3.1.5 Nucleic acids biology
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What is a nucleotide?
Monomer unit of nucleic acid, composed of an organic base, a pentose sugar and phosphate
What is an organic base?
Nitrogen containing heterocyclic compounds, which can differ:
DNA: adenine, guanine, thymine, cytosine
RNA: adenine, cytosine, guanine, uracil
What is a pentose sugar?
Sugar that possesses five carbon atoms e.g. Ribose (RNA), deoxyribose (DNA)
What is a polynucleotide?
Many nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds
What is a phosphodiester bond?
Bond formed between deoxyribose sugar of one nucleotide and phosphate group of another nucleotide
What is DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) composed of?
Composed of two polynucleotide chains (DNA nucleotides). The chains are joined together by hydrogen bonds. Each chain has a helical structure
What is RNA (Ribonucleic acid) composed of?
Composed of a single polynucleotide (RNA nucleotides) chain
What is complementary base pair?
Where the bases in DNA pair with each other: A to T, G to C. Base pairs (DNA) are held together by hydrogen bonds
What is a hydrogen bond?
Dipole-dipole interaction between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom, such as nitrogen or oxygen. It’s a weak bond that forms between complementary bases.
What is DNA helicase?
Enzyme that breaks the hydrogen bonds between DNA bases causing the two strands to separate and expose nucleotide bases in that region.
What is DNA polymerase
Enzyme that catalyses the formation of the phosphodiester bond between nucleotides.
What is semi-conservative replication?
The means by which DNA makes identical copies of itself by unwinding the double helix so that each strand acts as a template for new strand synthesis. The new copies therefore possess one original and one new strand of DNA.
Why is DNA and RNA part of the nucleic acids group?
Due to their initial discovery within the nucleus
Presence of phosphate groups (providing acidic properties).
What does DNA and RNA do?
DNA: Molecule that stores genetic information
RNA: Molecule that transfers genetic information from DNA to ribsomes (made from RNA + Protein)
What 3 components is a nucleotide made of?
Pentose sugar
Nitrogen-containing organic base
Phosphate group (comprising a phosphate ion)
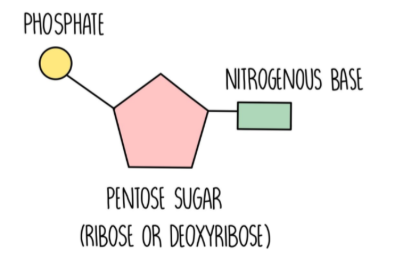
How is the polynucleotide chain held together?
phosphate group of each nucleotide is linked to the sugar of the next by strong covalent bonds (phosphodiester bonds), forming the sugar-phosphate ‘backbone’.
What is the only way in which one polynucleotide chain can differ from another?
The sequence of bases in the polynucleotide
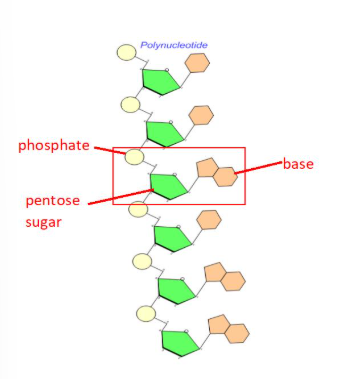
What does a polynucleotide look like?
Which 2 people worked out the structure of DNA in the early 1950’s at Cambridge University?
James Watson and Francis Crick, figuring out that DNA consists of two polynucleotide chains (or strands), one running the opposite way to the other (anti-parallel), twisting to form a double helix. The bases in each strand are held together by hydrogen bonding.
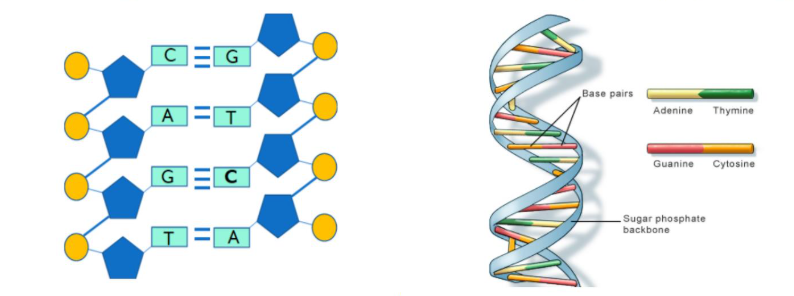
How many hydrogen bonds does different bases form?
Adenine form 2 with Thymine
Cytosine forms 3 with Guanine
Some viruses have single stranded DNA. How could an analysis of a piece of DNA tell you if it was single stranded?
There would not be equal proportions of A and T, or G and C
There would not be an equal number of purines and pyrimidines
How does the structure of DNA relate to its function
DNA consists of 2 strands and has a sugar-phosphate backbone so provides strength and stability
Double stranded so replication can occur semi-conservatively (both strands can act as templates)
Complementary base pairing (A-T and G-C) so accurate replication (identical copies) can occur
Weak hydrogen bonds allow the DNA strands to separate easily for replication
It has a sugar phosphate backbone which protects the internal bases
It is a helix so is compact (can store a lot of information in a a small space)
Specific base sequence allows information to be stored
Many hydrogen bonds so stable / strong molecule
The genetic code on the DNA must be transferred from nucleus to cytoplasm, why is that?
DNA of a eukaryotic organism is stored in the nucleus, but protein synthesis occurs on ribosomes found in the cytoplasm and the rough endoplasmic reticulum
What does RNA contain?
Ribose
Nitrogenous organic base
Phosphate group
Is uracil a purine or pyrimidine base?
Pyrimidine
What are the 3 types of RNA?
mRNA (messenger)
tRNA (transfer)
rRNA (ribosomal)
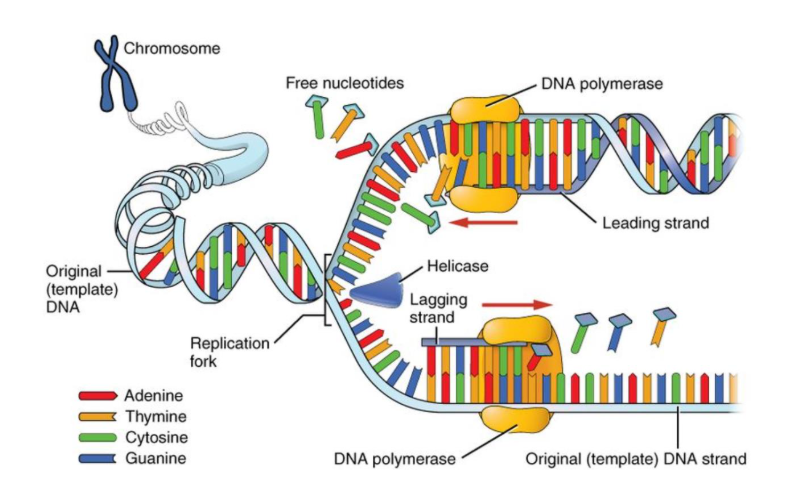
Semi-conservative replication occurs in the following steps:
An enzyme called DNA helicase is required to unwind the DNA double helix, by breaking the weak hydrogen bonds between complementary bases in the polynucleotide strands. This separates the strands
Each exposed strand of DNA can now act as a template for the formation of a new strand
New DNA nucleotides (present in the nucleus) are attracted to the exposed bases on the template strands, and attach by complementary base pairing. New hydrogen bonds form between the bases
The enzyme DNA polymerase joins the adjacent nucleotides with a phosphodiester bond to form a new polynucleotide strand. Phosphodiester bonds are formed between adjacent nucleotides via condensation reactions.
What does the process of semi-conservative replication rely on?
Relies on complementary base pairs (cytosine with guanine and thymine with adenine) to accurately produce identical daughter DNA molecules.
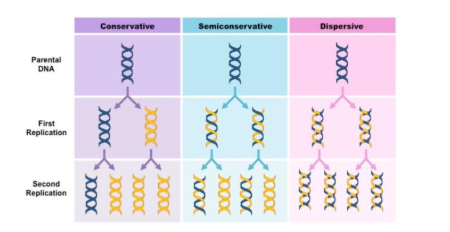
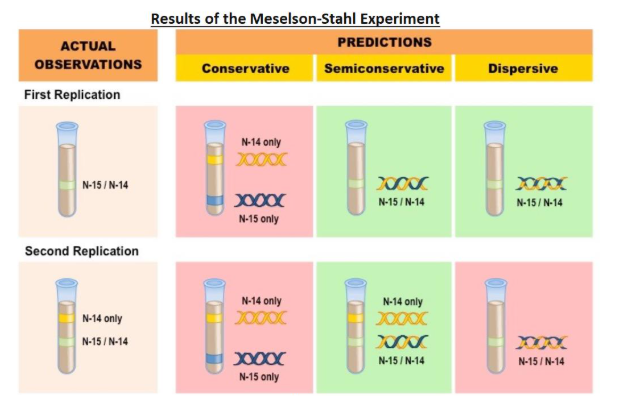
What were the 3 proposed hypotheses for the method of replication of DNA before Meselson-Stahl confirmed it was semi-conservative in 1958?
Conservative Model – An entirely new molecule is synthesised from a DNA template (which remains unaltered)
Semi-Conservative Model – Each new molecule consists of one newly synthesised strand and one template strand
Dispersive Model – New molecules are made of segments of new and old DNA
How were Meselson and Stahl able to experimentally test the validity of Conservative, Semi-Conservative and Dispersive models using radioactive isotopes of nitrogen?
Nitrogen is a key component of DNA and can exist as a heavier 15N or a lighter 14N
DNA molecules were prepared using the heavier 15N and then induced to replicate in the presence of the lighter 14N
DNA samples were then separated via centrifugation to determine the composition of DNA in the replicated molecules
The results after two divisions supported the semi-conservative model of DNA replication
After one division, DNA molecules were found to contain a mix of 15N and 14N, disproving the conservative model
After two divisions, some molecules of DNA were found to consist solely of 14N, disproving the dispersive model
What elements does deoxyribose and ribose only contain?
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
(exam) Give three features of DNA and explain how each one is important in semi-conservative replication of DNA. (3)
Weak hydrogen bonds between bases allow two strands to separate
Two strands, so both can act as templates
Complementary base pairing allows accurate replication
The replication of the second strand of mtDNA only starts after two-thirds of the first strand of mtDNA has been copied.
A piece of mtDNA is 16 500 base pairs long and is replicated at a rate of 50 nucleotides per second. How long would it take to copy this mtDNA
16500 ÷ 50 = 330
330 x \frac23 = 220
330 + 220 = 550
(exam) Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleotides derivative. Contrast the structures of ATP and a nucleotide found in DNA to give differences (3)
ATP has ribose and DNA nucleotide has deoxyribose
ATP has 3 phosphate groups and DNA nucleotide has 1 phosphate group
ATP base always adenine and in DNA nucleotide base can be different
(exam) Explain how structure of DNA is related to its functions (6)
Sugar-phosphate backbone so provides strength
Long molecule so can store lots of information
Helix so compact
Base sequence allows information to be stored
Double stranded so replication can occur semi-conservatively
Weak hydrogen bonds for replication
(exam) Describe the process of semi-conservative replication of DNA (5)
DNA helicase unwinds DNA
Both strands act as templates
Free DNA nucleotides line up in complementary pairs
DNA polymerase joins nucleotides of new strand
Forming phosphodiester bonds
Each new DNA molecule consists of one old strand and one new strand

(exam) Explain why DNA from generation 1 is found in the position shown (2)
It has been produced by semi-conservative replication
One strand has 15N bases and the other 14N

(exam) Complete the diagram to show results for generation 2 (2)

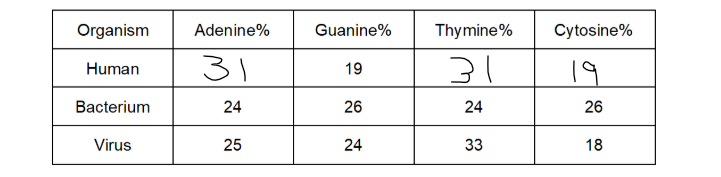
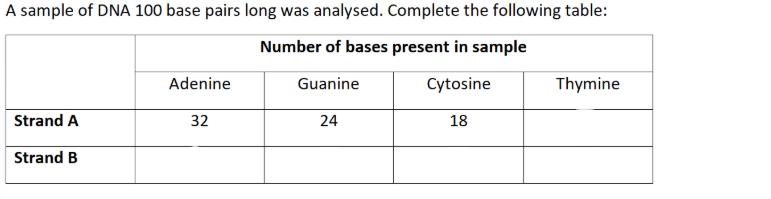
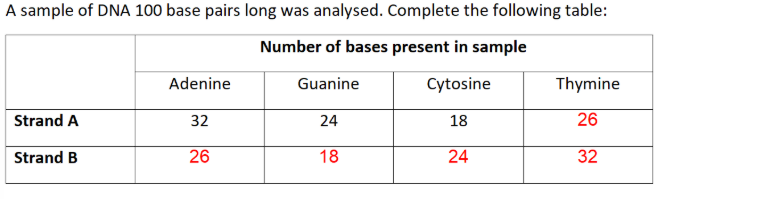
(exam) Structure of virus DNA is different from DNA of other two organisms. Giving evidence from the table, suggest what this difference might be. (2)
Viral DNA single-stranded
No equal amount of Adenine and Thymine or Cytosine and Guanine
(exam) DNA helicase is important in DNA replication. Explain why. (2)
Separates strands
So nucleotides can attach
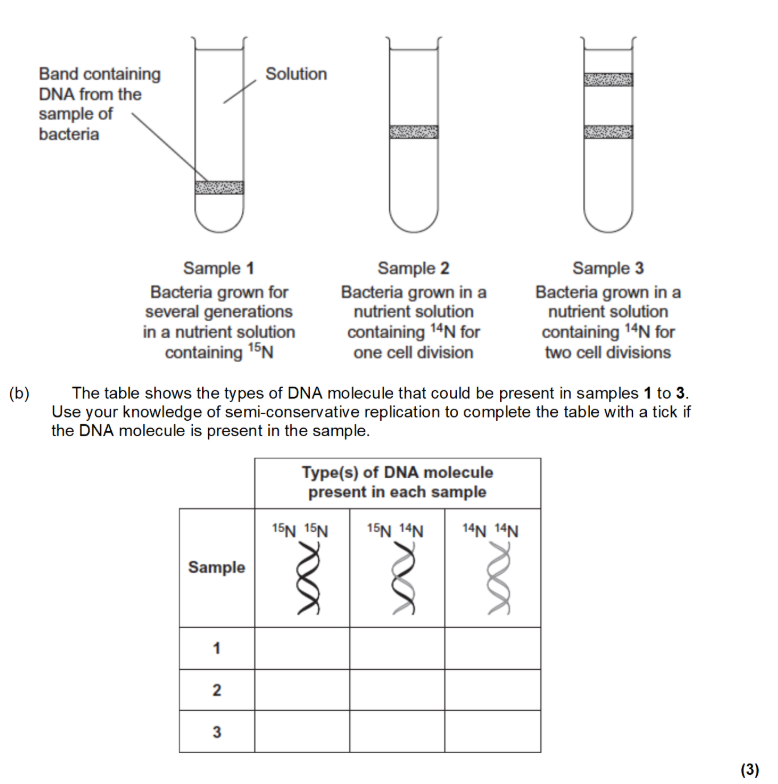
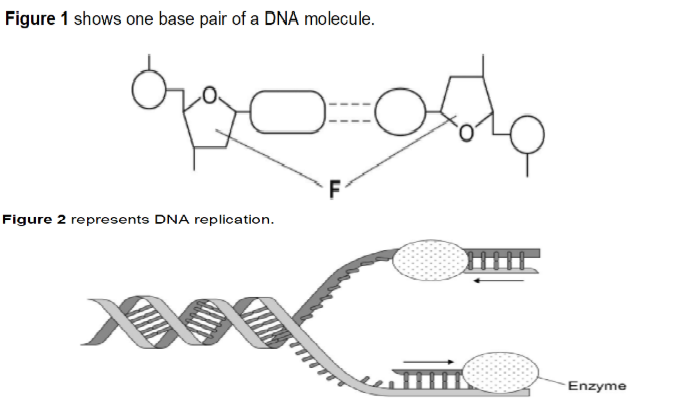
(exam) Use figure 1 and 2 and your own knowledge of enzyme action to explain why the arrows point in opposite directions (4)
Figure 1 shows DNA has antiparallel strands
Figure 1 shows shape of the nucleotides is different
Enzymes have active sites with specific shape
Only substrates with complementary shape can bind with active site of enzyme