Lecture 17: Cardiac Glycosides & Antianginal Drugs
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
red dot slides only
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What are 5 compensatory mechanisms in CHF (congestive heart failure?
increased ventricular volume (Frank-starling compensation)
tachycardia (reflex adrenergic activity)
salt and water retention: renin-angiotensin mech
increased systemic vascular resistance
cardiac hypertrophy
congestive heart failure: heart muscle weakened and can’t pump blood effectively
compensatory mechanisms try to increase cardiac output
In heart failure, the contractility of the heart is __, and the cardiac function curve is __.
reduced; suppressed
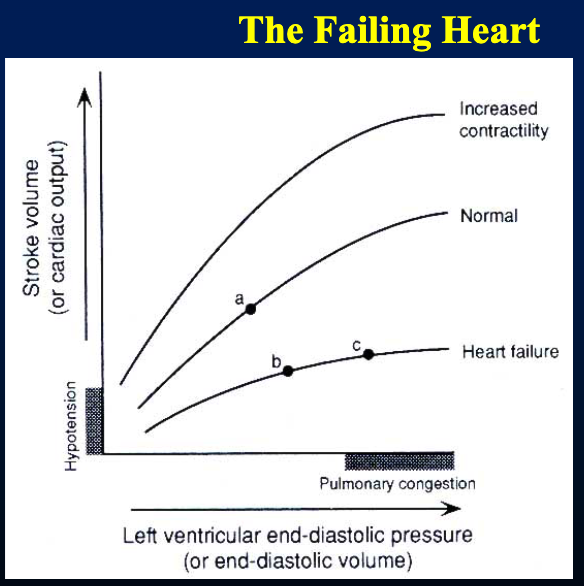
In the Frank-Sterling compensation, for any given state of the heart, if end diastolic volume increases, then force of contraction __.
increases
The Frank Sterling compensation increases the __ to increase cardiac output and overcome __ symptoms, but this can lead to __ symptoms.
EDV/preload; hypotensive; pulmonary congestion
hypotensive = reduced blood flow
pulmonary congestion bc during heart failure (when heart can’t efficiently pump the excess blood), blood gets backed up in pulmonary circulation and causes fluid to leak out of blood vessels into lung tissues
__ can be used to treat CHF.
cardiac glycosides
What are 5 characteristics of digoxin?
(therapeutic range, half life, bioavailability, excretion method, plasma protein binding)
therapeutic range: 0.5-2 ng/mL
half life: 1.5 days
variable bioavailability
excreted by kidney
25% plasma protein binding
What are 5 characteristics of digitoxin?
(therapeutic range, half life, bioavailability, excretion method, plasma protein binding)
therapeutic range: 10-35 ng/mL
half life: 7 days (very long)
consistent bioavailability
relies on hepatic metabolism for excretion
95% plasma protein binding
Cardiac glycosides __ increase isometric and isotonic indices (= plural index) of myocardial contractility, which result in: (4). This mode of action is a __ inotropic effect.
directly
decreased duration of systole
increased ventricular filling time
shortened ventricular ejection with more complete emptying
increased cardiac output
positive
explanation:
cardiac glycosides block Na/K pump, which increases Na concentration inside cell. this causes decreased Na/Ca exchanger function bc no concentration gradient for Na to come into cell —> increases Ca concentration in cell
increased cardiac output —> more complete emptying —> less preload
In normal hearts, __ cancel out the positive effects of digitalis (digitoxin and digoxin) on cardiac contractility.
reflex mechanisms
Cardiac glycosides have a __ effect on __ of vascular smooth muscle. In normal subjects, this results in increased __.
direct; constriction; systemic vascular resistance
Cardiac glycosides have a __ effect on electrical activity changes in the heart. This results in: (4)
direct
decreased resting potential or maximal diastolic potential
decreased action potential amplitude and conduction velocity
increased rate of phase-4 depolarization (faster depolarization)
appearance of delayed afterdeloparizations
Cardiac glycosides can __ enhance vagal impulse activity, which leads to: (2)
indirectly
reduction of SA node automaticity
increased refractoriness and decreased conduction at the AV node
Cardiac glycosides can __ sensitize baroreceptors, which leads to: (1)
indirectly; decreased blood pressure
The combination of direct and indirect effects in cardiac glycosides accounts for the __ effect of digitalis in CHF patients.
diuretic
What are 3 untoward effects of cardiac glycosides in terms of cardiac toxicity?
sinus bradycardia or block
AV block
ventricular extrasystoles (aka premature ventricular contractions: irregular heartbeats that originate in ventricles)
untoward = bad
What are 4 untoward GI effects as a result of cardiac glycosides?
anorexia
nausea
vomiting
diarrhea
What are 6 untoward neurological effects as a result of cardiac glycosides?
headache
fatigue
drowsiness
visual disturbances
neuralgic pain (usually involving lower third of face)
paresthesias (tingling, prickling, burning, numbness)
__ drugs are used to treat digitalis toxicity. In severe cases, a digoxin __ may be administered.
antiarrhythmic; antibody
What are 5 drug interactions with cardiac glycosides?
quinidine —> decreased renal clearance of digitalis (quinidine= antiarrhythmic drug)
sympathomimetic amines
anticholinergics
antibiotics —> decreased metabolism of ingested digoxin
corticosteroids, thiazides —> decreased serum [K+]
If a patient is on cardiac glycosides indicating they have CHF, what precautions should be taken in a dental setting? (4)
check vital signs
be sure pt is under adequate medical control
minimize stress and pain
determine if prophylactic antibiotics are needed
If a patient has low BP, HR and labored breathing while in a supine position, there may need to be __ of a dental procedure.
postponement
How does stable angina pectoris develop?
exercise, emotional stress, cold, meals, posture, smoking, drugs
catecholamine release —> inc venous return, inc ventricular size, inc ventricular pressure
increased myocardial oxygen demand
autoregulation: coronary artery dilatation
fixed blood flow from coronary sclerosis
VS coronary vasodilatation in a NORMAL response ›
inadequate oxygen supply
angina
angina pectoris = chest pain/discomfort bc of reduced blood flow to heart muscle
Hypoxia of coronary vasculature results in decreased __. Acid-sensing nociceptive sensory fibers in coronary vasculature convey this signal to spinal cord and brain, where it is perceived as __.
pH; pain
How do nitrates affect stable angina?
dec O2 demand by dilating veins, which decreases preload
How do nitrates affect variant angina?
inc O2 supply by relaxing coronary vasospasm
variant angina = caused by spasms in coronary arteries
An injected nitrate has __ effect, while a sublingual tablet provides __.
no; relief
How do beta blockers affect stable angina?
dec O2 demand by decreasing HR and contractility
How do beta blockers affect variant angina?
not used for variant angina bc they don’t affect vasospasm and bc unopposed alpha-adrenoceptor mediated vasoconstriction is detrimental, esp when nonselective beta blockers are used
How do Ca2+ channel blockers affect stable angina? (2)
Dec O2 demand by dilating arterioles, which decreases afterload (all calcium channel blockers do this)
dec HR and contractility (only in verapamil and diltiazem)
How do Ca2+ channel blockers affect variant angina?
inc O2 supply by relaxing coronary vasospasm
What are 4 untoward effects of organic nitrates?
headache (migraines for those migraine-prone)
orthostatic hypotension (w/ dizziness, flushing, and syncope)
tolerance
dependence
can also have alcohol/drug interactions
How do diltiazem, nifedipine, and verapamil (Ca channel blockers) affect coronary vasodilation?
diltiazem: +++
nifedipine: +++
verapamil: ++
How do diltiazem, nifedipine, and verapamil affect peripheral vasodilation?
diltiazem: +
nifedipine: +++
verapamil: ++
How do diltiazem, nifedipine, and verapamil affect contractility?
diltiazem: ←→ = no change
nifedipine: reflex tachycardia
verapamil: decreases a lot
How do diltiazem, nifedipine, and verapamil affect heart rate?
diltiazem: dec or ←→
nifedipine: reflex tachycardia
verapamil: dec
How do diltiazem, nifedipine, and verapamil affect AV nodal CV?
diltiazem: dec
nifedipine: ← →
verampil: dec a lot
Combination therapy allows delivery of lower __ of individual drugs with different mechanisms of action. In combination therapy for angina, some of these drugs preferentially affect __ at low concentrations, which allow for greater therapeutic effect and __ side effects.
dosages; vascular beds; minimized
In combination therapy, DHP (dihydropyridine) is often combined with __ or __.
beta blockers or organic nitrate
In combination therapy, beta blockers can be combined with (2)
DHP or organic nitrate
In combination therapy, organic nitrate can be combined with (2)
DHPs or beta blockers
If a patient on antianginal drugs is in a dental setting, what should the dentist take precaution of? (7)
medical history
stress
emergency meds
orthostatic hypotension
preop sedation
sympathomimetics
gingival hyperplasia