Week 3: The Production function and economic profit
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
The short run
a period of time in which at least one factor of production is fixed; usually capital.
The long run
a period of time in which all factors of production are variable but the state of technology is fixed.
All planning takes place in this period.
production function
the relationship between the quantity of inputs used to make a good and the quantity of output of that good
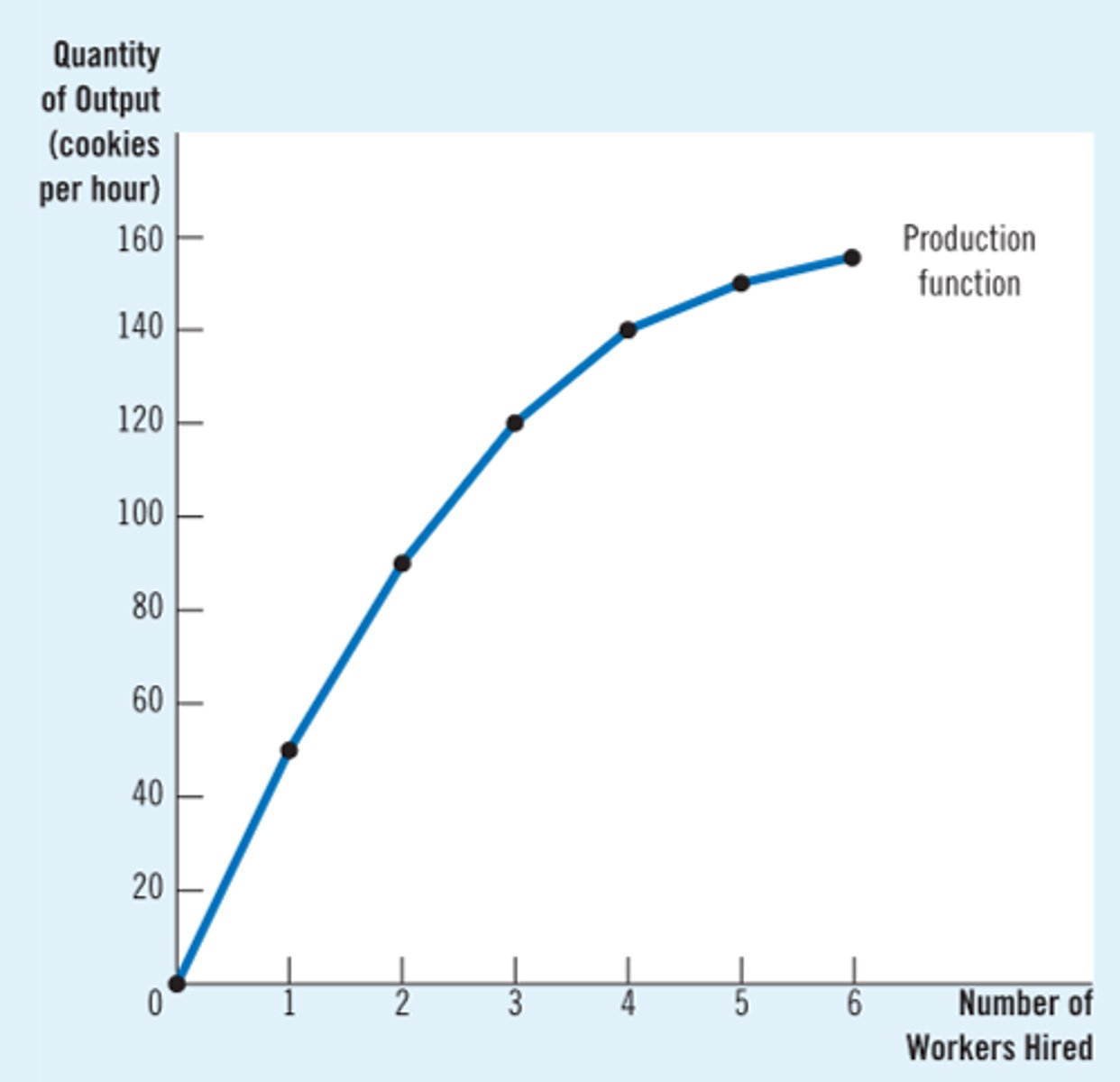
Total product (TP):
the total output that a firm produces using its fixed and variable factors in a given time period
In the short run, output can only be increased by applying more units of the variable factors to the fixed factors.
Marginal product (MP)
the extra output that is produced by using an extra unit of variable factor
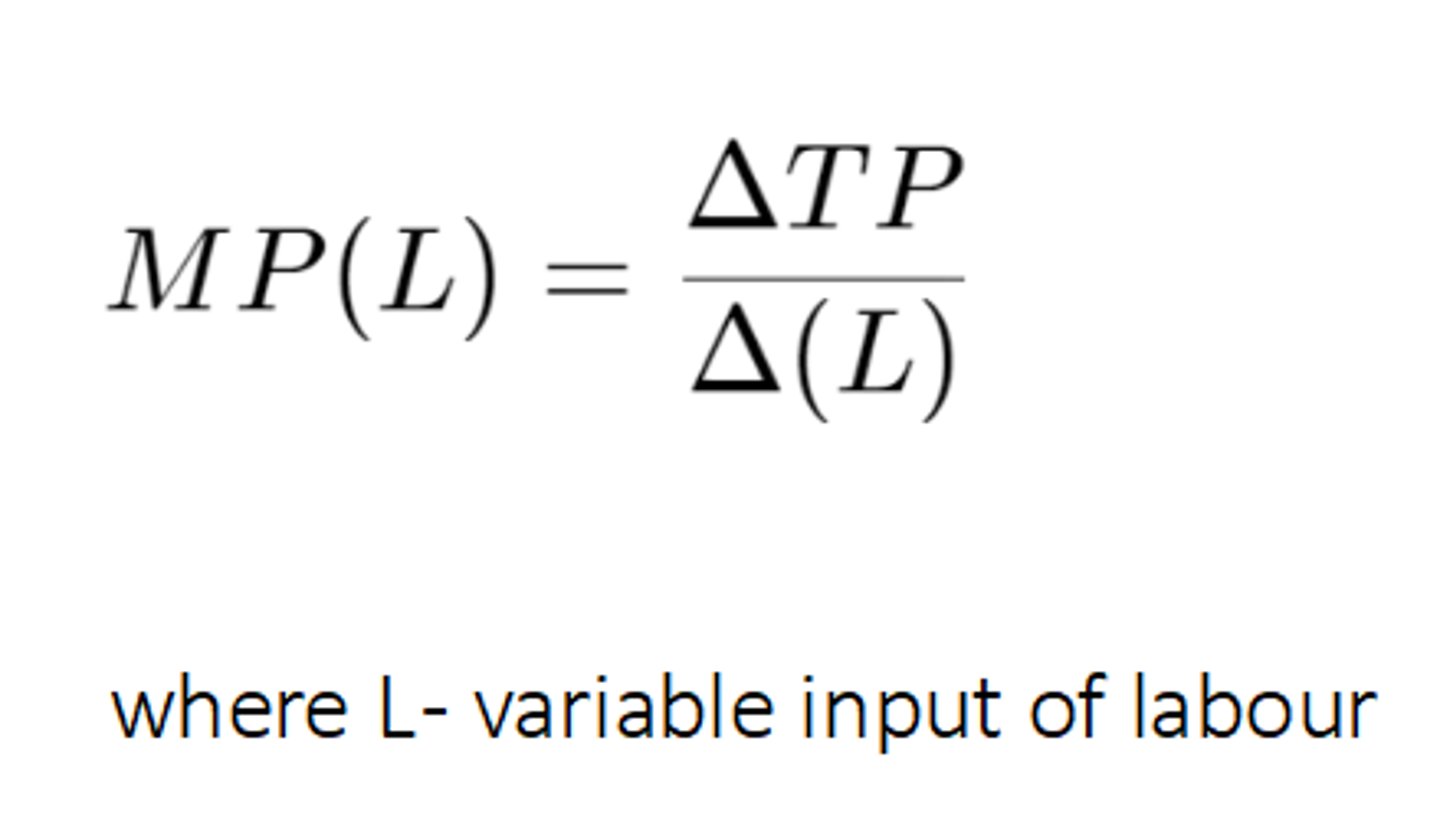
The law of diminishing marginal returns
as the extra units of a variable factor are added to a given quantity of a fixed factor, the output from each additional unit of the variable factor will eventually diminish.
Economic cost
The economic cost of producing a good is the opportunity cost of the firms production. It is the opportunity cost of the factors of production that have been used in producing the good or service.
explicit costs
input costs that require an outlay of money by the firm
Self-test: give examples
(see your class notes)
implicit costs
input costs that do not require an outlay of money by the firm
Self-test: give examples
(see your class notes)
Profit theory
In economics, profit is driven from the following:
πₑ= TR - TCₑ
where
TCₑ = explicit costs + implicit costs
If total revenue = total economic costs
economic profit = 0
(normal profit)
profit that covers the opportunity cost of capital and is just enough to stay operating in the industry and not switch to the next best alternative
If total revenue > total economic costs
economic profit > 0
(abnormal profit or supernormal profit)
terms referring to profits that exceed normal profit
If total revenue < total economic costs
economic profit < 0
(economic loss or subnormal profit)
If a firm maintains subnormal profits, it will eventually be forced to exit the market and put its resources into something else.