Chemical equilibrium
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What does dynamic mean?
Involving continuous movement, change, or activity.
What is the law of mass action?
The reactant that is moving forward (or backwards) ∝ the product of the active masses of the reactants and their S.C that is represented as powers.
What is the formula that gives the relation between Kp (or Kc) with temperature
k = A e -∆H/RT
where:-
K = equilibrium constant (Kp or Kc)
A = pre-exponential factor (kind of constant here)
ΔH = enthalpy change
R = gas constant
T = absolute temperature in K
The exponent is:
−ΔH∘RT
What are miscible liquids?
Liquids that can mix with one another
What is the formula for the Degree of dissociation?
where,
Mt = Theoretical molar mass (which you get from calcluating for GMM/ Other word for GMM)
Mo = Observed molar mass
n = number of gaseous molecules formed by the dissociation of 1 gas molecule
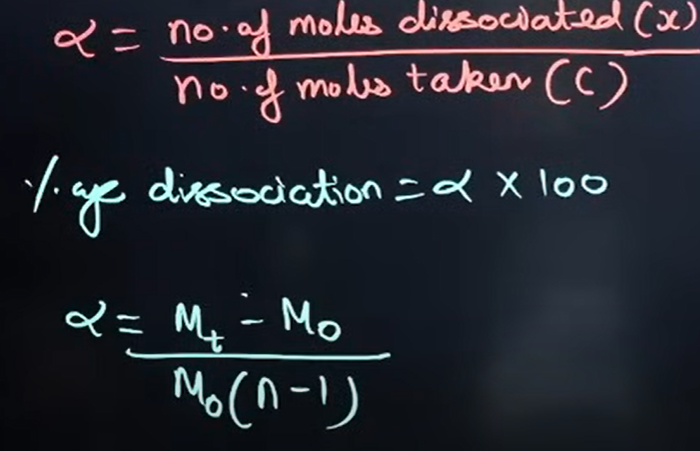
What is the formula for calculating partial pressure?
Px = Mole fraactionx* Total Pressure
What is the formula that gives the relation between gibbs free energy and gibbs free standard energy??
ΔG = Gibbs free energy change at any point in the reaction (J/mol)
ΔG∘= Standard Gibbs free energy change (J/mol), measured under standard conditions
R = Universal gas constant = 8.314Jmol−1K−1
T = temperature in Kelvin (K)
K=Equilibrium constant (dimensionless)
This can be Kc (based on concentration) (or) Kp (based on partial pressure)

What is Le cahteliers principal?
It states that the equilibrium shifts to oppose the change and try to keep the same value of the equilibrium constant
What are the 3 special substances that decrease in volume as you heat them up?
Water, diamond and quartz