Investment appraisal
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Investment appraisal
qualitative technique used in evaluating viability or attractiveness of investment
methods of investment appraisal
Payback Period : Method that estimates the length of
time required for an investment project to pay back
its initial cost outlay.
The average rate of return : Method that measures
the annual net return on an investment as a
percentage of its capital cost.
Net present value : The difference in the summation
of present values of future cash inflows or returns
and the original cost of investment.
Payback Period definition
Payback Period calculates how long a business will
take to recover its principal investment amount
from its net cash flows.
Formula of payback period :
initial investment cost / annual cash flow investment
A construction company plan to invest $200,000 in
new cement-mixing machine and estimates that it
will generate about $50,000 in annual cash flow.
Calculate payback period.
200,000 / 50,000 = 4 years
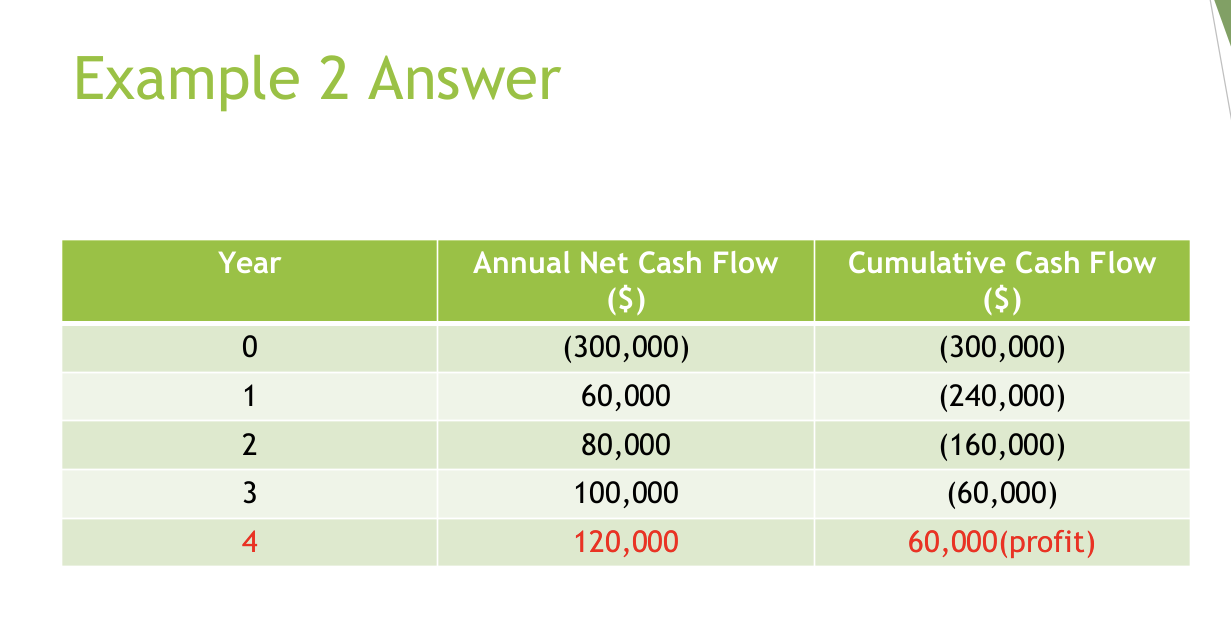
Another construction engineer aims to invest $300,000 in a
new timber-cutting machine. The machine is expected to
generate the following cash flows in the first 4 years :
$60,000, $80,000, $100,000, and $120,000. Calculate
payback period.
payback period = extra cash inflow required / annual cash flow in year 4 × 12 months
payback period = 60,000/120,000 × 12 months
Advantages of payback period
It is simple and fast to calculate.
It is a useful method in rapidly changing industries such as technology.
It helps firms with cash-flow problems.
It is less prone to the inaccuracies of long-term forecasting.
Business managers can easily comprehend and use the results obtained.
Disadvantages of the payback period
It does not consider the cash earned after the payback period which could
influence major investment decisions.
It ignores the overall profitability of an investment project by focusing only
on how fast it will payback.
The annual cash flows could be affected by unexpected external changes in
demand which could negatively affect the payback period.
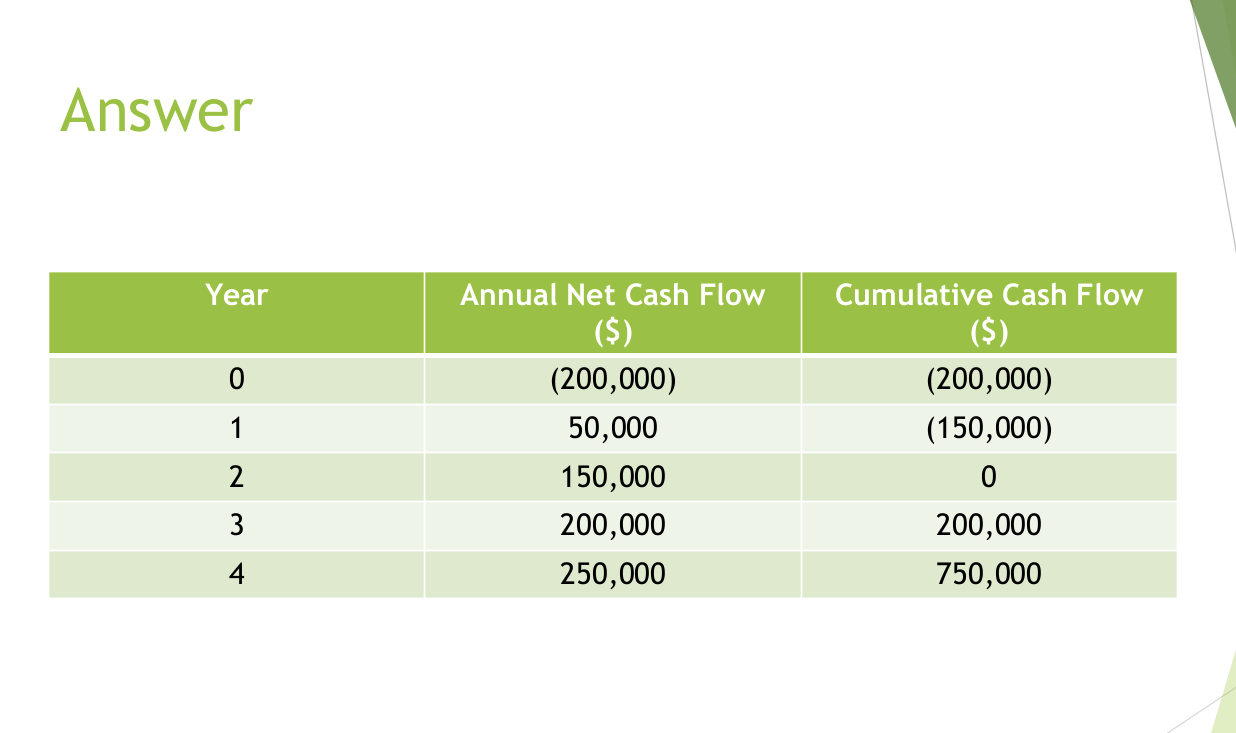
A building engineer aims to invest $200,000 in a new
timber-cutting machine. The machine is expected to
generate the following cash flows in the first 4 years :
$50,000, $150,000, $200,000, and $250,000. Calculate
payback period.
payback period = 200,000 / 200,000 × 12 months
payback period = 1 × 12 months = 12 months
payback period = 2 years 12 months = 3 years
ARR definition
Measures the annual
net return on an investment as a percentage of its capital.
It assesses the profitability per annum generated by a
project over a period of time.

ARR formula
ARR = years of usage (total returns-capital cost) / capital cost x 100
A business considers purchasing a new commercial
photocopier at a cost of $150,000. It expects the following
revenue streams for the next 5 years : $30,000, $50,000,
$75,000, $90,000, and $100,000.
Calculate ARR.
Step 1 : Calculate total returns.
Total returns = $30,000 + $50,000 + $75,000 + $90,000 + $100,000
= $345,000
Step 2 : Calculate Net Return per Annum.
Net Return per Annum = Total returns – Capital Cost / 5 years
Net Return per Annum = $345,000 - $150,000 / 5 years
= $39,000
Step 3 : Calculate ARR.
Net Return per Annum
ARR = ---------------------------- x 100
Capital Cost
$39,000
ARR = ----------- x 100 = 26 %
$150,000
ADVANTAGES OF THE ARR
The ARR shows the profitability of an investment project over a
given period of time.
Unlike the payback period, it makes use of all the cash flows in a
business.
It allows for easy comparisons with other competing projects, for
better allocation of investment funds.
A business can use its own criterion rate and check this with the
ARR for a project, to assess the viability of the venture.
DISADVANTAGES OF THE ARR
A-Since it considers a longer time period or useful life of the
project, there are likely to be forecasting errors.
-It does not consider the timing of cash inflows.
-The effects on the time value of money are not considered.
A Car Rental considers purchasing a new mini bus at a
cost of $350,000. It expects the following revenue streams
for the next 4 years : $150,000, $250,000, $200,000, and
$250,000.
Calculate ARR.
Total returns = $150,000 + $250,000 + $200,000 + $250,000
= $850,000
Net return per annum = $850,000 - $350,000 / 4 years
= $125,000
ARR = $125,000 / $350,000 x 100
= 35.71 %
Net present Value
The difference in the summation of present
values of future cash inflows or returns and the original cost of
investment.
Present value is today’s value of an amount of money available in
the future.
For example, $100 invested at the beginning of the year in a bank
account offering 10% interest would be worth $110 at the end of
the year.
(10% x $100) + 100 = $110
Discounted Cash-Flow Method
A technique that considers how interest rates affect the
present value of future cash flows.
It uses a discount factor that converts these future cash flows
to their present value today.
Advantages of Net Present Value
The opportunity cost and time value of money is put into
consideration in its calculation.
All cash flows including their timing are included in its
computation.
The discount rate can be changed to suit any expected
changes in economic variables such as interest rate
variations.
Disadvantages of Net Present Values
It is more complicated to calculate than the payback
period or ARR.
It can only be used to compare investment projects with
the same initial cost outlay.
The discount rate greatly influences the final NPV result
obtained, which may be affected by inaccurate interest rate
predictions.
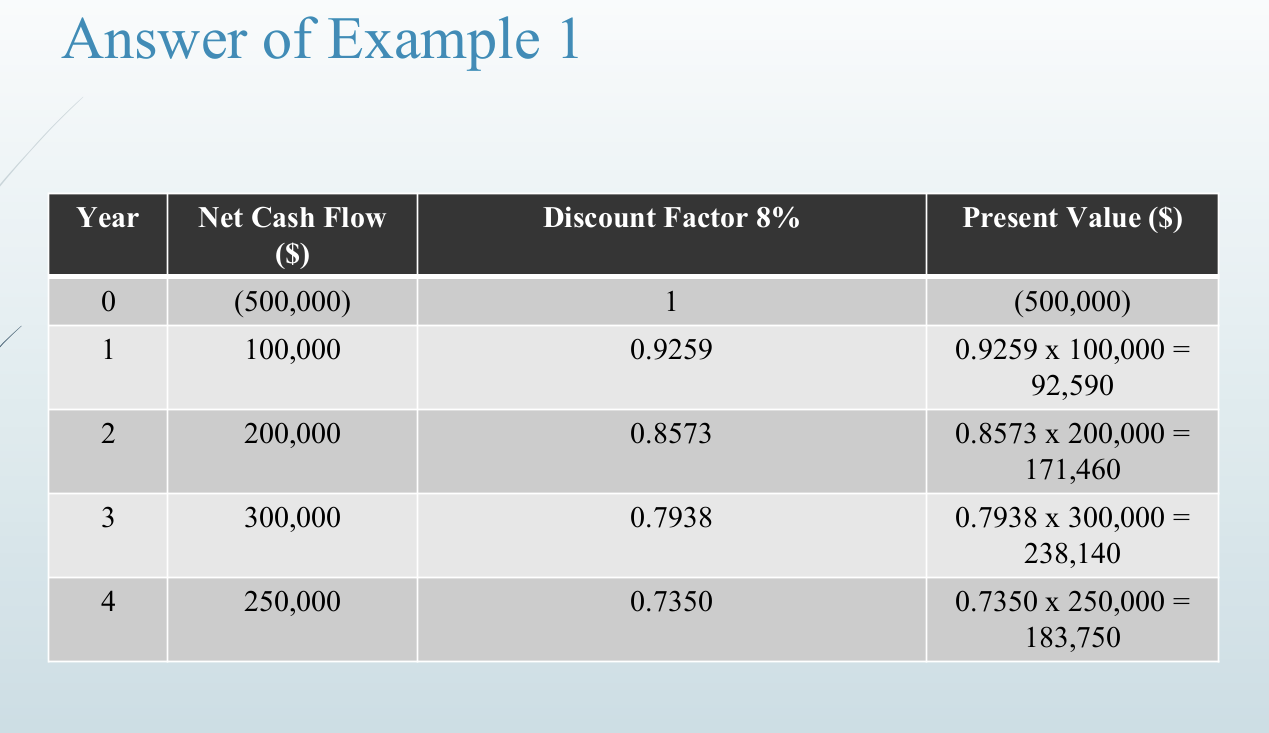
Consider an investment project that costs $500,000 and
produces net cash flow over the next four years as follows,
Year 1 = $100,000
Year 2 = $200,000
Year 3 = $300,000
Year 4 = $250,000
Calculate the Net Present Value at a discount factor 8%.
Net Present Value = Total Present Values – Original Cost
Total Present Values = $92,590 + $171,460 + $238,140 +
$183,750 = $685,940
Original Cost = $500,000
Net Present Value = $685,940 - $500,000 = $185,940