1. biolab exam 1002
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
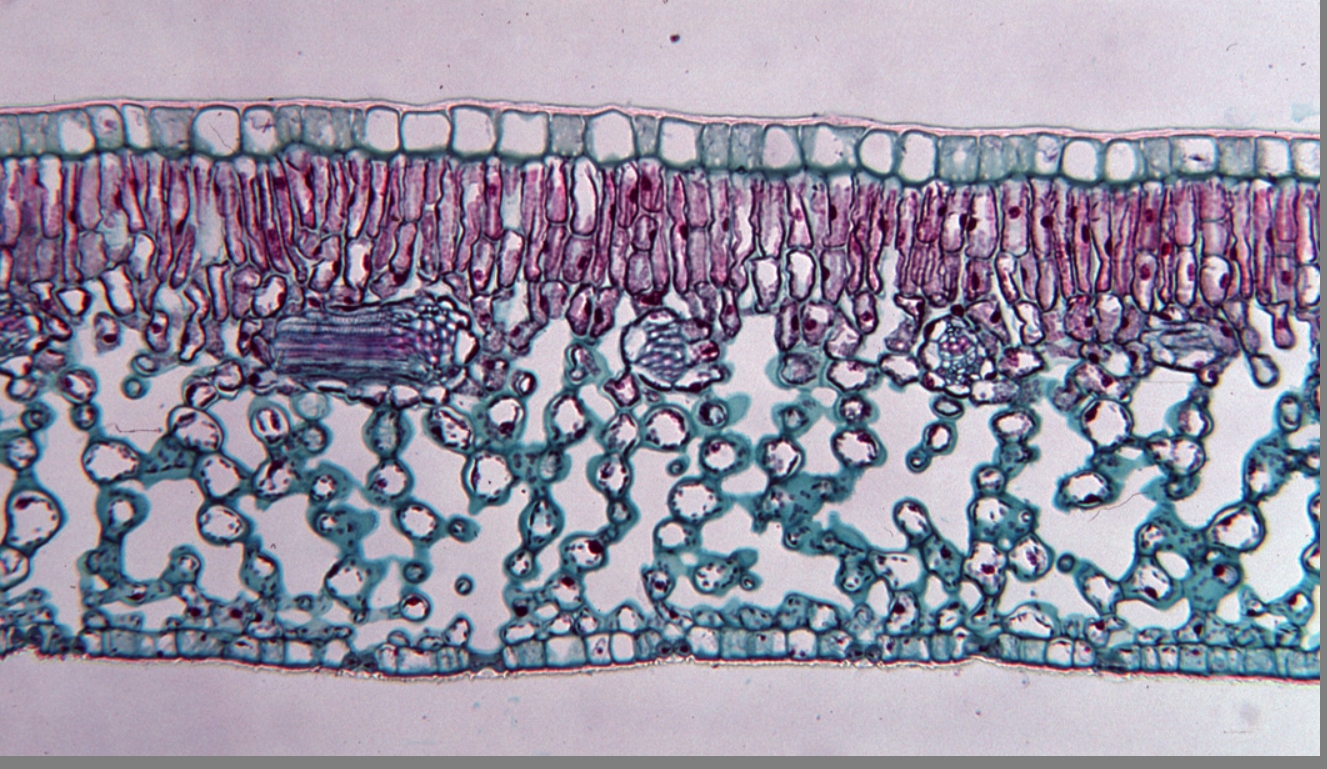
which is the mesophyte
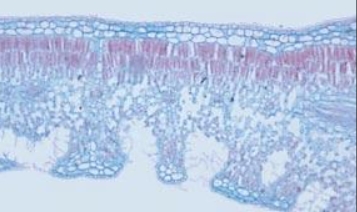
which is the xerophyte
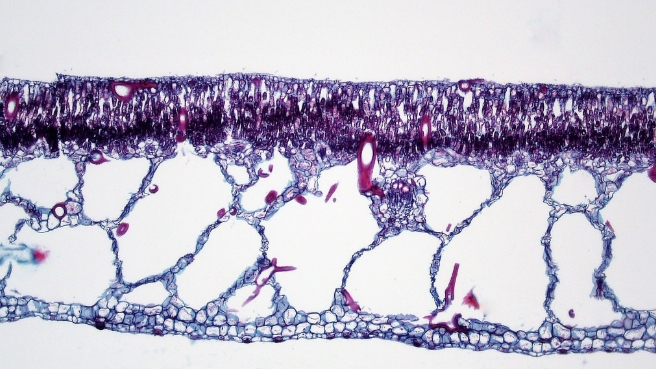
which is the hydrophyte
cuticle layer
The waxy layer outside the epidermis protects structure
palisade mesophyll
rectangular cells that are filled with chloroplast and are involved with photosynthesis
spongy mesophyll
oddly shaped cells that aid in gas exchange aka parenchyma
stomata
pathway for gas exchange regulated and protected by guard cells
gaurd cells
flank the opening of the stomata and regulates opening and closing
vascular bundles
clumps of thick walled xylem cells and thin walled pholem cells, carry water, minerals and nutrients.
xylem cells
cells that transport water
pjloem cells
cells that transport sugars
concurrent exchange
declining gradient, fluid flows in same direction, theoretical process
countercurrent exchange
constant gradient, two flows in opposite directions, occurs organically in nature.
concurrent exchange graph

countercurrent exchange
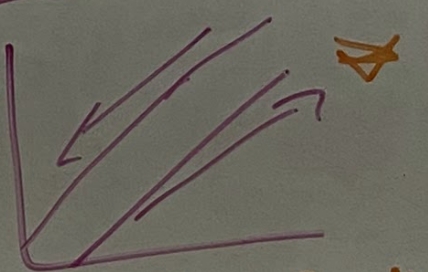
define transpiration
The loss of water in plant leaves from evaporation causes all water to be pulled upwards in the plant.
heats effect on transpiration
rate increases, higher evap rate and movement through plant
inc humidty effect on transpiration
rate decreases, water vapour gradient decreases,
dec humidty effect on transpiration
rate increases, water vapour gradient increases
darkness’s effect on transpiration
rate dec, stomata closes in the dark, and therefore less transpiration occurs
inc air movement
rate inc, moves saturated air around the leaf and therefore creates a higher difference in water vapor concentration
dec surface area
rate dec, less stomata to perform transpiration