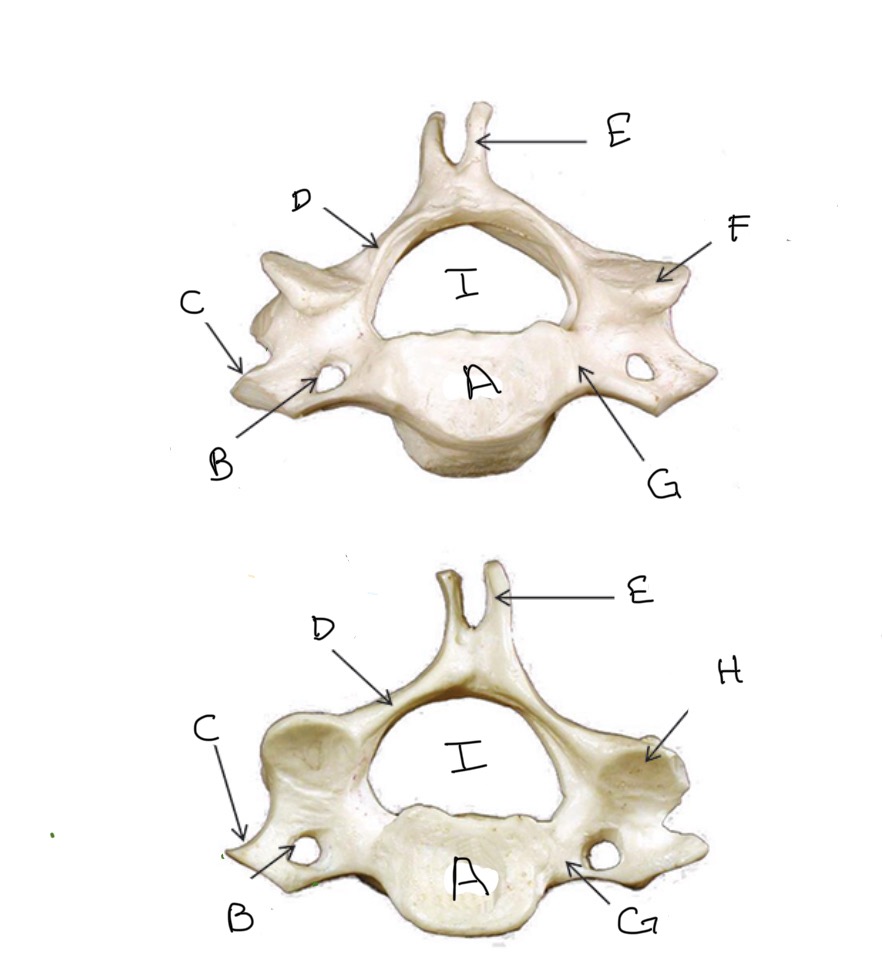
Transverse Process
Type of Bone: Cervical Vertebrae
What is C?
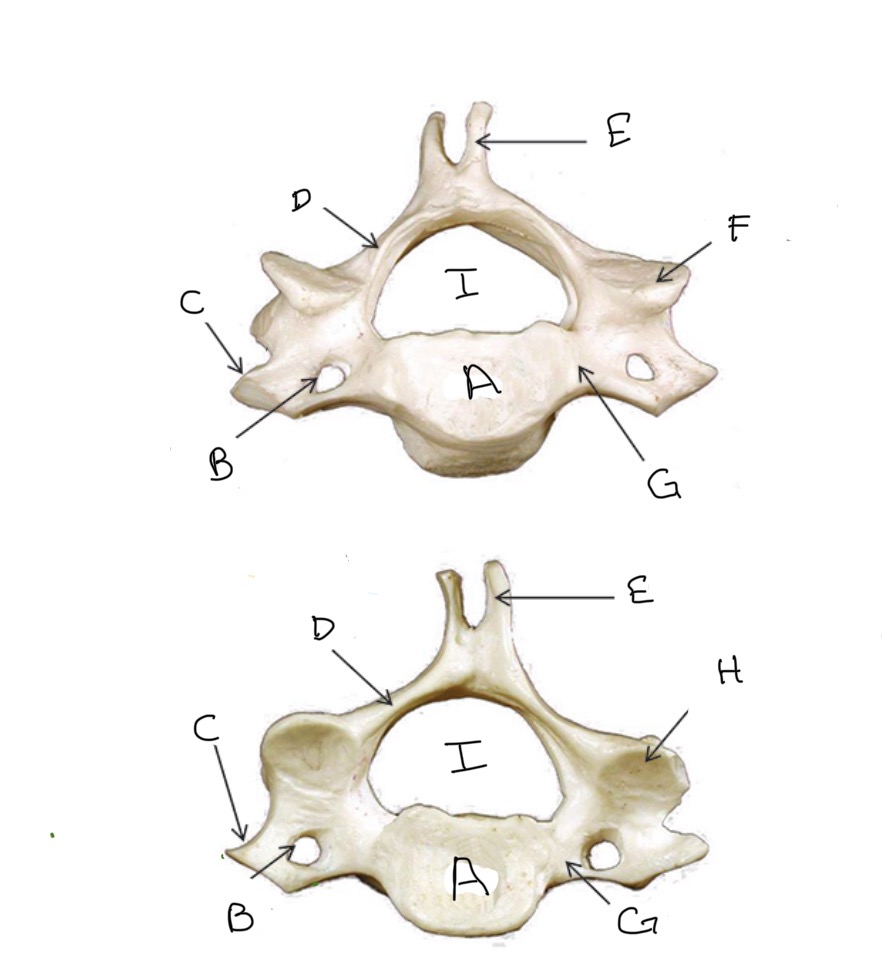
Lamina
Type of Bone: Cervical Vertebrae
What is D?
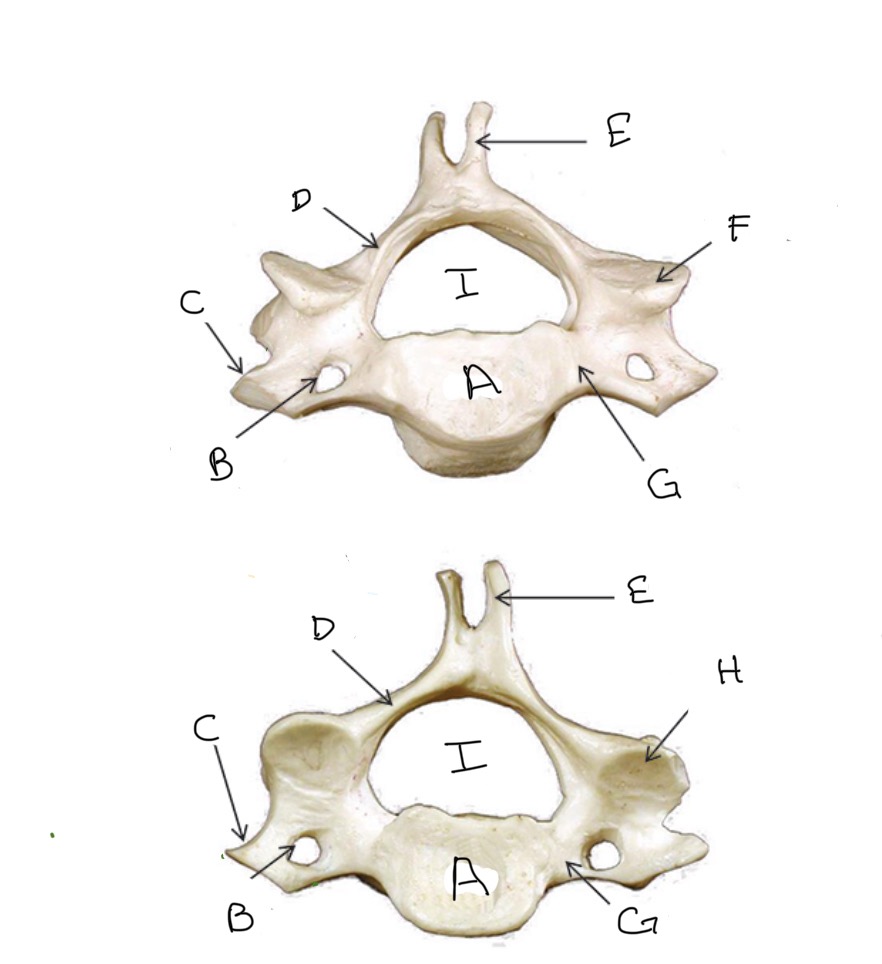
Spinous Process
Type of Bone: Cervical Vertebrae
What is E?
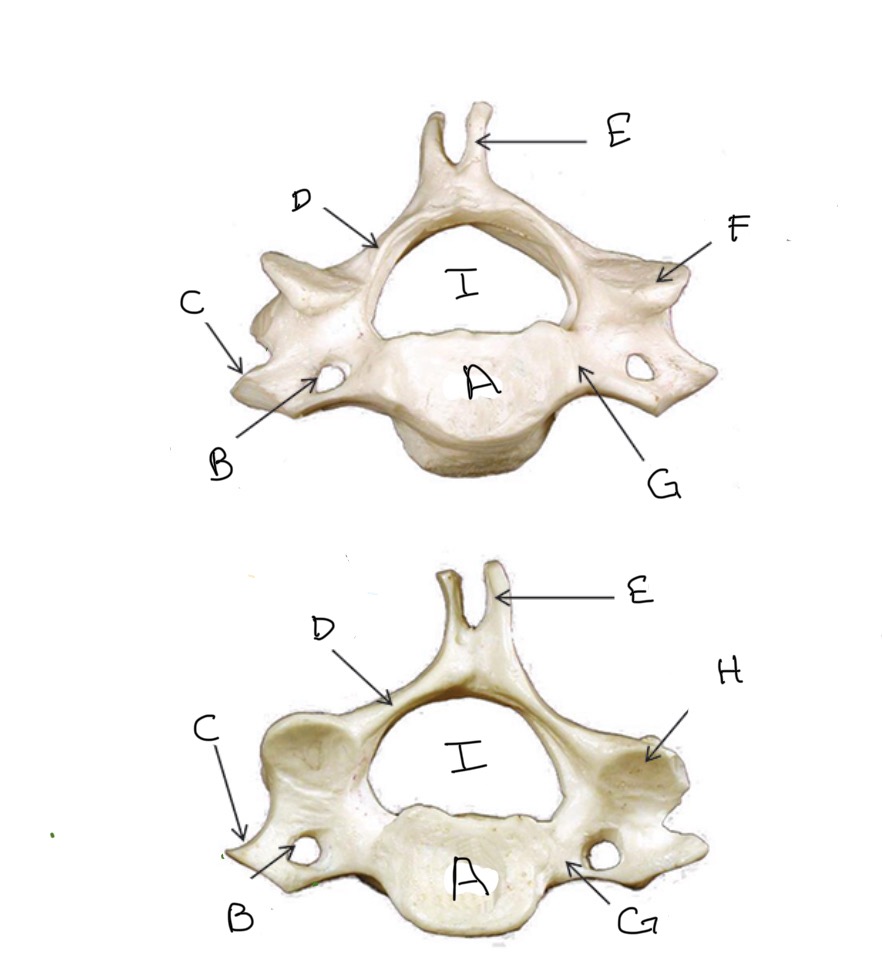
Superior Articular Process
Type of Bone: Cervical Vertebrae
What is F?
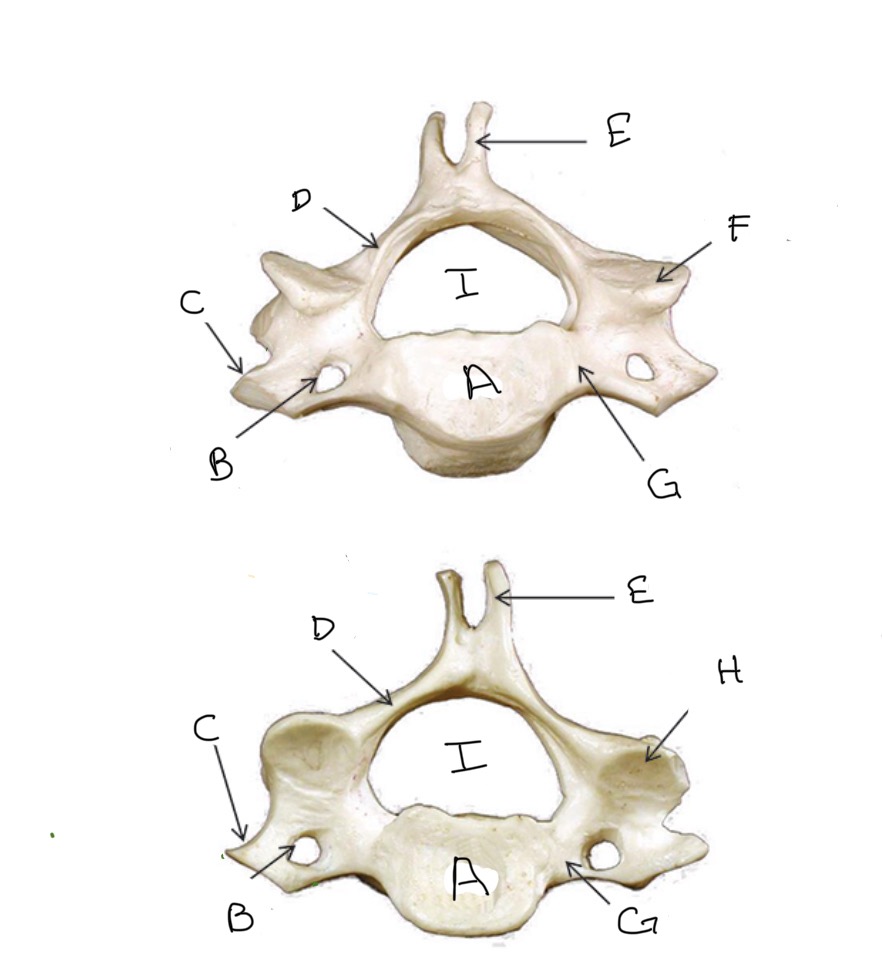
Pedicle
Type of Bone: Cervical Vertebrae
What is G?
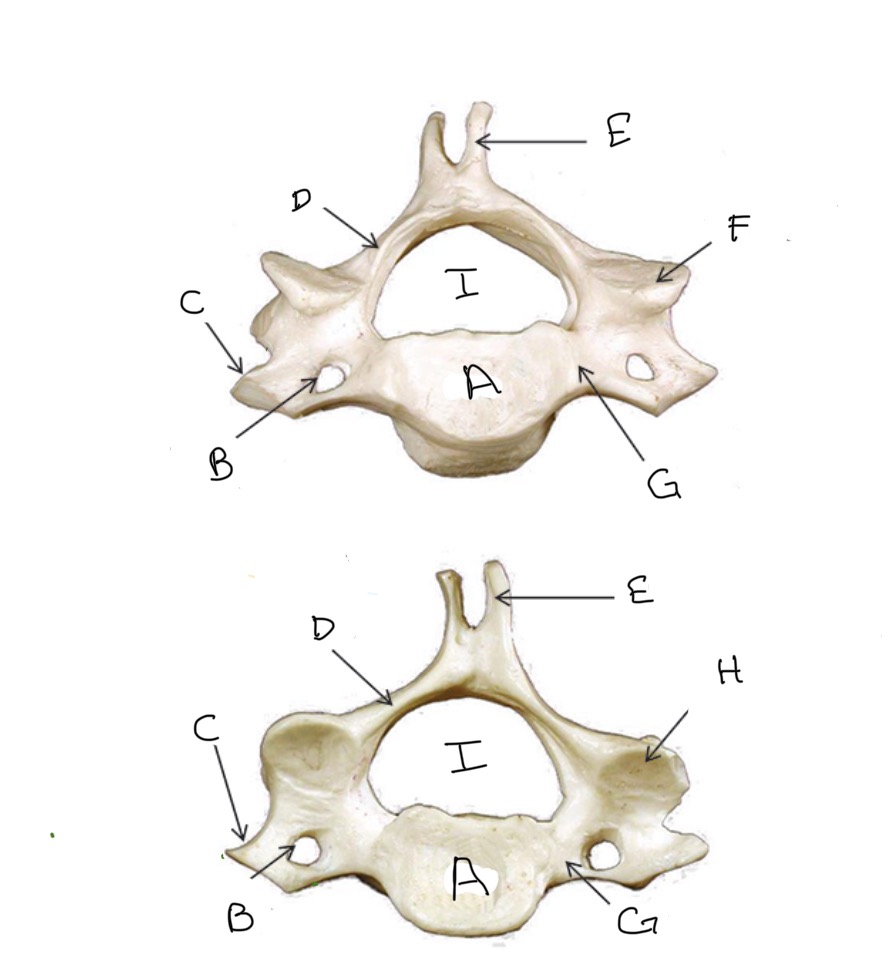
Inferior Articular Process
Type of Bone: Cervical Vertebrae
What is H?
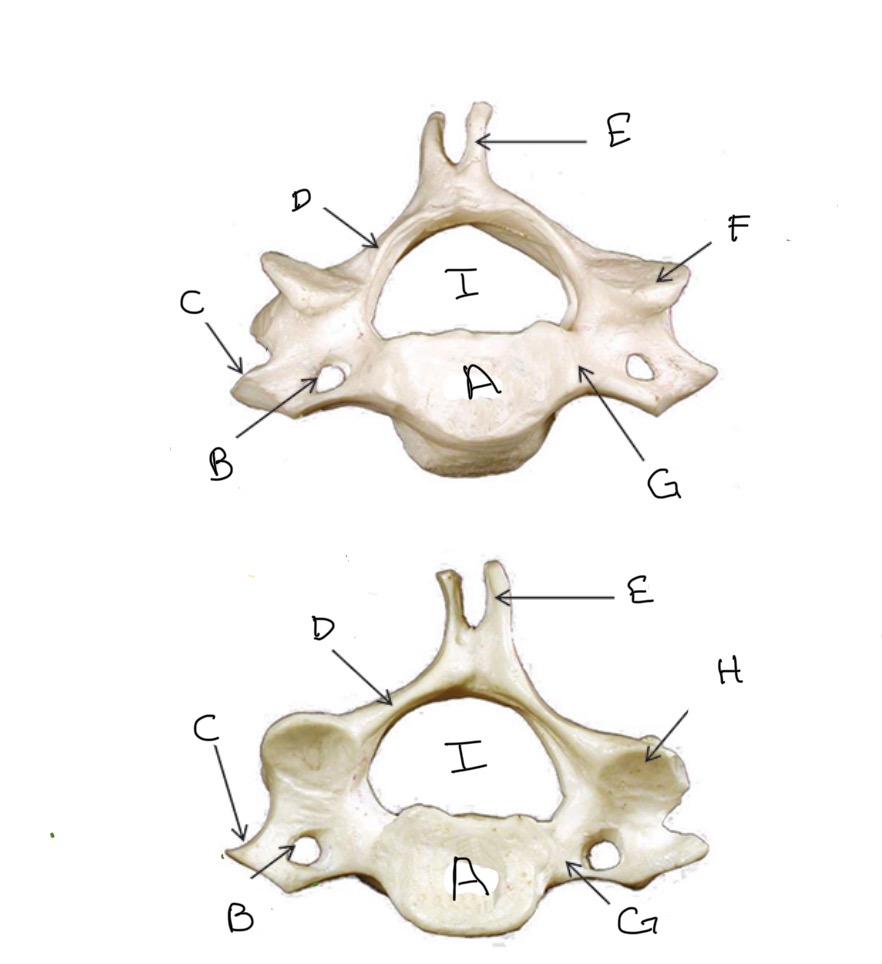
Veterbral Foramen
Type of Bone: Cervical Vertebrae
What is I?
Body
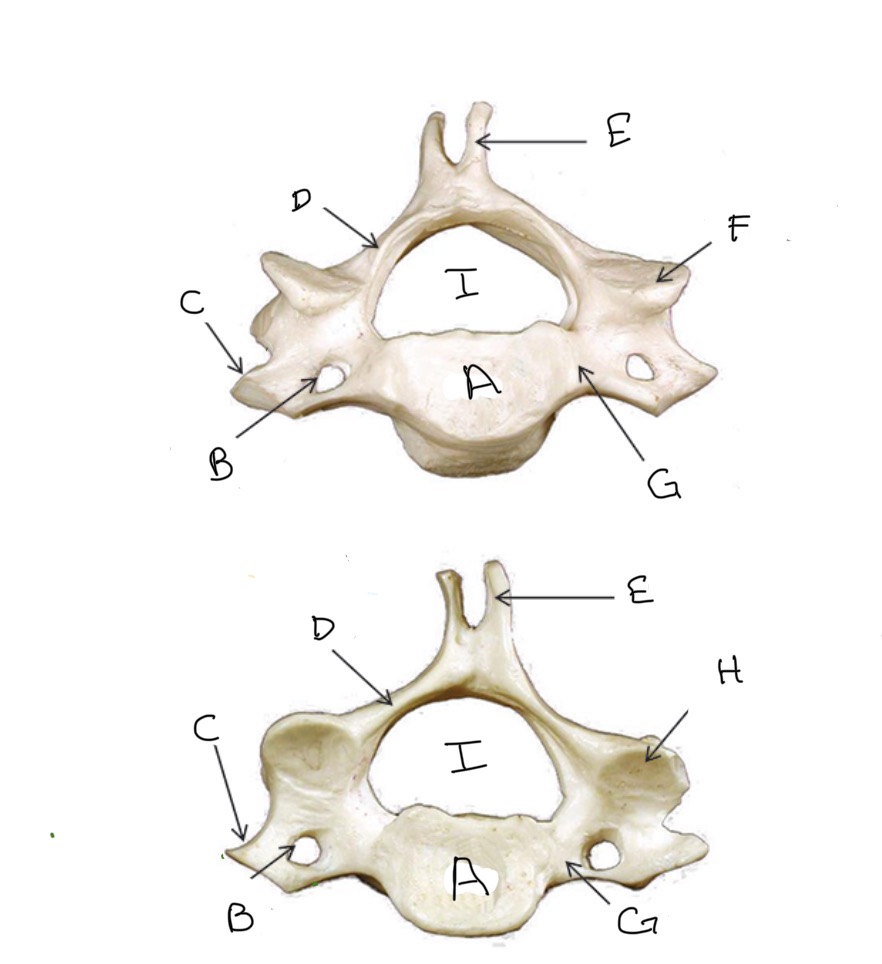
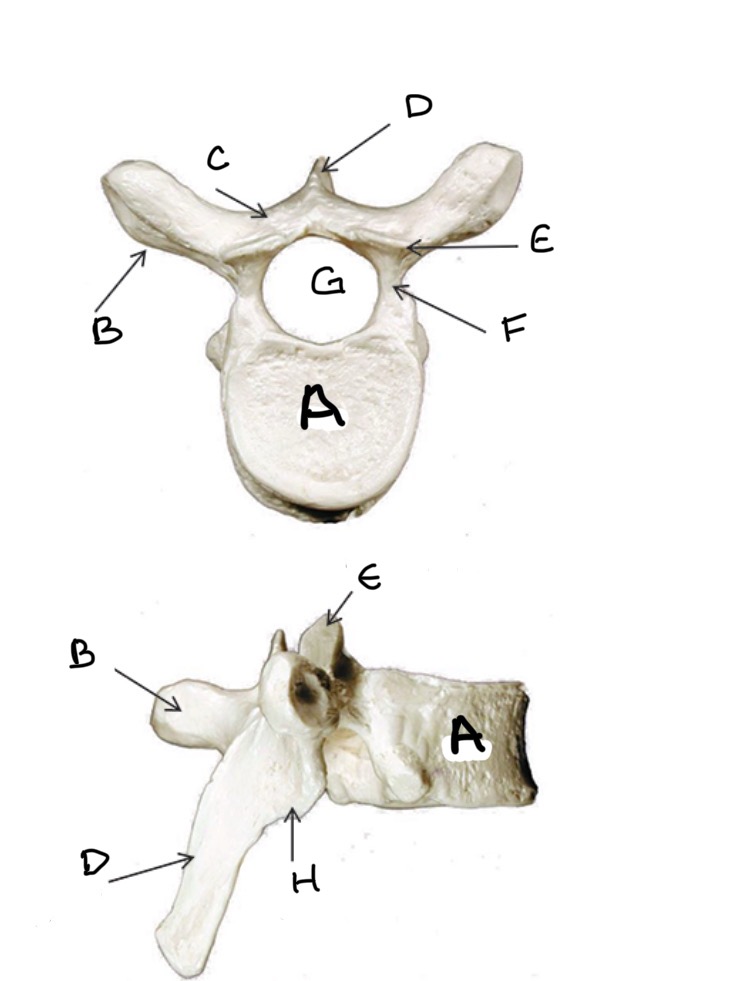
Type of Bone: Thoracic Vertebrae
What is A?
Transverse Process
Type of Bone: Thoracic Vertebrae
What is B?
Lamina
Type of Bone: Thoracic Vertebrae
What is C?
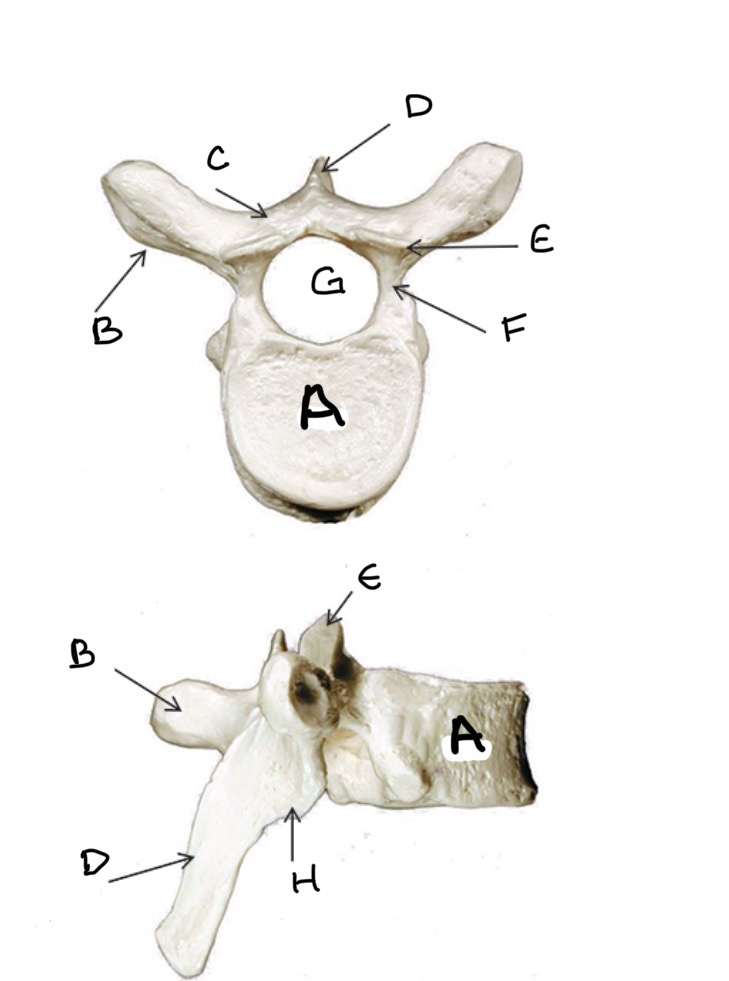
Spinous Process
Type of Bone: Thoracic Vertebrae
What is D?
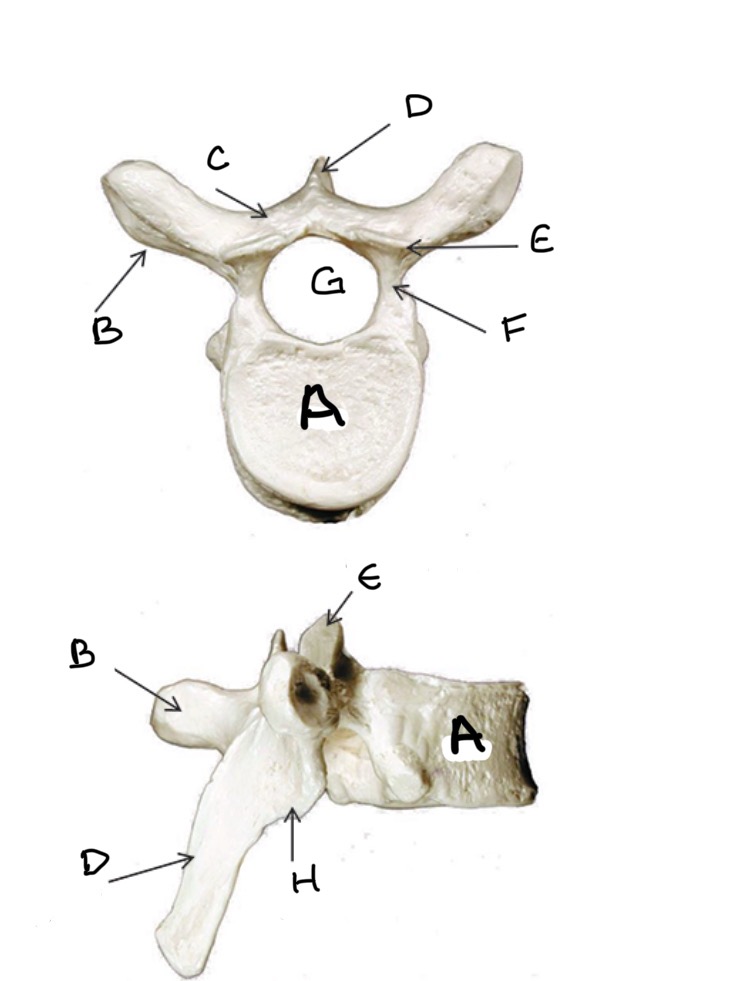
Superior Articular Process
Type of Bone: Thoracic Vertebrae
What is E?
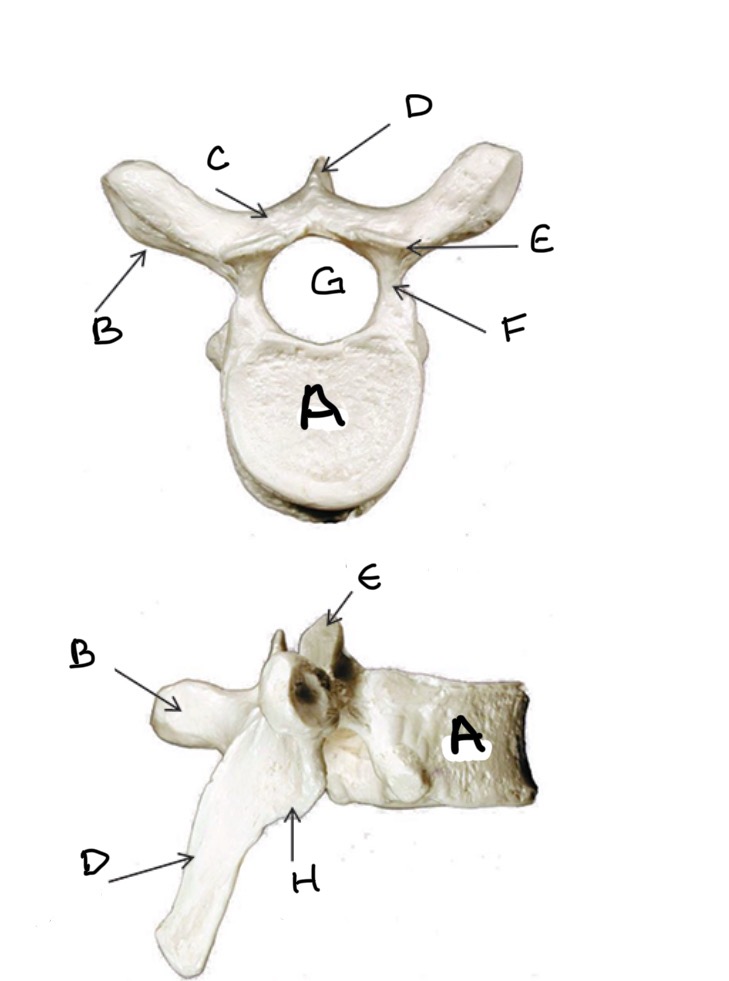
Pedicle
Type of Bone: Thoracic Vertebrae
What is F?
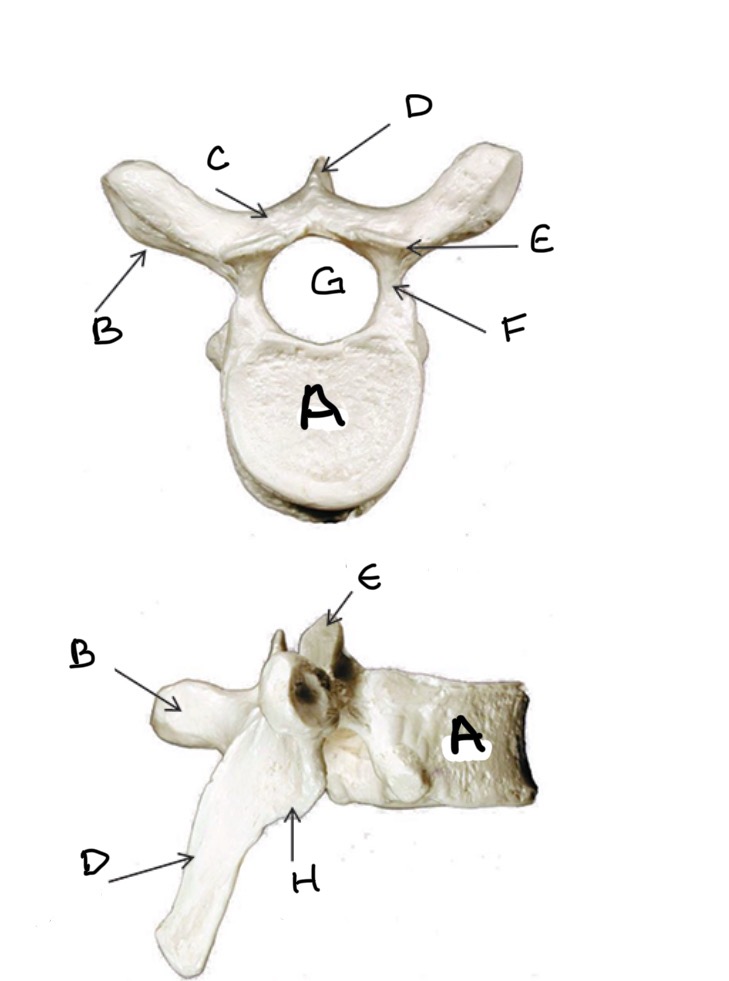
Vertebral Foramen
Type of Bone: Thoracic Vertebrae
What is G ?
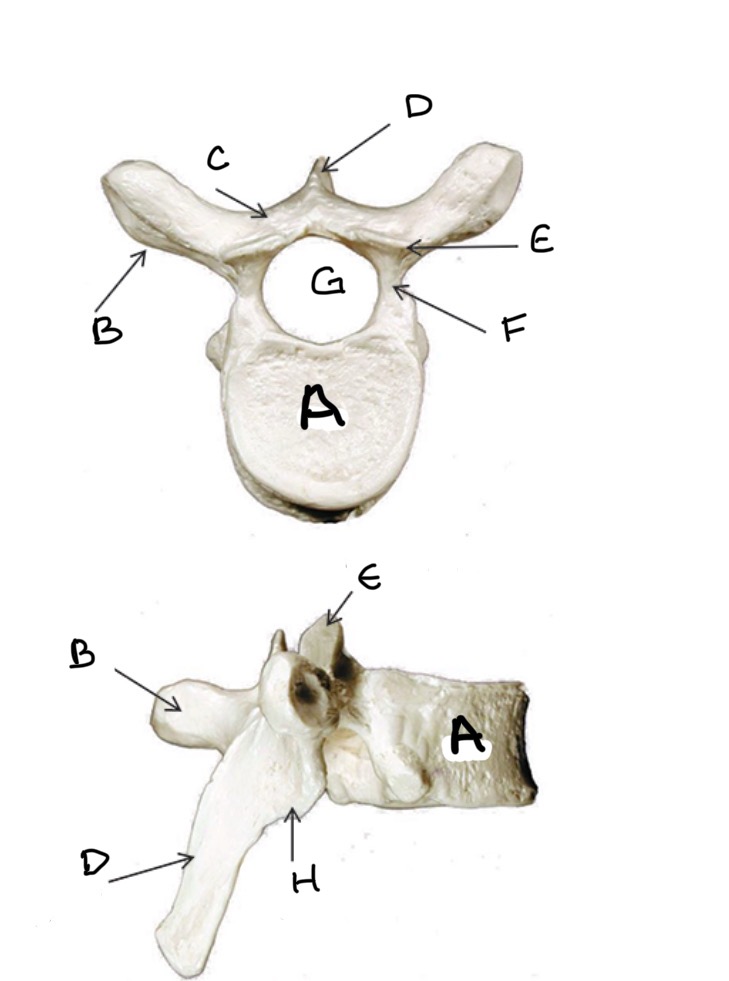
Inferior Articular Process
Type of Bone: Thoracic Vertebrae
What is H?
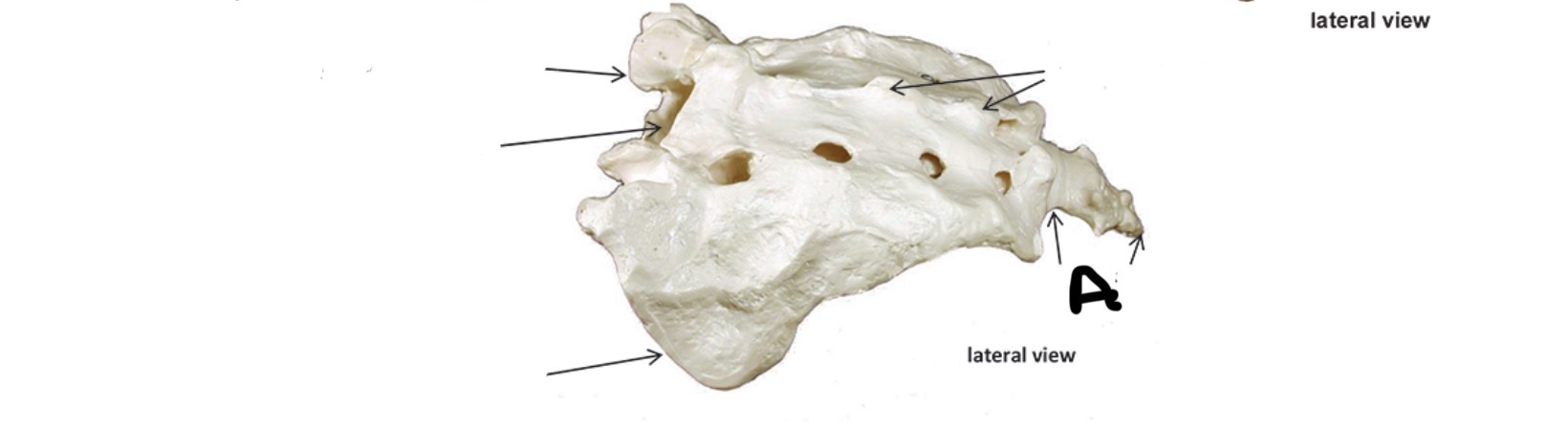
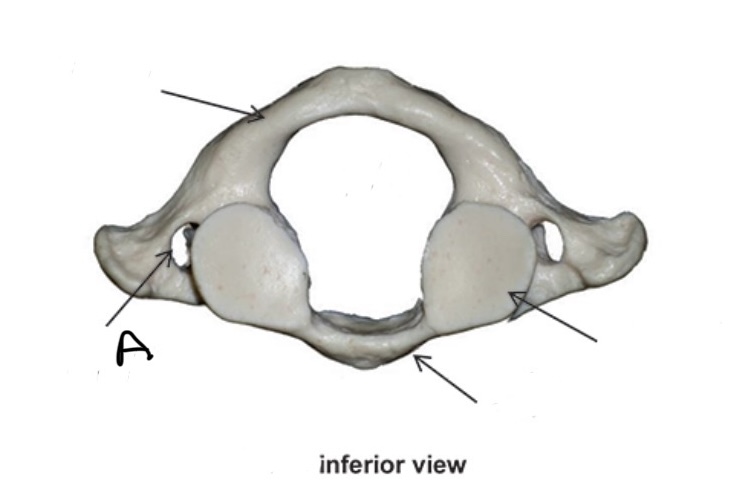
Atlas
Transverse Foramen
What Vertebra bone is this?
What is A?
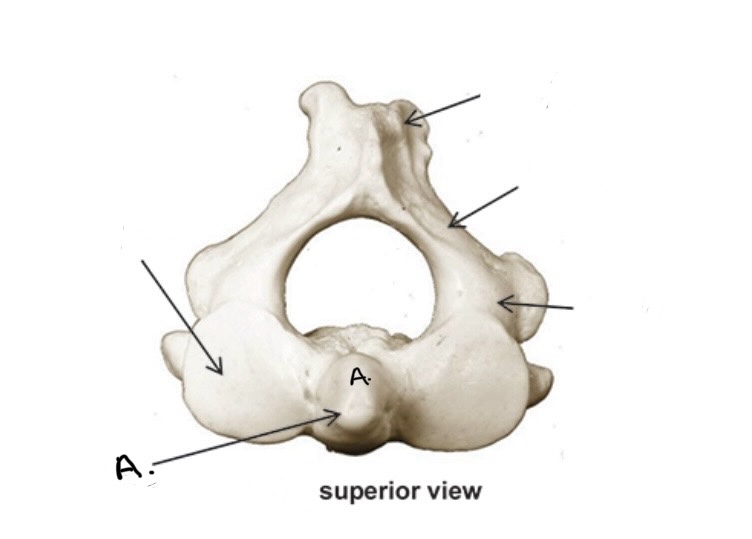
Axis
Dens
What Vertebra bone is this?
What is A?
Body
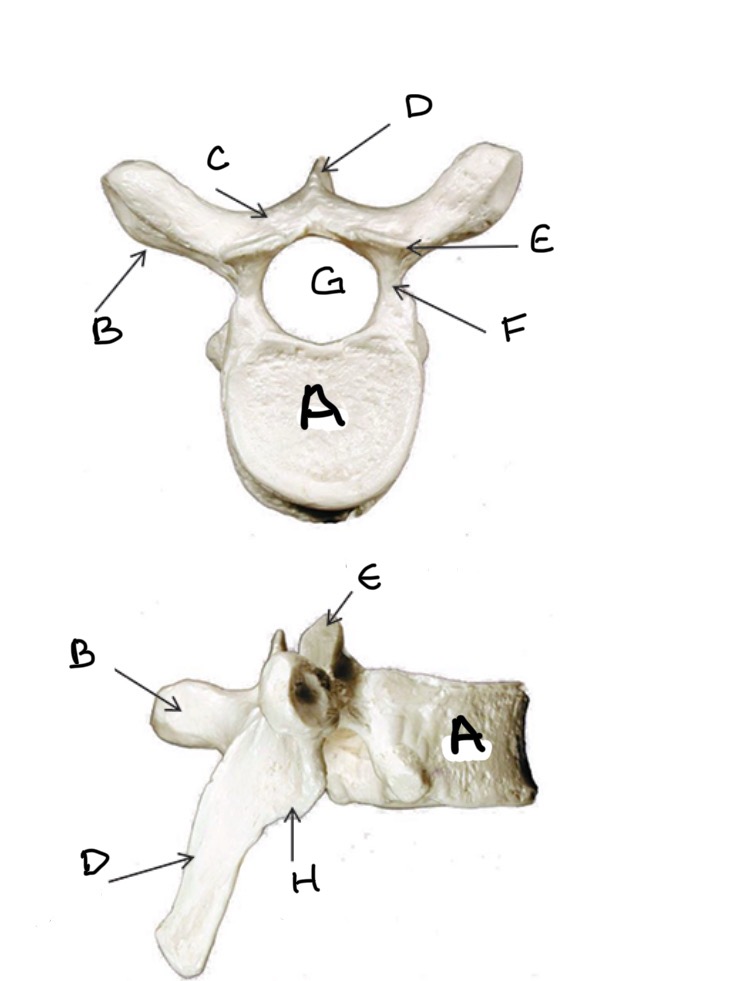
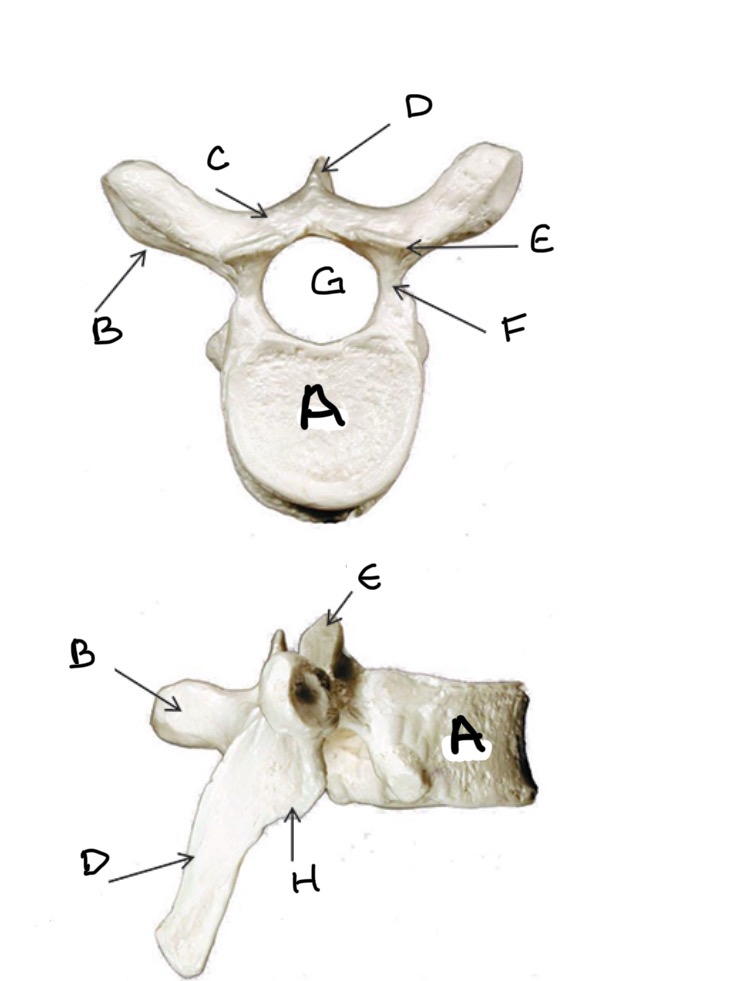
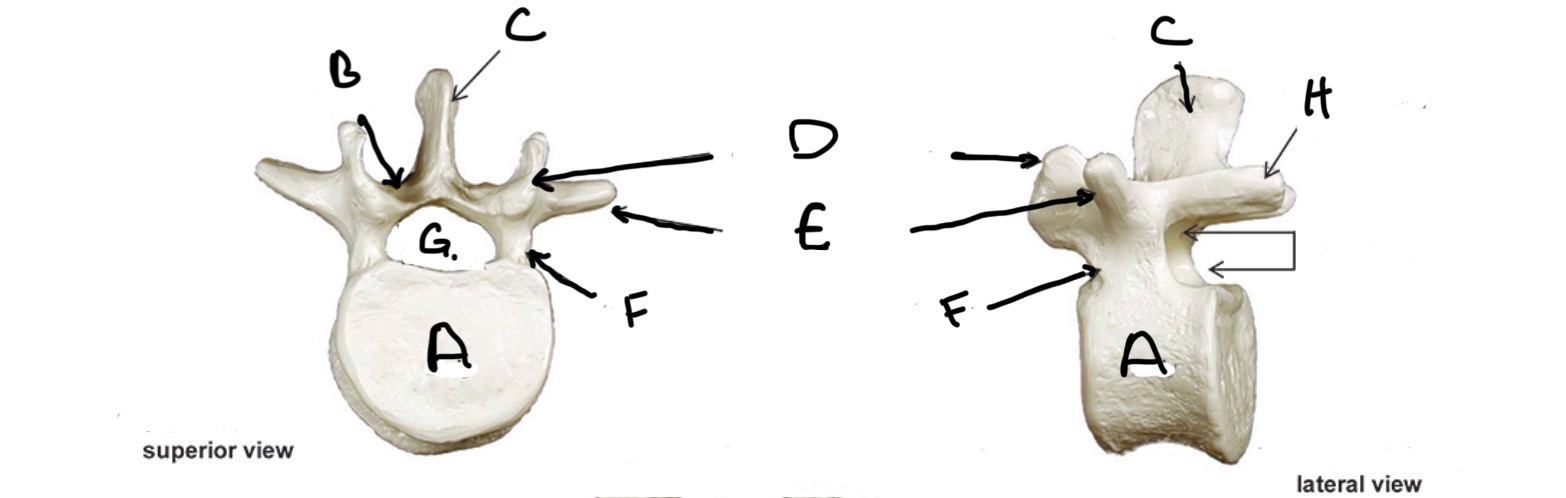
Type of Bone: Lumbar Vertebrae
What is A?
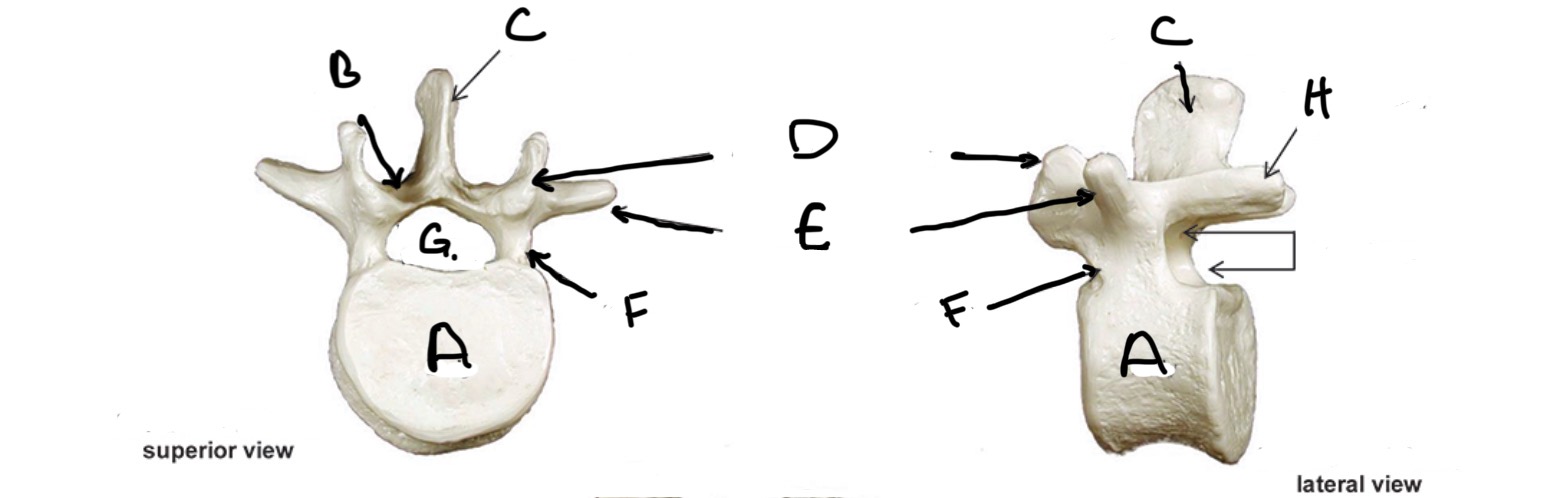
Lamina
Type of Bone: Lumbar Vertebrae
What is B?
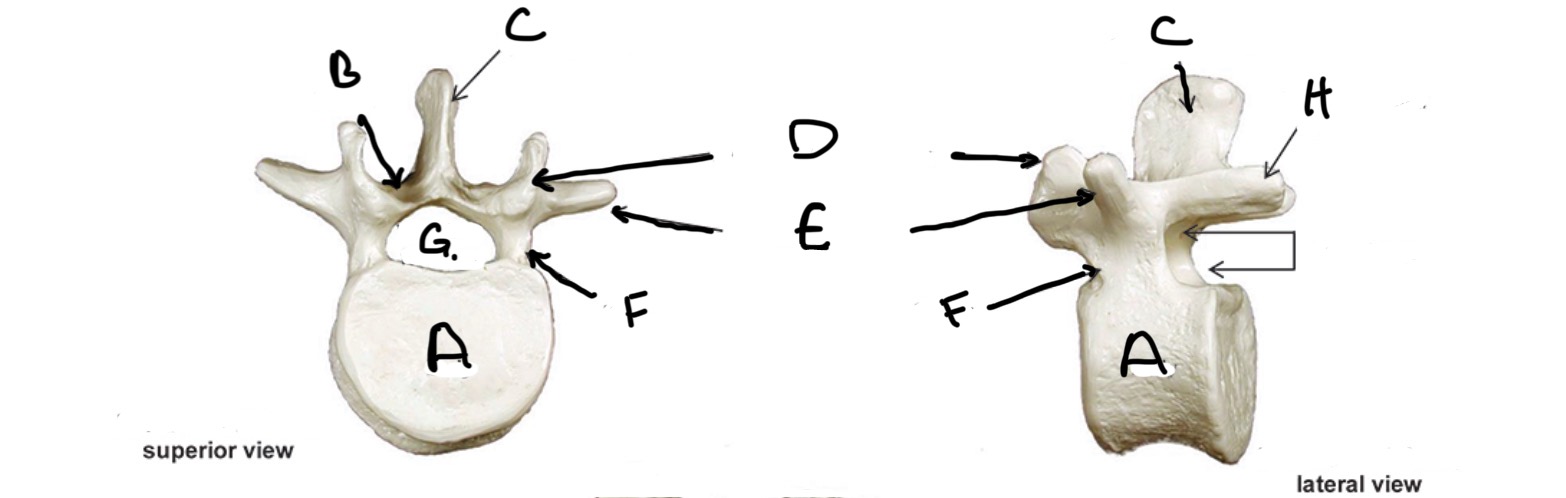
Spinous Process
Type of Bone: Lumbar Vertebrae
What is C?
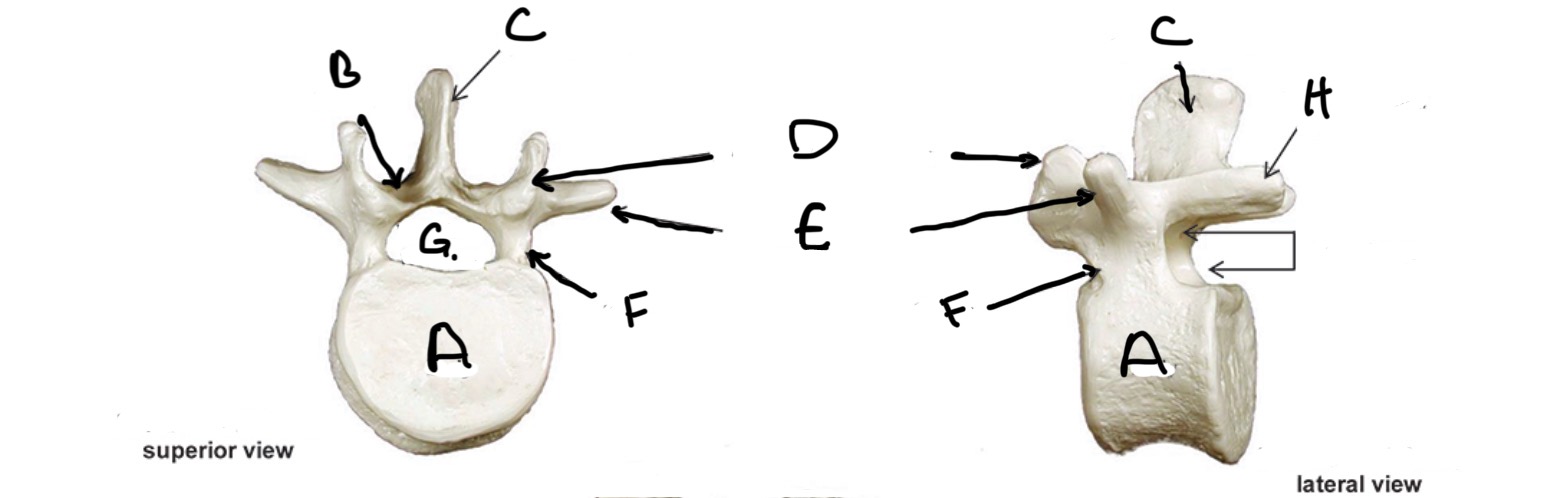
Superior Articular process
Type of Bone: Lumbar Vertebrae
What is D?
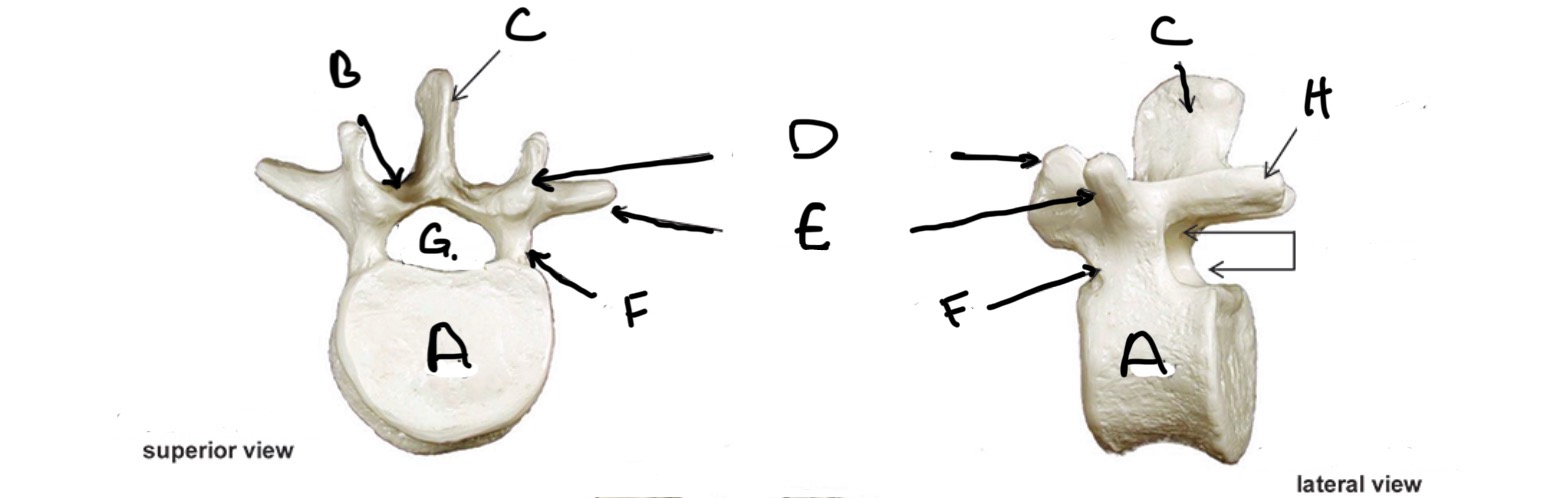
Transverse Process
Type of Bone: Lumbar Vertebrae
What is E?
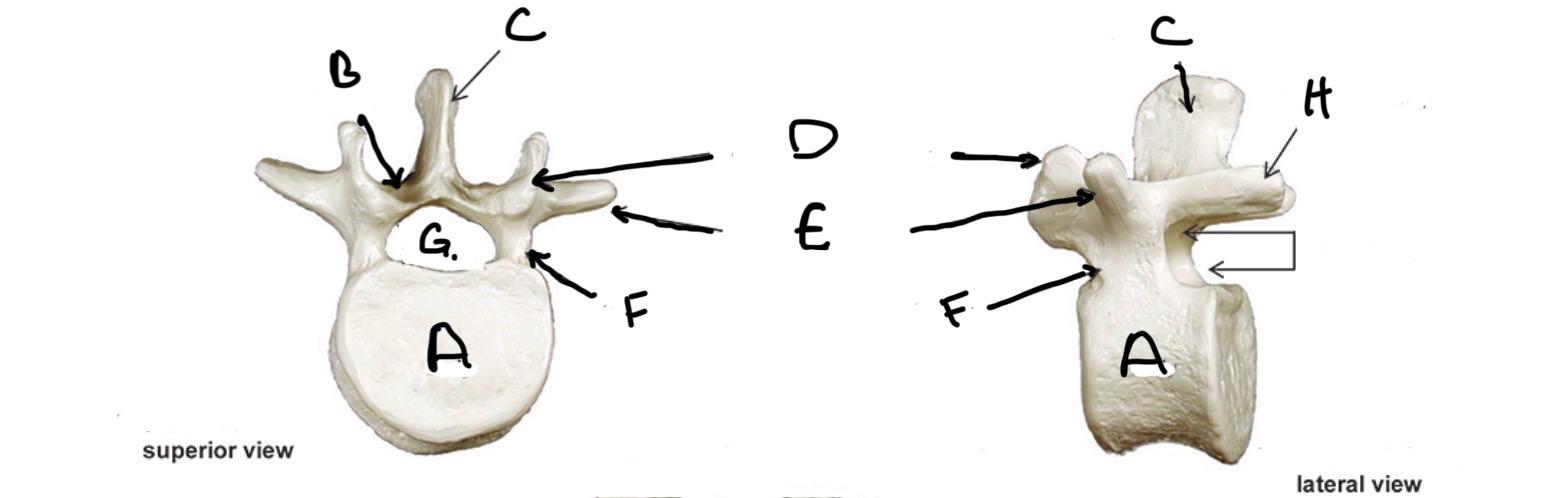
Pedicle
Type of Bone: Lumbar Vertebrae
What is F?
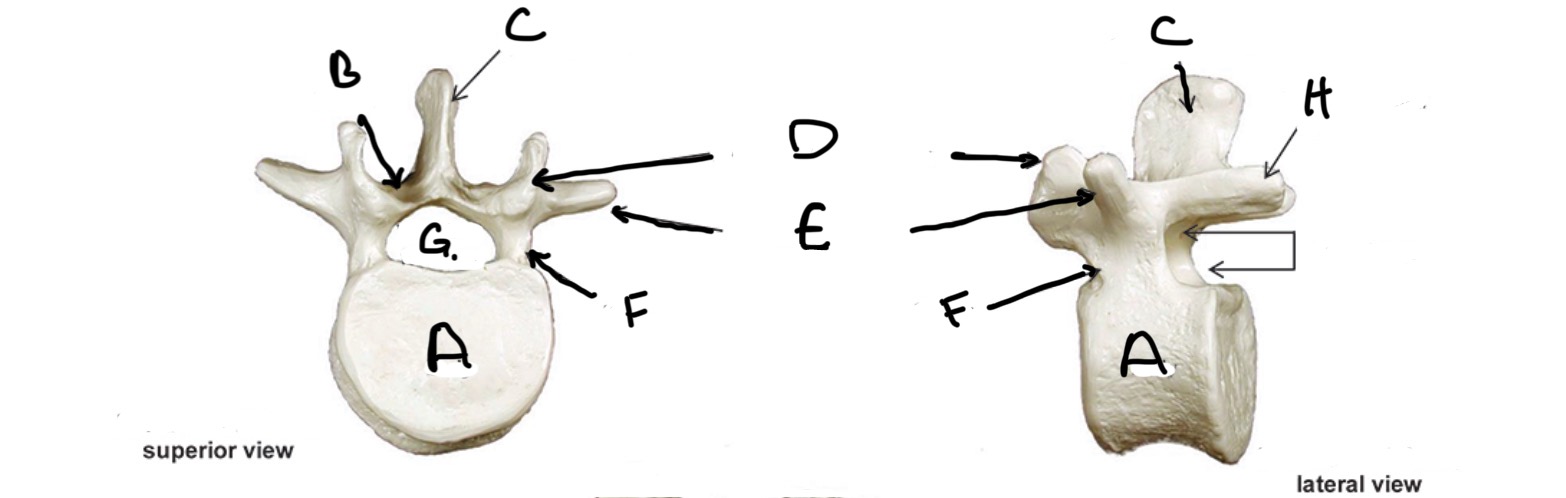
Vertebral Foramen
Type of Bone: Lumbar Vertebrae
What is G?
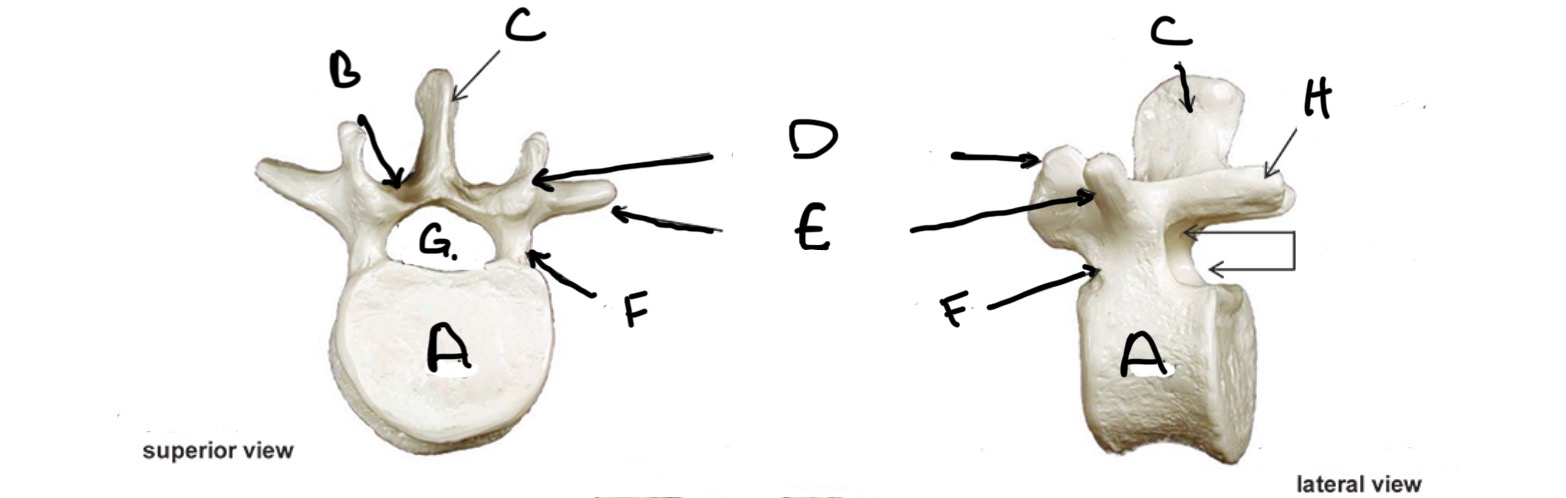
Inferior Articular Process
Type of Bone: Lumbar Vertebrae
What is H?
Sacrum
Coccyx
What bone is this?
What is A?