Lesson 11 - Sampling Distributions
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
DEGREES OF FREEDOM
NORMAL
For the student's t-distribution, as the __________ increases, the distribution approaches a standard _______ distribution.
FIVE
NORMAL
If X is a binomial random variable and both np and n(1−p) are both greater than _____ then we can approximate the distribution of X using a ______ distribution with a mean of np and a standard deviation of sqrt[np(1−p)].
standard deviation
sqrt[np(1-p)] is the _____ for a binomial random variable
mean
np is the _____ for a binomial random variable
standard deviation
sqrt(λ) is the _____ for a Poisson random variable
mean
λ is the _____ for a Poisson random variable
FIVE
NORMAL
If X is a Poisson random variable and λ is greater than _____ then we can approximate the distribution of X using a ______ distribution with a mean of λ and a standard deviation of sqrt(λ).
INDEPENDENT
RANDOM SAMPLE
A set of n _______ random variables X1,X2,...,Xn with the same distribution are called a _____________.
STATISTIC
The probability distribution of a ______ (calculated from a sample) is called its sampling distribution.
SAMPLE
The probability distribution of a statistic is calculated from a ________.
POPULATION
The mean or expected value of the sample mean, x̄, is equal to the ______ mean μ and the standard deviation of the sample mean, x̄, is equal to σ divided by THE SQUARE ROOT OF THE SAMPLE SIZE.
sample mean
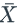
EXACTLY
If the population is normal then the distribution of the sample mean will be _______ normal.
APPROXIMATELY
If the population is NOT normal but the sample size is large enough then the distribution of the sample mean will be __________ normal.
INFERENCE
Sampling distributions allow us to perform statistical _________.
PARAMETERS
HYPOTHESIS
Using the results of sampling distributions we can:
Estimate unknown _______ with a specified confidence level
Conduct _____ tests about parameters to compare them to target values
standard deviation of the sampling distribution of x̄
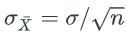
Normal Approximations to Binomial and Poisson