Fundamentals of Artificial Intelligence Concepts
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
What is not the fundamental property of a rational agent?
Inference capability
Which agent’s category is definable using the Turing test method?
Acting humanly
Which agent’s category can explain Aristotle’s philosophical approach?
Thinking rationally
General problem solver program is a type of:
Thinking humanly
Which of the following options is not required to understand the human brain working process:
Which of the following capability is not required to pass Turing test?
Computer Vision
Which of the following capability is not required to pass total Turing test?
Introspection
Cognitive Science is a type of:
Thinking humanly
A rational agent is one that only uses a logical approach to reasoning.
False
To explain a reflexive reaction like withdrawing your hand from a hot stove, you would look to models of acting rationally.
False
“Acting appropriately when there is not enough time to do all the computation one might like.” It is a definition of _____________.
limited rationality
The problem of achieving agreement between our true presences and the objective we put into the machine is called the ___________.
value alignment problem
The theory of ____________ provides a basis for analyzing the tractability of problems.
NP-completeness
The _______________ showed that in any formal theory, there are necessarily true statements that have no proof within the theory.
incompleteness theorem
____________ is a branch of philosophy and mathematics that deals with the study of reasoning and inference through the use of formal systems.
Logic
_____________ which combines probability theory with utility theory, provides a framework for making decision under uncertainty.
Decision theory
Which agent can only make decision in a fully observable environment?
Simple reflex agent
What is not the difference between “performance measure” and “utility function”?
"Performance measure improves the performance of an agent, but the utility function is useful in designing the agent’s architecture.
What are the properties of the time-controlled chess game environment?
Semi-dynamic, deterministic, discrete, sequential
What are the properties of the medical diagnosis system environment?
Fully observable, non-deterministic, discrete
What is the best program to design an autonomous taxi driver?
Utility-based agent
Which choices is not correct about an agent relying only its prior knowledge?
Fully autonomous
Which one is not an element of a learning agent?
Knowledge element
A self-driving car navigating through a busy city is an example of non-observable environment.
False
Agent consists of ________.
Architecture and program
The more the agent uses his internal knowledge and pays less attention to his perception, the _____autonomous it is, and a completely autonomous system is _____ intelligent.
less, more
What type of agents are problem-solving agents?
Goal-based agent
What is the computational process for considering a sequence of actions that form a path to a goal state?
Search
Which of the following is NOT a main step in the problem-solving process?
Learning from experience
How is a search problem formally defined?
By specifying the initial state, actions and their costs, and goal test
What is the main difference between a graph and a tree in search problems?
Graphs can contain cycles, while trees cannot
When is graph search more effective than tree search?
When the state space contains repeated states
A ________ is a representation of a problem that includes the states, actions, and the transition model.
search problem
The branching factor of a search tree refers to the number of ________ from any given node. (use small letters to answer this question)
possible actions
The transition model defines how the world evolves in response to an action.
True
In a tree search, nodes can represent repeated states.
True
A state space includes all possible configurations of a problem that can be reached through a series of actions.
True
The performance of a problem-solving agent is solely measured by the speed of finding a solution.
False
Completeness
Whether the algorithm is guaranteed to find a solution when one exists.
Optimality
Whether the strategy finds the best possible solution
Time Complexity
How long it takes to find a solution.
Space Complexity
How much memory is required to perform the search.
Why is an abstract mathematical description used in problem-solving?
To omit irrelevant factors and focus only on what is necessary for finding solutions
Three admissible heuristic functions, h1(n), h2(n), and h3(n), satisfy the following relation: h1(n)>h2(n)>h3(n). Which of these heuristics will require the least amount of time to find the solution using the A* algorithm?
ℎ 1 ( 𝑛 ) is the most informed and will result in fewer explored nodes
Which of the following statements is true about RBFS (Recursive Best-First Search)?
It is more efficient than IDA*
You are tasked with solving the Robot Navigation Problem, where a robot must navigate through a grid from a starting point to a goal point while avoiding obstacles. The robot can move up, down, left, and right but cannot pass through grid cells that contain obstacles. Which of the following options are admissible heuristics to solve this problem?
Weighted Manhattan Distance (h(n)=weight×(∣x goal −x n ∣+∣y goal −y n ∣))
You are implementing an A* search algorithm for pathfinding in a weighted graph. Consider a heuristic function h(n) used to estimate the cost from a node n to the goal.
Which of the following statements correctly describes the implications of using a non-consistent heuristic h(n) in the A algorithm?*
The algorithm may fail to find the optimal path to the goal, as it could overlook potentially shorter paths due to inflated heuristic values.
The algorithm will always terminate without finding a solution, regardless of the graph's structure.
The use of a non-consistent heuristic could result in increased computational time due to unnecessary expansions of nodes.
A non-consistent heuristic guarantees that the solution found will be suboptimal but will always be reachable within a finite number of steps.
1 and 3
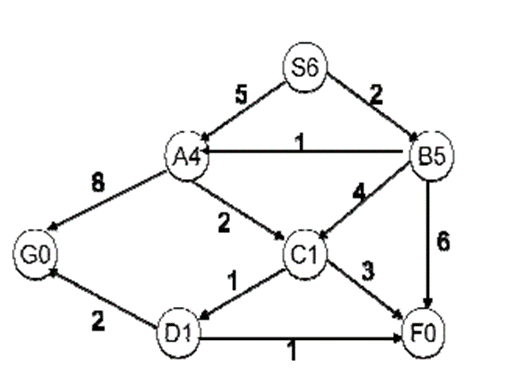
what is the solution using A*?
[S,B,A,C,D,G] with cost of 8
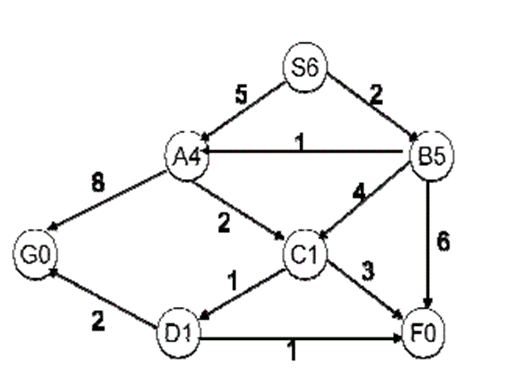
Use the greedy search algorithm to solve the above problem.
[S,A,G] with the cost of 13.
Which of the following algorithms is not complete?
DFS
A rational agent must always make decisions that are optimal given its current knowledge.
False
Limited Information
Agents may not have access to all relevant information, leading to suboptimal decisions.
Uncertainty
The world is often uncertain, and agents may have to make decisions based on probabilistic models, which can lead to unexpected outcomes.
A partially observable environment is one where the agent has the necessary information about the state of environment.
False
This means that even if the agent has the access to some of the information, it may still be missing crucial details that allow it to make fully informed decisions.
A table-driven agent is highly adaptable to new situations
False
In a semi-dynamic environment, the state of the environment can change while the agent is deliberating.
False
a semi-dynamic environment, the environment itself does not change, only the performance score is affected by the passage of time during deliberation
An autonomous agent relies entirely on pre-programmed rules without learning from its environment
False
Which of the following is a property of a goal based agent?
Plans actions based on future goals
Which of the following environments is most suitable for a utility-based agent?
Dynamic and partially observable
Which of the following is not an advantage of model-based reflex agents?
They only require current percepts to function
Which of the following is required for a simple reflex agent to operate effectively?
Predefined condition-action rules
Which of the following best describes the goal of "thinking like a human"?
Creating models that mimic human thought processes and decision-making
A chess-playing Al that evaluates possible moves and selects the best one based on logic and probability is an example of:
Acting rationally
An Al system that drives a car by observing the environment and making decisions to safely navigate traffic is an example of
Acting rationally
General Problem Solver (GPS) is best categorized under which Al approach
Thinking like a human
Which agent type would struggle in a non-deterministic environment?
Simple reflex agent
Which of the following is the primary objective of the Turing Test?
To assess a machine's ability to exhibit intelligent behavior indistinguishable from a human.
Which of the following best describes a situation involving a "known environment" in Al?
An Al agent playing a board game with predefined rules and a fixed board layout.
What is the environmental description for Playing soccer?
Partially observable, stochastic, sequential, dynamic, continuous, multi-agent.
What is an essential component for passing the Total Turing Test that is not required for the standard Turing Test?
computer vision
A ______ environment requires the agent to account for uncertainty in its decision-making process.
uncertain
An agent's _______ is the abstract mathematical representation of its behavior, while the _________ is the concrete implementation.
Element, Logic
A(n) ________agent learns from its environment and adapts its behavior over time, while it may still require human guidance.
learning
Observable
The agent's sensors give it access to the complete state of the environment at each point in time, for a fully observable environment. For a partially observable environment, sensors are noisy/inaccurate or parts of the state are missing
Deterministic
The next state of the environment is completely determined by the current state and the action executed by the agent. Otherwise, the environment is stochastic or nondeterministic
Static
The environment does not change while an agent is deliberating. If it can change, it is dynamic. If the environment doesn't change but the score does, it's semidynamic
Episodic
The agent's experience is divided into atomic episodes, where in each episode the agent receives a percept and performs a single action, and the next episode does not depend on actions taken in previous episodes. In contrast, in sequential environments, the current decision affects future decisions
Learning Element
Responsible for making improvements. It modifies the performance element based on feedback from the critic. It can change the agent's knowledge components and learns from what it perceives, such as observing successive states of the environment to learn how the world evolves and the results of its actions. It brings the components into closer agreement with available feedback information, improving overall performance. This aligns with the function of Acquiring new knowledge.
Performance Element
Responsible for selecting external actions. This component is what we previously considered to be the entire agent, taking in percepts and deciding on actions. It "keeps doing the actions that are best, given what it knows," unless directed otherwise by the problem generator. This aligns with the function of Selecting and executing actions
Critic
Tells the learning element how well the agent is doing with respect to a fixed performance standard. It provides feedback to the learning element. The critic is necessary because percepts alone may not indicate the agent's success. It conceptually sits outside the agent so the agent cannot modify the standard to fit its own behavior. This aligns with the function of Evaluating the agent's actions.
Problem Generator
Responsible for suggesting actions that will lead to new and informative experiences. Its job is to suggest exploratory actions, even if they are potentially suboptimal in the short term, to help the agent discover better actions in the long run. This aligns with the function of Suggesting actions or tasks.
Which of the following is true regarding the importance of time complexity vs. space complexity in search algorithms?
Assume that you place n rooks on a n*n board. They should not attack each other. What is the maximum size of the state space?
n!
Prove/disprove:
If h1(s) and h2(s) are two admissible A* heuristics, then their sum h(s) = h1(s)+h2(s) is also admissible.
admissible: h(s)<=h'(s)
So, if h1(s)<=h'(s) and h2(s) <h'(s) assuming that h'(s) is the same throughout, if h1=3,h2=4, and h'=5, then 3+4 <= 5, which is false, therefore h1(s) + h(2) is not admissible.
Match every search algorithm with its two characteristics.
Algorithm
1. IDA*
2. RBFS
Characteristics:
A. Uses limited memory by only storing the current exploring path.
B. Performs iterative deepening strategy by increasing path cost on each iteration.
C. Keeps track of the current path and the best alternative paths. but discards others.
D. Performs depth-first strategy by considering path costs or heuristic
estimates.
IDA*: B,D
RBFS: A, C