BIOL 2048 - Histamine and 5HT
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
histamine and 5HT similarities
biogenic amines
small 100mw
local hormones or autocoids (self drugs)
neurotransmitters, local hormones
overactivation of histamine
CONDITIONS ASSOCITED W/ OVERACTIVATION
Allergy: sensitivity to specific conditions occurs through skin, inhaled or injected. Associated w H1 receptor
Peptic Ulcer: break in the lining of the stomach, small intesting or oesophagus caused by overacitve histamine. Related to H2
structure and synthesis of histamine
STRUCTURE
has an imidazole ring w a pKa of 5.74 which is usually uncharged at pH
amino acid group w a pKa of 9.8 which is usually charged at physiological pH
SYNTHESIS
synthesised from histidine
histidine decarboxylase which removes the amino acid
enzyme found in mast cells, rapidly growing tissues or gastric mucosal cells
enzyme upregulated in stress
histamine found in food but doesn’t contribute to the body’s pool as its degraded
metabolism and storage of histidine
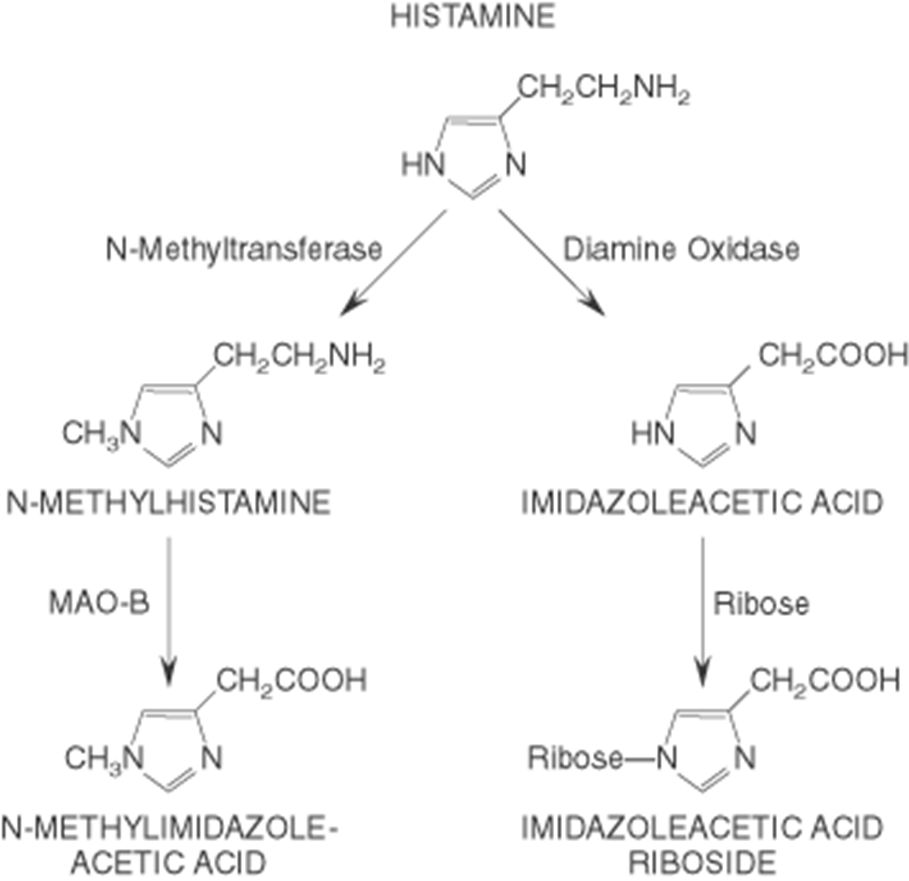
METABOLSIM
rapidly metabolised via 2 routes
STORAGE
stored in mast cells —> long lived tissue resident cells that contain up to 1000 granules per cell (3-4pg/cell)
also stored in
lung (15ug)
skin (6-8ug)
gut (60-80ug)
stomach (10ug)
upon stimulation granules released
granules contain histamine bound to a proteoglycan core, usually heparin
the granules also contain enzymes such as tryptase and chymase
release of histamine
IGE DEPENDENT RELEASE
when IgE present it binds to receptors on mast cells and causes the release of histamine
associated w allergy
OTHER STIMULI
activated by bacterial products like liposaccharides
activated by complement peptides C3a and C5a
both require specific receptors on CSM
occurs in infection
NON SPECIFIC RELEASE
a number of basic drugs such as morphine tubocurarine cause release of histamine
also can be released following trauma to tissues including UV radiation, burns, changes in osmolarity
H1 receptors
NOTE: ALL HISTAMINE RECEPTORS ARE GPCRS
H1
wide distribution in CV system, smooth muscle and peripheral nerves
causes
vasodilation associated w heat and redness
increased vascular permeability
—> causes fluid, clotting proteins, complement and antibodies to move into the surrounding circulation
stimulation of peripheral nerves:
stimulation of the CNS which causes pain and itch.
Also causes the release of vasodilators into the system
smooth muscle contractions:
histamine causes bronchial smooth muscle contraction associated w asthma
histamine able to contract smooth muscle in the GI and reproductive tract
actions of histamine on the skin, CV system, brain
SKIN
wheal and flare reactions
pain and itch due to stimulation of PNS
reddening as capillaries dilate
blanching and swelling as fluid moves into the tissue
redness from neuronal stimulation
CV SYSTEM
small doses of histamine causes a drop in the peripheral resistance —> low bp
large doses of histamine cause a profound decrease in BP and a loss of fluid from the capillaries —> circulatory collapse (anaphylactic shock)
BRAIN
can act as a nt, found in histaminergic neurons
H1 receptor antagonists
classical H1 antagonist is mepyramine
orally available, excellent safety
side effects include drowsiness and effects on cholinergic receptors
newer H1 antagonist such as cetirizine —> doesn’t cross BBB so fewer drowsiness side effects
used to treat allergies, sedatives, and for motion sickness
Alternative method of inhibition: some drugs used to stabilise the membrane of the mast cells to block the release of histamine
most antihistamines non competitive inhibitors —> stabilise the inacvtive conf.
anti adrenergic and anti serotonin effects as the receptor is the same class of GPCR
H2 receptor action
STIMULATE GASTRIC ACID SECRETION
H2 receptor in gastric mucosa
activation of mast cells controlled by muscarinic receptor (uses Ach) and the gastrin receptor which recognises gastrin
histamine binds to receptors on parietal cells —> activation of proton pump
treatment of peptic ulcer: target H2 receptor or gastrin receptor
prostaglandins can inhibit the release of gastric acid
CARDIAC SYSTEM
histamine increases rate and force of contraction
also releases NAdr from adrenergic nerves
OTHER EFFECTS
H2 receptors found on a no of cells in the immune system like mast cells and lymphocytes
may provide a negative feedback inhibiting the release of histamine from degranulating mast cells
H2 receptor antagonists
cimetidine
orally availible, very safe
inhibits cytochrome p450 and can retard the metabolism of anticoagulants and tricyclic antidepressants
used to treat gastric ulcers, reflux oesophagitis, anti cancer activity
actions of histamine on H3
no H3 receptor antagonists clinally used
thioperamide used in research
potential use of antagonists include control of sleep wake cycle and sedation, control of food and water intake, thermoregulation
actions of H4
H4 receptors on inflammatory cells
appear to regulate cytokine networks in the inflammatory response
antagonists and other agonists not clear
5HT location, structure and source
LOCATION
5 hydroxy tryptamine
found in CND, Gi tract and vascular system
STRUCTURE
indole ring, hydroxyl group, amino group
SOURCE
found in bananas, strawberries, pineapple and tomatoes
doesn’t affect the body’s pools of 5HT but is rapidly metabolised and excreted in urine
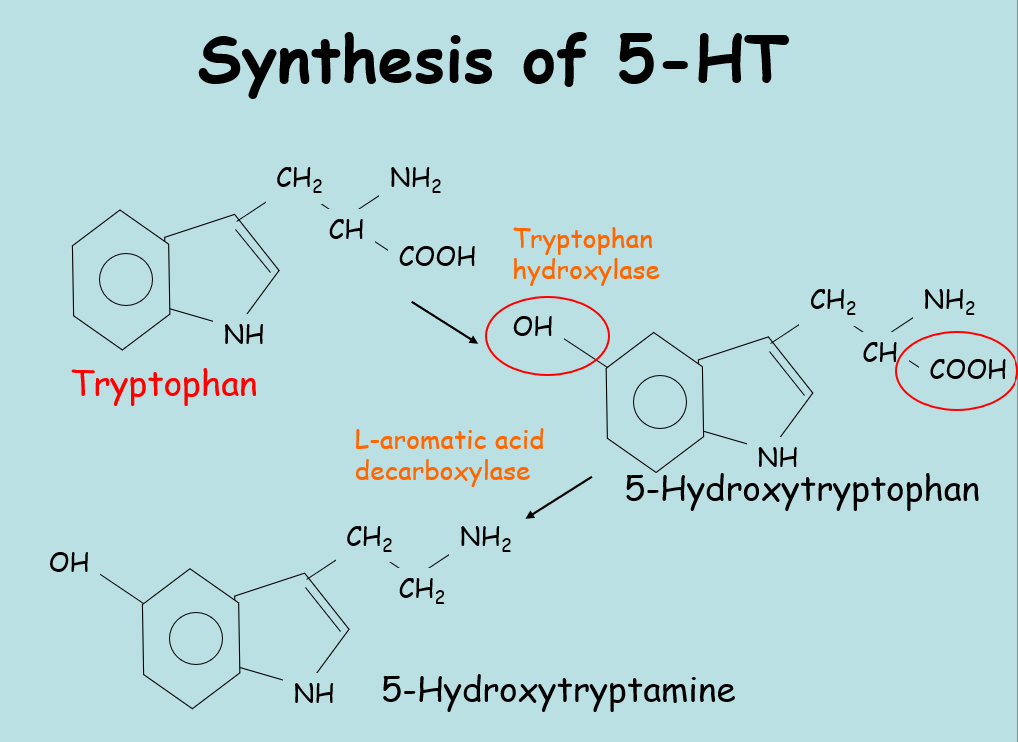
synthesis of 5HT
synthesised in the enterochromaffin cells in the gut
90% of teh bodys 5HT found in the gut
can be stored in platelets but not synthesised there
avg adult contains 5mg of 5HT
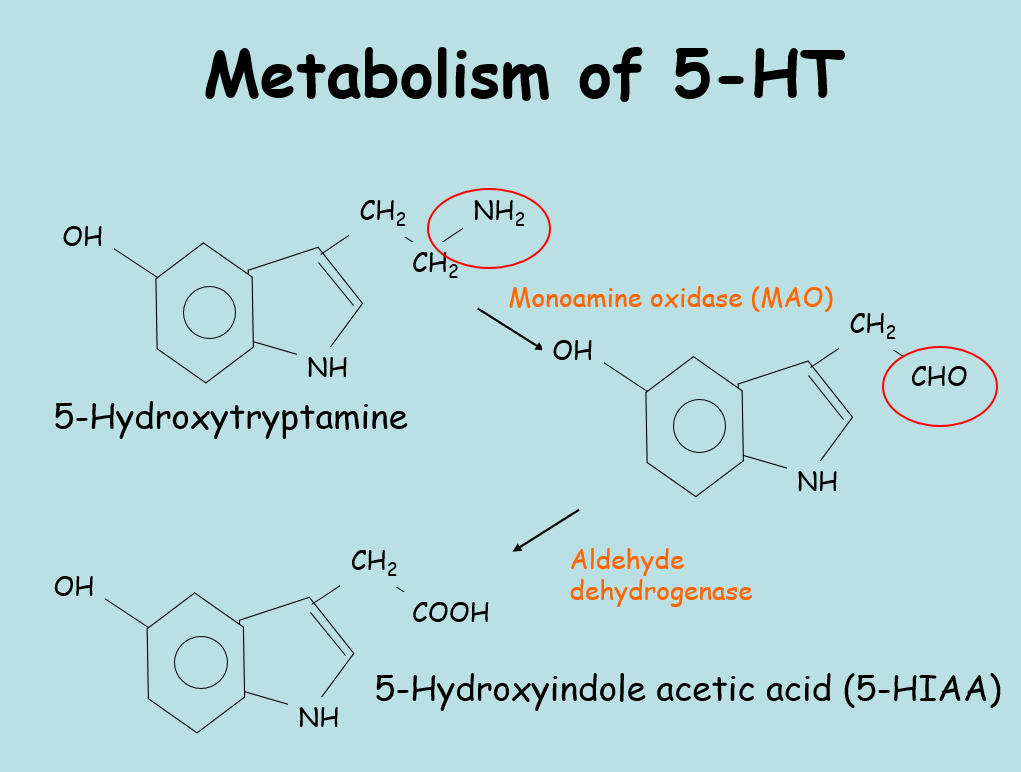
metabolism of 5HT
DRUGS THAT INCREASE THE CONCENTRATION OF 5HT
fenfluramine inhibits apetite and decreases 5HT
ecstasy increases 5HT
carbohydrate rich diet boosts levels of 5HT
receptors
many receptors - at least 7 main types as well as subtypes
all GPCR apart from 3 ligand gated ion channels
for all receptors apart from 2, the second messenger is cAMP but for 2 its IP3/DAG
5HT 1 RECEPTOR
mainly found in CNS
controls mood, behaviour, thermoregulation, feeding and sleep
activation = vasoconstriction and neural inhibiton
associated w migraine
5HT 2 RECEPTOR
occurs in CNS, widely distributed in periphery
lysergic acid dimethylamine (LSD) acts as an agonist at the central 5HT2 receptors causing hallucinations
LSD is an antagonist of 5HT2 receptors in periphery
5HT 3 RECEPTORS
antagonists such as ondansetron are used as antiemetics
they are effective at controlling severe vomiting and nausea that come w chemotherapy
may be anxiolytic drugs
5HT 4 RECEPTORS
found in the CNS but their main physiological role is regulating GI motility
5HT4 receptor agonists used to relieve abdominal discomfort associated with chronic idiopathic constipation
5HT in the body
MIGRAINE
known to cause vasoconstriction in cerebral arteries
5HIAA found in the urine of patients w migraine
5HT IN GUT
can regulate fluid secretion and motility of the gut
IN CIRCULATION
causes constriction of arterioles
but this is followed by dilation as 5HT triggers the release of NO and inhibits the release of noradrenaline from the sympathetic nerve terminal
IN PLATELETS
can act on receptors and trigger platelet aggregation or growth