Rates of Reaction - Chp 16 nf
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Formula for average rate of reaction:
Average rate = Total vol. given off (cm3)/Total time for reaction to reach completion (mins)
Rate of Reaction
the change in concentration per unit of time of any one reactant of product
Instantaneous rate of reaction
the rate of reaction at any one particular time during the reaction
How do you find the instantaneous rate of reaction?
Find the slope of the tangent at the time
plot results on a graph
draw a tangent to the time
find the rise/run = slope
What are the 5 factors affecting the rate of reaction
nature of reactants
particle size
concentration
temperature
catalysts
How does the nature of reactants affect the rate of reaction?
reactions occur more quickly when ions exist as free ions in solution
this is because the oppositely charged ions are coming together + no bonds need to be broken
reactions involving covalent compounds occur much more slowly
the covalent bonds must first be broken so new bonds can be formed in the reaction
How does the particle size affect the rate of reaction?
the smaller the particle size the greater the overall surface area is
(this means that there can be more successful collisions)
Draw a diagram + describe an experiment that shows how particle size affects rate of reaction
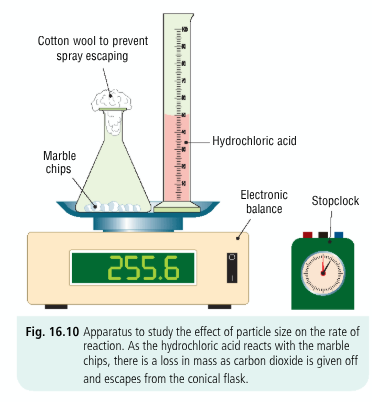
find the mass of a known mass of marble chips in a conical flask and a known volume of dilute HCl in a graduated cylinder using a mass balance
a cotton wool ball is placed in the mouth of the conical flask to prevent loss of spray + allows CO2 to escape
the dilute HCl is added to conical flask and the cotton wool is replaced, the stopclock is started
mass is recorded every 30s
the difference in mass is the mass of carbon dioxide produced
What is a dust explosion?
a build up of very fine dust in the air that can lead to an explosion
Draw a diagram for an experiment to illustrate materials in a powdered state undergo very fast reactions
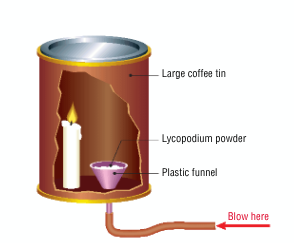
What conditions are needed for a dust explosion to take place?
must occur in an enclosed space
particles must be combustible
must be a source of ignition
particles must be dry
must be oxygen present
How does the concentration affect the rate of reaction?
the higher the concentration the faster the reaction occurs
there are more reactants colliding so there is a higher chance of successful collisions
How does the temperature affect the rate of reaction?
the higher the temperature the more energy the particles have
this leads to more collisions and a higher chance of successful collisions
Catalyst
a substance that alters the rate of a chemical reaction but is not consumed in the reaction
What are the general properties of catalysts?
they are recovered chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction
they are specific: they will work for one particular reaction or a class of similar reactions
needed only in small amounts
can be destroyed by certain substances called catalyst poisons
Enzyme
a substance that is produced by a living things and acts as a biological catalyst
What are the types of catalysis?
homogenous catalysis
heterogenous catalysis
autocatalysis
Homogenous catalysis
catalysis in which both the reactants and catalyst are in the same phase/there is no boundary between them
Give an example of an experiment to demonstrate homogenous catalysis:
The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide with a potassium iodide catalyst
concentrated potassium iodide solution is added to washing up liquid
hydrogen peroxide solution is added + decomposes into oxygen + water
oxygen released and carries foam from the washing-up liquid
Heterogenous catalysis
catalysis in which the reactants and catalysts are in different phases/there is a boundary between them
Give an example + describe an experiment to demonstrate heterogenous catalysis:
Catalytic oxidation of methanol by platinum
Method
some methanol is placed in a conical flask
a T shaped piece of cardboard covered in aluminium foil is put in conical flask
in the fume cupboard the methanol is warmed
a spiral of platinum wire is heated until red hot using a Bunsen burner
the hot wire is hung inside the conical flask
Observation
the hot wire glows red hot (exothermic reaction), popping sounds (H2 in the absence of sufficient oxygen) are heard
a cycle takes place; the wire glows, popping, the wire cools then repeats
smell of methanol and a flame may be observed
Explanation
T piece acts as a chimney to allow waste gases to leave + more air to flow into the conical flask
T covered in foil to prevent it from burning
glowing ceases for a while as CO is formed due to incomplete combustion which poisons the catalyst: after the CO leaves the platinum, it starts working as a catalyst again and glows again
the flame is caused by the wire igniting the methanol vapour
Autocatalysis
catalysis in which one of the products of the reaction acts as a catalyst for the reaction
Give an example of an experiment to demonstrate autocatalysis:
Reaction between permanganate ions and iron (II) ions
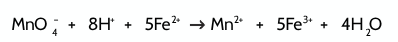
What are the 2 mechanisms of catalysts?
The Intermediate Formation Theory
The Surface Adsorption Theory
Describe the intermediate formation theory:
one or more of the reactants combine with the catalyst to form an intermediate compound
the intermediate then reacts with the other reactant to give the final produce and regenerate the catalyst
Give an example for the intermediate formation theory:
Oxidation of the tartrate ion using hydrogen peroxide catalysed by Co2+ ions
the solution is pink at the start due to the presence of cobalt ions
after adding hydrogen peroxide fizzing is observed due to the formation of carbon dioxide
solution changes to green due to the formation of the intermediate
the fizzing stops and the solution returns to pink as the cobalt ions have not been used up in the reaction + has been regenerated
Describe using an example the surface adsorption theory:
adsorption stage - the hydrogen and oxygen molecules diffuse towards the surface and adsorb to the surface of the platinum; they are held on the surface by temporary bonds
reaction on surface - the higher concentration of the molecules on the surface of the catalyst makes it more likely that the molecules will collide with eachother; covalent bonds holding the atoms together are weakened by the formation of these new temporary bonds
desorption stage - products/gaseous water leave the surface of the catalyst and diffuse away from it, then more reactants adsorb to its surface

Catalytic converter
a device in the exhaust system of a motor vehicle which contains catalysts to convert pollutants in the exhaust gases to less harmful substances
What fumes are released by motor vehicles prior to being catalysed?
CO
NO
NO2
unburned hydrocarbons
Why are fumes are released by motor vehicles prior to being catalysed more harmful?
CO is highly poisonous
NOx compounds dissolve in water to produce nitric acid/acid rain
unburned hydrocarbons contribute to smog
What metals are found in a catalytic converter?
platinum, paladium, rhodium
Catalyst poison
a substance that makes a catalyst inactive
What gives the catalytic converter a large surface area?
the ceramic honeycomb surface
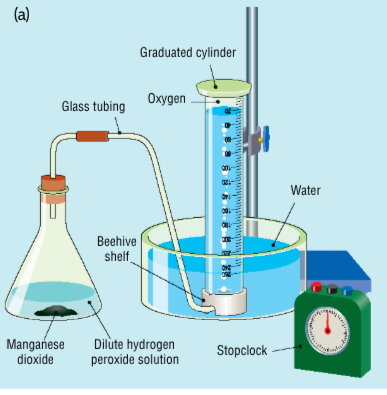
Write an equation for the experiment for the rate of production of oxygen from hydrogen peroxide using a manganese dioxide catalyst
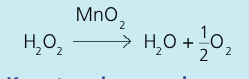
Describe the experiment for the rate of production of oxygen from hydrogen peroxide using a manganese dioxide catalyst
dilute hydrogen peroxide is placed in a conical flask
the delivery tube is connected to an inverted graduate cylinder filled with water in a basin of water
a small amount (a tip of a spatula) of manganese dioxide is added to the conical flask
the stopper is inserted quickly and the stopwatch is started and the solution is swirled
the volume of gas produced is measured at regular intervals
the results are graphed
Write an equation for the experiment to show the effect of concentration on the reaction rate using sodium thiosulfate and hydrochloric acid
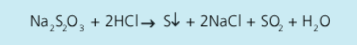
Describe the experiment to show the effect of concentration on the reaction rate using sodium thiosulfate and hydrochloric acid
using a graduation cylinder a known volume of 0.2M sodium thiosulfate solution is poured into a conical flask
the flask is placed on a white sheet of paper which has been marked with a cross
using another graduated cylinder another known volume of HCl solution is quickly added
the flask is swirled and the stopclock is started
the cross is observed, the solution in the flask becomes more milky, a creamy yellow colour is observed
the stopclock is stopped when the cross is no longer visible
the equipment is rinsed
0.2 M sodium thiosulfate is diluted to different degrees and the process is repeated
graph the results
Describe the experiment to show the effect of temperature on the reaction rate using sodium thiosulfate and hydrochloric acid
using a graduated cylinder a fixed quanitity of 0.05M sodium thiosulfate is poured into a conical flask
the flask is placed on a white sheet of paper which has been marked with a cross
using another graduated cylinder another known volume of HCl solution is quickly added
the flask is swirled and the stopclock is started
the cross is observed, the solution in the flask becomes more milky, a creamy yellow colour is observed
the stopclock is stopped when the cross is no longer visible
the equipment is rinsed
the same quantity of sodium thiosulfate and HCl solution is heated to a higher temperature
graph the results