Lecture 14- transcriptional regulation in eukaryotes- how transcription is initiated.
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
what are the 3 types of RNA polymerase in eukaryotes?
RNA polymerase I, II and III
What genes does RNA polymerase I transcribe?
28s rRNA, 18s rRNA, 5.8S rRNA
what genes does rna polymerase II transcribe?
all genes that encode proteins, snoRNA, most snRNA
what genes does rna polymerase III transcribe?
5s rRNA, tRNA, some snRNAs
Which RNA polymerase requires general transcription factors to allow transcription to begin?
II
Why is transcription initiation more complex in eukaryotes?
Eukaryotic DNA is packaged into nucleosomes.
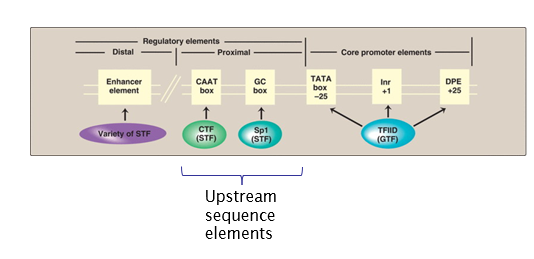
Draw the typical arrangement of a eukaryotic promoter region.
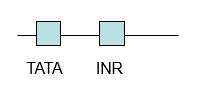
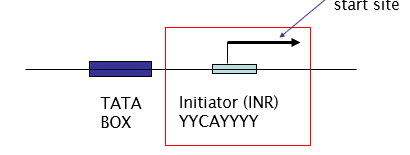
Draw a TATA containing core promoter.
INR= initiator, a core promoter element.
Draw a TATA less core promoter.
DPE= downstream promoter element.
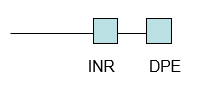
What id DPE recognised by?
TF2I
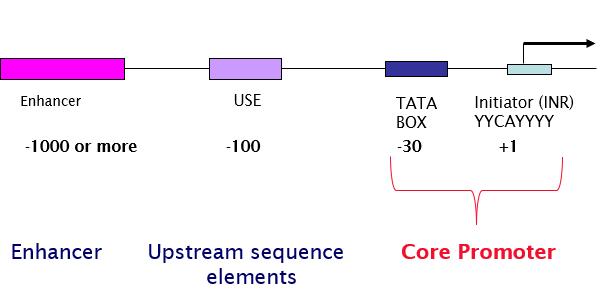
Draw the typical arrangement of a TATA core promoter recognised by RNA pol II.
Functon of the initiator element (INR)
Simplest functional promoter
Can initiate basal transcription in absence of TATA box
conserved Y is pyrimidine
Facilitates binding of TFIID.
All genes that are transcribes and expressed via mRNA are transcribed by…
RNA polymerase II
how many subunits does RNA pol have?
12
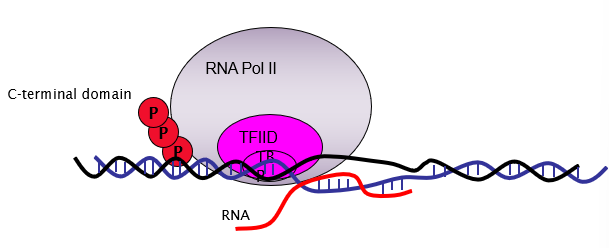
What happens during initiation at the core promoter?
An RNA polymerase II pre-initiation complex needs to be assembled.
This positions the RNA polymerase II over transcription strart sites.
INITIATION
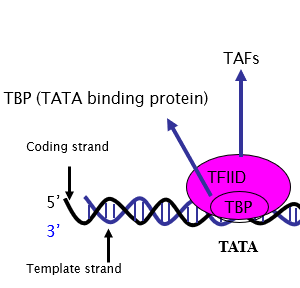
What binds to the TATA box?
General transcription factors
What is the first transcription factor to bind to the TATA box?
TFIID
What 2 things does TFIID consist of?
TBP and TAF
What is TBP?
TATA binding protein.
What are TAFs?
Involved in binding other TFs to help attach RNAP II to the DNA and attaching proteins that unwind the chromatin structure.
What 2 molecules join to TFIID?
TFIIB and TFIIA
What recruits RNApol II to the TATA box?
TFIIB
What molecule accompanies and stabilises RNA pol II?
TFIIF
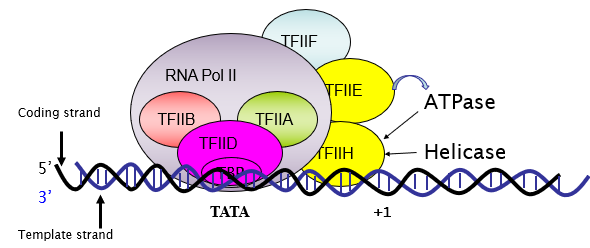
what molecules bind and make the initiation complex?
TFIIE and TFIIH.
ELONGATION
What is the role of TFIIH?
Melts the DNA and transcription starts.
10 subunit complex containing ATPase, helicase, protein kinase.
Phosphorylation of C terminal domain of RNA pol II by TFIIH kinase.
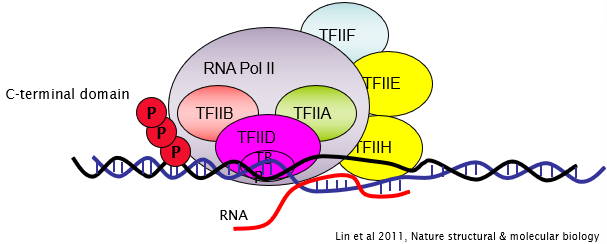
After phosphorylation, what is released from the complex?
TFs
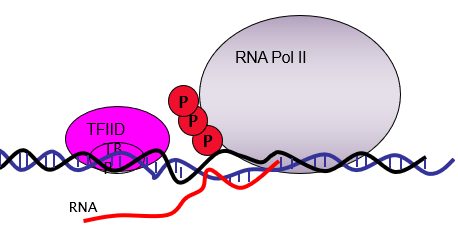
How does elongation take place?
TFIIH is central to this process
A conformational change causes RNApol II to tighten grip.
It aquires elongation factors that help process RNA and increase elongation rate.
What 3 factors determine cell fate?
Gene expression
Cell-cell/cell-matrix interactions
External factors, e.g., hormones.
What are upstream sequence elements (USE)?
Upon binding basal/upstream/specific transcription factors to sites ~100 bp upstream of PIC, transcription is enhanced.
Give 2 examples of USE.
GC box and CAAT box
Role of GC box?
Bings SP1 TF (specifity protein 1 transcription factor).
Role of CAAT box?
Binds CAAT box TF.
Role of enhancers?
Regulatory sequences that act at a distance.
Cis acting (up to 1mb away) with reversible orientation
Bound by activator proteins
These interact with mediator complex
Encouraging binding of RNApol II
What is evidence for existence of enhancers?
Simian Virus 40 (SV40)- promoter: found that deletion of a 72 bp sequence led to a 100-fold decrease in expression.
What are properties of enhancer elements? (3)
Can activate transcription when placed thousands of bp away from TATA box
Act in either orientation (5’ to 3’ or 3’ to 5’)
Can act when placed upstream or downstream of TATA box or when placed within an intron.