Pop & Soc Final
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
What are some problems that can come from too few humans?
too few workers, depleted tax base, Social Security insolvency, society without kids, empty biuldings
What is Social Security?
Government funded retirement benefits, covers other programs like disability but retirement is the biggest, single largest social welfare system, covers 90% of Americans
When was Social Security implemented?
1935, with the social security act by FDR
What are the Qualifications for SS?
62 or older, worked and paid into fund for total of 10 years or more, partial benefits to spouses, widows, dependents, etc.
How is SS funded?
We(plus our employers) pay SS tax, goes into giant fund, current beneficiaries draw from that fund
Retirement age and SS income
Minimum: 62 (avg $1,275)
Full: 67 (avg $1,767)
Max: 70 (avg $1,963)
Max possible for age 70: $4,873
What is the SS solvency crisis?
Current SS benefits are paid out of taxes from current workers + giant general trust fund, but since 1935 people live longer and have fewer kids
What does SS solvency crisis mean?
The fund is due to run out by 2034, SS payments will be reduced to what is covered by current taxes, immediate drop in benefits by 25%
How can SS be fixed?
Raise the tax, raise retirement age, cut benefits, only give SS to low income, switch to privatized system
What is tied to women's roles in society?
fertility levels
What are some tensions with women"s roles in society?
How much does having children conflict with other aspects of living a flourishing life? How much can/should the tradeoffs be shared by men? How much is motherhood a socially valued endeavor?
WR: Traditionalism
Resist social change and stick to tradition, restrict women's professional opportunities or emphasize value of caregiving
WR: Partial egalitarianism
Open career opportunities but maintain family responsibilities for women, largely what has been done(the second shift), leads many women to feel overburdened, recipe for low fertility
WR: Full Egalitarianism
reduce opportunity cost, make it easier for women to do both, find ways to make motherhood more engaging and fulfilling, get men more involved in caregiving, housework etc.
Lowest fertility rate
S. korea, japan, italy, greece
What do low fertility rate countries have in common?
They tend to have somewhat modern economies but are culturally traditional
What is the current theory with fertility?
More gender egalitarianism = higher fertility, women want careers and kids, but men need to add more
What are barriers of having more kids?
Expenses, housing, lack of time, family work balance, lack of social support
What US policies help (low-income) families?
Child tax credit, special supplemental nutrition program for women infants and children, food stamps, medicaid, head start
What are some marriage penalties?
Progressive tax rate, married people end up paying more than two single people, causing reduced eligibility for benefits
What is paid family leave?
Family leave and Medical act guarantees 12 weeks unpaid leave for birth of a child, some states/employers more generous
Other policy suggestions?
Special tax breaks(Hungary), Special loans or home buying help(Hungary), Subsidized childcare(Scandinavia), Monthly checks(Poland, France)
What makes a Family-Friendly culture?
religious communities, sidewalks, parks, city design, activities, businesses, culture of kids
What are the big life steps: 18-29
Completing education, Starting a career, Dating, Starting a family, Traveling, Deciding where to live, Starting to accumulate wealth, Learning everything about being on your own
What are the big life steps: 30-45
Employment and job opportunities, promotions, Having kids and raising them, Figuring out kids' education, Lots of financial responsibilities, Buying a house, Body slowing down, more tired
What are the big life steps: 46-65
A lot of stability, Peak of professional career, Paying for kids' college, Kids moving out, Maybe having grandchildren, Different relationship with kids, Not retired yet
What are the big life steps: 66+
Retirement, Freedom and financial stability, Senior citizen age, Social Security, Being put in a home, Start having grandkids, Health starts to fail, Closer to death, dementia
When do you become an adult? How do you know?
Living independently, Paying your own way, Having own insurance, not financially dependent, Graduating college, Having a job/career to support yourself, Maturity, Not partying so much, What people talk/think/care about, Ready to start family/settle down
What is it called when a society expects you to grow up faster?
emerging adulthood
How does age effect social change?
What changes as we get older?
How does period effect social change?
What kinds of events affect everyone?
How does cohort effect social change?
What changes between generations? Some argue historical events effects different generations differently
Cohort
people in a given age group
Religious decline social change in the US?
Age: people leaving religion as they move from childhood to young adult
Period: Broad social changes 1990-2000's
Cohort: Why are younger generations less religious
Sex Imbalance?
More boys than girls born every year, Natural ratio of 105 M: 100 F
Why is sex ratio higher around the world?
Son preference, sex-selective abortion, missing girls
Who has a lower mortality rate?
women
Consequences of disproportionately male society?
only successful men get married, women have prized status but may face familial constraints
Consequences of disproportionately female society?
men can be more demanding on women, less incentive for men to commit
What are the 4 age structures?
Rapid growth, slow growth, stable, declining
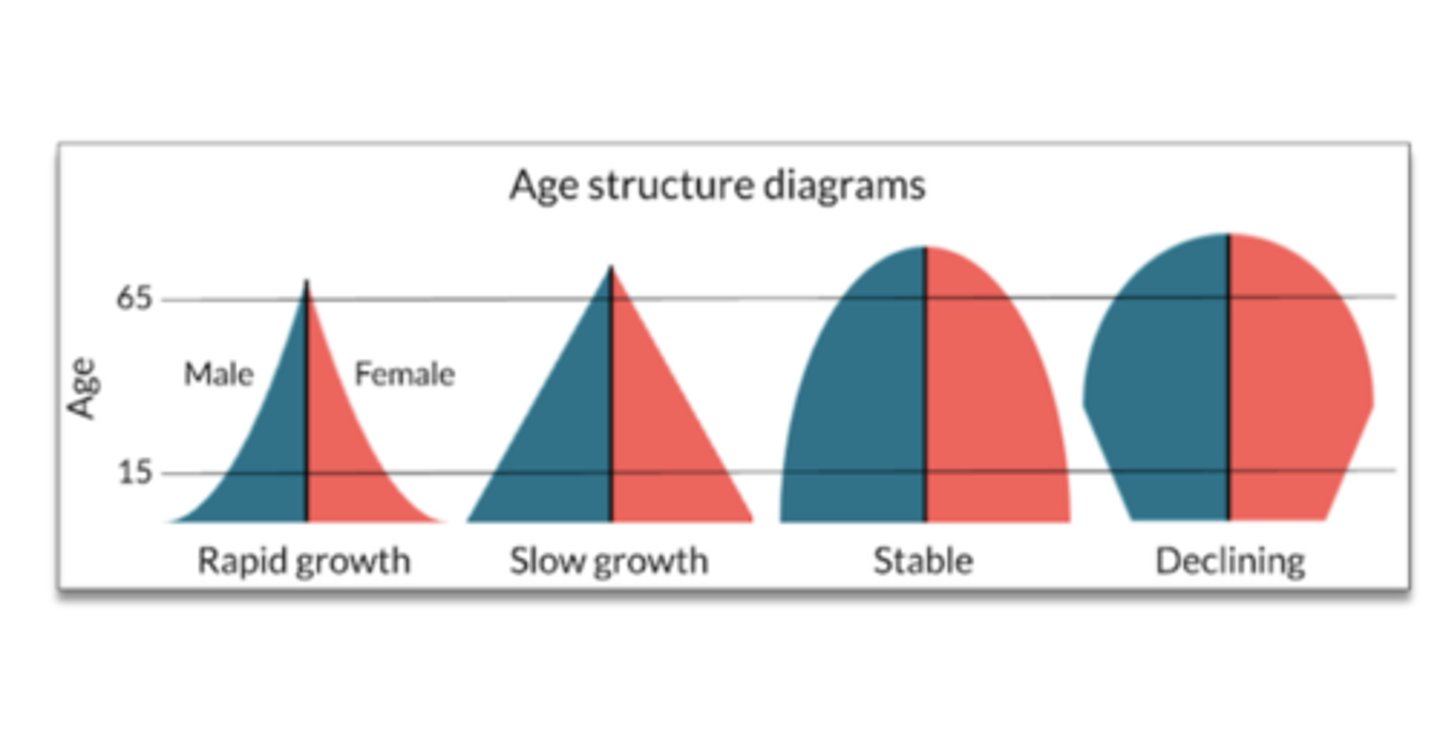
What is a demographic dividend?
after both fertility and mortality drop, you get a large generation
What does a demographic dividend mean?
when that generation is working age society is uber-productive, but it can only happen in one period of time
extrapolation
the act of estimation by projecting known information, taking compared data and projecting it to determine characteristics of later generations
cohort component method
Population projection method using birth, death, and migration rates. Steps:
1. calculate death rates
2. project survivors
3. project births
4. project migration
Why do people live in or visit cities?
Closer to stores, job opportunities, stuff to do, closer to people, easier to get around, more services/educational opportunities
What does it mean to be Urban?
population size, land area, population density, economic and social organization
Census Criteria to be Urban
Area of >5K people, at least 2K housing units, includes residential, commercial, and other non-residential areas, core of 425 housing units per sq mi + adjacent blocks
What part of the US is Urban?
80%
What is the Urban transistion?
Large-scale shift from rural to urban life
Why the Urban shift?
advancing tech, advancing knowledge/networks, economic differentiation, expanding/shifting opportunities, ease of transportation
What qualifies a Standard Metropolitan Area?
Core of >50K
Mega-city?
City with more than 10 million people, used to only be Tokyo and NYC now 34 cities
What are the social advantages of cities?
Efficiency, economies of scale, buyers sellers & manufacturers in one place, storage, transport, divers opportunities, creativity, collective enterprises, concentrated governing, niches
Urban living challenges
Past: low mortality
Present: low fertility, loneliness, low social trust, overcrowding, crime
Slum
a neighborhood lacking one or more:
clean water, sewer system, adequate housing space or durability, security of tenure
Cultural Urban challenges
inequality, segregation, cultural conflict, NIMBY-ism, unaffordability, blight
Max Weber: Life Chances
the extent to which individuals have access to important societal resources such as food, clothing, shelter, education, and health care
What are relevant factors of life chances?
How we grew up, ascriptive characteristics, opportunity structure of society
Family demography
describes characteristics and behaviors as they relate to family
What is the changing structure of US households?
single parents and living alone are increasing while married parents are decreasing
Modern Marriage
marriage happens later in life, permanent nonmarriage more common, changes in who is getting married
Marriage age change 1956-2022
20.1(F), 22.5(M) - 28.2(F), 30.1(M)
What women are less likely to marry?
less educated women
Who is the most and least married?
most - asians
least - african americans
What do changes in marriage mean?
From cornerstone to capstone, changing expectations, deinstitutionalization, uncoupling of marriage from shared household, sex, children
What is the general divorce trend?
Rise in 60's/70's, decline in 80's
What causes rising divorce?
culture changes from tradition to autonomy, women in workforce, availability of no-fault divorce
What causes declining divorce?
tradition revival, difficult experiences w/ divorce, change in composition of who is married
How common is cohabitation?
more common than married
What is sliding cohabitation?
just sort of happens, not planned, early in relationship, not necessarily stepping stone to marriage, may already have kids, more prominent in less-educated, usually promotes divorce not marriage
What is deciding divorce?
carefully planned, intentional stepping stone, may be engaged or planning it, typically don't have kids, typically more-educated, likely to promote marriage
What causes a rise in single parenthood?
culture changes from tradition to autonomy, women in workforce, availability of no-fault divorce, or same as divorce rise
What economic and cultural changes effect single parenthood?
economic- harder for men to support family, easier in the pas for women to support kids
cultural- destigmatization of single parenthood, so children are the necessity marriage is the luxury
How does more educational/professional opportunity affect family formation?
delayed marriage, delayed fertility, different life goals, different time horizons
Eternal debate: Are these social changes more due to structure or culture?
Structure: technology, economy, legal regime
Culture: religion, norms, values
What is the purpose of a college education?
key to success/status, most middle class jobs require a degree, degrees are increasingly obtainable
Good & Bad news of a modern economy?
Good: education, wealth, etc. have increased
Bad: inequality increased
Hourglass economy
middle-class is squeezed forcing many to move up of down
Doomerism
malthus was right about population just wrong timeline, on track to exceed carrying capacity, war, famine, water shortages, pollution on the horizon
Boomerism
more humans = more innovation, managed to expand carrying capacity, expanding food production, harness clean water, develop green energy
Earth's Challenges
Scarce resources: food(land to produce it), clean water, fossil fuels
Environmental damage: pollution, deforestation, global warming
Extensive land use
use more and more land to produce food
Intensive land use
getting more food out of each acre of land
how to intensively maximize food production
irrigation, mechanization, fertilizer, pesticides, consolidation(bigger commercial farms)
The Green Revolution
effort to develop high-yield crops, dwarf wheat(less stem, more stalk), high nutrient rice, soybeans, peanuts, quinoa, goa
Pitfalls of Green Revolution
more nutrition in less land requires more water, fuel, pesticides, some people resist modified food so organic food becomes a luxury good
Food production concerns
77% of ag-land is used for pasture
demand for food is growing faster than population
Water
makes up 71% of earth, only 3% is fresh(more or less), 70% of fresh water is used for irrigation, converting salt to fresh is resource-intensive
Global Warming
Human carbon emissions are warming the earth, glacier melting, sea level rising, droughts and floods, desertification, natural disasters
Who had a higher carbon footprint?
Wealthier countries: more tech use, more travel, more other energy usages, or larger countries: more people = bigger carbon footprint
World Target carbon footprint vs Actual?
2 & 5
carbon footprint
the total carbon dioxide emissions produced by an individual, group, or location
Sustainable development
Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Care for God's Creation
to live their faith in relationship with all of creation by protecting the health of people and the planet
What can be done against global warming?
consume and produce less
direct aid to places most affected
address negative externalities(taxes, regulations)
incentivize practices that reduce impact
invest in renewable energy
What can be done? Boomers:
human inivation
What can be done? Doomers:
fewer humans, more regulations, sacrifices