Quiz 4
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
1
New cards
**____, or pinkeye, results from damage to or irritation of the conjunctival surface.**
a. Fuch’s dystrophy
b. Conjunctivitis
c. Glaucoma
d. Myopia
e. Uveitis
a. Fuch’s dystrophy
b. Conjunctivitis
c. Glaucoma
d. Myopia
e. Uveitis
b. Conjunctivitis
2
New cards
**Light refraction takes place at the**
a. cornea and lens
b. lens only
c. optic disc
d. cornea and optic disc
e. cornea only
a. cornea and lens
b. lens only
c. optic disc
d. cornea and optic disc
e. cornea only
a. cornea and lens
3
New cards
**Which of the following is not true regarding image formation?**
a. the greatest amount of refraction occurs at the cornea
b. the focal distance must equal the distance between the center of the lens and the retina to form a sharp image
c. a round lens has a short focal distance
d. images arrive at the retina upside down and reversed
e. to view a distant object the lens will become rounder
a. the greatest amount of refraction occurs at the cornea
b. the focal distance must equal the distance between the center of the lens and the retina to form a sharp image
c. a round lens has a short focal distance
d. images arrive at the retina upside down and reversed
e. to view a distant object the lens will become rounder
e. to view a distant object the lens will become rounder
4
New cards
**The visible spectrum for humans extends between a wavelength of**
a. 700 and 1000 nm
b. 100 and 200 nm
c. 200 and 400 nm
d. 2000 and 2500 nm
e. 400 and 700 nm
a. 700 and 1000 nm
b. 100 and 200 nm
c. 200 and 400 nm
d. 2000 and 2500 nm
e. 400 and 700 nm
e. 400 and 700 nm
5
New cards
**In the human eye, most refraction occurs when light passes through the**
a. iris
b. cornea
c. lens
d. aqueous humor
e. vitreous humor
a. iris
b. cornea
c. lens
d. aqueous humor
e. vitreous humor
b. cornea
6
New cards
**The ciliary muscle contracts to**
a. control the amount of light reaching the retina
b. adjust the shape of the lens for distant vision
c. adjust the shape of the lens for near vision
d. control the production of aqueous humor
e. adjust the shape of the cornea
a. control the amount of light reaching the retina
b. adjust the shape of the lens for distant vision
c. adjust the shape of the lens for near vision
d. control the production of aqueous humor
e. adjust the shape of the cornea
c. adjust the shape of the lens for near vision
7
New cards
**During accommodation, the ciliary muscle ____ causing the ciliary body to move ____ and apply ____ tension on the lens**
a. relaxes; toward the lens; more
b. contracts; toward the lens; less
c. contracts; away from the lens; more
d. relaxes; inward; less
a. relaxes; toward the lens; more
b. contracts; toward the lens; less
c. contracts; away from the lens; more
d. relaxes; inward; less
b. contracts; toward the lens; less
8
New cards
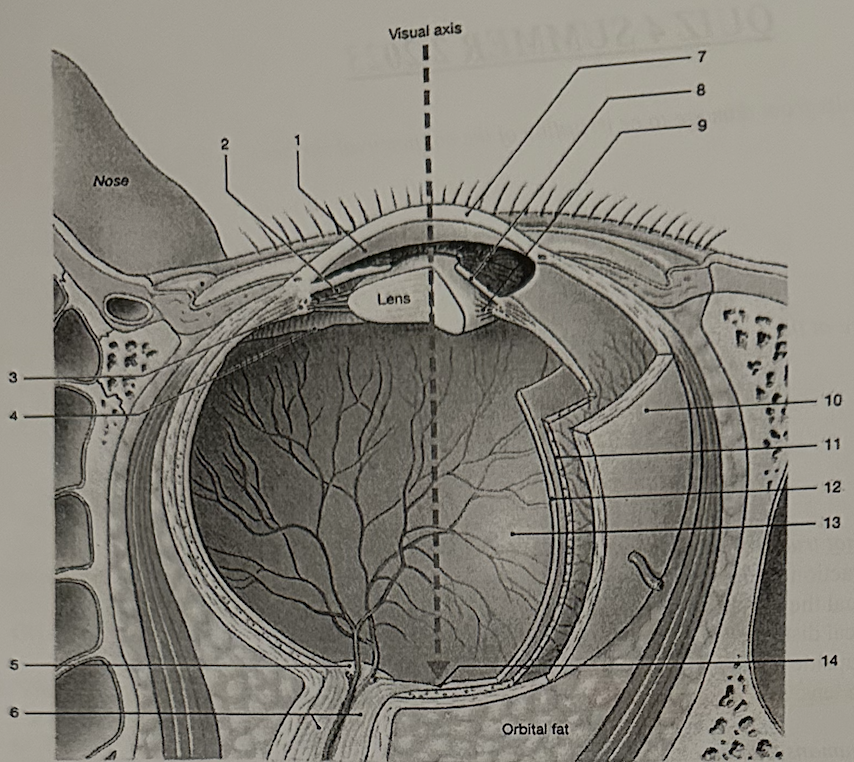
**Identify the space labeled “1.”**
a. posterior cavity
b. posterior chamber
c. pupil
d. anterior chamber
e. vitreous chamber
a. posterior cavity
b. posterior chamber
c. pupil
d. anterior chamber
e. vitreous chamber
d. anterior chamber
9
New cards
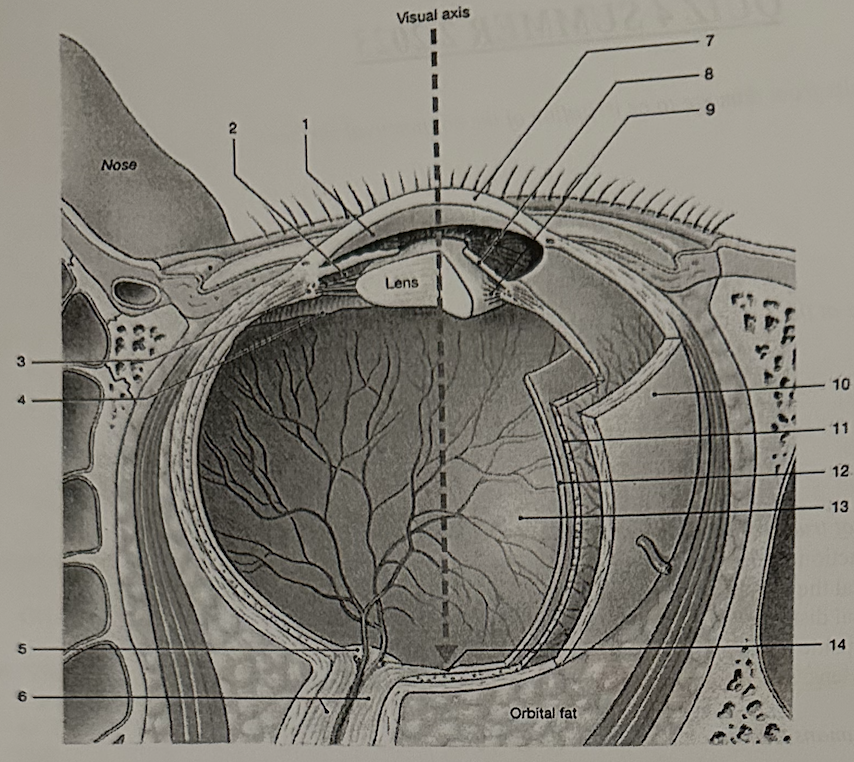
**Identify the structure labeled “7”**
a. choroid
b. optic disc
c. sclera
d. retina
e. cornea
a. choroid
b. optic disc
c. sclera
d. retina
e. cornea
e. cornea
10
New cards
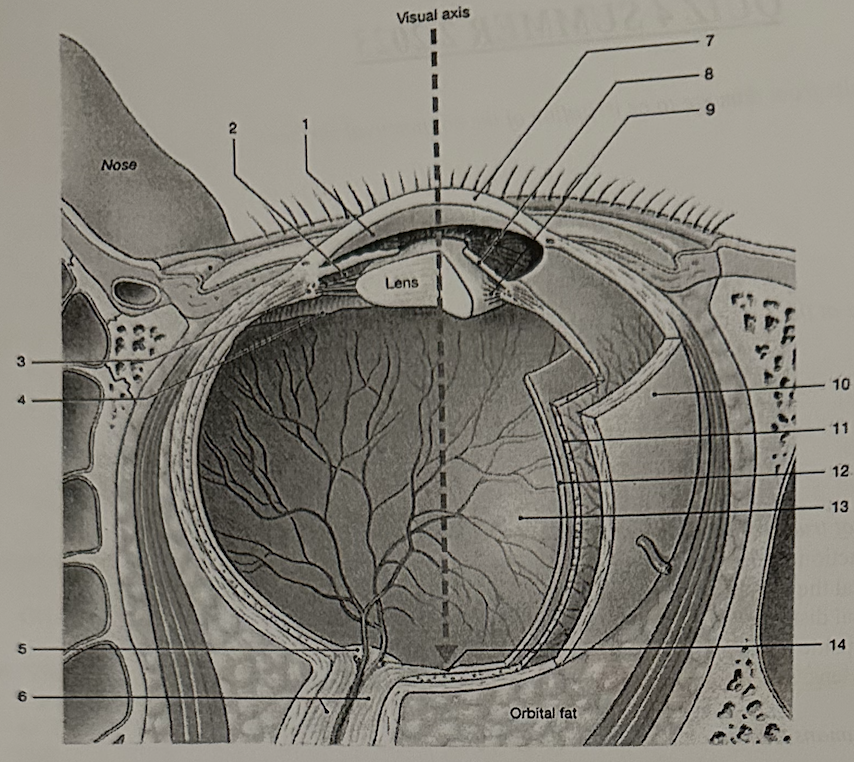
**Which structure is commonly called the blind spot?**
a. 4
b. 10
c. 14
d. 5
e. 6
a. 4
b. 10
c. 14
d. 5
e. 6
d. 5
11
New cards
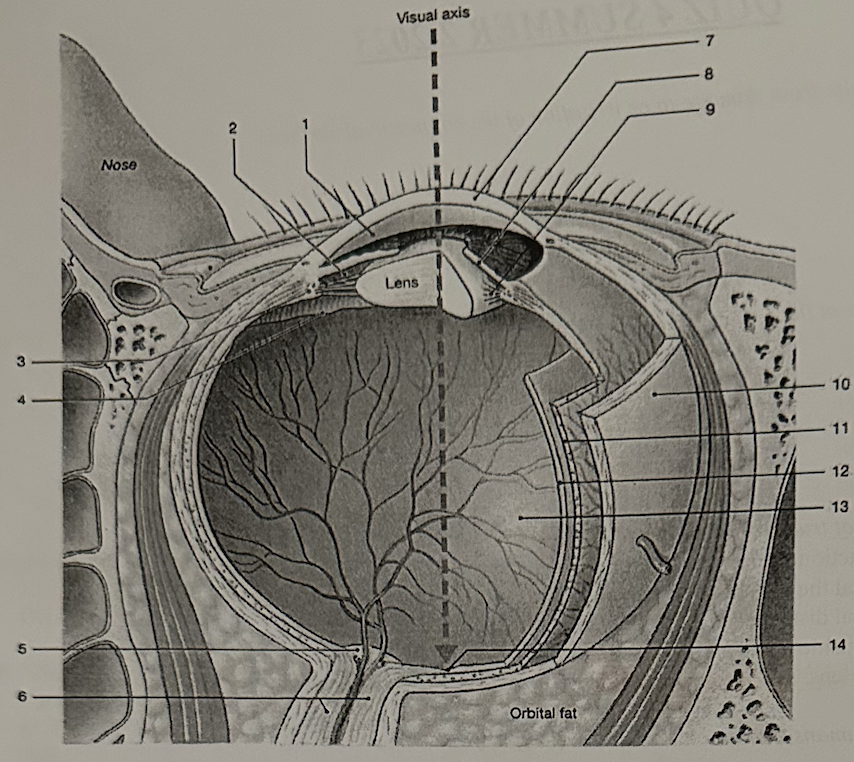
**Identify the structure labeled “12”**
a. pupil
b. optic disc
c. sclera
d. fovea
e. retina
a. pupil
b. optic disc
c. sclera
d. fovea
e. retina
e. retina
12
New cards
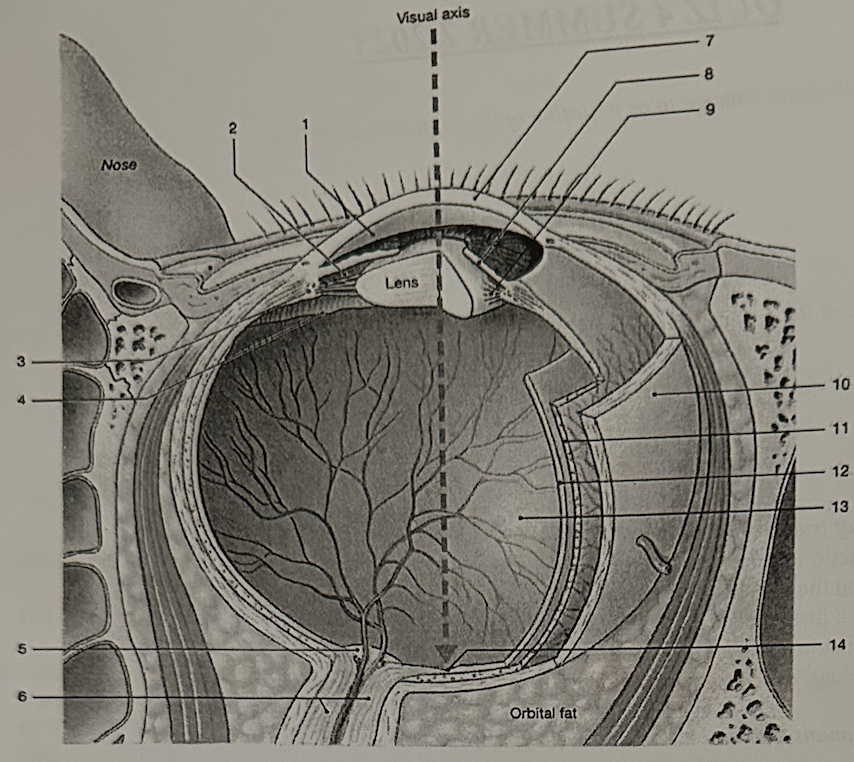
**Identify the structure labeled “14”**
a. pupil
b. optic disc
c. sclera
d. fovea
e. suspensory ligaments
a. pupil
b. optic disc
c. sclera
d. fovea
e. suspensory ligaments
d. fovea
13
New cards
**When you spin quickly, you may feel dizzy. Which component of the inner ear generates the sensations that can lead to this feeling?**
a. spiral organ
b. maculae
c. otoliths
d. semicircular canals
e. ossicles
a. spiral organ
b. maculae
c. otoliths
d. semicircular canals
e. ossicles
d. semicircular canals
14
New cards
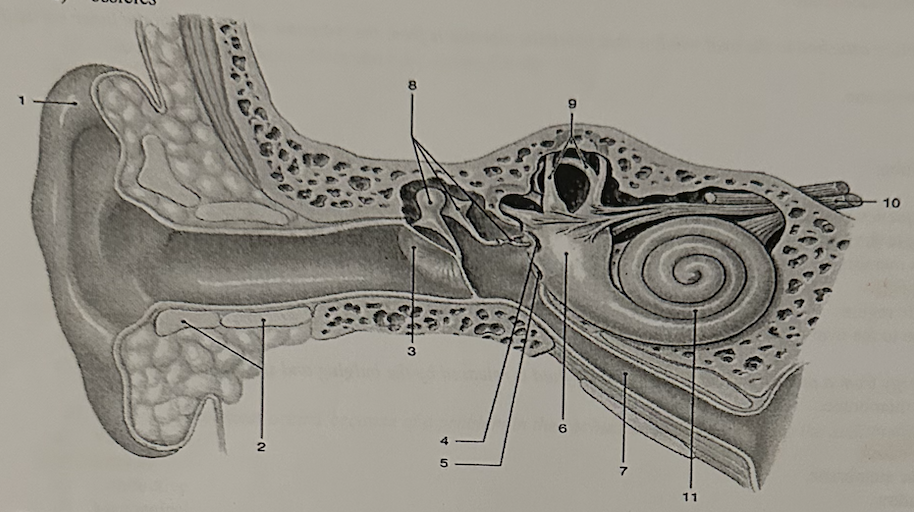
**Identify the structures labeled “8”**
a. cochlea
b. auditory ossicles
c. auricle
d. tympanic membrane
e. vestibule
a. cochlea
b. auditory ossicles
c. auricle
d. tympanic membrane
e. vestibule
b. auditory ossicles
15
New cards
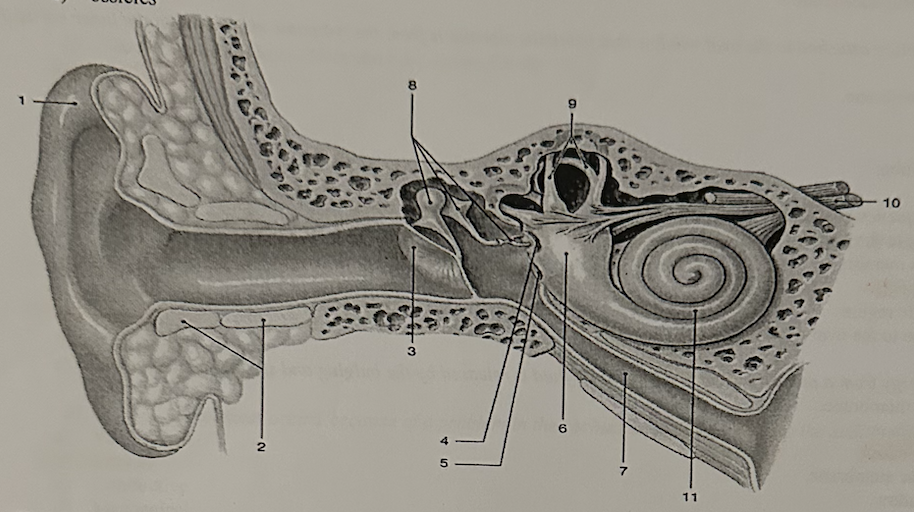
**Which structure contains the receptors for hearing?**
a. 6
b. 8
c. 9
d. 10
e. 11
a. 6
b. 8
c. 9
d. 10
e. 11
11
16
New cards
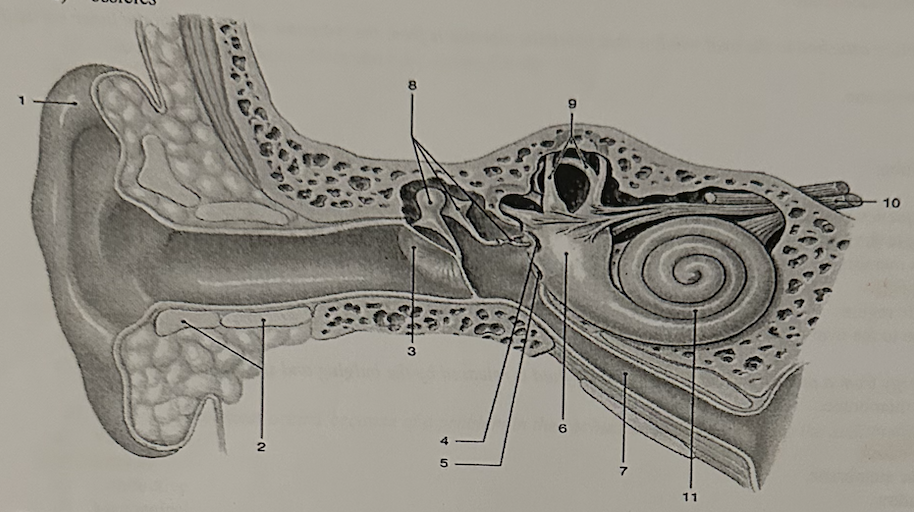
**Which structure is known as the vestibule?**
a. 6
b. 8
c. 9
d.10
e. 11
a. 6
b. 8
c. 9
d.10
e. 11
e. 11
17
New cards
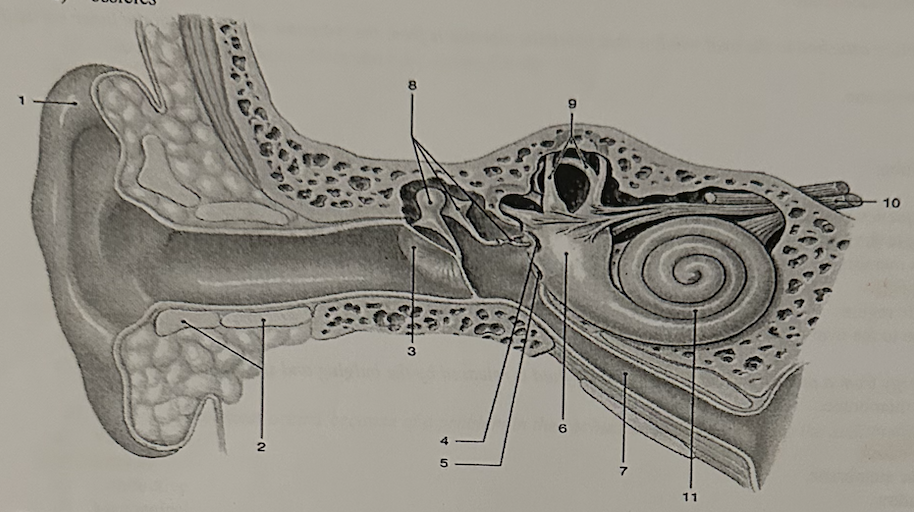
**Identify the structure that is called the pinna or auricle**
a. 1
b. 5
c. 6
d. 8
e. 9
a. 1
b. 5
c. 6
d. 8
e. 9
a. 1
18
New cards
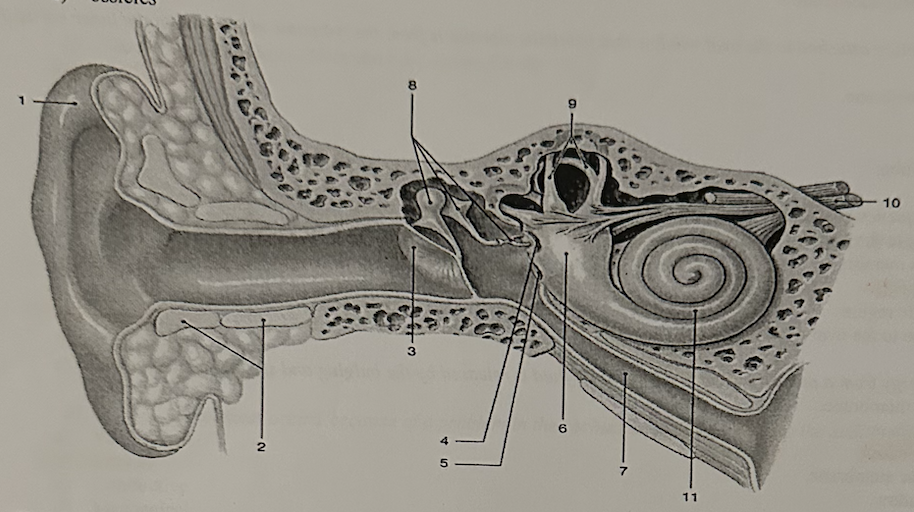
**Identify the structure labeled “3”**
a. cochlea
b. semicircular canals
c. auricle
d. tympanic membrane
e. vestibule
a. cochlea
b. semicircular canals
c. auricle
d. tympanic membrane
e. vestibule
d. tympanic membrane
19
New cards
**Movement of the endolymph in the semicircular canals**
a. produces a rushing sound
b. allows us to hear low tunes
c. signals rotational movements
d. signals body position with respect to gravity
e. signals linear acceleration
a. produces a rushing sound
b. allows us to hear low tunes
c. signals rotational movements
d. signals body position with respect to gravity
e. signals linear acceleration
c. signals rotational movements
20
New cards
**The structure attached to the oval window that transmits vibrations from the tympanic membrane to the inner ear is the**
a. malleus
b. basilar membrane
c. incus
d. stapes
e. auditory tube
a. malleus
b. basilar membrane
c. incus
d. stapes
e. auditory tube
d. stapes
21
New cards
**Low frequency sounds stimulate hair cells on which part of the basilar membrane?**
a. area close to the round window
b. the entire membrane
c. the distal end
d. the middle region
e. area close to the oval window
a. area close to the round window
b. the entire membrane
c. the distal end
d. the middle region
e. area close to the oval window
c. the distal end
22
New cards
**The energy from a pressure wave in the cochlear fluid is released by the bulging and stretching of the**
a. tectorial membrane
b. cochlear duct
c. round window
d. vestibular membrane
e. oval window
a. tectorial membrane
b. cochlear duct
c. round window
d. vestibular membrane
e. oval window
c. round window
23
New cards
**The function of the auditory tube is to**
a. help maintain equilibrium
b. amplify sounds
c. equalize air pressure on both sides of the tympanic membrane
d. redistribute endolymph after hearing a sound
e. provide a passageway for sound waves to enter the ear
a. help maintain equilibrium
b. amplify sounds
c. equalize air pressure on both sides of the tympanic membrane
d. redistribute endolymph after hearing a sound
e. provide a passageway for sound waves to enter the ear
c. equalize air pressure on both sides of the tympanic membrane
24
New cards
**The cell bodies of sensory neurons that innervate the hair cells of the cochlea form the ____ ganglion**
a. vestibular
b. spiral
c. cochlear
d. acoustic
e. auditory
a. vestibular
b. spiral
c. cochlear
d. acoustic
e. auditory
b. spiral
25
New cards
**Which of the following descriptions best matches the term stereocilia?**
a. move up and down when the stapes move back and forth
b. transmit movement of the tympanic membrane to the inner ear
c. bending these produces receptor potential in hair cells
d. tiny wights necessary for the static sense of equilibrium
a. move up and down when the stapes move back and forth
b. transmit movement of the tympanic membrane to the inner ear
c. bending these produces receptor potential in hair cells
d. tiny wights necessary for the static sense of equilibrium
c. bending these produces receptor potential in hair cells
26
New cards
**____ fills the membranous labyrinth**
a. perilymph
b. CSF
c. interstitial fluid
d. endolymph
e. blood
a. perilymph
b. CSF
c. interstitial fluid
d. endolymph
e. blood
d. endolymph
27
New cards
**The ____ is a region of dense bone that surrounds and protects the membranous labyrinth**
a. sella turcica
b. ossicle
c. auditory canal
d. membranous labyrinth
e. bony labyrinth
a. sella turcica
b. ossicle
c. auditory canal
d. membranous labyrinth
e. bony labyrinth
e. bony labyrinth
28
New cards
**____ is a fluid similar to cerebrospinal fluid that fills the space between the bony labyrinth and the membraneous labyrinth**
a. perilymph
b. endoplasma
c. interstitial fluid
d. endolymph
e. blood
a. perilymph
b. endoplasma
c. interstitial fluid
d. endolymph
e. blood
a. perilymph
29
New cards
**The hair cells of the cochlear duct are located in the**
a. spinal organ
b. ossicles
c. ampullary crest
d. utricle
e. saccule
a. spinal organ
b. ossicles
c. ampullary crest
d. utricle
e. saccule
a. spiral organ
30
New cards
**____ deafness results from conditions in the outer or middle ear the block the transfer of vibrations from the environment to the oval window**
a. sensory
b. nerve
c. conductive
d. mechanical
e. macular
a. sensory
b. nerve
c. conductive
d. mechanical
e. macular
c. conductive
31
New cards
**____ deafness occurs because of a problem in the cochlea or somewhere along the auditory pathway**
a. vibrational
b. nerve
c. conductive
d. mechanical
e. macular
a. vibrational
b. nerve
c. conductive
d. mechanical
e. macular
b. nerve
32
New cards
**Abnormal jumpy eye movements that may appear after brain stem or inner ear damage are called**
a. tinnitus
b. vertigo
c.strabismus
d. nystagmus
e. trismus
a. tinnitus
b. vertigo
c.strabismus
d. nystagmus
e. trismus
d. nystagmus
33
New cards
**____ sensations inform us of the position of the head in space by monitoring gravity, linear acceleration, and rotation**
a. nociceptor
b. proprioceptor
c. olfactory
d. gustatory
e. vestibular
a. nociceptor
b. proprioceptor
c. olfactory
d. gustatory
e. vestibular
e. vestibular
34
New cards
**When you spin quickly, you may feel dizzy. Which component of the inner ear generates the sensations that can lead to this feeling?**
a. spiral organ
b. maculae
c. otoliths
d. semicircular canals
e. ossicles
a. spiral organ
b. maculae
c. otoliths
d. semicircular canals
e. ossicles
d. semicircular canals
35
New cards
**Light refraction takes place at the**
a. cornea and lens
b. lens only
c. optic disc
d. cornea and optic disc
e. cornea only
a. cornea and lens
b. lens only
c. optic disc
d. cornea and optic disc
e. cornea only
a. cornea and lens
36
New cards
**Which of the following is not true regarding image formation?**
a. the greatest amount of refraction occurs at the cornea
b. the focal distance must equal the distance between the center of the lens and the retina to form a sharp image
c. a round lens has a short focal distance
d. images arrive at the retina upside down and reversed
e. to view a distant object the lens will become rounder
a. the greatest amount of refraction occurs at the cornea
b. the focal distance must equal the distance between the center of the lens and the retina to form a sharp image
c. a round lens has a short focal distance
d. images arrive at the retina upside down and reversed
e. to view a distant object the lens will become rounder
e. to view a distant object the lens will become rounder
37
New cards
**The visible spectrum for humans extends between a wavelength of**
a. 700 and 1000 nm
b. 100 and 200 nm
c. 200 and 400 nm
d. 2000 and 2500 nm
e. 400 and 700 nm
a. 700 and 1000 nm
b. 100 and 200 nm
c. 200 and 400 nm
d. 2000 and 2500 nm
e. 400 and 700 nm
400 and 700 nm
38
New cards
**In the human eye, most refraction occurs when light passes through the**
a. iris
b. cornea
c. lens
d. aqueous humor
e. vitreous humor
a. iris
b. cornea
c. lens
d. aqueous humor
e. vitreous humor
b. cornea
39
New cards
**The ciliary muscle contracts to**
a. control the amount of light reaching the retina
b. adjust the shape of the lens for distant vision
c. adjust the shape of the lens for near vision
d. control the production of aqueous humor
e. adjust the shape of the cornea
a. control the amount of light reaching the retina
b. adjust the shape of the lens for distant vision
c. adjust the shape of the lens for near vision
d. control the production of aqueous humor
e. adjust the shape of the cornea
c. adjust the shape of the lens for near vision
40
New cards
**During accommodation, the ciliary muscle ____ causing the ciliary body to move ____** ***and apply*** **____ tension on the lens**
a. relaxes; toward the lens; more
b. contracts; toward the lens; less
c. contracts; away from the lens; more
d. relaxes; inward; less
a. relaxes; toward the lens; more
b. contracts; toward the lens; less
c. contracts; away from the lens; more
d. relaxes; inward; less
contracts; toward the lens; less
41
New cards
**When light encounters a medium of different density, it is**
a. refracted
b. diffracted
c. reflected
d. angled
e. absorbed
a. refracted
b. diffracted
c. reflected
d. angled
e. absorbed
a. refracted
42
New cards
**An irregularity in curvature in the cornea or lens, called ____, causes a reduction in visual acuity**
a. astigmatism
b. glaucoma
c. a cataract
d. macular degeneration
e. corneal atrophy
a. astigmatism
b. glaucoma
c. a cataract
d. macular degeneration
e. corneal atrophy
a. astigmatism
43
New cards
**A person suffering from ____ can see objects that are close, but distant objects appear blurred**
a. myopia
b. hyperopia
c. emmetropia
d. presbyopia
e. diplopia
a. myopia
b. hyperopia
c. emmetropia
d. presbyopia
e. diplopia
a. myopia
44
New cards
**A person suffering from ____ can see distant objects more clearly than those that are close**
a. myopia
b. hyperopia
c. emmetropia
d. presbyopia
e. diplopia
a. myopia
b. hyperopia
c. emmetropia
d. presbyopia
e. diplopia
b. hyperopia
45
New cards
**Which of the following best describes the function of the iris?**
a. controls amount of light entering eye
b. gives the eye its color
c. refracts light through the pupil
d. adjusts the shape of the lens
a. controls amount of light entering eye
b. gives the eye its color
c. refracts light through the pupil
d. adjusts the shape of the lens
a. controls amount of light entering eye
46
New cards
Which of the following is the best explanation for our perception of color?
a. rods contain a single kind of visual pigment
b. cones come in three types, each sensitive to different wavelength of light
c. the foveae are densely packed with cones
d. as many as 100 cones may converge on one ganglion cell
a. rods contain a single kind of visual pigment
b. cones come in three types, each sensitive to different wavelength of light
c. the foveae are densely packed with cones
d. as many as 100 cones may converge on one ganglion cell
b. cones come in three types, each sensitive to different wavelength of light
47
New cards
**The elasticity of the lens decreases with age. This leads to which of the following?**
a. a clouding of the lenses known as a cataract
b. less accommodation of the lenses and difficulty focusing on nearby objects
c. less light getting to the retina and diminished visual acuity
d. lowered accommodation of the pupillary reflex and blurry vision
a. a clouding of the lenses known as a cataract
b. less accommodation of the lenses and difficulty focusing on nearby objects
c. less light getting to the retina and diminished visual acuity
d. lowered accommodation of the pupillary reflex and blurry vision
b. less accommodation of the lenses and difficulty focusing on nearby objects
48
New cards
**Paralysis of which eye muscle would prevent the right eye from looking to the left?**
a. lateral rectus
b. superior rectus
c. medial rectus
d. inferior rectus
a. lateral rectus
b. superior rectus
c. medial rectus
d. inferior rectus
c. medial rectus
49
New cards
**Overlap in the visual field of our eyes ____**
a. allows us to subconsciously estimate the distance of objects based on the different angels the image strikes our two retinas
b. gives us higher visual acuity for small detail by doubling the number of photoreceptors that are being stimulated
c. is essentially a waste of brain processing for what is essentially the same image
d. leaves a blind spot anterior to the nose and in the lateral fields of vision
a. allows us to subconsciously estimate the distance of objects based on the different angels the image strikes our two retinas
b. gives us higher visual acuity for small detail by doubling the number of photoreceptors that are being stimulated
c. is essentially a waste of brain processing for what is essentially the same image
d. leaves a blind spot anterior to the nose and in the lateral fields of vision
a. allows us to subconsciously estimate the distance of objects based on the different angels the image strikes our two retinas
50
New cards
**If you shine a light into one eye both pupils will constrict. The best explanation for this is ____**
a. sensory input from the retinas of both eyes converges at the optic chiasm and information from each eye is delivered to both the left and right sides of the brain
b. a small portion of light always enters the other eye
c. information from one eye is directly and immediately transferred to the other eye to maintain alignment of the eyes
d. this, in fact, does not occur; information from both eyes is always separated
a. sensory input from the retinas of both eyes converges at the optic chiasm and information from each eye is delivered to both the left and right sides of the brain
b. a small portion of light always enters the other eye
c. information from one eye is directly and immediately transferred to the other eye to maintain alignment of the eyes
d. this, in fact, does not occur; information from both eyes is always separated
a. sensory input from the retinas of both eyes converges at the optic chiasm and information from each eye is delivered to both the left and right sides of the brain
51
New cards
**Humans can see several thousand shades of color but have cone photoreceptors that are sensitive to only three (perhaps four) wavelengths of light. What is the best explanation for why we see so many colors?**
a. color perception is dependent on the millions of rods as well as cone photoreceptors
b. color perception is achieved of various combinations between the three cone types
c. colors are added and enhanced in the primary visual cortex of the brain
d. shades of color are purely psychological and learned by association with age, infants only seeing in black and white
a. color perception is dependent on the millions of rods as well as cone photoreceptors
b. color perception is achieved of various combinations between the three cone types
c. colors are added and enhanced in the primary visual cortex of the brain
d. shades of color are purely psychological and learned by association with age, infants only seeing in black and white
b. color perception is achieved of various combinations between the three cone types
52
New cards
**Color vision has much greater resolution that night vision (vision that mostly in shades of gray). Which of the following is the best explanation for why this is so?**
a. a single cone photoreceptor often connects to a single bipolar cell and a single ganglion cell while as many as 100 rods will converge to a single ganglion cell
b. a larger proportion of the brains visual cortex is active during the day when our cone photoreceptors are most active
c. there are many more cone photoreceptors in the eye than rod photoreceptors
d. there are several types of cone photoreceptors, each of which enrich the clarity and resolution of vision
a. a single cone photoreceptor often connects to a single bipolar cell and a single ganglion cell while as many as 100 rods will converge to a single ganglion cell
b. a larger proportion of the brains visual cortex is active during the day when our cone photoreceptors are most active
c. there are many more cone photoreceptors in the eye than rod photoreceptors
d. there are several types of cone photoreceptors, each of which enrich the clarity and resolution of vision
a. a single cone photoreceptor often connects to a single bipolar cell and a single ganglion cell while as many as 100 rods will converge to a single ganglion cell
53
New cards
**As light travels through the eye, it passes through several structures of chambers before reaching the retina. Which list below gives those structures in the correct order?**
a. cornea, lens, pupil, anterior chamber, posterior segment
b. cornea, pupil, anterior chamber, lens, posterior segment
c. cornea, pupil, lens, anterior chamber, posterior segment
d. cornea, anterior chamber, pupil, lens, posterior sengment
a. cornea, lens, pupil, anterior chamber, posterior segment
b. cornea, pupil, anterior chamber, lens, posterior segment
c. cornea, pupil, lens, anterior chamber, posterior segment
d. cornea, anterior chamber, pupil, lens, posterior sengment
d. cornea, anterior chamber, pupil, lens, posterior sengment
54
New cards
**Toms is a 45 year old male that has lost his ability to hear high frequency sounds. The most likely explanation for this would be ____**
a. a perforated tympanic membrane
b. a middle ear infection
c. damage to the hair cells near the oval window in the cochlear duct
d. an overgrowth of bony tissue, fusing the ossicles together
a. a perforated tympanic membrane
b. a middle ear infection
c. damage to the hair cells near the oval window in the cochlear duct
d. an overgrowth of bony tissue, fusing the ossicles together
c. damage to the hair cells near the oval window in the cochlear duct
55
New cards
**What is the main function of the roads in the eye?**
a. depth perception
b. color vision
c. vision in dim light
d. accommodation for near vision
a. depth perception
b. color vision
c. vision in dim light
d. accommodation for near vision
c. vision in dim ligt
56
New cards
**What structure regulates the amount of light passing to the visual receptors of the eye?**
a. aqueous humor
b. lens
c. cornea
d. iris
a. aqueous humor
b. lens
c. cornea
d. iris
d. iris
57
New cards
**Receptors for hearing are located in the ____**
a. cochlea
b. semicircular canals
c. tympanic membrane
d. vestibule
a. cochlea
b. semicircular canals
c. tympanic membrane
d. vestibule
a. cochlea
58
New cards
**Which of the following types of neurons are replaced throughout adult life?**
a. olfactory receptor cells
b. retinal bipolar cells
c. retinal ganglion cells
d. auditory outer and inner hair cells
a. olfactory receptor cells
b. retinal bipolar cells
c. retinal ganglion cells
d. auditory outer and inner hair cells
a. olfactory receptor cells
59
New cards
**Bitter taste is elicited by ____**
a. hydrogen ions
b. alkaloids
c. acids
d. metal ions
a. hydrogen ions
b. alkaloids
c. acids
d. metal ions
b. alkaloids
60
New cards
**The ability to clearly see objects at a distance but not close up is properly called____**
a. myopia
b. hypopia
c. hyperopia
d. presbyopia
a. myopia
b. hypopia
c. hyperopia
d. presbyopia
c. hyperopia
61
New cards
Nerve fibers from the medial aspect of each eye ____
a. go to the superior colliculus only
b. pass posteriorly without crossing over at the chiasma
c. divide at the chiasma, with some crossing and some not crossing
d. cross over to the opposite side at the chiasma
a. go to the superior colliculus only
b. pass posteriorly without crossing over at the chiasma
c. divide at the chiasma, with some crossing and some not crossing
d. cross over to the opposite side at the chiasma
d. cross over to the opposite side at the chiasma
62
New cards
**Ordinarily, it is NOT possible to transplant tissues from one person to another, yet corneas can be transplanted without tissue rejection. This is because the cornea ____**
a. is not a living tissue
b. has no nerve supply
c. has no blood supply
d. does not contain connective tissue
a. is not a living tissue
b. has no nerve supply
c. has no blood supply
d. does not contain connective tissue
c. has no blood supply
63
New cards
**The oval window is connected directly to which passageway?**
a. scala vestibuli
b. external acoustic meatus
c. pharyngotympanic tube
d. scala tympani
a. scala vestibuli
b. external acoustic meatus
c. pharyngotympanic tube
d. scala tympani
a. scala vestibuli
64
New cards
**As sound levels increase in the spiral organ (of Corti), ____**
a. outer hair cells stiffen the basilar membrane
b. outer hair cells bend the cilia away from the kinocilium
c. inner hair cells stiffen the basilar membrane
d. inner hair cells bend the cilia away from the kinocilium
a. outer hair cells stiffen the basilar membrane
b. outer hair cells bend the cilia away from the kinocilium
c. inner hair cells stiffen the basilar membrane
d. inner hair cells bend the cilia away from the kinocilium
a. outer hair cells stiffen the basilar membrane
65
New cards
**Taste buds are NOT found ____**
a. in fungiform papillae
b. in filiform papillae
c. in circumvallate papillae
d. lining the buccal cavity
a. in fungiform papillae
b. in filiform papillae
c. in circumvallate papillae
d. lining the buccal cavity
b. in filiform papillae
66
New cards
**Which of the following describes a response of the eye to sympathetic stimulation?**
a. pupil dilation
b. pupil constriction
c. ciliary muscle contraction
d. ciliary muscle relaxation
a. pupil dilation
b. pupil constriction
c. ciliary muscle contraction
d. ciliary muscle relaxation
a. pupil dilation
67
New cards
**Which of the following taste sensations is incorrectly matched to the chemicals that produce it?**
a. sweet-organic substances such as sugar and some lead salts
b. sour-acids
c. salty-metal ions
d. bitter-alkaloids
e. umami-triglycerides and fatty acids
a. sweet-organic substances such as sugar and some lead salts
b. sour-acids
c. salty-metal ions
d. bitter-alkaloids
e. umami-triglycerides and fatty acids
e. umami-triglycerides and fatty acids
68
New cards
**Conscious perception of vision probably reflects activity in the ____**
a. thalamus
b. occipital lobe of the cortex
c. chiasma
d. superior colliculus
a. thalamus
b. occipital lobe of the cortex
c. chiasma
d. superior colliculus
b. occipital lobe of the cortex
69
New cards
**In the visual pathways to the brain, the optic radiations project to the ____**
a. medial retina
b. lateral geniculate body
c. primary visual cortex
d. optic chiasma
a. medial retina
b. lateral geniculate body
c. primary visual cortex
d. optic chiasma
c. primary visual cortex
70
New cards
**Which of the following types of receptors are located in the mouth?**
a. chemoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, thermreceptors, and nociceptors
b. chemoreceptors only
c. chemoreceptors, thermreceptors, and nociceptors only
d. thermreceptors, mechanoreceptors, and nociceptors only
a. chemoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, thermreceptors, and nociceptors
b. chemoreceptors only
c. chemoreceptors, thermreceptors, and nociceptors only
d. thermreceptors, mechanoreceptors, and nociceptors only
a. chemoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, thermreceptors, and nociceptors
71
New cards
**Motion sickness seems to ____**
a. respond best to medication taken after salivation and pallor begins
b. respond best to medication that “boosts” vestibular inputs
c. result from activation of nausea center in the brain stem
d. result from mismatch between visual and vestibular input
a. respond best to medication taken after salivation and pallor begins
b. respond best to medication that “boosts” vestibular inputs
c. result from activation of nausea center in the brain stem
d. result from mismatch between visual and vestibular input
d. result from mismatch between visual and vestibular input
72
New cards
**Most newborns____**
a. are myopic
b. often use only one eye at a time
c. see in tones of red and green only
d. produce more tears when they cry than a toddler
a. are myopic
b. often use only one eye at a time
c. see in tones of red and green only
d. produce more tears when they cry than a toddler
b. often use only one eye at a time
73
New cards
**The blind spot of the eye is caused by ____**
a. more rods than cones within the retina
b. the macula lutea interrupts the nerve pathway
c. an absence of cones in the foveae
d. an absence of photoreceptors where the optic nerve leaves the eye
a. more rods than cones within the retina
b. the macula lutea interrupts the nerve pathway
c. an absence of cones in the foveae
d. an absence of photoreceptors where the optic nerve leaves the eye
d. an absence of photoreceptors where the optic nerve leaves the eye
74
New cards
**Endocrine cells**
a. are a type of nerve cell
b. release their secretions onto epithelial surface
c. release their secretions directly into body fluids
d. contain very few vesicles
e. are modified connective-tissue cells
a. are a type of nerve cell
b. release their secretions onto epithelial surface
c. release their secretions directly into body fluids
d. contain very few vesicles
e. are modified connective-tissue cells
c. release their secretions directly into body fluids
75
New cards
**Peptide hormones are**
a. composed by amino acids
b. produced by cells in the adrenal glands
c. derived from the amino acid tyrosine
d. lipids.3.
e. chemically related to cholesterol
a. composed by amino acids
b. produced by cells in the adrenal glands
c. derived from the amino acid tyrosine
d. lipids.3.
e. chemically related to cholesterol
a. composed by amino acids
76
New cards
**All of the following are true of steroid hormones, except that they**
a. are produced by the adrenal medulla
b. are structurally similar to cholesterol
c. are produced by reproductive glands
d. bind to receptors within the cell
e. are lipids
a. are produced by the adrenal medulla
b. are structurally similar to cholesterol
c. are produced by reproductive glands
d. bind to receptors within the cell
e. are lipids
a. are produced by the adrenal medulla
77
New cards
**Each of the following hormones is an amino acid derivative, except**
a. epinephrine
b. norepinephrine
c. thyroid hormone
d. thyroid-stimulating hormone
e. melatonin
a. epinephrine
b. norepinephrine
c. thyroid hormone
d. thyroid-stimulating hormone
e. melatonin
d. thyroid-stimulating hormone
78
New cards
**Which of the following statements concerning peptide hormones is false?**
a. peptide hormones are first synthesized as prohormones
b. prohormones can be activated before or after their release
c. peptide hormones remain in circulation for relatively short periods of time
d. peptide hormones are always found in the bloodstream bound to carrier proteins
e. peptide hormones interact with receptors on the surface of their target cells
a. peptide hormones are first synthesized as prohormones
b. prohormones can be activated before or after their release
c. peptide hormones remain in circulation for relatively short periods of time
d. peptide hormones are always found in the bloodstream bound to carrier proteins
e. peptide hormones interact with receptors on the surface of their target cells
d. peptide hormones are always found in the bloodstream bound to carrier proteins
79
New cards
**Steroid hormones**
a. are proteins
b. cannot diffuse through cell membranes
c. bind to receptors in the nucleus of their target cells
d. remain in circulation for relatively short periods of time
e. are transported in the blood dissolved in the plasma
a. are proteins
b. cannot diffuse through cell membranes
c. bind to receptors in the nucleus of their target cells
d. remain in circulation for relatively short periods of time
e. are transported in the blood dissolved in the plasma
c. bind to receptors in the nucleus of their target cells
80
New cards
**The link between a first messenger and a second messenger in a cell that responds to peptide hormones is usually**
a. cAMP
b. cGMP
c. adenyl cyclase
d. G protein
e. calcium
a. cAMP
b. cGMP
c. adenyl cyclase
d. G protein
e. calcium
d. G protein
81
New cards
**When adenyl cyclase is activated,**
a. calcium ions are released from intracellular stores
b. cAMP is formed
c. cAMP is broken down
d. protein kinases are metabolized
e. steroids are produced
a. calcium ions are released from intracellular stores
b. cAMP is formed
c. cAMP is broken down
d. protein kinases are metabolized
e. steroids are produced
b. cAMP is formed
82
New cards
**The most complex endocrine responses involve the**
a. thyroid gland
b. pancreas
c. adrenal glands
d. hypothalamus
e. thymus gland
a. thyroid gland
b. pancreas
c. adrenal glands
d. hypothalamus
e. thymus gland
d. hypothalamus
83
New cards
**Coordinating centers in the hypothalamus regulate the activities of the nervous and endocrine system by all of the following, except**
a. autonomic neurons that directly control the endocrine cells of the adrenal medulla
b. acting as an endocrine organ itself and releasing hormones
c. a modified positive feedback loop involving the pars intermedia of the pituitary gland
d. secreting inhibiting hormones that inhibit the production and release of hormones rom the anterior pituitary gland
e. secreting releasing hormones that stimulate the production and release of hormones from the anterior pituitary gland
a. autonomic neurons that directly control the endocrine cells of the adrenal medulla
b. acting as an endocrine organ itself and releasing hormones
c. a modified positive feedback loop involving the pars intermedia of the pituitary gland
d. secreting inhibiting hormones that inhibit the production and release of hormones rom the anterior pituitary gland
e. secreting releasing hormones that stimulate the production and release of hormones from the anterior pituitary gland
c. a modified positive feedback loop involving the pars intermedia of the pituitary gland
84
New cards
**Changes in blood osmotic pressure would affect the levels of ____ in the blood**
a. ACTH
b. ADH
c. oxytocin
d. TSH
e. LH
a. ACTH
b. ADH
c. oxytocin
d. TSH
e. LH
b. ADH
85
New cards
**The hypothalamus controls secretions of the anterior pituitary by way of**
a. direct neural stimulation
b. direct mechanical control
c. releasing and inhibiting hormones
d. altering ion concentrations in the anterior pituitary
e. gap junctions
a. direct neural stimulation
b. direct mechanical control
c. releasing and inhibiting hormones
d. altering ion concentrations in the anterior pituitary
e. gap junctions
c. releasing and inhibiting hormones
86
New cards
**Neurons of the supraoptic nuclei of the hypothamalmus manufacture**
a. FSH
b. TSH
c. ADH
d. oxytocin
e. growth hormone
a. FSH
b. TSH
c. ADH
d. oxytocin
e. growth hormone
d. oxytocin
87
New cards
Neurons of the paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus manufacture
a. FSH
b. TSH
c. ADH
d. oxytocin
e. GH
a. FSH
b. TSH
c. ADH
d. oxytocin
e. GH
d. oxytocin
88
New cards
**The posterior pituitary gland secrets**
a. FSH
b. TSH
c. ACTH
d. ADH
e. MSH
a. FSH
b. TSH
c. ACTH
d. ADH
e. MSH
d. ADH
89
New cards
**The hormone produced by the pars intermedia of the adenohypophysis is**
a. FSH
b. ADH
c. TSH
d. MSH
e. ACTH
a. FSH
b. ADH
c. TSH
d. MSH
e. ACTH
d. MSH
90
New cards
**Each of the following hormones is produced by the paras distalis of the adenohupophysis, except**
a. FSH
b. ADH
c. TSH
d. ACTH
e. GH
a. FSH
b. ADH
c. TSH
d. ACTH
e. GH
b. ADH
91
New cards
**The hormone oxytocin**
a. promotes uterine contractions
*b*. is responsible for milk production in the mammary glands
c. regulates blood pressure
d. governs the ovarian cycle
e. governs the levels of tissue androgens
a. promotes uterine contractions
*b*. is responsible for milk production in the mammary glands
c. regulates blood pressure
d. governs the ovarian cycle
e. governs the levels of tissue androgens
a. promotes uterine contractions
92
New cards
**Growth hormone does all of the following, except that is**
a. promotes bone growth
b. promotes muscle growth
c. promotes neuron growth and development
d. is glucose sparing
e. promotes amino acid uptake by cells
a. promotes bone growth
b. promotes muscle growth
c. promotes neuron growth and development
d. is glucose sparing
e. promotes amino acid uptake by cells
c. promotes neuron growth and development
93
New cards
**The pituitary hormone that triggers the release of thyroid hormone from the thyroid gland is**
a. TSH
b. ACTH
c. FSH
d. LH
e. GH
a. TSH
b. ACTH
c. FSH
d. LH
e. GH
a. TSH
94
New cards
**The pituitary hormone that controls the release of glucocoritcolds from the adrenal cortex is**
a. TSH
b. ACTH
c. FSH
d. LH
e. GH
a. TSH
b. ACTH
c. FSH
d. LH
e. GH
b. ACTH
95
New cards
The pituitary hormone that promotes egg development in ovaries and sperm development in testes is
a. TSH
b. ACTH
c. FSH
d. LH
e. GH
a. TSH
b. ACTH
c. FSH
d. LH
e. GH
c. FSH
96
New cards
**The pituitary hormone that promotes ovarian secretion of progesterone and testicular secretion of testosterone is**
a. TSH
b. ACTH
c. FSH
d. LH
e. GH
a. TSH
b. ACTH
c. FSH
d. LH
e. GH
d. LH
97
New cards
**The pituitary hormone that stimulates milk production by the mammary glands is**
a. TSH
b. ACTH
c. growth hormone
d. FSH
e. prolactin
a. TSH
b. ACTH
c. growth hormone
d. FSH
e. prolactin
e. prolactin
98
New cards
**The pituitary hormone that stimulates cell growth and replication by accelerating protein synthesis is**
a. ACTH
b. MSH
c. prolactin
d. insulin
e. somatotropin
a. ACTH
b. MSH
c. prolactin
d. insulin
e. somatotropin
e. somatotropin
99
New cards
**The pituitary hormone that stimulates melanocytes to produce melanin is**
a. TSH
b. FSH
c. MSH
d. STH
e. ADH
a. TSH
b. FSH
c. MSH
d. STH
e. ADH
c. MSH
100
New cards
**____ are chemical messengers that are released in one tissue and transported in the bloodstream to alter the activities of specific cells in other tissues**
a. hormones
b. neuropeptides
c. neurotransmitters
d. humoral antibodies
e. none of the above
a. hormones
b. neuropeptides
c. neurotransmitters
d. humoral antibodies
e. none of the above
a. hormones