Mendelian Genetics and Modes of Inheritance
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Genes
Segments of DNA that determine traits.
Alleles
Variations of a gene influencing traits.
Genotype
Combination of alleles for a trait.
Phenotype
Physical expression of a trait.
Autosomal Dominant
Trait expressed if one dominant allele is present.
Autosomal Recessive
Trait expressed only if two recessive alleles are present.
Mendel's Law of Segregation
Alleles segregate during gamete formation.
Monohybrid Cross
Cross examining one trait's inheritance.
Punnett Square
Tool for predicting offspring genotype ratios.

Test Cross
Cross to determine an unknown genotype.
Selective Breeding
Choosing parents for desired traits in offspring.
Homozygous Dominant
Genotype with two dominant alleles (BB).
Heterozygous
Genotype with one dominant and one recessive allele (Bb).
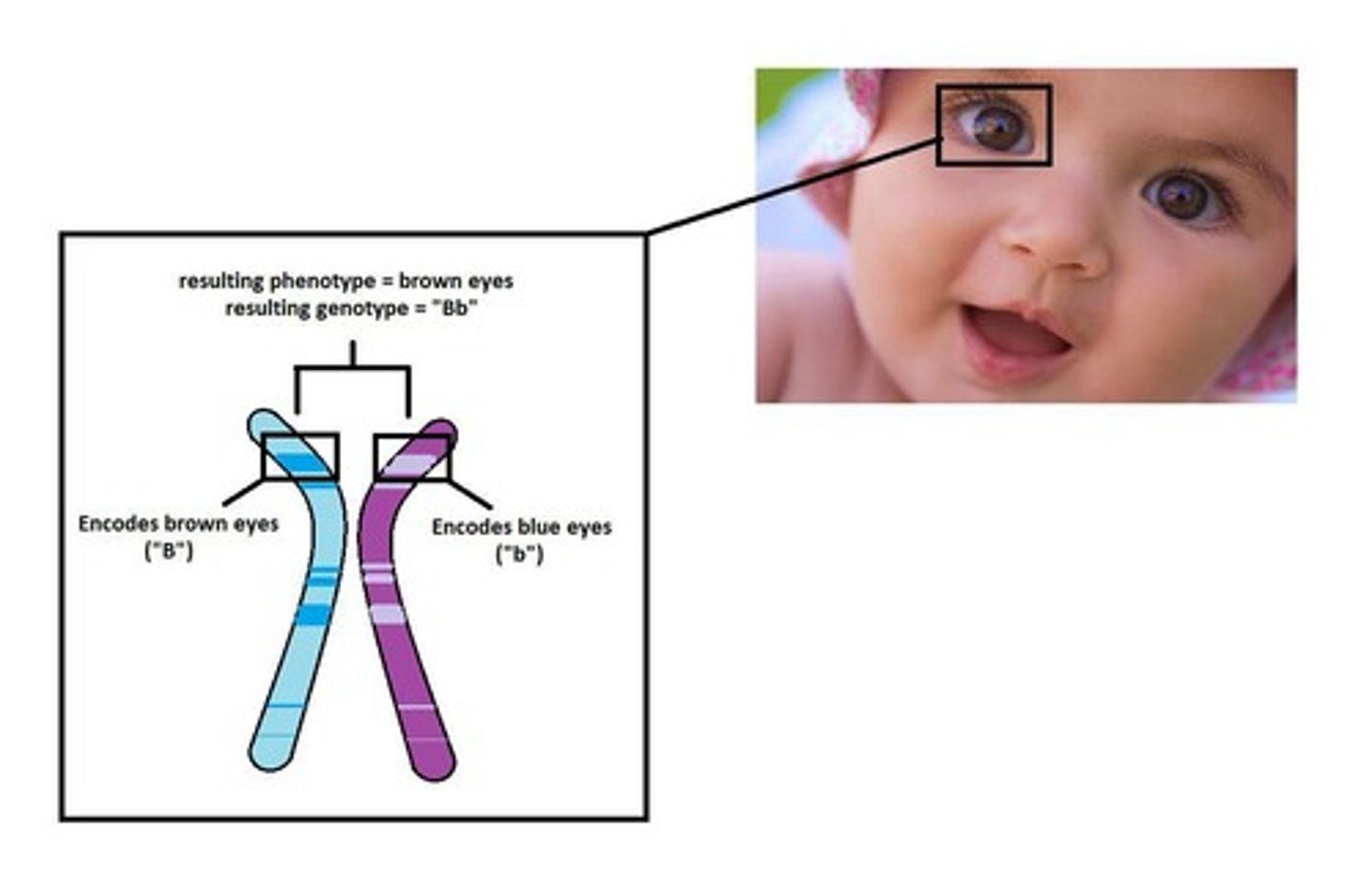
Homozygous Recessive
Genotype with two recessive alleles (bb).
Dominant Allele
Allele that masks the effect of a recessive allele.
Recessive Allele
Allele whose effect is masked by a dominant allele.
Blending Theory
Outdated theory suggesting traits blend in offspring.
F1 Generation
First filial generation from a cross.
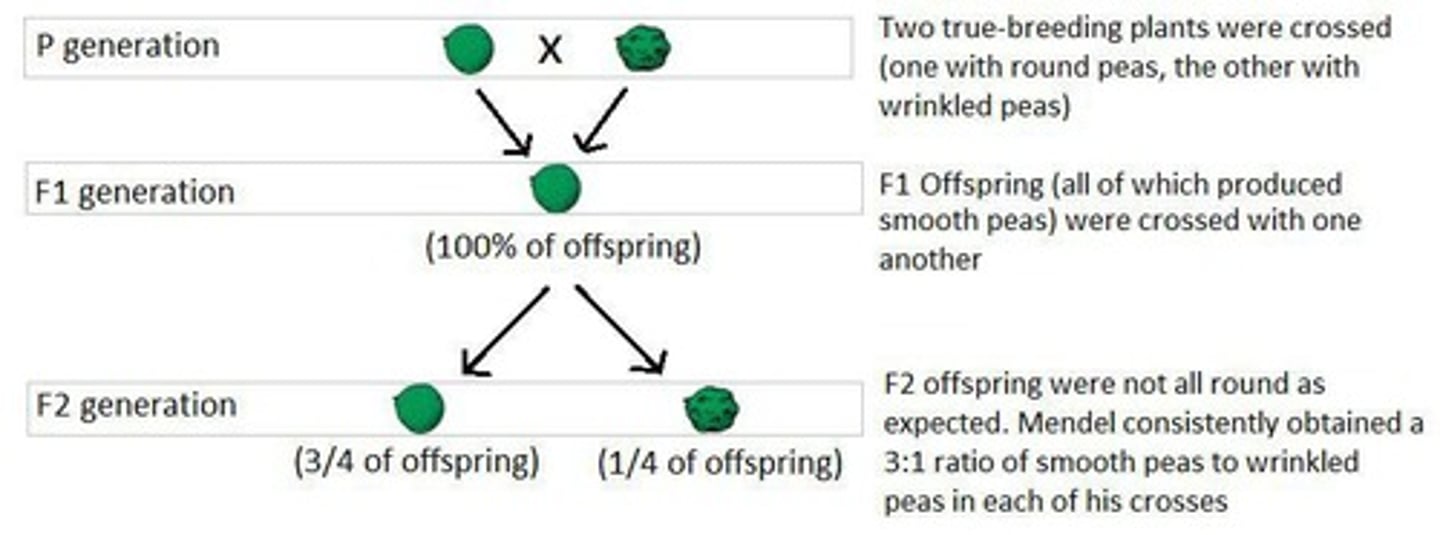
F2 Generation
Second filial generation from F1 self-cross.
True-Breeding
Organisms that produce offspring identical to themselves.
Phenotypic Ratio
Ratio of different phenotypes in offspring.
Genotypic Ratio
Ratio of different genotypes in offspring.
Gregor Mendel
Father of genetics; studied inheritance in peas.
Predictable Ratios
Consistent ratios of traits in offspring.
Accidental Selective Breeding
Unintentional selection of traits in agriculture.
Purebred
Organisms with identical alleles for a trait.
Genotype
Genetic makeup of an organism.
Phenotype
Observable traits of an organism.
F1 Generation
First filial generation from parental cross.
F2 Generation
Second filial generation from F1 cross.
Law of Segregation
Alleles segregate randomly during gamete formation.
Autosomal Dominant
Trait expressed if at least one dominant allele present.
Autosomal Recessive
Trait expressed only with two recessive alleles.
Monohybrid Cross
Cross examining a single trait inheritance.
Dihybrid Cross
Cross examining two traits simultaneously.
Independent Assortment
Genes segregate independently during gamete formation.
Homozygous
Having two identical alleles for a trait.
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a trait.
Allele
Different forms of a gene.
Gamete Formation
Process of forming reproductive cells.
Meiosis
Cell division producing gametes with half chromosomes.
Mendel's Experiments
Studies on inheritance patterns using pea plants.
Phenotypic Ratio
Proportion of different phenotypes in offspring.
Incomplete Dominance
Neither allele is completely dominant.
Co-dominance
Both alleles fully expressed in phenotype.
Sex-linked Traits
Traits associated with genes on sex chromosomes.
Blood Types
Classification based on specific antigens.
Sickle-cell Anemia
Condition showing incomplete dominance in inheritance.
Heterozygote
Individual with two different alleles.
Homozygous
Individual with identical alleles for a trait.
Dominant Allele
Allele that masks the effect of another.
Recessive Allele
Allele whose effect is masked by dominant.
X-linked Recessive
Trait requiring two recessive alleles in females.
Colour Blindness
X-linked recessive trait affecting vision.

Carrier
Individual carrying one recessive allele.
Barr Bodies
Inactivated X-chromosome in female cells.
Blood Type Alleles
IA, IB, and i determine human blood types.
Blood Type A
Genotype IAIA or IAi produces A phenotype.
Blood Type B
Genotype IBIB or IBi produces B phenotype.
Blood Type AB
Genotype IAIB produces AB phenotype.
Blood Type O
Genotype ii produces O phenotype.
Dominance Order
IA = IB > i indicates allele dominance.
Polygenic Inheritance
Traits controlled by multiple genes, showing continuous variation.
Continuous Traits
Traits that vary gradually, not in discrete forms.
Pleiotropic Genes
Single gene influences multiple traits or conditions.
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Disorder caused by mutation affecting phenylalanine levels.
PKU Symptoms
Include seizures, stunted growth, and skin conditions.
Genotype Prediction
Using pedigrees to determine an individual's genotype.
X-linked Recessive
Trait expressed in males if allele is present.
Generation Analysis
Assess traits and genotypes across family generations.
Trait Expression
Visible characteristics resulting from genotype interactions.
X-linked Dominant
Trait expressed in both genders, no father-son transmission.
Autosomal Dominant
Trait appears in every generation, affected parents can have unaffected children.
Autosomal Recessive
Trait skips generations, unaffected parents can have affected children.
X-linked Recessive
Only males affected, no father to son transmission.
X-linked Dominant Example
Females affected more than males, no father-son transmission.
Gene Linkage
Genes close together on the same chromosome, inherited together.
Parental Gametes
Gametes that retain the same allele combinations as parents.
Recombinant Gametes
Gametes with new allele combinations due to crossing over.
Independent Assortment
Mendel's law predicting separate inheritance of traits.
Epigenetics
Gene expression influenced by environmental factors and methylation.
Methylation
Chemical modification that can turn genes on or off.
Phenotypic Ratio
Proportion of different observable traits in offspring.
Genotypic Ratio
Proportion of different genetic combinations in offspring.
Trait Transmission
Inheritance patterns determining how traits are passed.
Trait Skipping Generations
When traits are not expressed in every generation.
Affected Children
Children showing a trait inherited from affected parents.
Environmental Triggers
Factors that can influence gene expression and methylation.
Gamete Production
Process of forming reproductive cells with genetic material.
Crossing Over
Exchange of DNA between homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
Linked Genes
Genes that do not assort independently due to proximity.
Example of Linked Genes
Brown eyes and brown hair genes often inherited together.
Genotype BbHh
Individual with brown eyes and brown hair.
Less than 50% Recombinants
Linked genes produce fewer recombinant gametes than independent genes.
Linked Genes
Genes on the same chromosome with reduced crossing over.
Gene Mapping
Determining relative distances between genes on chromosomes.
Crossing Over
Exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes.
Recombination Frequency
Percentage of recombinant gametes produced.
Map Units
Distance between genes based on recombination frequency.
Non-Linked Genes
Genes that assort independently, producing 1:1:1:1 ratio.