Mizzou BIO_1020 Exam #1 Fall2024
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
concentration gradient
Difference in solute concentration between two areas
diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
hypertonic
when comparing two solutions, the solution with the greater concentration of solutes
Hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solution
Isotonic
when the concentration of two solutions is the same
osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
selective permeability
A property of biological membranes that allows some substances to cross more easily than others.
Solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances (generally water)
What is turgor pressure?
The pressure that water molecules exert against the cell wall.
What provides turgor pressure in plant cells?
Vacuoles and cell wall.
water potential
the potential energy of a volume of water, expressed as a pressure
cell
Basic unit of life
cell membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
What is a cell wall?
A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms.
Where are cell walls present?
Cell walls are present in most prokaryotes (except mollicute bacteria), in algae, fungi, and eukaryotes including plants but are absent in animals.
Chloroplast
organelle found in cells of plants and some other organisms that captures the energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy
Cristae
finger like projectional folds of the inner membrane of a mitochondrion that houses the electon transport chain and the enzyme catalyzing the synthesis of ATP.
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
Endoplasmic Reticulum
a network of membranous sacs and channels inside cells, of ten bearing ribosomes.
Difference in Rough ER & Smooth ER
Rough ER - contains ribosomes
Smooth - No ribosomes
Eukaryotic
A cell characterized by a nucleus and notably membrane-bound organelles
Grana
disc-like structures inside chloroplasts
Golgi body
A structure in a cell that receives proteins and other newly formed materials from the endoplasmic reticulum, packages them, and distributes them to other parts of the cell.
mitochrondrion
rod-shaped cell structures that produce most of the energy needed to carry out the cell's functions (powerhouse of the cell)
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
Nucleus
membrane bound oganelle containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction, as well as the nucleolus
Organelle
any of a number of organized or specialized structures within a living cell.
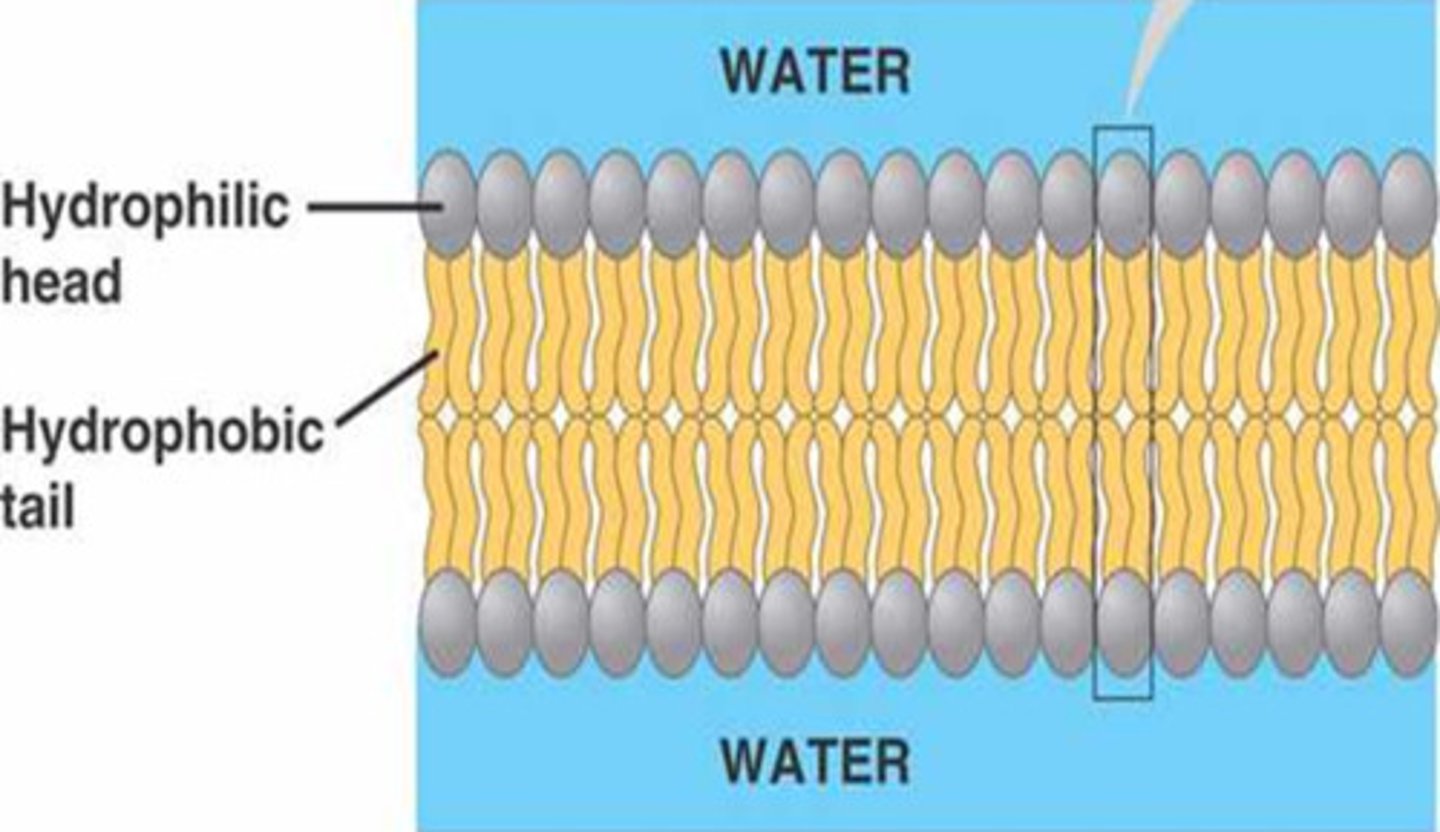
Phosopholipids
Primary structural component of cellular membrane. head is hydrophilic. tail is hydrophobic. composed of fatty acids and phosphate groups
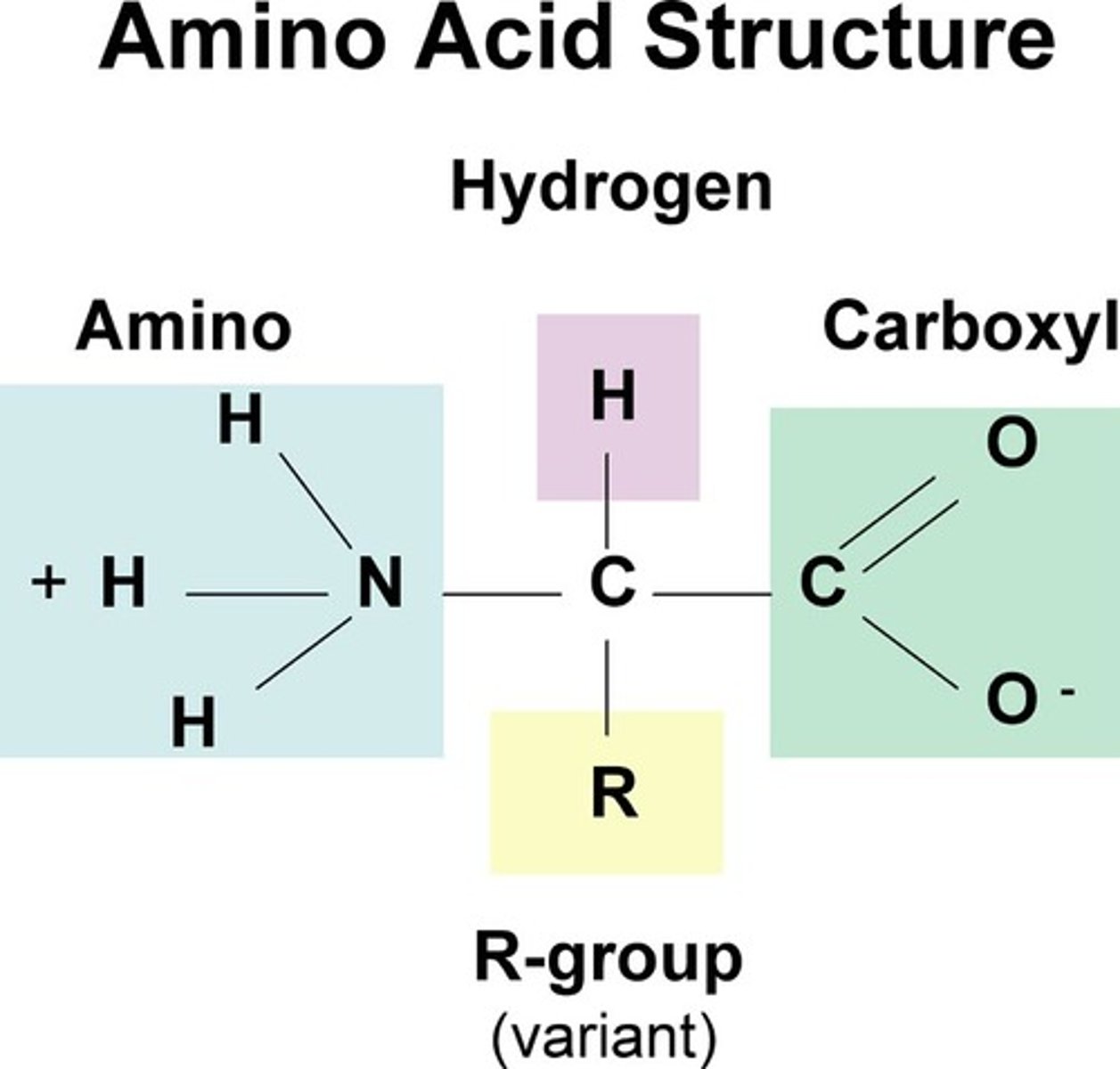
Protein
An organic compound that is made of one or more chains of amino acids and that is important for structure in membrane, as well as acting as enzymes. R group give it definition
prokaryotic
An organism whose cells do not have a nucleus nor membrane bound organelles, such as bacteria.
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
Stroma
fluid portion of the chloroplast; outside of the thylakoids
Vacuole
membrane bound cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates. often large in plant cells
assumption
A belief or statement taken for granted without proof.
bar graph
A graph that uses horizontal or vertical bars to display data
categorical data
Data that consists of names, labels, or other nonnumerical values
continuous variable
a quantitative variable that has an infinite number of possible values that are not countable
control group
In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.
Data
Facts and statistics collected together for reference or analysis
dependent variable
The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable.
experiment
A research method in which an investigator manipulates one or more factors to observe the effect. Proving or disproving a hypothesis.
experimental error
inaccuracy due to procedural faults
extrapolation
the act of estimation by projecting known information
Histogram
a bar graph depicting a frequency distribution
Hypothesis
a supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation.
independent variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.
Inference
A conclusion reached on the basis of evidence and reasoning
Interpolation
an estimation of a value within two known values in a sequence of values
line graph
A graph that uses line segments to show changes that occur over time
mean
average value
median
the absolute middle in a series of numbers, ordered high to low
prediction
A statement of what will happen next in a sequence of events.
Replication
repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the basic finding extends to other participants and circumstances
sampling error
an error that occurs when a sample somehow does not represent the target population
treatment group
the participants in an experiment who are exposed to the level of the independent variable that involves a medication, therapy, or intervention
plasma membrane
biological barrier that surrounds and protects the cell, regulating the movement of substances in and out. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates, playing a key role in communication and signaling. It maintains homeostasis and supports cell structure.
signal protein
type of protein that transmits signals within and between cells, often involved in communication processes. These proteins can bind to specific receptors, triggering a response that influences cellular activities, such as growth, metabolism, or immune responses. Examples include hormones and neurotransmitters.
transport protein
A type of protein that facilitates the movement of substances across a cell membrane. These proteins can help in the passive or active transport of ions, nutrients, and other molecules, ensuring that cells maintain homeostasis and acquire necessary compounds for function.