Unit 3 Study Guide
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
Alveolus
A tiny air sac in the lungs where gas exchange occurs.
Aortic Valve
Valve that regulates blood flow from the heart into the aorta.
Arteriole
A small branch of an artery leading into capillaries.
Artery
A blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood away from the heart.
Atrioventricular Node
A cluster of cells that serves as a gatekeeper for electrical impulses between the atria and ventricles.
Atrium
The upper chamber of the heart that receives blood. (two atria, thin-walled)
Autorhythmic cells
“Pacemaker cells,” Specialized heart cells in the right atrium that generate their own electrical signals.
Bicuspid Valve
Also known as the mitral valve, it has two flaps and is located between the left atrium and left ventricle.
Blood
Fluid that circulates in the heart and vessels, delivering nutrients and oxygen.
Blood Vessels
The network of tubes through which blood flows, including arteries, veins, and capillaries.
Bohr Effect
The physiological phenomenon where increased carbon dioxide and decreased pH result in hemoglobin releasing oxygen more readily.
normal pH, normal temp = high affinity
low pH, high temp = low affinity
CO2 and lactic acid promote off-loading of O2
Bronchiole
Small air passages that lead to the alveoli in the lungs.
Bronchus
The main passageway that directs air into the left and right lungs.
Capillary
The smallest blood vessels where nutrient and gas exchange occurs.
Cardiac Muscle
Specialized muscle tissue of the heart that is autorhythmic.
Cardiomyocyte
A cardiac muscle cell responsible for the contraction of the heart, have a single nucleus, linked to neighbors by gap junctions and are striated and branched
Chemoreceptors
Sensory receptors that respond to chemical stimuli, particularly in blood gases.
Deoxygenated
Referring to blood that has a low level of oxygen, returning from the body and pumped toward the lungs/heart
Diastole
The phase of the heartbeat when the heart muscle relaxes.
Electrocardiogram
A recording of the electrical activity of the heart.
Endocardium
The inner lining of the heart chambers, forms valve structures.
Endothelial Cells
Cells that line the blood vessels, playing a role in vascular health.
Epiglottis
The flap of cartilage that covers the windpipe during swallowing.
Erythrocyte
A red blood cell that carries oxygen to body tissues.
Gap Junctions
Intercellular connections that allow for rapid electrical communication between heart cells.
Globin
The protein portion of hemoglobin responsible for binding oxygen.
Heart
The organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
Hematocrit
The proportion of blood volume occupied by red blood cells.
Heme Complex
The iron-containing structure in hemoglobin that binds oxygen, a human Hb has four of these and can carry 4 O2 molecules
Hemoglobin
The protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
Inferior Vena Cava
The large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the lower body (below the arms) to the heart.
Iron
A mineral essential for the formation of hemoglobin.
Larynx
The voice box that also plays a role in protecting the trachea against food aspiration.
Leaky Na+ Channels
Ion channels that allow sodium ions to enter cells, influencing heart rhythm.
Myocardium
The muscular middle layer of the heart wall responsible for contractions.
Myoglobin
An iron-containing, oxygen-binding protein found in muscle tissue, greater affinity for O2 than Hb, which promotes transfer better
Oxygenated
Referring to blood that is rich in oxygen, typically leaving the lungs.
P Wave
The part of an electrocardiogram that represents atrial depolarization.
Pericardium
The protective fibrous sac/membrane surrounding the heart, fluid-filled.
Plasma
The liquid component of blood that carries cells and proteins.
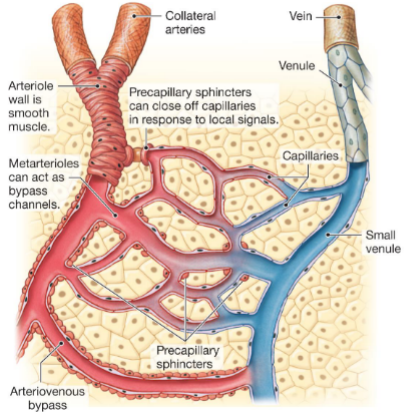
Precapillary Sphincter
A band of smooth muscle that controls blood flow into capillaries.
Pulmonary Valve
Valve that regulates blood flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery.
Pump
The function of the heart to circulate blood.
QRS Complex
The depiction of ventricular depolarization on an electrocardiogram.
Red Blood Cell
Another term for erythrocyte, responsible for transporting oxygen.
Sinoatrial Node
The natural pacemaker of the heart that initiates the heartbeat.
Smooth Muscle
Involuntary muscle type found in the walls of blood vessels and organs.
Stroke Volume
The amount of blood pumped by the heart with each beat.
Superior Vena Cava
The large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the upper body (head and arms) to the heart.
Systole
The phase of the heartbeat when the heart muscle contracts.
T Wave
The part of an electrocardiogram that represents ventricular repolarization.
Trachea
The windpipe that carries air to and from the lungs.
Tricuspid Valve
Valve that regulates blood flow between the right atrium and right ventricle.
Vasoconstriction
The narrowing of blood vessels, which increases blood pressure.
Vasodilation
The widening of blood vessels, which decreases blood pressure.
Vein
A blood vessel that carries deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
Ventricle
The lower chamber of the heart that pumps blood out of the heart. (two, thick-walled)
Venule
Small blood vessel that collects blood from capillaries.
Major arteries
aorta and pulmonary arteries carry blood away from the heart
Major veins
vena cava and pulmonary veins return blood to heart
oxygenated blood
blood rich in oxygen, returning from the lungs and pumped toward the body.
flow of deoxygenated blood in the human heart
deoxy blood from body enters the right atrium, arrives at RA via superior vena cava & inferior vena cava, then deoxy blood moves from RA to right ventricle through the tricuspid valve, then deoxy blood gets pumped to the lungs via the pulmonary artery through the pulmonary valve, then is oxygenated in the lungs
flow of oxygenated blood in the human heart
oxygenated blood from the lungs enters the left atrium, transported to LA from lungs via pulmonary veins, oxygenated blood moves from LA to left ventricle, valve between LA and LV is the bicuspid valve, oxygenated blood gets pumped to the body via the aorta, valve between LV and aorta is the aortic valve, blood becomes deoxygenated in the body
action potential in autorhythmic cardiomyocytes
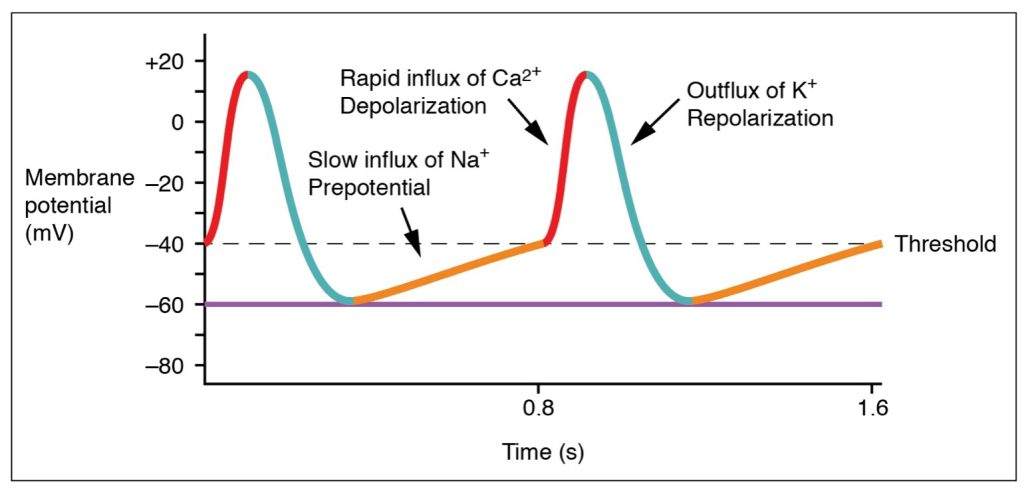
action potential in contractile cardiomyocytes
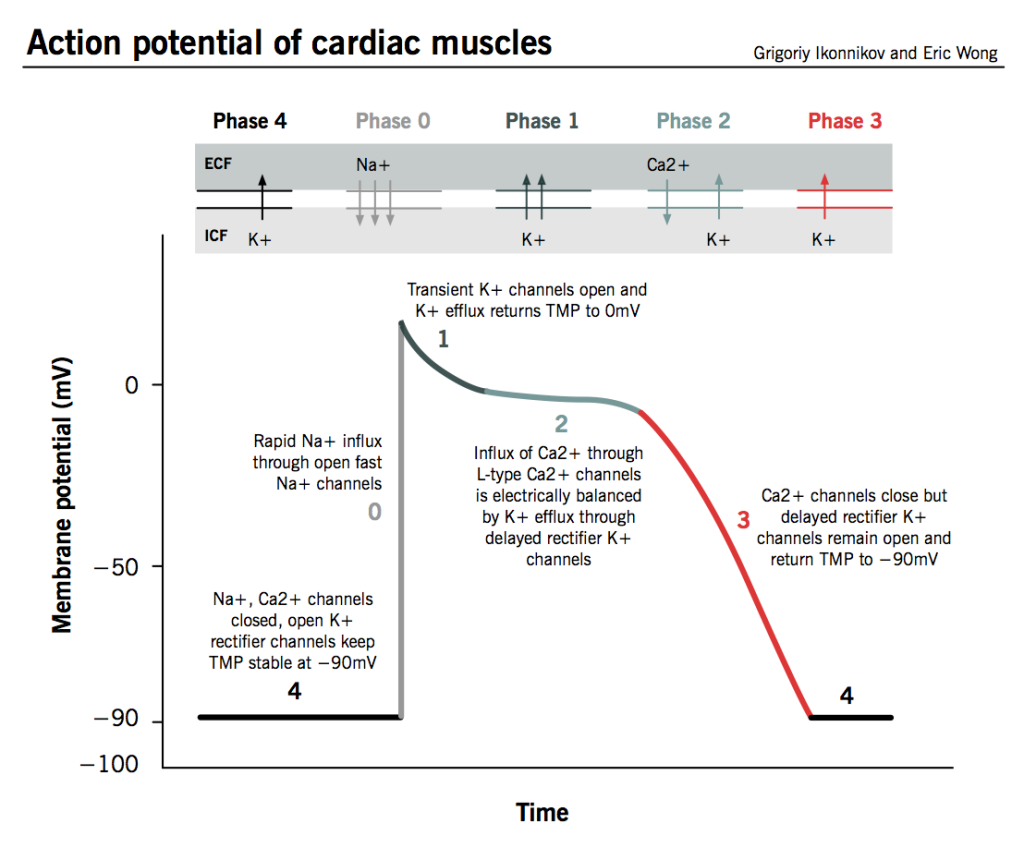
autonomic control of arteriolar tone (vasoconstriction)
sympathetic control, norepinephrine maintains arteriolar tone. when norepinephrine is released by a neuron, it binds to alpha receptors and causes vasoconstriction.
Epinephrine released by adrenal medulla binds:
• α receptors = vasoconstriction
• β receptors = vasodilation
autonomic control of autorhythmic cardiomyocytes
Parasympathetic fibers reach the heart via the Vagus nerve and act on the autorhythmic cells through the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
components of blood
~58% plasma, <1% white blood cells, 42% packed red cell volume
H2O
Ions (Na+, Cl-, K+, Ca2+)
Dissolved gases (O2 and CO2)
Sugars (glucose)
Amino acids, proteins, N waste
Various cells of the immune system (lymphocytes, macrophages; white blood cells)
Platelets (clotting factors)
Red blood cells
Electrical conduction throughout the heart
pacemakers set the heart rate, electrical signals coordinate contraction; internodal pathway from sinoatrial node to atrioventricular node; routes direction of signals so heart contracts from apex to base
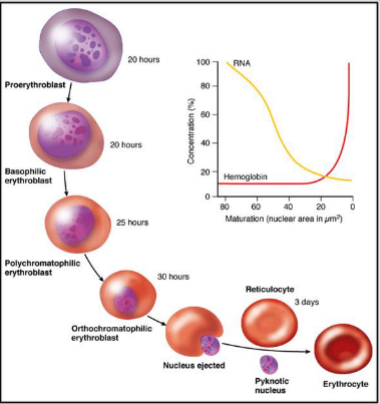
formation of red blood cells
RBCs are formed in the bone marrow from stem cells, takes 7 days, mature RBCs are unnucleated, and live in blood for 120 days
hierarchical organization of blood vessels
arteries → arterioles → capillaries → venules → veins
nervous control of breathing
neurons projecting from the medulla oblongata controls ventilatory muscles, chemoreceptors that can detect pH, PO2, PCO2, initiate sensory signals towards medulla oblongata,; increases PCO2 is a primary trigger for breathing
“Onloading” of O2 onto hemoglobin in alveoli
CO2 diffuses much faster than O2
CO2 is removed, blood pH increases
blood temp decreases via proximity to air in alveoli
increase in pH and decrease temperature at alveoli promotes O2 on-loading to Hb (“Bohr Effect”)
“Offloading” of O2 from hemoglobin
a decrease in pH and increase temperature at target tissue promotes O2 off-loading from Hb (“Bohr Effect”)
organization of a capillary bed
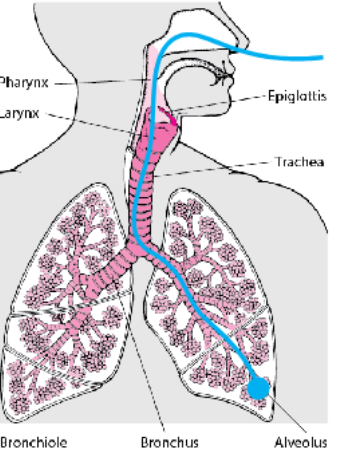
path of inhaled air
→ air is inhaled via the nasal passages or the mouth
→ inhaled air enters windpipe when the epiglottis is
open, arriving at the larynx
• epiglottis: a muscular flap preventing food from entering
trachea
→ air moves to trachea, which branches into two
bronchi leading to each lung
→ each bronchus branches into smaller bronchioles
→ a bronchiole ends at an alveoli
• alveoli: air sac, site of gas exchange
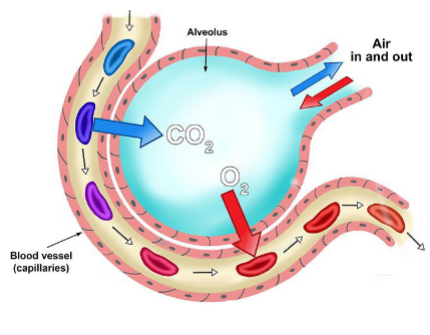
path of inhaled O2
→ dissolves in alveolar epithelial surface fluid
→ crosses lung epithelial cell
→ crosses endothelial cell, enters capillary
→ enters red blood cell, binds to hemoglobin
sounds of a heartbeat
“Lub” = atrioventricular valves closing (ventricular systole)
“Dup” = semilunar valves closing (ventricular diastole)
structure and organization of cardiomyocytes
striated: the contractile fibrils (containing actin and myosin) are aligned in parallel bundles
branching, and linked to neighbors by gap junctions
structure of blood vessels
Endothelium: inner layer of cells lining all blood vessels
Vascular smooth muscle: surrounds endothelial layer, contraction/relaxation drives vasoconstriction/dilation
Connective tissue: outer layer that provides supports and anchors blood vessels within tissues
systolic and diastolic blood pressure
sys: arterial blood pressure during ventricular systole, cardiac muscle contraction
dia: arterial blood pressure during ventricular diastole, cardiac muscle relaxation
vasoconstriction vs vasodilation
narrowing of bllood vessel diameter vs expanding of blood vessel diameter
properties of arteries
thickest blood vessel walls (all layers present)
site of highest blood pressure
carries blood from heart
properties of arterioles
less elastic and more muscular
divergent pattern of flow
site of variable resistance to direct blood flow
properties of capillaries
smallest vessels (only endothelial cells)
most abundant blood vessel type in body
primary site of material exchange
properties of venules
some connective tissue
convergent pattern of flow
properties of veins
not as thick as arteries (all layers present)
contains one-way valves
returns blood to heart