Test 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/228
Last updated 4:47 PM on 11/29/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
229 Terms
1
New cards
appendicular skeleton
Pectoral girdle, upper extremity, pelvic girdle, and lower extremity
2
New cards
axial skeleton
Skull, vertebrae, sternum, ribs, sacrum, and hyoid
3
New cards
270 bones
number of bones at birth
4
New cards
pectoral girdle
Consists of two bones on each side of the body: clavicle and scapula
5
New cards
Sternoclavicular joint
medial joint between clavicle and scapula
6
New cards
Acromioclavicular joint
lateral joint between clavicle and scapula
7
New cards
purpose of the clavicle
• Braces shoulder, keeps arm away from midline
• Resists medial and anterior movement
• Resists medial and anterior movement
8
New cards
acromion
Articulates with clavicle to form the sole point of attachment of scapula and upper limb to the rest of the skeleton
9
New cards
coracoid process
shaped like a bent finger
• Provides attachment for tendons of biceps brachii and other arm muscles
• Provides attachment for tendons of biceps brachii and other arm muscles
10
New cards
glenoid cavity
shallow socket that articulates with the head of the
humerus
• Helps form glenohumeral joint
humerus
• Helps form glenohumeral joint
11
New cards
brachium
arm proper: extends from shoulder to elbow
• Only one bone-humerus
• Only one bone-humerus
12
New cards
antebrachium
forearm: extends from elbow to wrist
• Radius and ulna
• Radius and ulna
13
New cards
proximal end of humerus
• Head articulates with the glenoid cavity of scapula
• Anatomical neck
• Greater and lesser tubercles
• Deltoid tuberosity
• Intertubercular sulcus holds biceps tendon
• Surgical neck
• Anatomical neck
• Greater and lesser tubercles
• Deltoid tuberosity
• Intertubercular sulcus holds biceps tendon
• Surgical neck
14
New cards
Interosseous membrane
What is between the radius and ulna?
15
New cards
purpose of carpal bones
• Form wrist
• Flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction
• Flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction
16
New cards
middle phalanx
what is the thumb lacking?
17
New cards
ox coxae
hip bone
18
New cards
ilium
Which bone houses the greater sciatic notch contains the sciatic nerve?
19
New cards
ischium
Which bears the body’s weight and is the site of sacral ligamentous attachment?
20
New cards
pubis
Where is the pubic symphysis?
21
New cards
acetabulum
What is the hip socket called?
22
New cards
obturator foreman
large hole below acetabulum
23
New cards
men pelvic area
heavier and thicker pelvis
24
New cards
femur
Which is the longest bone in the body?
25
New cards
femur
Which is the strongest bone of the body?
26
New cards
patella
Which is a triangular bone and has a gliding joint?
27
New cards
yes
Is the patella cartilaginous at birth or not?
28
New cards
tibia
Which is the weight bearing bone: Tibia or fibula?
29
New cards
fibula
Which helps stabilize the ankle? Tibia or fibula
30
New cards
due to the load bearing role of the ankle
Why are tarsal bones arranged and shaped differently then the carpal bones?
31
New cards
talus
Which is the most superior tarsal bones?
32
New cards
calcaneous
Which bone forms the heel?
33
New cards
base, shaft, and head
How does the big toe differ from all the other toes?
34
New cards
22 bones
How many bones are joined together by sutures in the skull?
35
New cards
8 bones
How many bones have direct contact with the meninges of the brain?
36
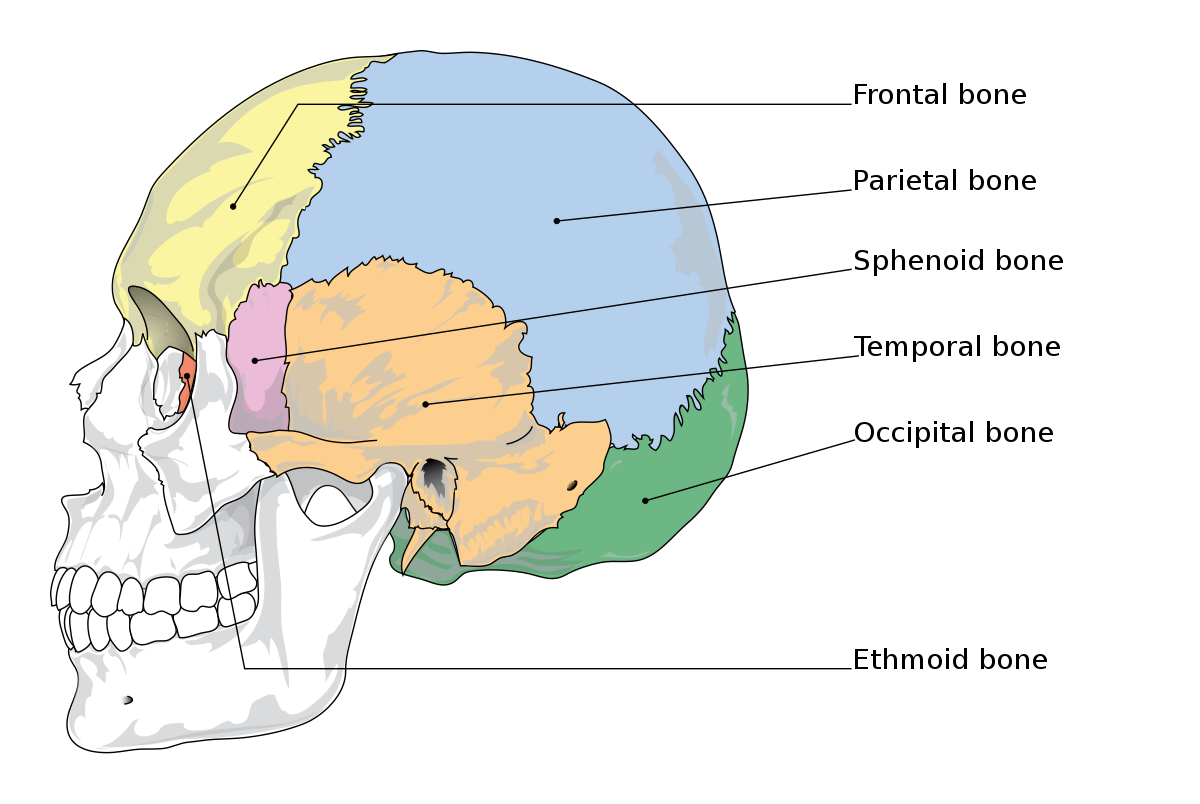
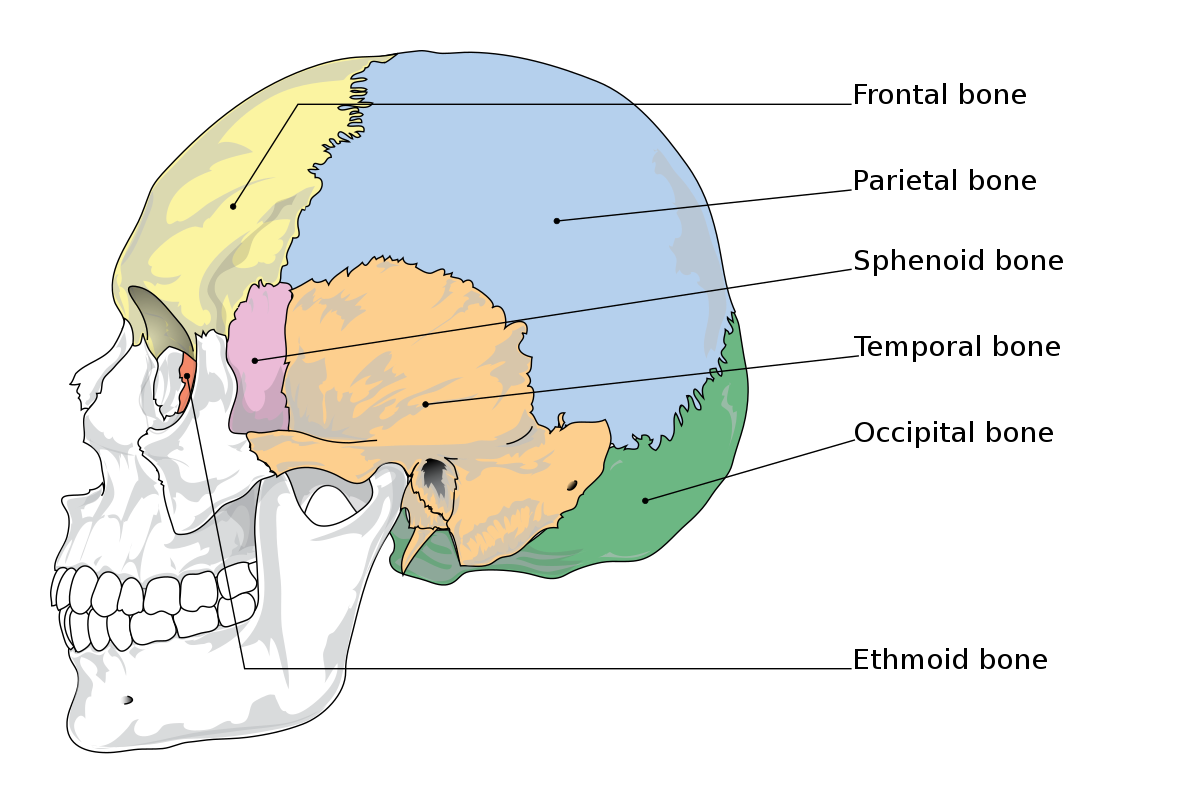
New cards
Frontal, occipital, ethmoid, sphenoid, parietal, temporal
What bones have direct contact with the meninges of the brain?
37
New cards
14 bones
How many bones have no direct contact with the brain or meninges?
38
New cards
foramina
What is a hole that allows passage for nerves and blood vessels in the skull called?
39
New cards
Frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, and maxillary
What are the names of the paranasal sinuses called?
40
New cards
maxillary, frontal, ethmoid, and sphenoid
What bones have sinus cavities?
41
New cards
anterior, middle, and posterior fossa
What are the three basins that comprise the cranial floor?
42
New cards
fontanels
What are the spaces between unfused bones called?
43
New cards
shifting of bones during birth and growth of brain
What do the spaces between unfused bones allow for while growing?
44
New cards
8
How many cranial bones are there?
45
New cards
frontal bone
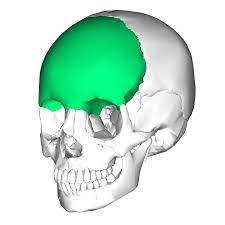
46
New cards
parietal bone
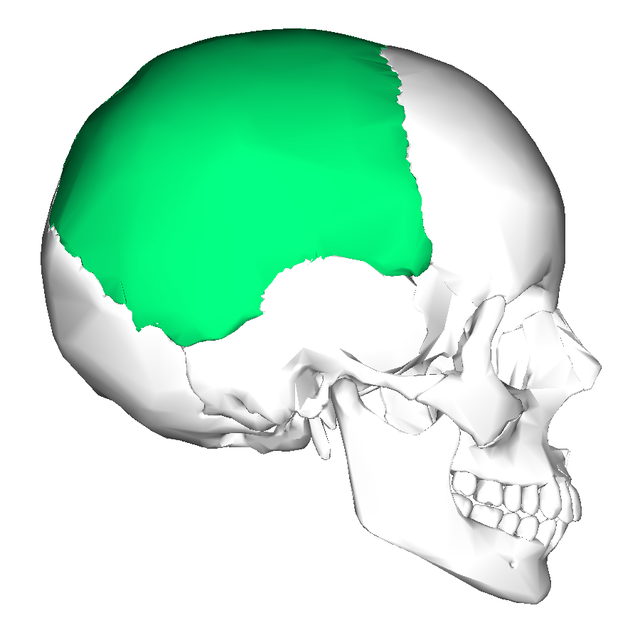
47
New cards
temporal bone
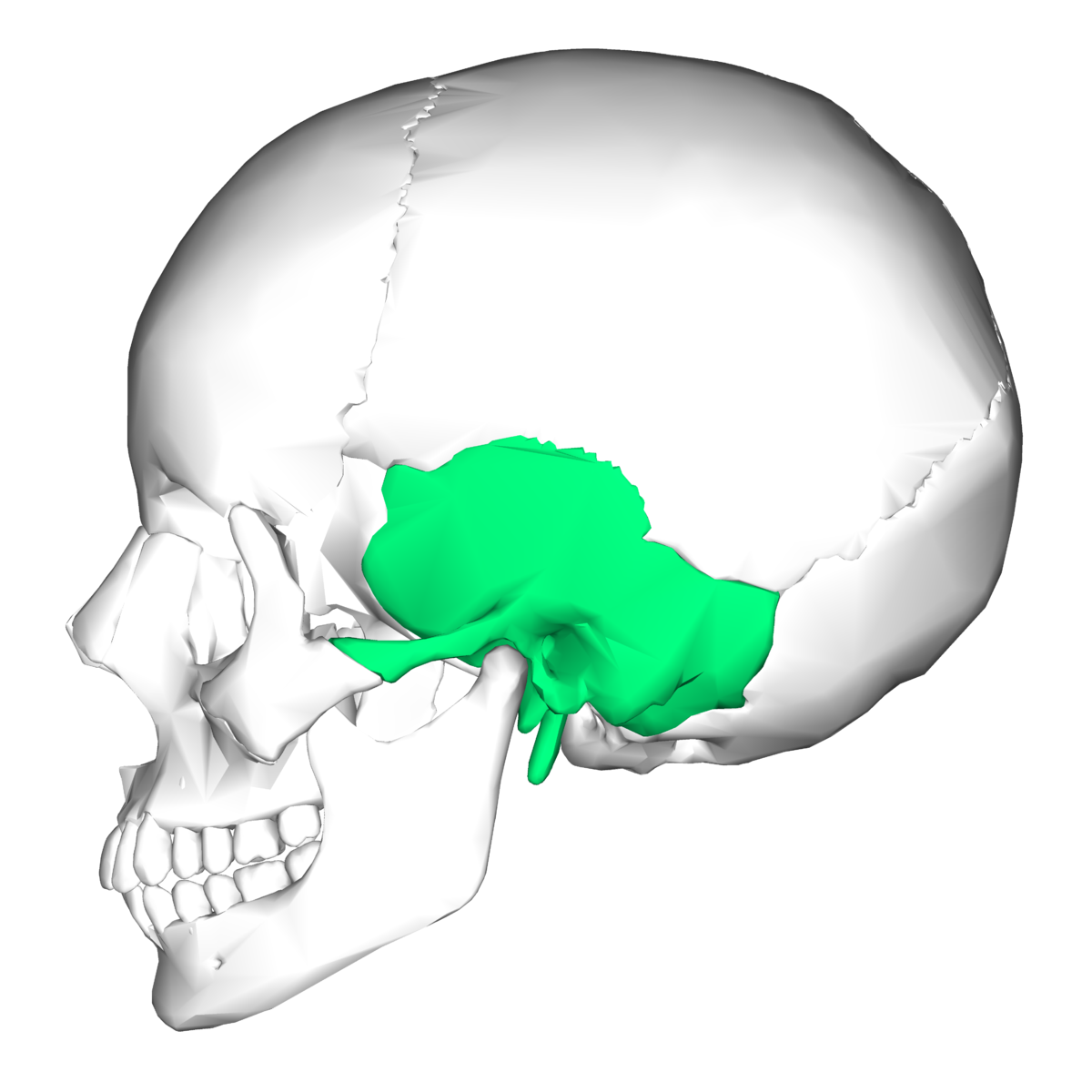
48
New cards
occipital bone
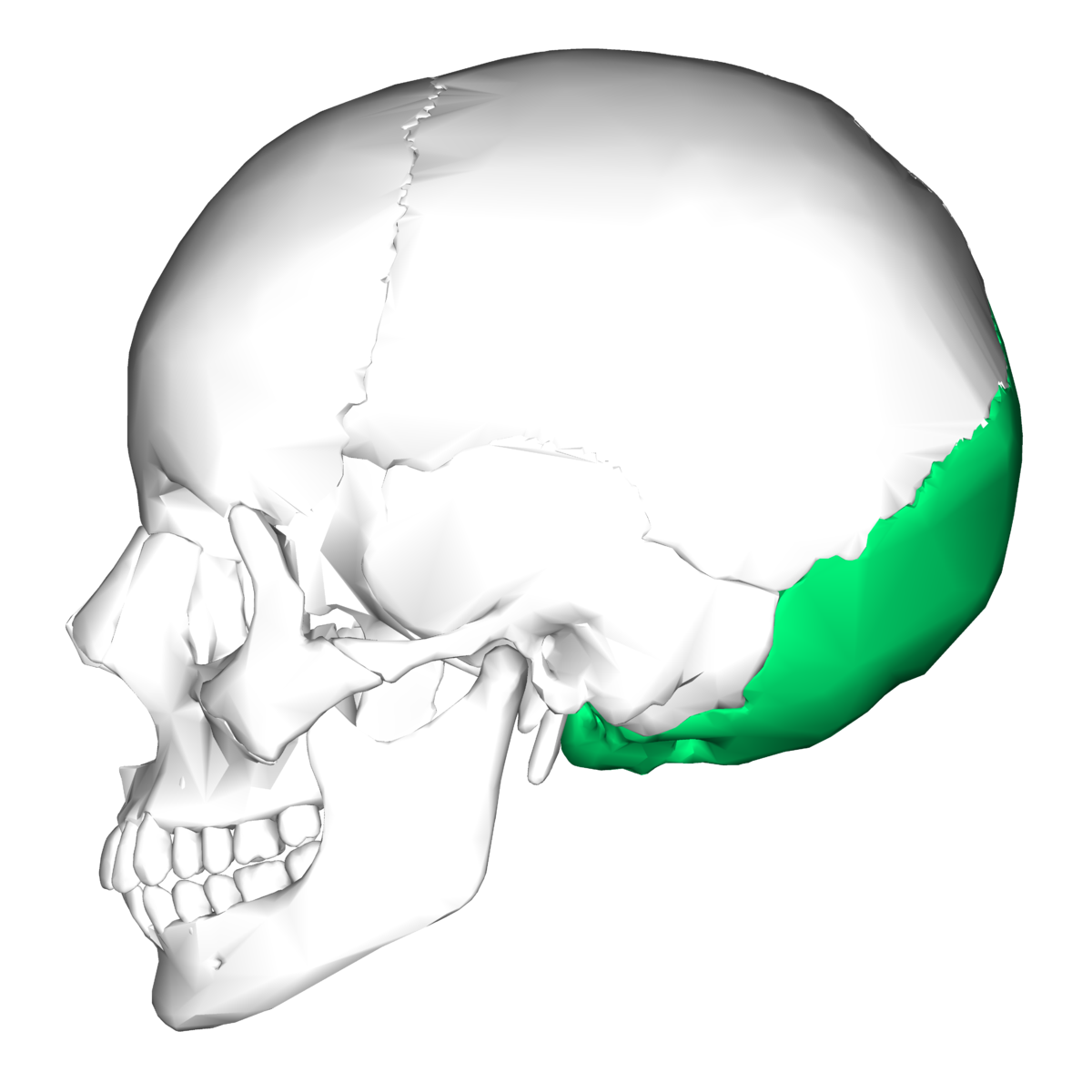
49
New cards
sphenoid bone
50
New cards
ethmoid bone
51
New cards
maxillary bone
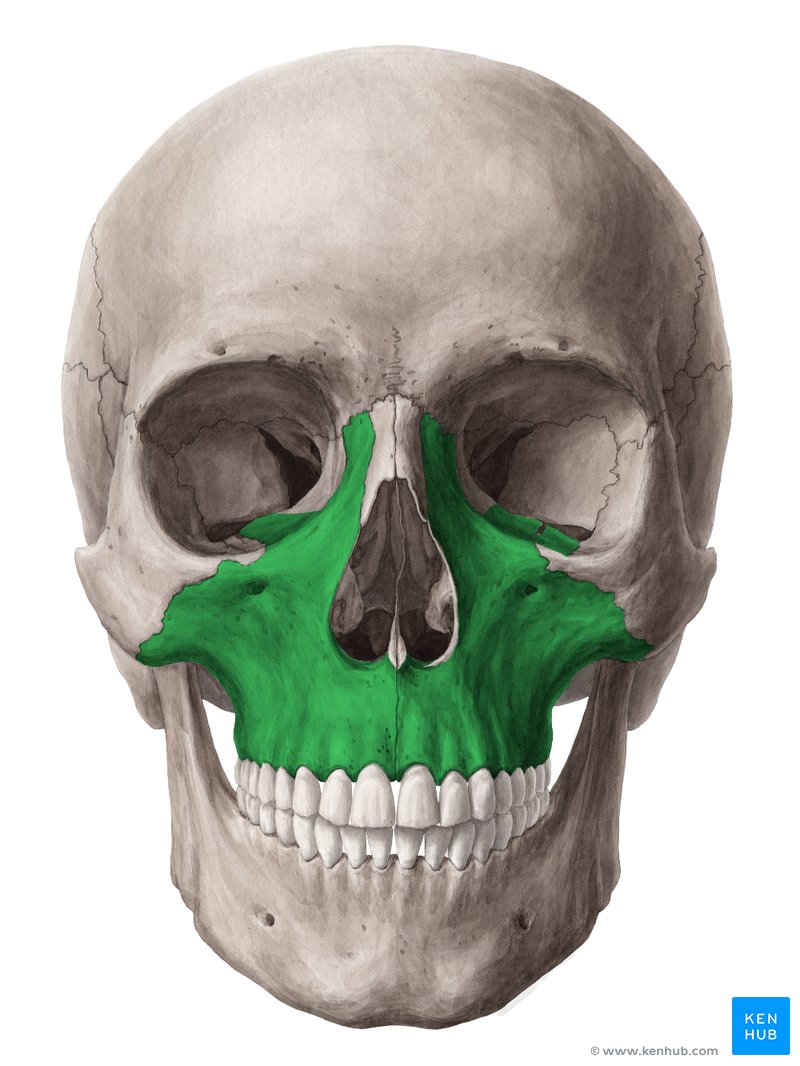
52
New cards
palatine bone
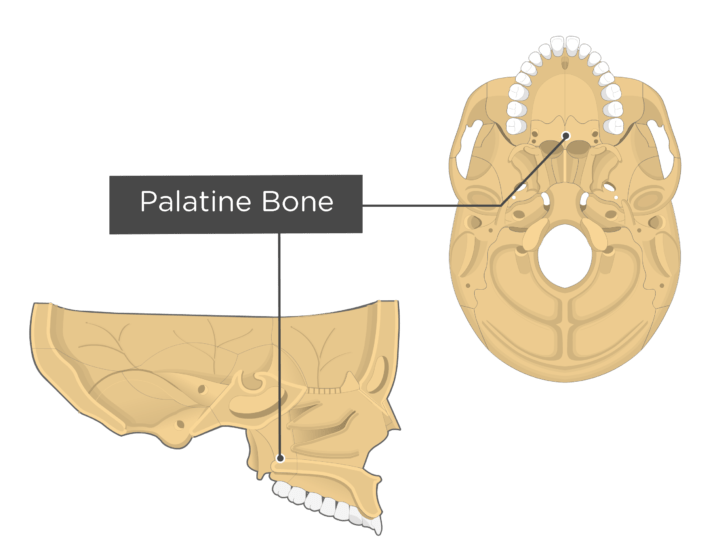
53
New cards
zygomatic bone
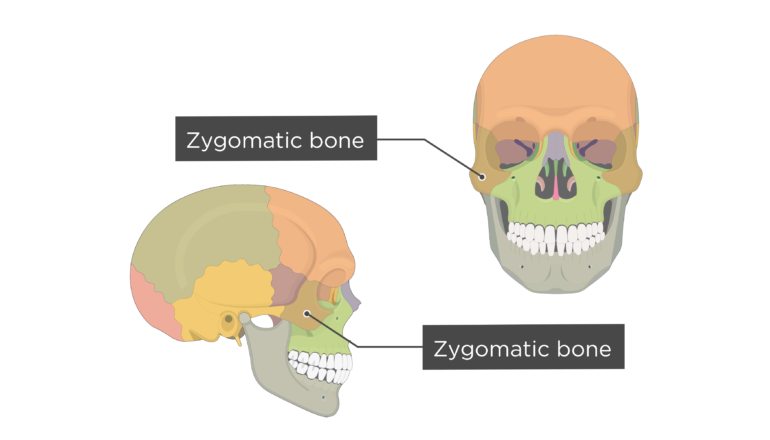
54
New cards
lacrimal bone
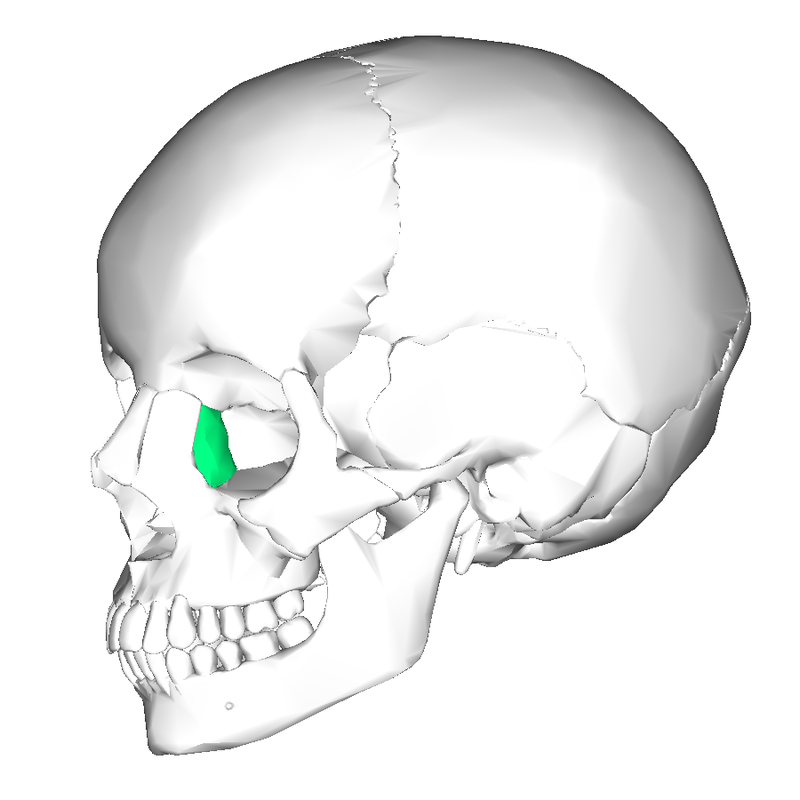
55
New cards
nasal bones
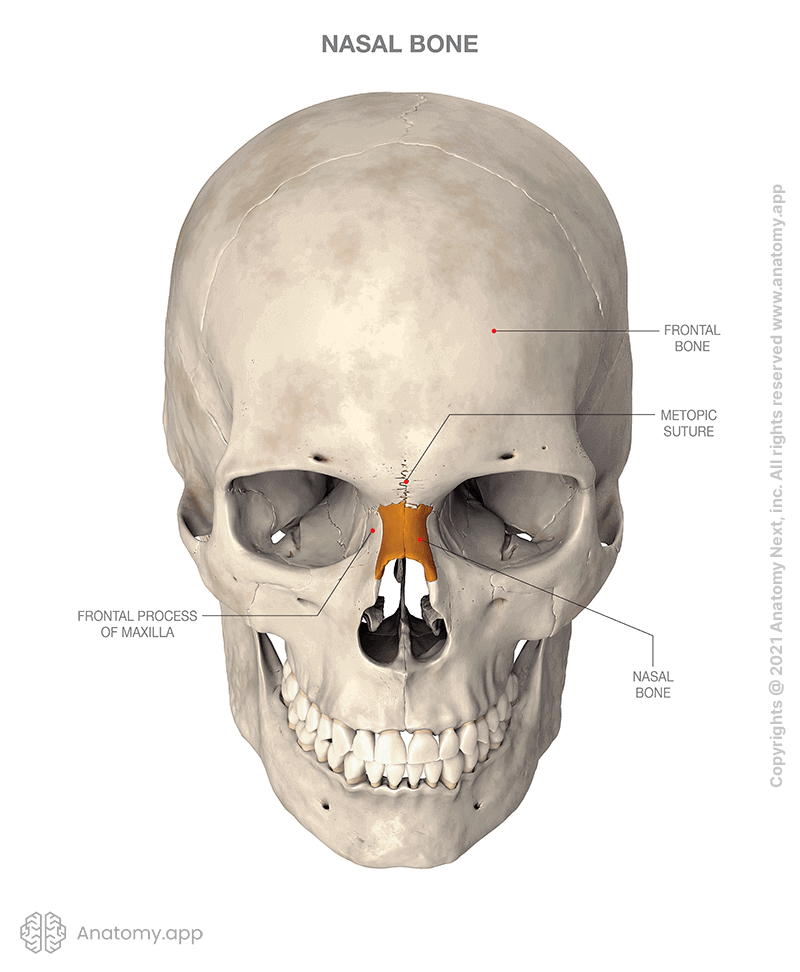
56
New cards
vomer
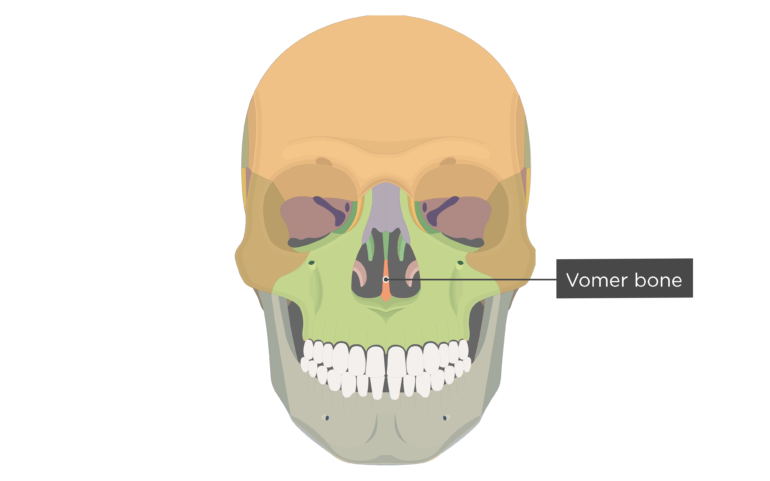
57
New cards
mandible
only movable bone
58
New cards
hyoid bone
• Slender U-shaped bone between chin and larynx
• Does not articulate with any other bone
• Suspended from styloid process of skull
• Fractured hyoid bone is evidence of strangulation
• Does not articulate with any other bone
• Suspended from styloid process of skull
• Fractured hyoid bone is evidence of strangulation
59
New cards
carotid canal
Passage for internal carotid artery supplying the brain
60
New cards
jugular foramen
• Between temporal and occipital bones
• Passageway for drainage of blood via internal jugular vein
• Passageway for drainage of blood via internal jugular vein
61
New cards
33 vertebrae
How many vertebrae total?
62
New cards
vertebral groups
• 7 cervical in the neck
• 12 thoracic in the chest
• 5 lumbar in lower back
• 5 fused sacral
• 4 fused coccygeal
• 12 thoracic in the chest
• 5 lumbar in lower back
• 5 fused sacral
• 4 fused coccygeal
63
New cards
functions of spine
• Supports skull and trunk and allows for their movement
• Protects spinal cord
• Absorbs stresses of movements
• Provides attachments for limbs, thoracic cage, and postural muscles
• Protects spinal cord
• Absorbs stresses of movements
• Provides attachments for limbs, thoracic cage, and postural muscles
64
New cards
intervertebral discs
What are between each intervertebral disc?
65
New cards
primary curvature
Spine exhibits one continuous C-shaped curve
66
New cards
4 curvatures
How many curvatures does the S-shaped vertebral column have?
67
New cards
after birth
When dose secondary curvature develop?
68
New cards
Scoliosis
lack of proper development of one vertebrae
69
New cards
kyphosis
from osteoporosis
70
New cards
lordosis
from weak abdominal muscles, pregnancy, or obesity
71
New cards
intervertebral disc
absorb shock
72
New cards
Nucleus pulposus
soft, gelatinous central portion of the intervertebral disk that moves within the disk with changes in posture
73
New cards
Anulus fibrosus
tough circular exterior of the intervertebral disc that surrounds the soft inner core, the nucleus pulposus
74
New cards
Notches between adjacent vertebrae
What are the intervertebral foramen?
75
New cards
C1 purpose
supports the skull
• Yes movement
• Yes movement
76
New cards
C2 purpose
No head motion
77
New cards
thoracic vertebrae
Which vertebrae have rib attachments?
78
New cards
costal facets
What are vertebrae rib attachments called?
79
New cards
26
When does the Sacrum fuse?
80
New cards
30
When does the coccyx fuse?
81
New cards
True ribs
(1 to 7) attach to sternum with hyaline cartilage
82
New cards
false ribs
8-12
83
New cards
floating ribs
11 and 12 are floating and not attached to sternum
84
New cards
sternum
(breastbone)—bony plate anterior to the heart
85
New cards
manubrium, body, xiphoid process
What three regions is the sternum divided into?
86
New cards
xiphoid
What part of the sternum is dangerous if fractured during CPR?
87
New cards
adaptions for bipedalism
• Strong, springy foot arches
• Great toe not opposable
• Femurs angle inward so knees are closer together—erect posture requires less muscular effort
• Viscera supported in bowl-shaped pelvis
• Insertions of gluteal muscles differ from other primates
• Great toe not opposable
• Femurs angle inward so knees are closer together—erect posture requires less muscular effort
• Viscera supported in bowl-shaped pelvis
• Insertions of gluteal muscles differ from other primates
88
New cards
arthrology
science of joint structure, function, and dysfunction
89
New cards
kinesiology
study of musculoskeletal movement
90
New cards
Joint
(articulation): any point where two bones meet
91
New cards
4 major joint categories
• Bony joints
• Fibrous joints
• Cartilaginous joints
• Synovial joints
• Fibrous joints
• Cartilaginous joints
• Synovial joints
92
New cards
bony joint/ syntosis
What is an immovable joint, formed between two bones when they ossify and become a single bone?
93
New cards
Fibrous joint
Adjacent bones are bound by collagen fibers that emerge from one bone and penetrate into the other
94
New cards
3
how many types of fibrous joints are there?
95
New cards
sutures
The immobile or slightly mobile fibrous joints in which short collagen fibers bind the bones of the skull to each other are known as:
96
New cards
Serrate
interlocking wavy lines
• Coronal, sagittal, and lamboid
• Coronal, sagittal, and lamboid
97
New cards
squamous
(lap) overlapping beveled edges
• Temporal and parietal bones
• Temporal and parietal bones
98
New cards
plane
(butt) straight, non-overlapping edges
• Palatine processes of the maxillae
• Palatine processes of the maxillae
99
New cards
gomphoses
What type of joint is found attaching teeth to their sockets?
100
New cards
fibrous periodontal ligament
Gomphoses are held in place by a ligament called what?