4.1 process of fat absorption
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
emulsification of fats
when dietary fats enter the small intestine they are in large insoluble droplets which bile salts break into smaller micelles via emulsification
bile salts increase the surface area
for pancreatic enzymes, lipase, to work
lipase digestion
pancreatic lipase breaks down triglycerides into free fatty acids and monoglycerides which are absorbed
without bile salt induced emulsification
lipase would be unable to access the hydrophobic fat molecules effectively
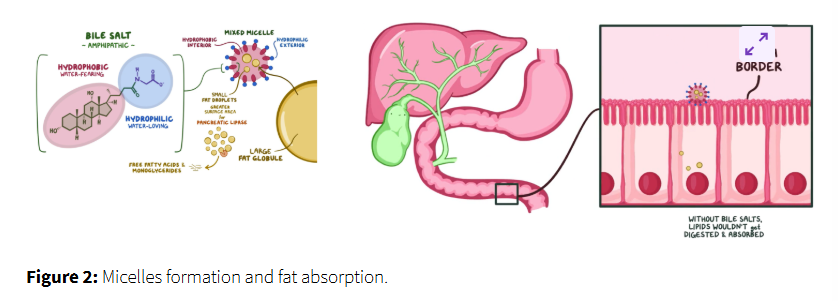
micelle formation
bile salts surround the breakdown products (free fatty acids monoglycerides cholesterol and fat-soluble vitamins) forming micelles
these micelles act as transport vehicles
allowing the fats to be absorbed across the water based environment of the intestinal lumen
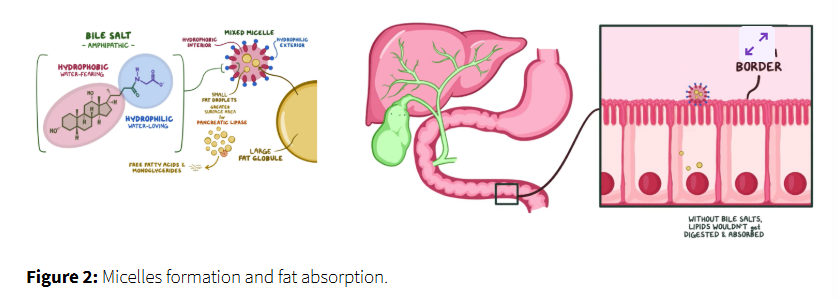
absorption into enterocytes
the micelles travel to the surface of the intestinal cells where the fat components are released and absorbed into the enterocytes, intestinal lining cells
inside the enterocytes
fats are reassembled into triglycerides
chylomicron formation
the reassembled triglycerides + cholesterol + fat soluble vitamins are packaged into chylomicrons, lipoprotein particles that are too large to enter the blood stream directly
chylomicrons enter the lymphatic system
before eventually reaching the bloodstream
bile salts are essential for the absorption of lipophilic drugs (fat soluble)
many drugs with poor water solubility rely on bile salts for their absorption
the most important function of bile salts in drug absorption is their ability to for micelles
the hydrophobic core of the micelle allows fat soluble drugs to be shielded by the aqueous environment of the intestinal lumen facilitating their solubilisation → absorption
emulsifcation of liophilic drugs
when bile salts are secreted into the small intestine they surround lipophilic drug molecules breaking them into smaller more manageable particles
micelle encapsulation
bile salt hydrophobic outer shell faces the watery environment of the intestiines why the hydrophobic core encapsules the lipophilic drug allowing them to be transported
transport to the entercyte surface
micelles carry the lipophilic drug to the surface of the enterocytes, intestinal cells, where the drugs are released from the micelle and absorbed across the cell membrane
absorption of drugs into entercytes
once the drug is released from the micelle at the enterocyte surface it diffuses across the lipid membrane and is taken into the lymphatic system if blood stream