Computer science basic
1/52
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Computer
An electronic device that stores, processes, (changes, moves, rewrites) information. It can perform complicated computations, organise and store huge amount of information.
What is computer science
The study of using computers to solve problems
Computation
The action of mathematical calculations
What are the 5 concept Areas (areas of study) of computer science
Computing systems
Algorithm and programming
Data and analysis
Network and the internet
Impacts of computing
What are computing systems
The machines that runs the programs and process information
example (laptop phone smart light)
all the basic hardware & basic software that work together to make the computer run
Algorithm
A set of instructions written in plain human language on how to complete a task.

Program
A set of instructions (an algorithm) that has been translated into commands that a computer can understand (code)
Without programs computers won’t understand what we want them to do

Data
Raw unorganised inputs / facts
Analysis
Organising, describing and understanding data
Networks
A group of connected devices which shares information and may even share resources like a printer
Internet
A worldwide network that connects millions of computer’s & devices
Is a CD a computer and why?
No. Although a CD can store information it cannot change it
What are the first computers
The Humans who make calculations. Sometimes with tools like the slide ruler to help them. (1600s)
What is the first electronic computer
Colossus Mark 1. It was made in 1944 and was used by the British government to help decipher German code (not the egnima)
ENIAC and what is it
Electronic numerical integrator and computer. The first programable general purpose computer.
What is the first mass-produced personal computer
APPLE II in 1977. It can run simple programs and play games

Hardware
The physical parts of a computer

Software
A set of programmes that tells a computer what to do. (Apps, web browser …)

what is an application
Application. A program design to help the user complete a task like photo editing
Not all programs are apps as some programs are for the computer use only.
what is input
The part used to send information to the computer like mouse, keyboard..

What is storage and its examples
Storage is the part of the computer that stores information.
Examples includes hard drive, CDs and RAM
RAM
Random access memory. A type of computer memory that can store information
CPU and what are its 3 main components
Central processing Unit
It’s the brains of the computer. It receives information and executes commands from other software and hardware.
It made up of the main memory, control unit and arithmetic logic unit
What is troubleshooting
A systematic step by step approach to tackling problems
Explain the difference between use case and test case
Use case are the broad test use to determine if the user can complete a general task. While test case are specific test that uses various input.
Why is testing different types of input important in case testing
Important to determine that your program can still run no matter what the user input. For example if your program only expect user
encoding
Converting data into code
Decoding
Turning code into data that is in a readable format
What is the difference between data and information
Data is the unprocessed raw facts while information is data that has been processed into usable facts
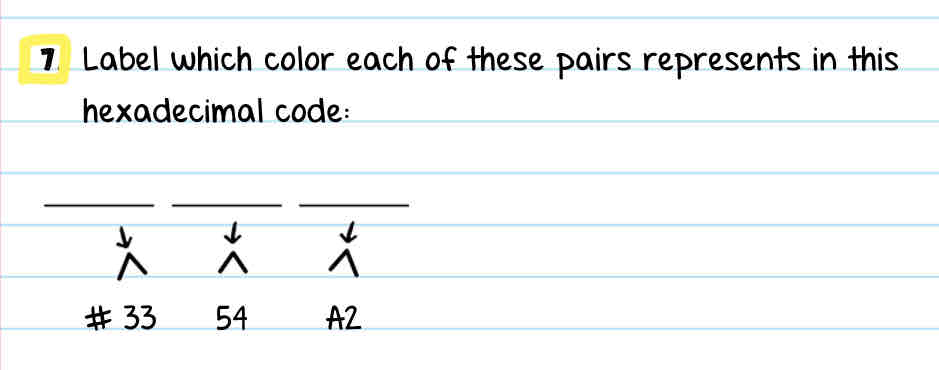
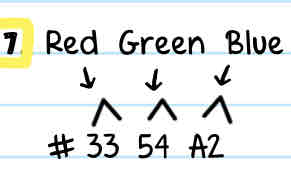
Label each of the blank spaces of the hexadecimal code
Red blue green
What is data encoding and why do we need it
Data encoding is converting data into a format the computer can read. Computers can only understand binary so data like text pictures and sound must be encoded for a computer
How social media companies make use of the information you share to make money
Targeted marketing . Every little detail gives businesses a clue about you and more specifically what you may buy so social media company sell these info to advertisers
Give 3 examples of data encoding schemes
Binary
Hexadecimal
RBG
What is defensive programming
A way to program what allows your programs to keep working even if things don’t go as planned

The difference between Use cases vs test cases
Use case is testing if a user is able to complete the general task while test cases are more specific test that use various inputs
What is documentation and its two types
Documentation is the information about the program. It’s two main types are
Comments (messages written by programmers about the code)
README files (gives info about the program)
If you wanted to add a note in your code as a reminder to come back and fix an error. What would you add?
#BUG /#FIXME
What is a user guide
It’s and information packet that helps user learn the functionality of the program
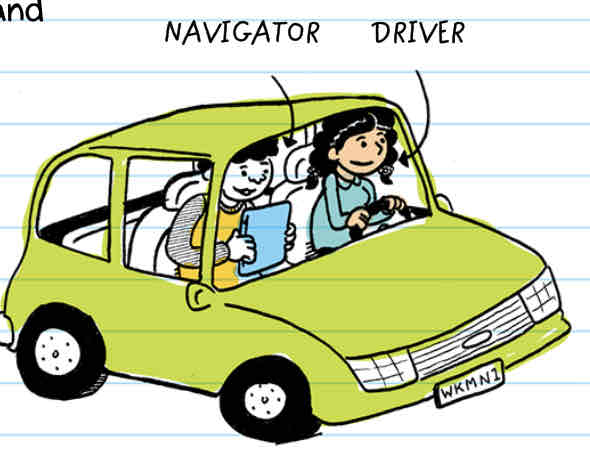
What is pair programming
It’s when 2 developers work on the same computer to complete a project. It helps them work faster and result in fewer mistakes
Webpages
A document that can be accessed on a web browser like the internet
Website
A collection of webpages
Mobile application
A software specifically made to be used on a mobile device
What is Front-end language and one example
It’s a programming language used to make what the user can see on the screen
Back-end language
used by programmers to build the internal systems that operate behind the scenes of a web application
What is compiling
Turning a computer language into binary for the computer to understand
How many BITs make a BYTE
A bit is the smallest unit of storage for a computer just one digit while a byte is made of 8 BITs (01010101)
What are the 2 types of planning method you can use for planning your program
Pseudo code and flow charts
What is computational thinking and it’s 4 major ideas. And which of the 4 ideas is considered the main one

What is the difference between a variable identifier and its value?
The Variable identifier is the name (don’t change) value is data Stored in the location designated by the variable (changes often)